Heavy mineral composition of the Songhua River system identified by manual and TIMA automatic methods and implications for provenance tracing
-
摘要:
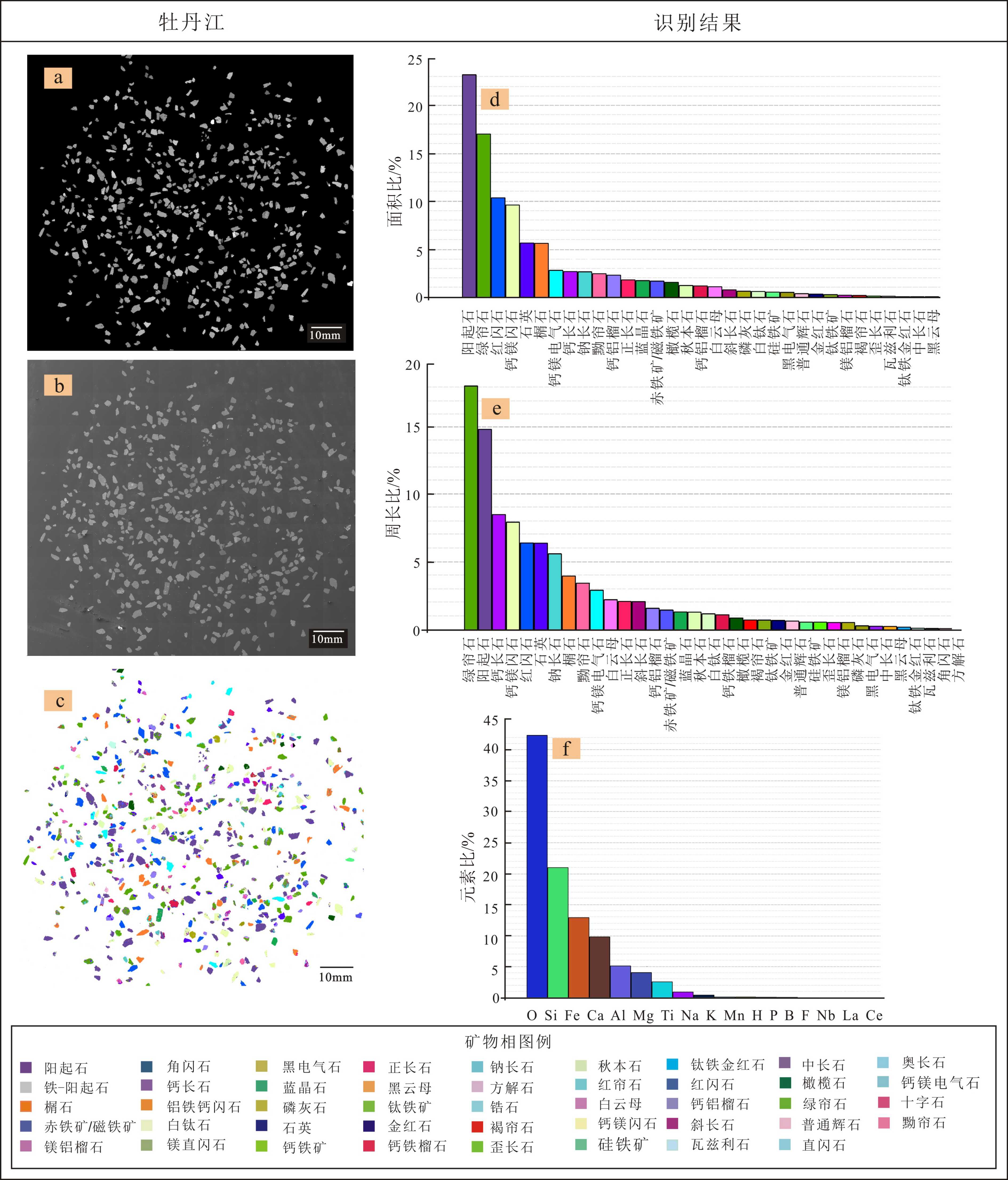
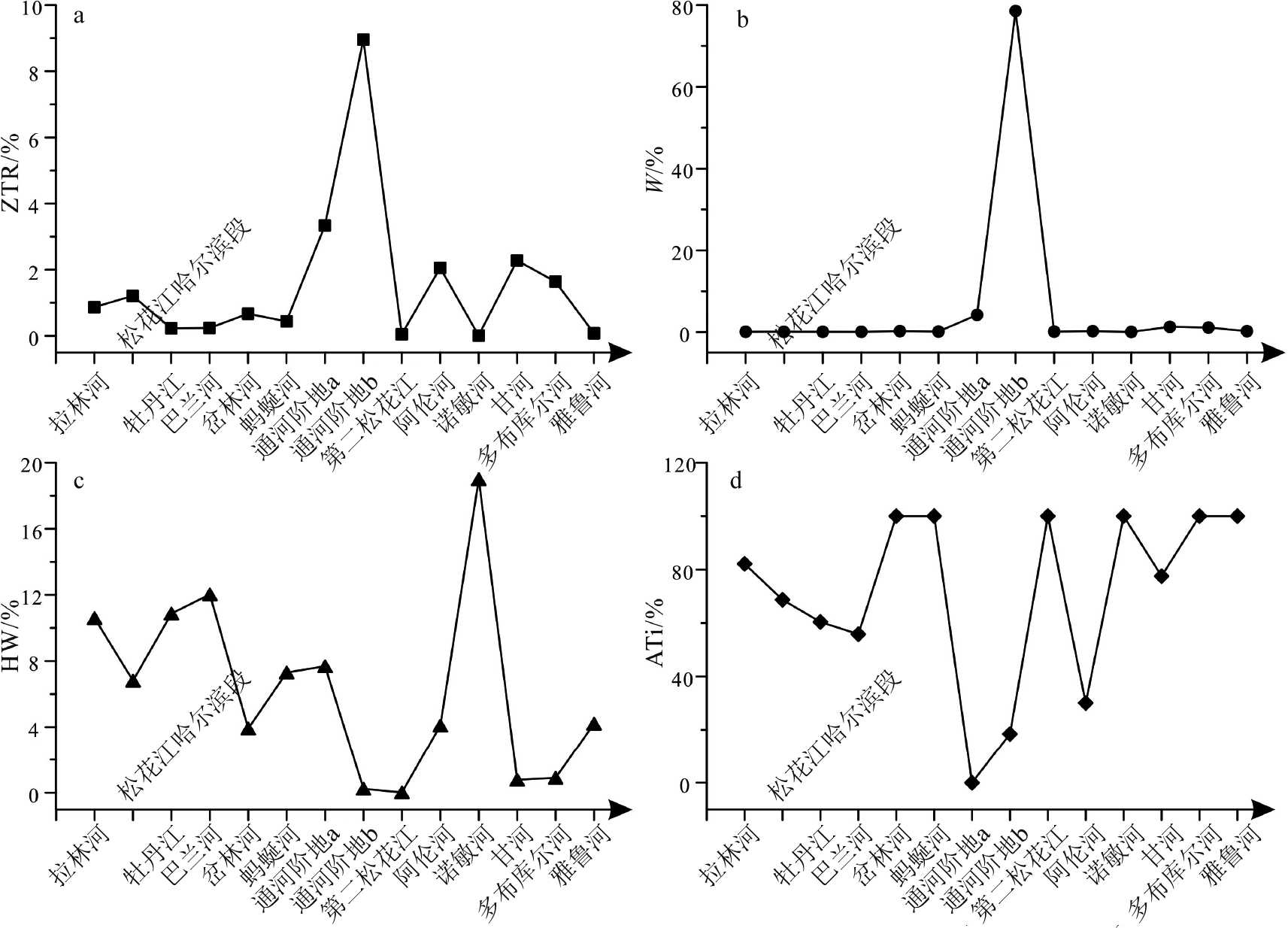
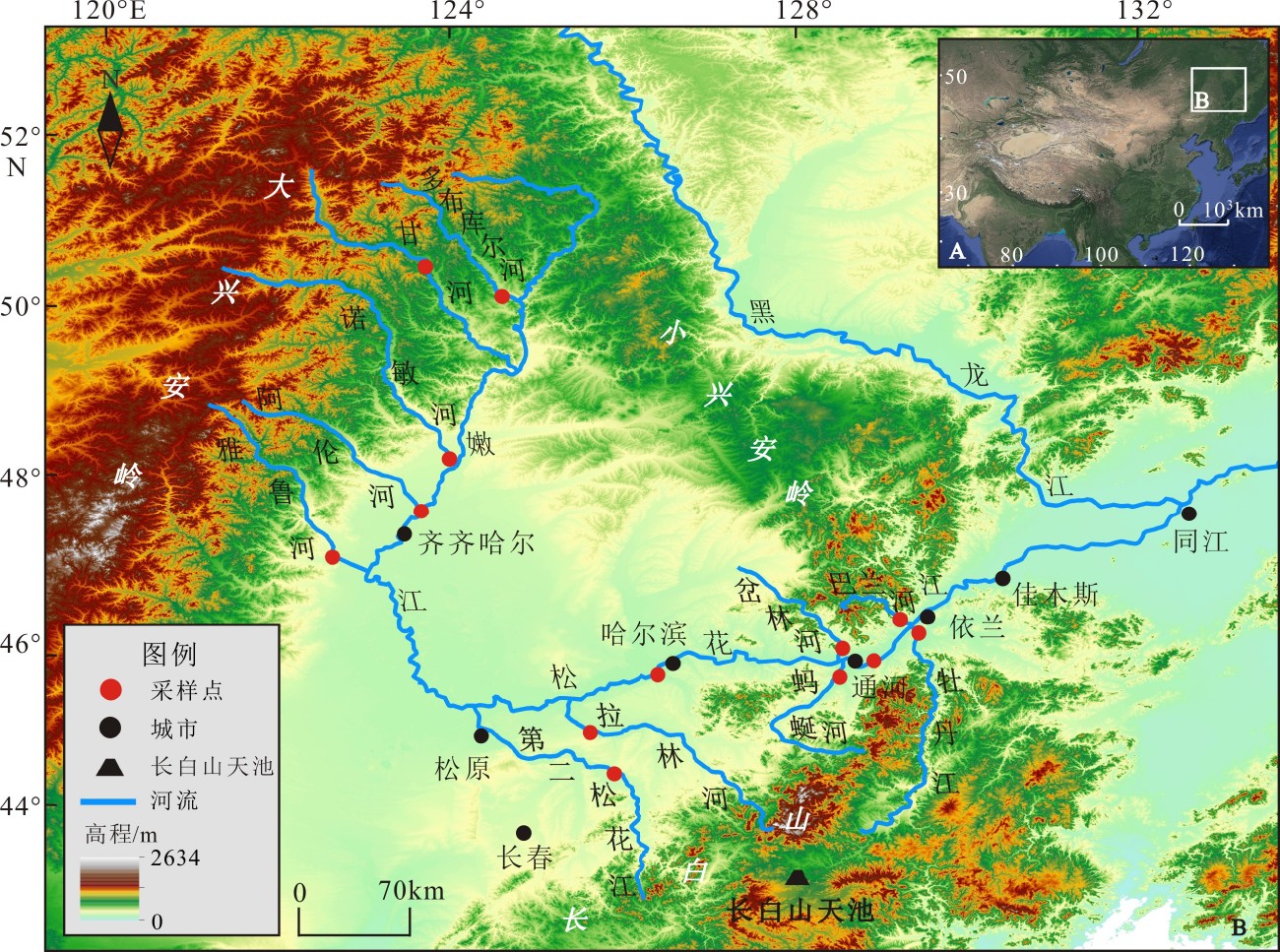
松花江水系作为中国东北地区最主要的河流系统,其重矿物组成对于揭示其沉积环境、沉积物源-汇过程和水系演化等地表过程具有重要意义。但目前对松花江水系重矿物组成了解有限,对影响其重矿物组成的控制因素尚不明晰。为此,在松花江干流和10个主要支流的边滩采集河流沙样品,在通河获取2个松花江T3阶地样品,分别采用TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer(TIMA)自动化矿物识别技术和人工方法,对63~250 μm粒级组分进行重矿物分析,旨在给出松花江水系的重矿物组成,并分析物源、河流过程和化学风化等因素对重矿物组成的影响和控制,以及评估人工和TIMA方法在重矿物鉴定中的应用情况。结果表明,发源于不同山岭(大兴安岭、小兴安岭和长白山)的各支流具有显著不同的重矿物组成,角闪石、榍石、绿帘石、白钛石、辉石、钛铁矿和赤、褐铁矿是区分各物源的指示性矿物。源自大兴安岭的嫩江支流具有显著高含量的辉石(诺敏河)、钛铁矿(甘河、多布库尔河和阿伦河)和赤、褐铁矿(甘河、多布库尔河和雅鲁河),显示了基性火成岩物质对重矿物组成的控制,这在现代河床砾石的岩性中得到证明。然而,在松花江干流中,这些重矿物含量显著降低,显示了极弱的大兴安岭源区信息,表明支流物源对重矿物组成的控制受到干流所携带沉积物的削弱,干流物源占据了主导地位。值得指出的是,松花江干流的重矿物组成显示出为拉林河和第二松花江物源的混合,表明干流更多地继承了松嫩平原东南山岭(长白山余脉)的重矿物信息。受到严重化学风化影响的通河T3阶地样品的重矿物组成简单,辉石和角闪石等抗风化能力弱的不稳定重矿物已完全消失,而稳定矿物高度富集,反映了化学风化对重矿物组成起到主要控制作用。相对于传统人工鉴定方法得到的重矿物组成(通常只能鉴定出20余种矿物相),TIMA方法能够给出更多的矿物种类信息(通常能识别出40余种矿物相),但在识别同质异相和多晶型矿物方面存在不足。
Abstract:The Songhua River is the most important fluvial system in northeast China and its heavy mineral composition is of great significance to the revealing of depositional environment, source-sink relationship and drainage evolution. However, the current study concerning the heavy mineral composition of the Songhua River system is very limited, and the factors affecting the composition of heavy minerals are not clear up to date. In order to solve the problem, sand samples are collected along the banks of the main stream and 10 major tributaries of the river system, in addition to the two from the T3 terraces of the Tonghe River. Using the new automated mineral identification technology TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer (TIMA) and the manual method respectively, heavy mineral analysis of the sample components in depth of 63~250 m is carried out for the samples. The influences of sediment sources, fluvial processes and chemical weathering on the heavy mineral composition of the Songhua River system are discussed. The results show that the tributaries sediments are sourced from different mountains, such as the Great Hinggan Mountains, the Lesser Hinggan Mountains and the Changbai Mountains. These mountains are significantly different in heavy mineral composition, and the heavy minerals of hornblende, titanite, epidote, leucoxene, augite, ilmenite and hematite+limonite are effective indicators to distinguish the water systems of different sources. The Nenjiang tributaries are originated from the Great Hinggan Mountains, of which sediments are rich in augite (the Nuomin River), ilmenite (the Ganhe River, Duobukuer River and Alun River) and hematite+limonite (the Ganhe River, Duobukuer River and Yalu River), showing the control of the basal source over heavy mineral composition, which can be observed in the modern riverbed gravels. However, in the main stream of the Songhua River, those heavy minerals are significantly reduced, suggesting that the influence of the Great Hinggan Mountains, as a source area, is extremely weak and the source control of heavy mineral composition is heavily influenced by river process. It is worth to point out that the heavy mineral composition of the Songhua River main stream is the mixture of the Lalin River and the Second Songhua River, indicating that the main stream of the Songhua River has inherited more heavy mineral information from the southeastern mountains of the Songnen Plain (the remnants of Changbai Mountain). The composition of heavy minerals in T3 terrace samples of Tonghe, which was severely affected by chemical weathering, is extremely simple, the unstable heavy minerals such as augite and hornblende have completely disappeared, and stable minerals are highly enriched, reflecting the control of chemical weathering over heavy mineral composition. Compared with the traditional manual identification of monotonous heavy mineral composition (usually only more than 20 mineral species can be identified), the TIMA method can reveal more mineral information (usually more than 40 mineral species can be identified), but there are shortcomings in identifying homogenous and polymorphic minerals.
-
Key words:
- heavy minerals /
- TIMA analyses /
- provenance /
- chemical weathering /
- river processes /
- Songhua River system
-

-
表 1 人工和 TIMA 检测松花江水系重矿物结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of artificial and TIMA results for heavy minerals in the Songhua River drainage
% 河流名 方法 Zr Ap Rt Ant Lcx Spn Amp Tur Gt Ep Px Ilm Hem+Lm Mag Ky 通河T3阶地a 人工 1.4 0.0 0.5 0.0 11.9 0.0 0.0 1.4 2.6 3.0 0.0 53.1 3.6 1.8 0.0 通河T3阶地b 3.9 1.1 0.4 0.07 0.8 2.0 0.0 4.7 2.7 0.07 0.0 74.4 2.7 0.0 0.0 牡丹江 0.01 0.3 0.03 0.03 0.6 7.2 56.7 0.2 3.5 14.0 6.0 1.2 1.0 1.2 0.0 第二松花江 0.05 0.5 0.0 0.0 1.5 3.2 59.2 0.0 2.8 12.7 6.0 2.8 2.8 1.8 0.05 拉林河 0.8 0.2 0.0 0.03 0.5 4.1 74.0 0.05 0.6 7.6 1.2 4.5 0.8 1.0 0.01 蚂蜒河 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.03 1.1 21.5 55.5 0.0 0.2 6.4 2.1 5.2 1.0 2.0 0.0 巴兰河 0.05 0.2 0.0 0.0 1.2 22.1 54.3 0.2 1.0 5.6 3.3 2.1 0.8 1.2 0.0 岔林河 0.6 0.8 0.04 0.07 0.4 28.5 46.8 0.0 0.2 4.7 1.6 5.1 2.6 5.1 0.0 阿伦河 1.2 0.3 0.1 0.2 3.8 7.0 8.1 0.7 0.07 57.9 1.1 11.7 1.8 0.5 0.0 诺敏河 0.01 0.3 0.0 0.0 3.9 2.3 14.6 0.0 0.0 37.2 27.1 1.4 2.3 0.5 0.0 甘河 2.1 0.4 0.06 0.2 1.8 6.7 8.3 0.1 0.06 25.9 4.0 19.6 23.2 4.2 0.0 多布库尔河 1.6 1.1 0.03 0.3 2.3 11.4 8.6 0.0 0.5 27.4 1.1 22.8 13.0 4.6 0.0 雅鲁河 0.08 0.2 0.0 0.05 2.7 6.8 5.1 0.0 0.1 60.9 1.2 4.5 10.2 1.2 0.0 松花江哈尔滨段 0.6 1.1 0.06 0.03 1.5 4.4 48.7 0.5 1.5 24.6 4.4 5.0 1.3 2.5 0.04 牡丹江 TIMA 0.02 0.7 0.7 0.0 1.0 7.2 48.2 3.9 4.8 23.8 0.5 0.5 0.0 3.2 2.3 第二松花江 0.03 0.1 0.3 0.0 0.1 4.0 54.2 1.0 0.9 25.8 0.1 1.6 0.0 6.1 0.0 拉林河 0.0 0.7 0.7 0.0 0.3 3.7 74.0 1.1 0.1 13.1 0.05 1.5 0.0 0.7 2.0 蚂蜒河 0.2 0.04 0.6 0.0 0.4 27.2 44.3 1.2 1.6 16.1 0.03 5.3 0.0 1.3 0.2 巴兰河 0.4 0.3 0.5 0.0 0.3 19.8 37.1 4.7 3.4 22.5 0.1 2.0 0.0 1.8 1.3 岔林河 0.2 0.7 1.9 0.0 2.1 32.4 35.8 0.5 0.5 8.9 0.1 9.9 0.0 4.4 0.09 阿伦河 0.05 0.3 3.1 0.0 2.6 6.9 11.6 0.4 1.7 67.7 0.01 1.2 0.0 1.5 1.8 诺敏河 0.01 0.9 1.3 0.0 2.0 2.8 12.1 0.7 2.6 43.3 25.2 1.4 0.0 4.8 0.0 甘河 1.0 0.2 3.4 0.0 2.3 12.4 10.0 1.0 4.1 42.0 0.03 13.5 0.0 9.1 0.0 多布库尔河 0.7 1.3 3.5 0.0 2.9 15.5 6.7 1.1 8.5 32.6 0.09 13.4 0.0 13.1 0.2 雅鲁河 0.1 0.1 2.2 0.0 1.9 5.0 6.6 1.1 3.2 72.4 0.04 3.6 0.0 2.9 0.4 松花江哈尔滨段 0.2 1.4 0.6 0.0 1.1 4.4 53.0 2.1 1.1 29.6 0.04 2.8 0.0 1.4 0.2 注:Zr为锆石,Ap为磷灰石,Rt为金红石,Ant为锐钛矿,Lcx为白钛石,Spn为榍石,Amp为角闪石,Tur为电气石,Gt为石榴子石,Ep为绿帘石,Px为辉石,Ilm为钛铁矿,Hem+Lm为赤铁矿+褐铁矿,Mag为磁铁矿,Ky为蓝晶石。 表 2 TIMA 鉴定松花江水系矿物分类
Table 2. Mineral classification of the Songhua River water system as identified by TIMA
矿物名称 矿物分类 金红石类 金红石、钛铁金红石 闪石类 角闪石、阳起石、钙镁闪石、红闪石、
铝铁钙闪石、直闪石电气石类 黑电气石、钙镁电气石 石榴子石类 钙铁榴石、钙铝榴石、镁铝榴石 帘石类 绿帘石、褐帘石、黝帘石、红帘石 辉石类 普通辉石、顽火辉石 -
[1] 曾方侣, 姜楷, 黄超, 等. 砂岩中重矿物的成因意义[J]. 四川地质学报, 2020, 40(1):26-29,50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2020.01.006
ZENG Fanglü, JIANG Kai, HUANG Chao, et al. Genetic significance of heavy minerals in sandstone [J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2020, 40(1): 26-29,50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2020.01.006
[2] 许苗苗, 魏晓椿, 杨蓉, 等. 重矿物分析物源示踪方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2021, 36(2):154-171
XU Miaomiao, WEI Xiaochun, YANG Rong, et al. Research progress of provenance tracing method for heavy mineral analysis [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2021, 36(2): 154-171.
[3] 王国茹, 陈洪德, 朱志军, 等. 川东南-湘西地区志留系小河坝组砂岩中重矿物特征及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 38(1):7-14
WANG Guoru, CHEN Hongde, ZHU Zhijun, et al. Characteristics and geological implications of heavy minerals in Lower Silurian Xiaoheba Formation sandstones in Southeast Sichuan-West Hunan [J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2011, 38(1): 7-14.
[4] 李明月, 孙学军, Karki K, 等. 喜马拉雅山中段柯西河跨境流域河流沉积物的矿物和元素特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(5):989-997
LI Mingyue, SUN Xuejun, Karki K, et al. Mineral and elemental characteristics of bed sediments in the Trans-boundary Koshi River Basin in the central Himalayas [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(5): 989-997.
[5] 周国华, 孙彬彬, 刘占元, 等. 中国东部主要河流稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):1028-1042 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.024
ZHOU Guohua, SUN Binbin, LIU Zhanyuan, et al. Geochemical feature of rare earth elements in major rivers of eastern China [J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 1028-1042. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.024
[6] Singh P, Rajamani V. REE geochemistry of recent clastic sediments from the Kaveri floodplains, southern India: Implication to source area weathering and sedimentary processes [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(18): 3093-3108. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00636-6
[7] Tripathi J K, Ghazanfari P, Rajamani V, et al. Geochemistry of sediments of the Ganges alluvial plains: evidence of large-scale sediment recycling [J]. Quaternary International, 2007, 159(1): 119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2006.08.016
[8] 童胜琪, 刘志飞, Le K P, 等. 红河盆地的化学风化作用: 主要和微量元素地球化学记录[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(3):218-225 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2006.03.002
TONG Shengqi, LIU Zhifei, Le K P, et al. Chemical weathering in the Red River Basin: records of major and trace elemental geochemistry [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(3): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2006.03.002
[9] 刘文, 徐士进, 杨杰东, 等. 金沙江河流悬浮物与沉积物的矿物学特征及其表生地球化学意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2007, 26(2):164-169 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2007.02.012
LIU Wen, XU Shijin, YANG Jiedong, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of suspended matters and sediments in the Jinshajiang River and their superficial geochemical significance [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2007, 26(2): 164-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2007.02.012
[10] 周天琪, 吴朝东, 袁波, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系重矿物特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1):65-78
ZHOU Tianqi, WU Chaodong, YUAN Bo, et al. New insights into multiple provenances evolution of the Jurassic from heavy minerals characteristics in southern Junggar Basin, NW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 65-78.
[11] Song H Y, Liu J Q, Yin P, et al. Characteristics of heavy minerals and quantitative provenance identification of sediments from the muddy area outside the Oujiang estuary since 5.8 kyr [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(6): 1325-1335. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3684-6
[12] 武法东, 陆永潮, 阮小燕, 等. 重矿物聚类分析在物源分析及地层对比中的应用: 以东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 1996, 10(3):106-112
WU Fadong, LU Yongchao, RUAN Xiaoyan, et al. Application of heavy minerals cluster analysis to study of clastic sources and stratigraphic correlation [J]. Geoscience, 1996, 10(3): 106-112.
[13] Herbig H G, Stattegger K. Late Palaeozoic heavy mineral and clast modes from the Betic Cordillera (southern Spain): transition from a passive to an active continental margin [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1989, 63(1-2): 93-108. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(89)90073-0
[14] 冉波, 王成善, 朱利东, 等. 距今40~30Ma时期青藏高原北缘酒西盆地沉积物重矿物分析和构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(5):388-397 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.05.040
RAN Bo, WANG Chengshan, ZHU Lidong, et al. Analysis of heavy minerals in sediments of Jiuxi Basin in north margin of the Xizang plateau in 40-30 Ma and its tectonic implication [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(5): 388-397. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.05.040
[15] 宋春晖, 孙淑荣, 方小敏, 等. 酒西盆地晚新生代沉积物重矿物分析与高原北部隆升[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(4):552-559 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.004
SONG Chunhui, SUN Shurong, FANG Xiaomin, et al. Analysis of tectonic uplift and heavy minerals of sediments on Jiuxi Basin in the northern margin of Xizang Plateau since the late Cenozoic [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(4): 552-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.004
[16] 方世虎, 郭召杰, 贾承造, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中-新生界沉积物重矿物分析与盆山格局演化[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(4):648-662 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.008
FANG Shihu, GUO Zhaojie, JIA Chengzao, et al. Meso-cenozoic heavy minerals' assemblages in the southern Junggar Basin and its implications for basin-orogen pattern [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(4): 648-662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.008
[17] 赵雪松, 高志勇, 冯佳睿, 等. 库车前陆盆地三叠系: 新近系重矿物组合特征与盆山构造演化关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1):68-77
ZHAO Xuesong, GAO Zhiyong, FENG Jiarui, et al. Triassic-neogene heavy minerals' assemblages characteristics and Basin-Orogen tectonic evolution relationship in the Kuqa Foreland Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 68-77.
[18] Cheng L Q, Song Y G, Chang H, et al. Heavy mineral assemblages and sedimentation rates of eastern Central Asian loess: paleoenvironmental implications [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 551: 109747. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109747
[19] 中国地质科学院地矿所. 砂矿物鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1977
Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. Handbook of Sand Mineral Identification[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1977.
[20] 谢小敏, 李利, 袁秋云, 等. 应用TIMA分析技术研究Alum页岩有机质和黄铁矿粒度分布及沉积环境特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1):50-60
XIE Xiaomin, LI Li, YUAN Qiuyun, et al. Grain size distribution of organic matter and pyrite in Alum shales characterized by TIMA and its paleo-environmental significance [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 50-60.
[21] 陈倩, 宋文磊, 杨金昆, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统的基本原理及其在岩矿研究中的应用: 以捷克泰思肯公司TIMA为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(2):345-368
CHEN Qian, SONG Wenlei, YANG Jinkun, et al. Principle of automated mineral quantitative analysis system and its application in petrology and mineralogy: an example from TESCAN TIMA [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(2): 345-368.
[22] Sutherland D N, Gottlieb P. Application of automated quantitative mineralogy in mineral processing [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1991, 4(7-11): 753-762. doi: 10.1016/0892-6875(91)90063-2
[23] Haberlah D, Williams M A J, Halverson G, et al. Loess and floods: high-resolution multi-proxy data of Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) slackwater deposition in the Flinders Ranges, semi-arid South Australia [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(19-20): 2673-2693. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.04.014
[24] Martin R S, Mather T A, Pyle D M, et al. Composition‐resolved size distributions of volcanic aerosols in the Mt. Etna plumes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2008, 113(D17): D17211. doi: 10.1029/2007JD009648
[25] Speirs J C, McGowan H A, Neil D T. Polar eolian sand transport: grain characteristics determined by an automated scanning electron microscope (QEMSCAN®) [J]. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 2008, 40(4): 731-743. doi: 10.1657/1523-0430(07-029)[SPEIRS]2.0.CO;2
[26] Meyer M C, Austin P, Tropper P. Quantitative evaluation of mineral grains using automated SEM–EDS analysis and its application potential in optically stimulated luminescence dating [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2013, 58: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2013.07.004
[27] 孙白云. 黄河、长江和珠江三角洲沉积物中碎屑矿物的组合特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1990, 10(3):23-34
SUN Baiyun. Detrital mineral assemblages in the Huanghe, Changjiang and Zhujiang River delta sediments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1990, 10(3): 23-34.
[28] 邵磊, 李长安, 张玉芬, 等. 长江川江段现代沉积物的重矿物组合特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(3):49-54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.03.007
SHAO Lei, LI Chang’an, ZHANG Yufen, et al. Heavy mineral assemblages in modern sediments of the Chuanjiang River [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(3): 49-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.03.007
[29] 李维东. 黄河上游晚新生代沉积物的物源分析与河流演化[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2020
LI Weidong. Provenance analysis of the Late Cenozoic sediment of the Upper Yellow River and its evolution[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2020.
[30] 王嘉新, 谢远云, 康春国, 等. 哈尔滨荒山岩芯重矿物特征对松花江第四纪水系演化的指示[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(1):79-94 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.01.08
WANG Jiaxin, XIE Yuanyun, KANG Chunguo, et al. The indication of the heavy mineral characteristics of the core in Harbin Huangshan to the Quaternary drainage evolution of Songhua River [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(1): 79-94. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.01.08
[31] 魏振宇, 谢远云, 康春国, 等. 早更新世松花江水系反转: 来自荒山岩芯Sr-Nd同位素特征指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(6):1192-1203
WEI Zhenyu, XIE Yuanyun, KANG Chunguo, et al. The inversion of the Songhua River system in the early pleistocene: implications from Sr-Nd isotopic composition in the Harbin Huangshan cores [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(6): 1192-1203.
[32] Xie Y Y, Kang C G, Chi Y P, et al. Reversal of the middle-upper Songhua River in the late Early Pleistocene, Northeast China [J]. Geomorphology, 2020, 369: 107373. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107373
[33] 宋国利, 刘钊, 于桂云. 黑龙江省松花江流域主要岩石类型中若干元素的背景含量及其环境意义[J]. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 1986(4):113-121
SONG Guoli, LIU Zhao, YU Guiyun. Background contents of some elements in the main rock types of the Songhua River basin in Heilongjiang Province and their environmental significance [J]. Natural Science Journal of Harbin Normal University, 1986(4): 113-121.
[34] 张玉娟, 赵鹤, 钟浩. 松花江流域(哈尔滨段)景观格局脆弱性高程分异[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2020, 43(5):11-15,18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2020.05.004
ZHANG Yujuan, ZHAO He, ZHONG Hao. Elevation differentiation of landscape pattern vulnerability in Songhua River Basin (Harbin Section) [J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2020, 43(5): 11-15,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2020.05.004
[35] 董爱民. 松花江流域地势图晕渲配色方案及优化[J]. 北京测绘, 2021, 35(7):981-985
DONG Aimin. Color scheme and optimization of shading in relief map of Songhua River Basin [J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 35(7): 981-985.
[36] 孙忠, 贾长青. 松花江流域蓄滞洪区建设有关问题探讨[J]. 东北水利水电, 2007, 25(10):31-33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2007.10.012
SUN Zhong, JIA Changqing. Discussion on detention basin construction in Songhuajiang river basin [J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China, 2007, 25(10): 31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2007.10.012
[37] Wu F Y, Yang J H, Lo C H, et al. The Heilongjiang Group: a Jurassic accretionary complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the western Pacific margin of northeastern China [J]. Island Arc, 2007, 16(1): 156-172. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2007.00564.x
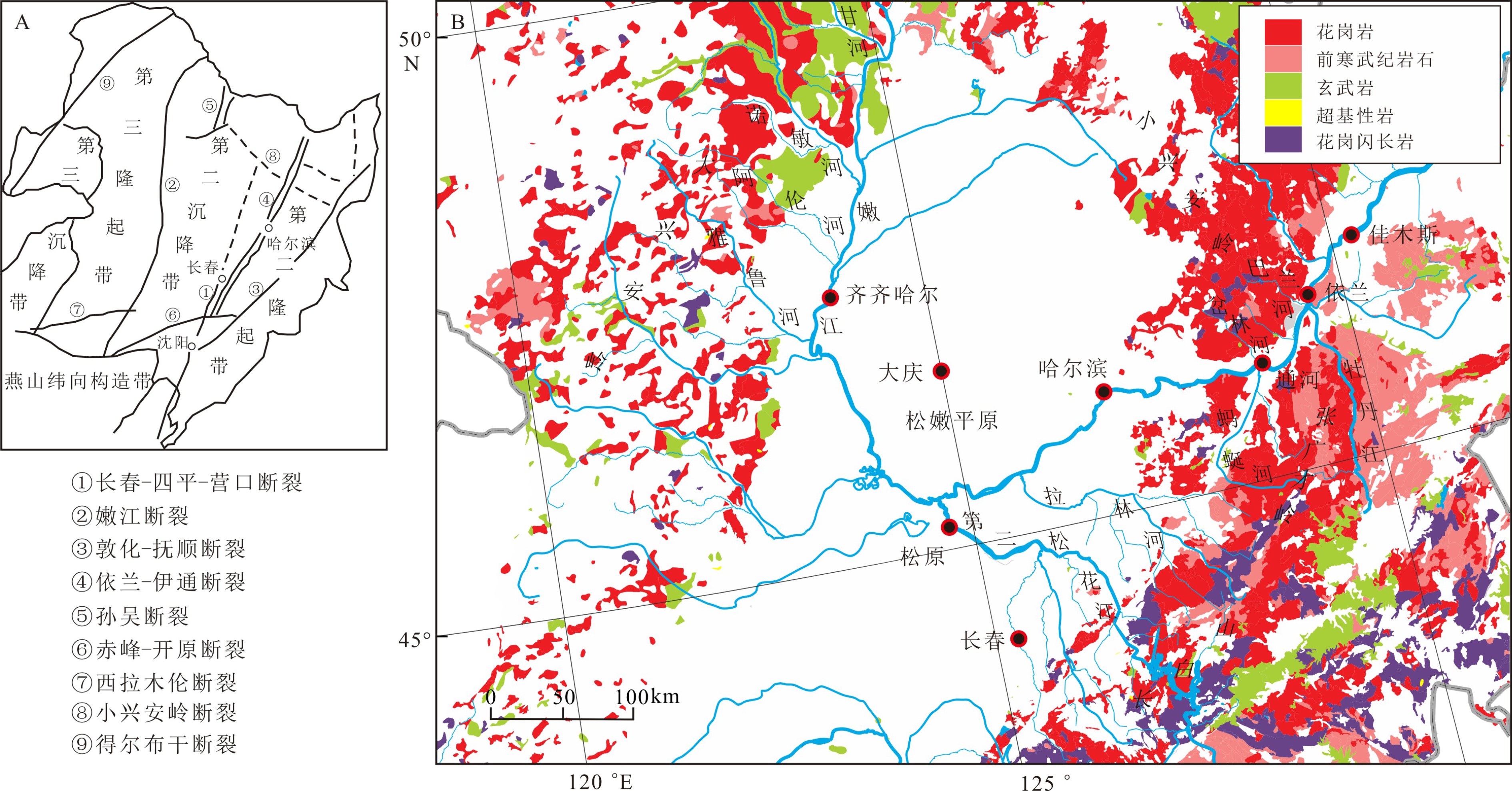
[38] 付俊彧, 朱群, 杨雅军, 等. 中华人民共和国(东北)地质图(1∶1500000)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2019: 1-147.
FU Junyu, ZHU Qun, YANG Yajun, et al. Geological map of the People’s Republic of China (Northeast) (1: 1500000)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009: 1-147.
[39] 韩梅, 梁贞堂. 关于松花江河源的再研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2004, 35(12):10-14,27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2004.12.003
HAN Mei, LIANG Zhentang. Another investigation for the source of Songhua River [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2004, 35(12): 10-14,27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2004.12.003
[40] 吴鹏, 谢远云, 康春国, 等. 早更新世晚期松花江水系袭夺: 地球化学和沉积学记录[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10):3144-3160 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.024
WU Peng, XIE Yuanyun, KANG Chunguo, et al. The capture of the Songhua River system in the late Early Pleistocene: geochemical and sedimentological records [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(10): 3144-3160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.024
[41] 康春国, 李长安, 王节涛, 等. 江汉平原沉积物重矿物特征及其对三峡贯通的指示[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(3):419-427 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.03.006
KANG Chunguo, LI Chang’an, WANG Jietao, et al. Heavy minerals characteristics of sediments in Jianghan Plain and its indication to the forming of the Three Gorges [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(3): 419-427. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.03.006
[42] 康春国, 李长安, 谢远云, 等. 哈尔滨地区风尘黄土重矿物特征及物源分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2011, 20(4):43-51
KANG Chunguo, LI Chang’an, XIE Yuanyun, et al. Heavy mineral characteristics of eolian loess deposits in Harbin area and its provenance implications [J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2011, 20(4): 43-51.
[43] Ward I, Merigot K, McInnes B I A. Application of quantitative mineralogical analysis in archaeological micromorphology: a case study from barrow is., western Australia [J]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2018, 25(1): 45-68. doi: 10.1007/s10816-017-9330-6
[44] Yue W, Yue X Y, Zhang L M, et al. Morphology of detrital zircon as a fingerprint to trace sediment provenance: case study of the Yangtze delta [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(7): 438. doi: 10.3390/min9070438
[45] Dunkl I, von Eynatten H, Andò S, et al. Comparability of heavy mineral data: the first interlaboratory round robin test [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 211: 103210. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103210
[46] Ishikawa S T, Gulick V C. An automated mineral classifier using Raman spectra [J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 54: 259-268.
[47] Haddad J E, de Lima Filho E S, Vanier F, et al. Multiphase mineral identification and quantification by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 134: 281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.02.025
[48] Rifai K, Paradis M M, Swierczek Z, et al. Emergences of new technology for ultrafast automated mineral phase identification and quantitative analysis using the CORIOSITY laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(10): 918. doi: 10.3390/min10100918
[49] Gu Y. Automated scanning electron microscope based mineral liberation analysis an introduction to JKMRC/FEI mineral liberation analyser [J]. Journal of Minerals & Materials Characterization & Engineering, 2003, 2(1): 33-41.
[50] Hrstka T, Gottlieb P, Skála R, et al. Automated mineralogy and petrology-applications of TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer (TIMA) [J]. Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 63(1): 47-63.
[51] Zhang X J, Pease V, Omma J, et al. Provenance of Late Carboniferous to Jurassic sandstones for southern Taimyr, Arctic Russia: a comparison of heavy mineral analysis by optical and QEMSCAN methods [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 329: 166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.09.008
[52] Schulz B, Sandmann D, Gilbricht S. SEM-based automated mineralogy and its application in geo- and material sciences [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(11): 1004. doi: 10.3390/min10111004
[53] 狄会哲, 邓宾, 赵高平, 等. 云贵高原河流水系演化与高原形成过程: 基于现代河流沉积物示踪[J]. 四川地质学报, 2018, 38(4):536-541 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2018.04.002
DI Huizhe, DENG Bin, ZHAO Gaoping, et al. The evolution of the river system on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and formation process of the plateau based on modern river sediment [J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2018, 38(4): 536-541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2018.04.002
[54] Nie J S, Peng W B, Pfaff K, et al. Controlling factors on heavy mineral assemblages in Chinese loess and Red Clay [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 381-382: 110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.020
[55] 和钟铧, 刘招君, 张峰. 重矿物在盆地分析中的应用研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2001, 20(4):29-32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.04.006
HE Zhonghua, LIU Zhaojun, ZHANG Feng. Latest progress of heavy mineral research in the basin analysis [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20(4): 29-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.04.006
[56] 赵红格, 刘池洋. 物源分析方法及研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(3):409-415 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.007
ZHAO Hongge, LIU Chiyang. Approaches and prospects of provenance analysis [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(3): 409-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.03.007
[57] 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 90-105.
ZHU Xiaomin. Sedimentary Petrology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 90-105.
[58] 康春国, 李长安, 邵磊. 江汉平原主要河流沉积物重矿物特征与物源区岩性的响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29(2):334-342 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.02.18
KANG Chunguo, LI Chang’an, SHAO Lei. Heavy mineral characteristics of river sediments in Jianghan Plain and its response to provenance rock types [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29(2): 334-342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.02.18
[59] 胡鹏, 鲍志东, 于兴河, 等. 碎屑重矿物差异与物源演化: 以长岭凹陷乾北地区青三段-姚一段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(2):375-387
HU Peng, BAO Zhidong, YU Xinghe, et al. Detrital heavy mineral difference and its implication for provenance: a case study of the third member of Qingshankou formation and the first member of Yaojia formation in Qianbei area, Changling sag [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(2): 375-387.
[60] 蔡芃睿, 王涛, 王宗起, 等. 大兴安岭中段乐平统-中三叠统沉积物源分析: 来自重矿物组合及碎屑锆石年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11):3549-3564 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.18
CAI Pengrui, WANG Tao, WANG Zongqi, et al. Lopingian to Middle Triassic provenance analysis of sedimentary rocks in the middle segment of the Da Hinggan Mountains: evidence from the heavy mineral assemblage and the detrital zircon U-Pb ages [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11): 3549-3564. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.18
[61] 马丽芳. 中国地质图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002
MA Lifang. Geological Atlas of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002.
[62] 和钟铧, 刘招君, 郭巍. 柴达木盆地北缘大煤沟剖面重矿物分析及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2001, 20(3):279-284,312 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2001.03.012
HE Zhonghua, LIU Zhaojun, GUO Wei. The heavy mineral analysis and its geological significance of Dameigou section in northern Caidam Basin [J]. World Geology, 2001, 20(3): 279-284,312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2001.03.012
[63] 苗小龙, 杜燕. 与胡修棉的讨论: 水流搬运与沉积过程中掺和作用对碎屑颗粒的重要影响[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(4):648-652 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.04.050
MIAO Xiaolong, DU Yan. Discussion with Hu: significant influence of mixing action to clastic particles during the process of flowing transportation and sedimentation [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(4): 648-652. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.04.050
[64] 胡修棉. 物源分析的一个误区: 砂粒在河流搬运过程中的变化[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(1):175-184 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.01.014
HU Xiumian. A misunderstanding in provenance analysis: sand changes of mineral, roundness, and size in flowing-water transportation [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(1): 175-184. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.01.014
[65] Morton A C, Hallsworth C. Identifying provenance-specific features of detrital heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3-4): 241-256. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)90041-8
[66] Morton A C, Hallsworth C. Chapter 7 stability of detrital heavy minerals during burial diagenesis [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58: 215-245.
[67] 蒋玺, 陈文奇, 宁凡, 等. 贵州高原北部河流阶地发育与喀斯特地貌演化[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(1):81-92 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200485
JIANG Xi, CHEN Wenqi, NING Fan, et al. River terraces in the northern Guizhou Plateau and their implications for karst landform evolution [J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(1): 81-92. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020200485
[68] 董铭, 苏怀, 史正涛, 等. 金沙江金江街段河流阶地年代及对河谷水系演化历史的启示[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(9):1728-1736 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201809009
DONG Ming, SU Huai, SHI Zhengtao, et al. The age of river terraces in the Jinjiangjie reach of the Jinsha River and its implications for valley and drainage evolution [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(9): 1728-1736. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201809009
[69] 陆洁民, 郭召杰, 赵泽辉, 等. 新生代酒西盆地沉积特征及其与祁连山隆升关系的研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004, 10(1):50-61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2004.01.004
LU Jiemin, GUO Zhaojie, ZHAO Zehui, et al. Cenozoic sedimentation characteristics of Jiuxi Basin and uplift history of northern Qilian Mountain [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(1): 50-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2004.01.004
[70] 程岩, 刘月, 李富祥, 等. 鸭绿江口及邻近浅海碎屑矿物特征与物源辨识[J]. 地理研究, 2010, 29(11):1950-1960
CHENG Yan, LIU Yue, LI Fuxiang, et al. Detrital mineral characteristics and material source identification in surface sediments of Yalu River estuary and adjacent waters [J]. Geographical Research, 2010, 29(11): 1950-1960.
[71] 牛东风, 李保生, 王丰年, 等. 不同沉积相重矿物组成及其对气候的指示: 以米浪沟湾全新统MGS1层段为例[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2015, 34(7):7-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2015.07.003
NIU Dongfeng, LI Baosheng, WANG Fengnian, et al. Heavy mineral composition and its climatic indication for the MGS1 Segment in the holocene in Milanggouwan [J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2015, 34(7): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2015.07.003
[72] 李艳, 李安春, 黄朋. 大连湾近海表层沉积物重矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(6):13-20
LI Yan, LI Anchun, HUANG Peng. Distribution of heavy mineral assemblages in subsurface sediments of Dalian bay and their implications for provenance and environment [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(6): 13-20.
[73] 马婉仙. 重砂测量与分析[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990
MA Wanxian. Heavy Sand Measurement and Analysis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990.
[74] 程瑜, 李向前, 赵增玉, 等. 苏北盆地TZK9孔磁性地层及重矿物组合特征研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4):994-1003 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.017
CHENG Yu, LI Xiangqian, ZHAO Zengyu, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and heavy minerals records of TZK9 core in Subei Basin [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(4): 994-1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.017
[75] Milliken K L, Mack L E. Subsurface dissolution of heavy minerals, Frio Formation sandstones of the ancestral Rio Grande Province, South Texas [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1990, 68(3): 187-199. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(90)90111-6
[76] 李双建, 石永红, 王清晨. 碎屑重矿物分析对库车坳陷白垩: 第三纪物源变化的指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(1):28-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.01.004
LI Shuangjian, SHI Yonghong, WANG Qingchen. The analysis of detrital heavy minerals in cretaceous-tertiary sandstones, Kuqa depression and their implications for provenance [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(1): 28-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.01.004
[77] Smale D, Morton A C. Heavy mineral suites of core samples from the McKee Formation (Eocene-Lower Oligocene), Taranaki: implications for provenance and diagenesis [J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1987, 30(3): 299-306. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1987.10552624
[78] 李红, 李飞, 龚峤林, 等. 混积岩中重矿物形貌学特征及物源意义: 以川北寒武系第二统仙女洞组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(3):525-539
LI Hong, LI Fei, GONG Qiaolin, et al. Morphological Characteristics and Provenance Significance of Heavy Minerals in the Mixed Siliciclastic-carbonate Sedimentation: a case study from the Xiannüdong Formation, Cambrian (Series 2), northern Sichuan [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(3): 525-539.
-



 下载:
下载: