Distribution and influencing factors of planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments of the Ninetyeast Ridge in Indian Ocean
-
摘要:
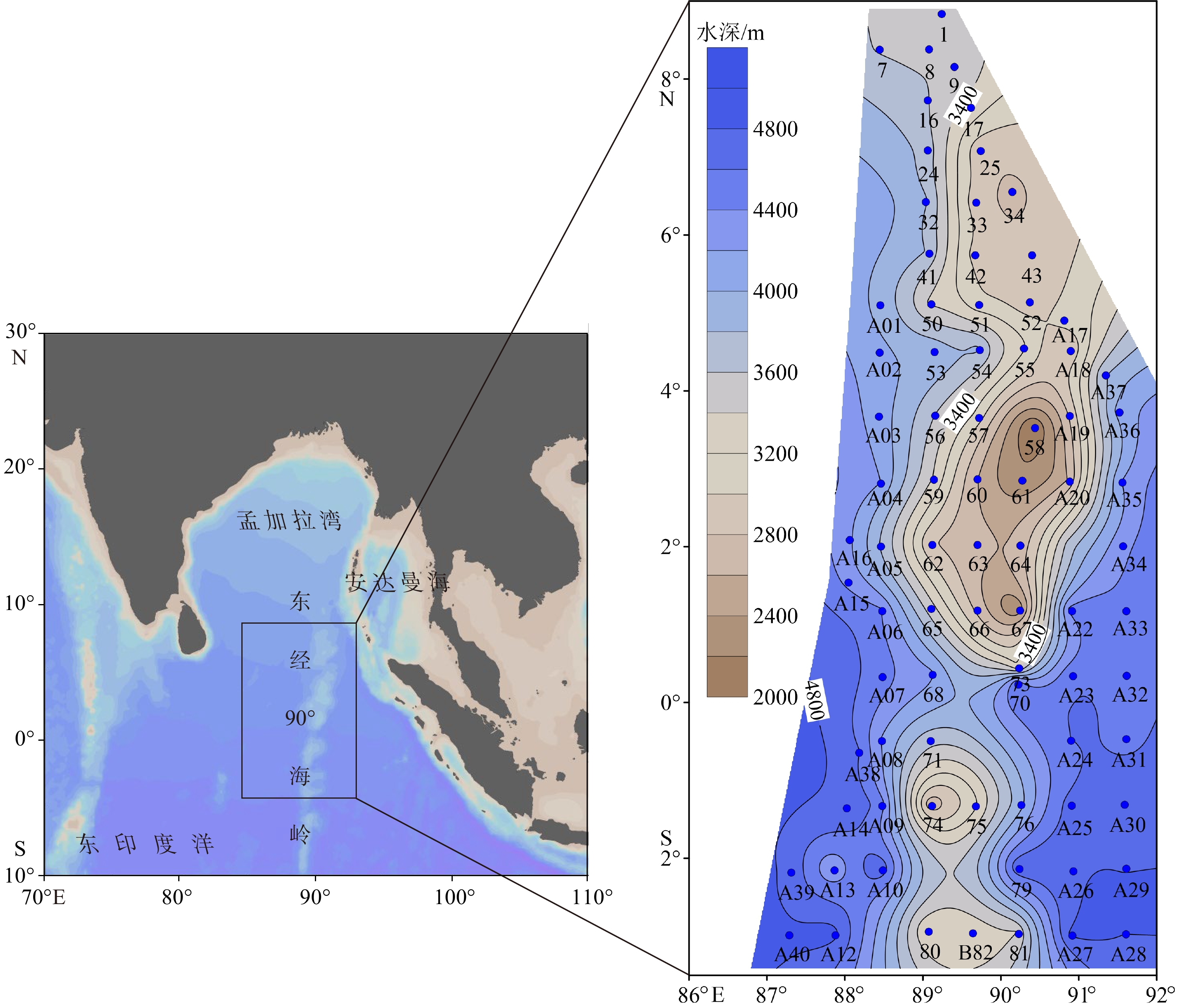
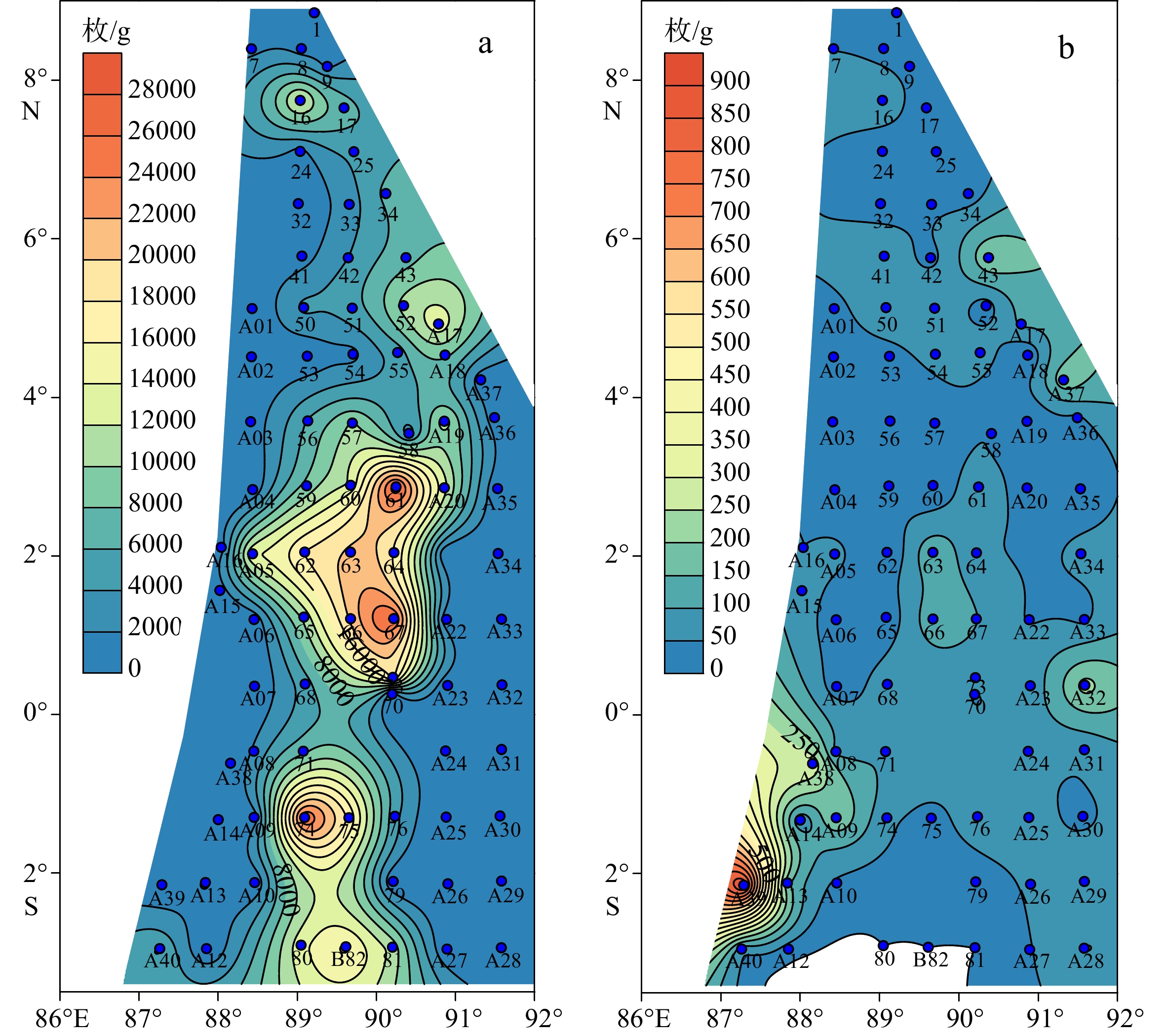
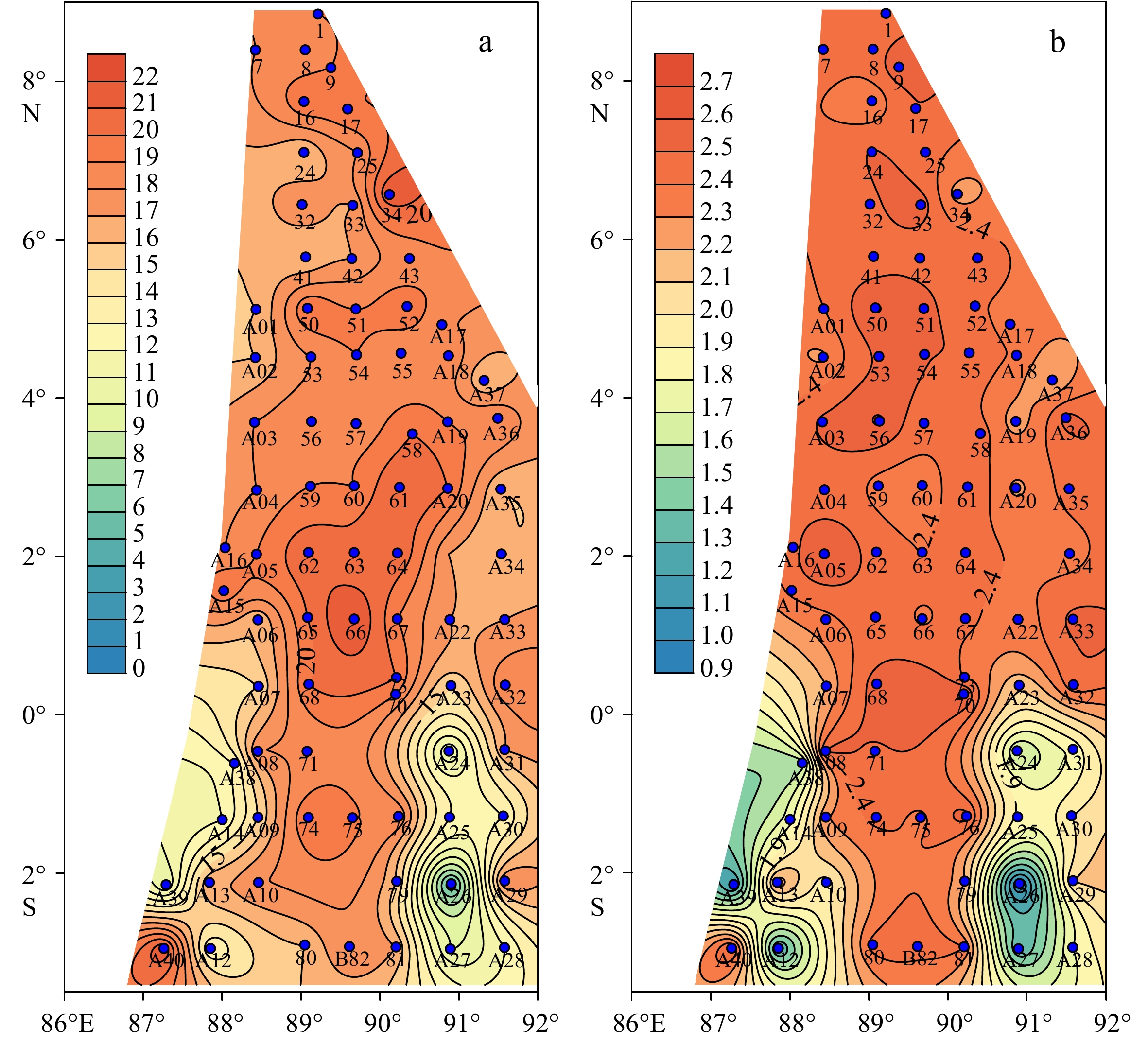
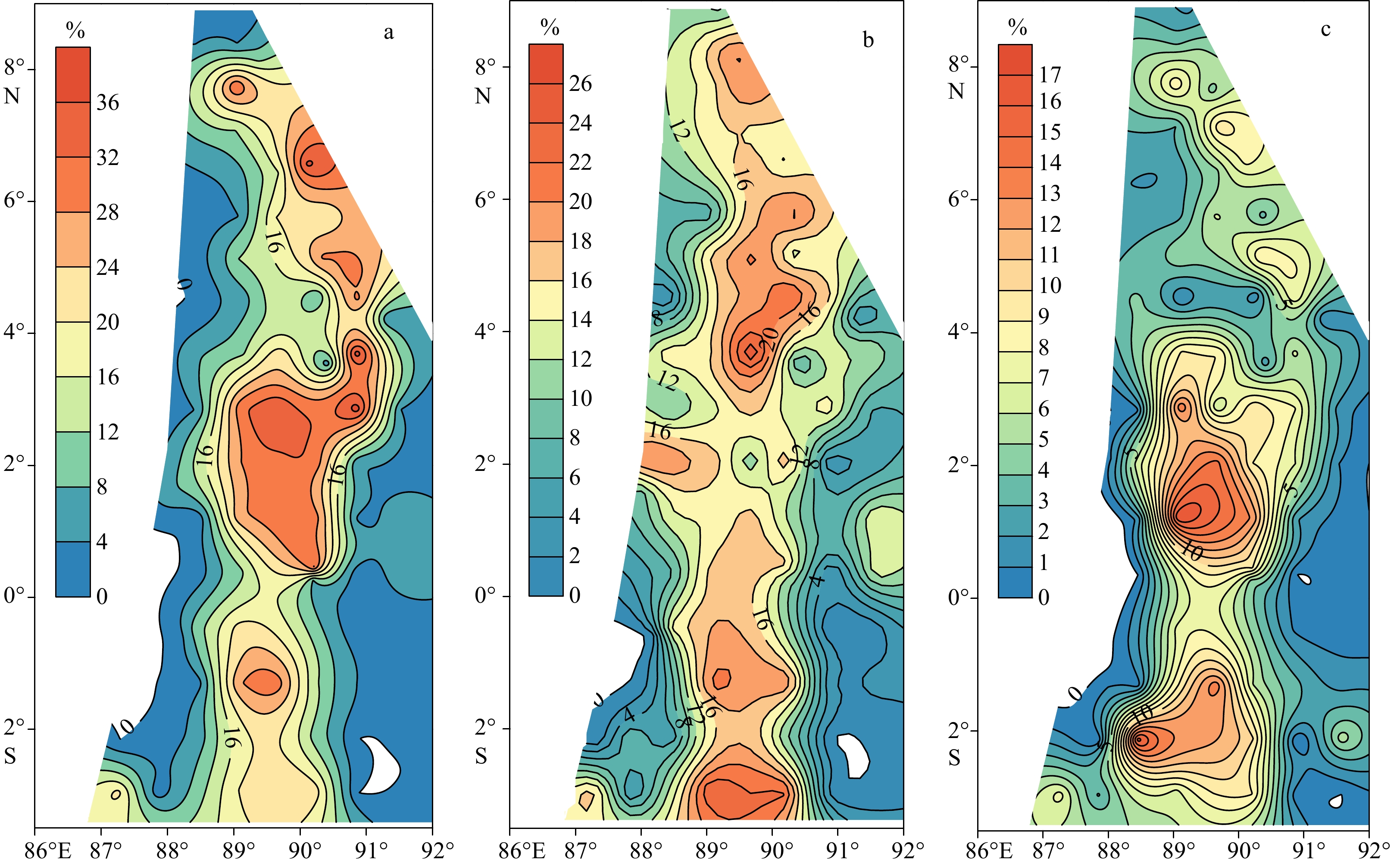
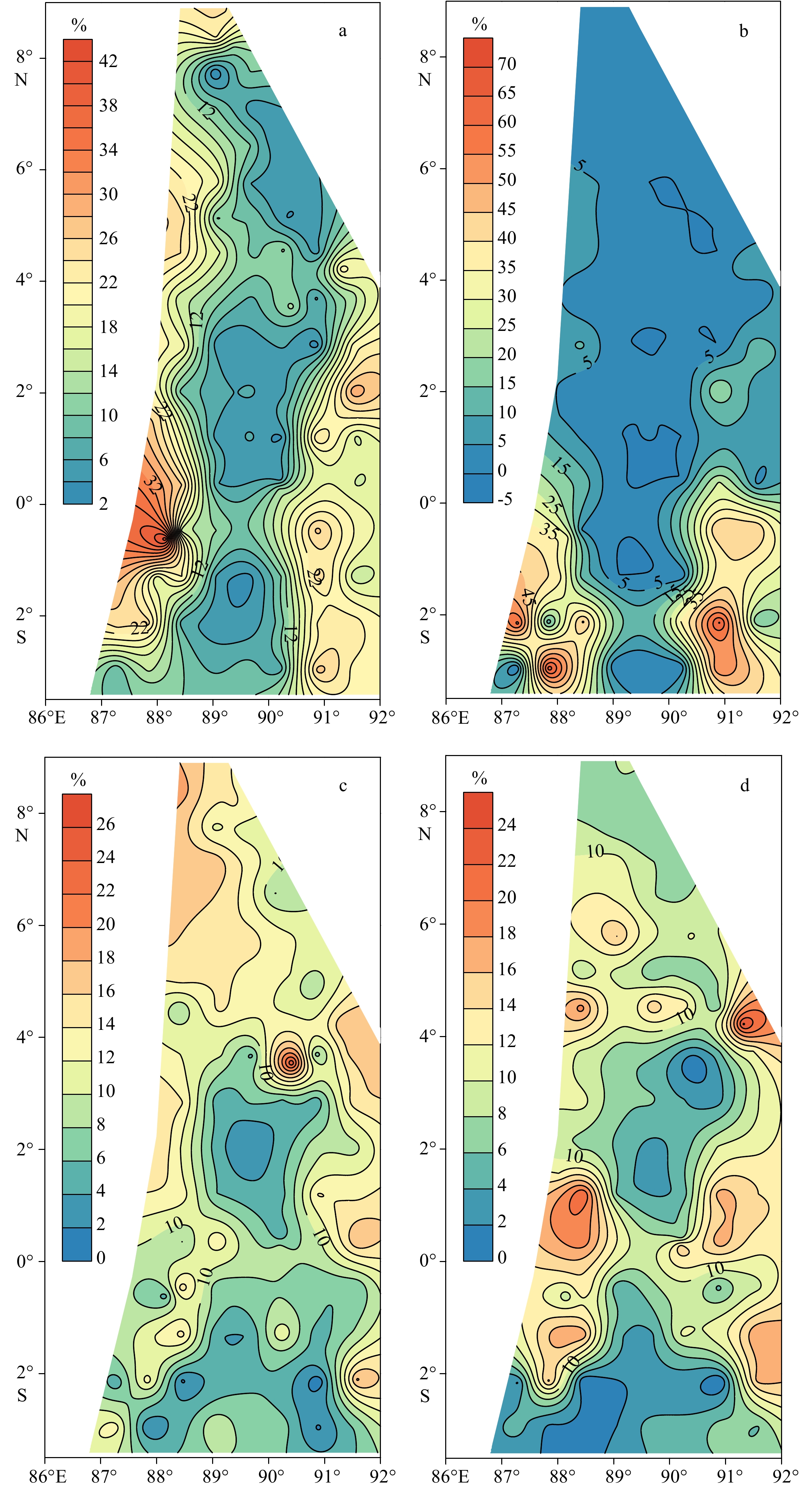
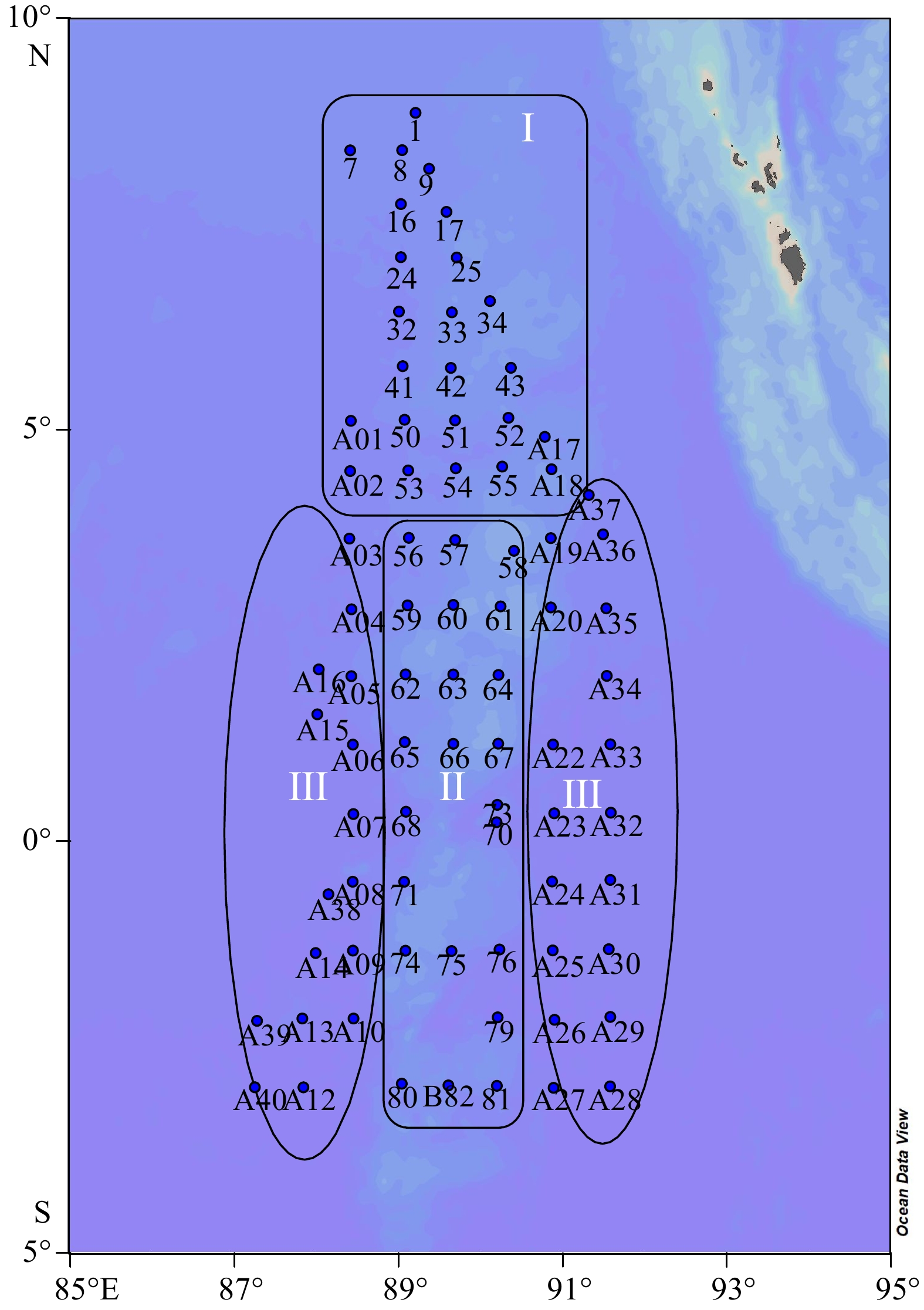
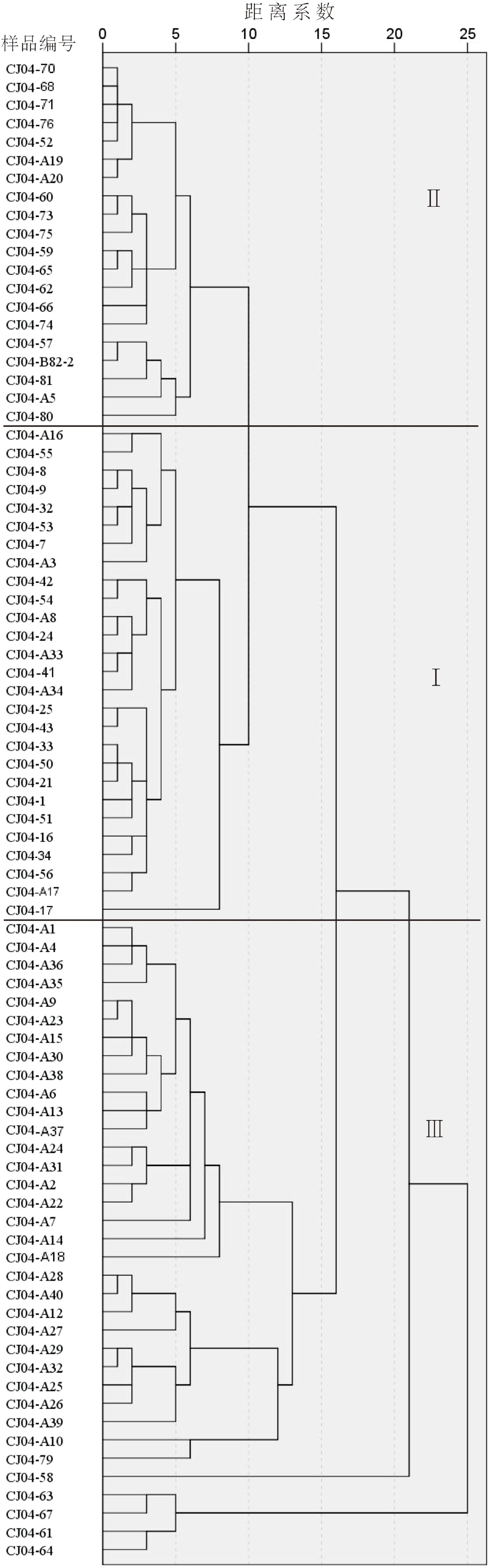
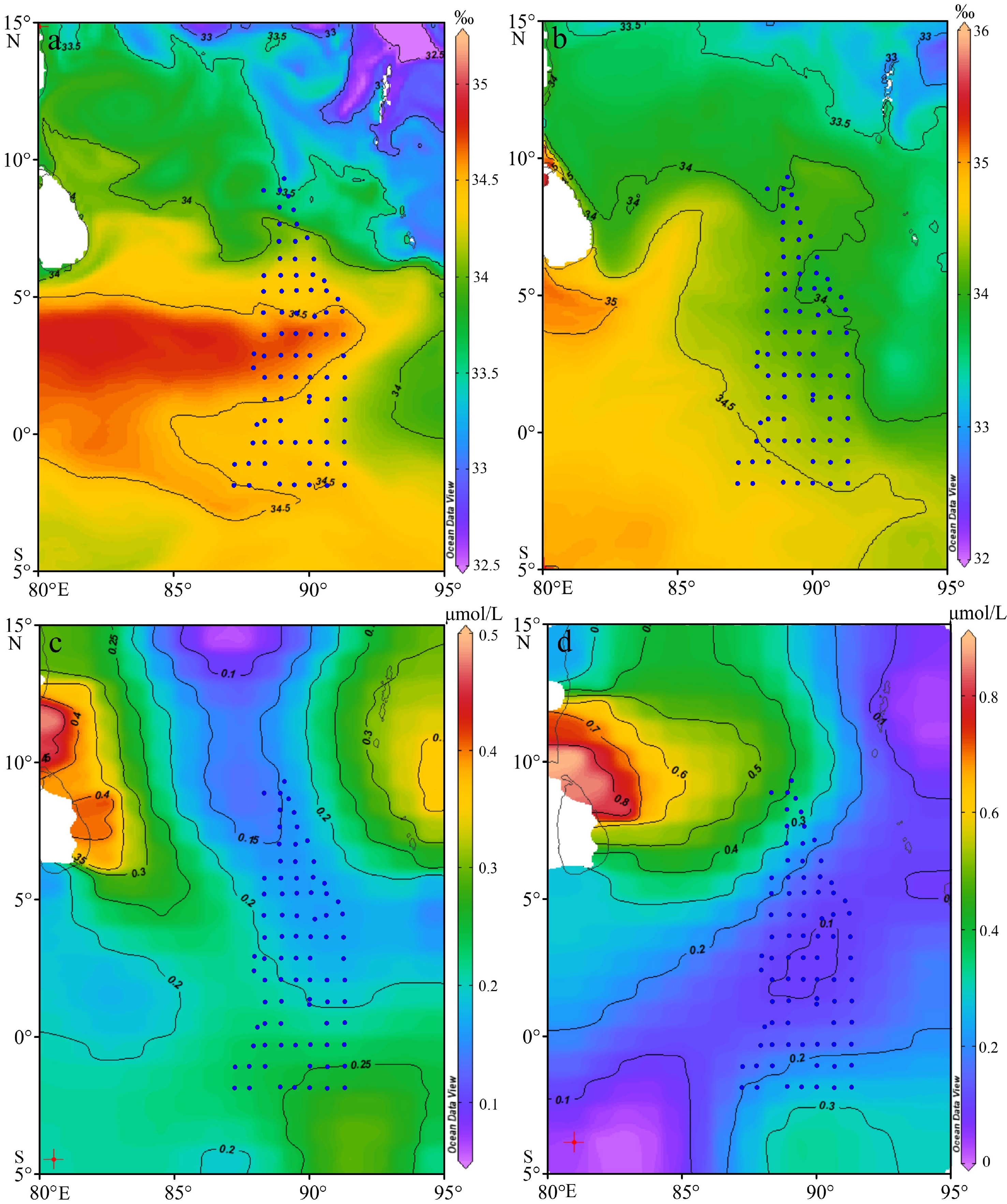
对东印度洋90°海岭附近海域82个表层沉积物样品中的浮游有孔虫进行鉴定统计分析,揭示了研究区表层沉积物中浮游有孔虫区域分布特征,并对其影响因素进行了初步探讨。研究表明,东印度洋90°海岭附近海域表层沉积物中浮游有孔虫呈现典型的热带-亚热带组合特征,共鉴定出浮游有孔虫30种。运用聚类分析,得到3个浮游有孔虫组合:组合类群I主要分布在5°~10°N的孟加拉湾南部开阔海域,主要种属包括Globigerinoides sacculifer,Globigerinoides ruber,Neogloboquadrina dutertrei,体现了生产力及海水盐度对有孔虫组合的影响;组合类群II主要在5°N至5°S,沿东经90°海岭分布。主要种属包括Globigerinoides ruber,Globorotalia menardii,Neogloboquadrina dutertrei,体现了水深及生产力对有孔虫组合的影响;组合类群III对称分布在组合类群II两侧水深较深的海域,主要种属包括Globorotalia tumida,Globorotalia menardi,Pulleniatina obliquiloculata,体现了水深对有孔虫组合特征的影响。根据有孔虫组合类群分布特征,推断水深、盐度及生产力是影响本海域浮游有孔虫分布的最主要因素。
Abstract:Eighty-two surface sediment samples were collected from the Ninetyeast Ridge of the eastern Indian Ocean, from which planktonic foraminifera community fossils were identified and statistically analyzed. The regional distribution characteristics of planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments were revealed, and the influencing factors discussed. Results show that the planktonic foraminifera displayed typical tropical-subtropical attributes, and 30 species of planktonic foraminifera were identified. The planktonic foraminifera were classified into groups (assemblages) in cluster analysis. Group I included mainly Globigerinoides sacculifer, Globigerinoides ruber, and Neogloboquadrina dutertrei, distributed mostly in the open sea area in the south of the Bay of Bengal from 5°N to 10°N, and affected by productivity and salinity of seawater. Group II included Globigerinoides ruber, Globorotalia menardii, and Neogloboquadrina dutertrei, occupied mainly between 5°N and 5°S along the Ninetyeast Ridge, and related to the depth and productivity. Group III contained mainly Globorotalia tumida, Globorotalia menardi, and Pulleniatina obliquiloculata, distributed symmetrically in deep water areas on both sides of Group 2, and were closely depth dependent. Therefore, the distribution patterns of planktonic foraminifer assemblages are closely affected by water depth, salinity, and productivity of planktonic foraminifera in the sea area.
-
Key words:
- surface sediments /
- planktonic foraminifera /
- sedimentary environment /
- Ninetyeast Ridge /
- Indian Ocean
-

-
表 1 研究区表层样浮游有孔虫优势种百分含量统计
Table 1. Statistical table of relative abundance of dominant planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments in the study area
属种名 最大值/% 最小值/% 平均值/% Globorotalia menardii 42.90 2.41 13.64 Globigerinoides ruber 31.73 0.00 13.54 Globigerinoides sacculifer 26.16 0.00 12.15 Neogloboquadrina dutertrei 19.28 0.83 10.33 Globorotalia tumida 65.56 0.00 10.20 Pulleniatina obliquiloculata 24.33 0.00 9.01 Globigerinita glutinata 16.95 0.00 5.21 表 2 各组浮游有孔虫主要种属含量分布
Table 2. Content distribution of main species of planktonic foraminifera in each group
种属 组合I 组合II 组合III Globigerinoides ruber 16.30% 19.68% 3.10% Globigerinoides sacculifer 17.31% 15.54% 4.80% Globorotalia menardii 10.04% 10.23% 21.15% Neogloboquadrina dutertrei 13.32% 10.22% 8.87% Pulleniatina obliquiloculata 9.12% 7.21% 11.01% Globoquadrina conglomerata 6.15% 6.17% 2.23% Globigerina bulloides 4.79% 3.85% 1.49% Globigerinita glutinata 4.68% 6.77% 2.44% Globorotalia tumida 1.24% 1.26% 27.04% -
[1] 丁旋, 方念乔, 万晓樵. 孟加拉湾晚第四纪的季风气候及其古海洋学记录[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(3):295-300 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2000.03.010
DING Xuan, FANG Nianqiao, WAN Xiaoqiao. Monsoon climate and its paleoceanographic records of the Bay of Bengal during Late Quaternary [J]. Geoscience, 2000, 14(3): 295-300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2000.03.010
[2] 吴雨. 安达曼海MIS25期以来浮游有孔虫记录的印度季风演化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2020.
WU Yu. The evolution of Indian monsoon recorded by planktonic foraminifera since the MIS25 Period in the Andaman Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
[3] 宣莉莉. 热带东印度洋上层海洋环流及其与孟加拉湾水交换的季节变化研究[D]. 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2013.
XUAN Lili. Seasonal variation of the upper ocean circulation in the eastern tropical Indian Ocean and its water exchange with the Bay of Bengal[D]. Master Dissertation of Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2013.
[4] 魏华玲. 3.5Ma来赤道东经90°海岭远洋记录与重大环境事件[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2006.
WEI Hualing. Pelagic recards from the equatorial ninetyeast ridge and significant environmental events during past 3.5 million years[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2006.
[5] 丁旋, 方念乔. 东北印度洋区BAR9427岩心末次冰期以来的古季风活动记录[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2006, 31(6):765-772
DING Xuan, FANG Nianqiao. Records of Paleo-monsoon of core BAR9427 in northeastern Indian Ocean during Last Glaciation [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2006, 31(6): 765-772.
[6] 王颖. 东印度洋中部缺氧区的季节变化特征[D]. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2018.
WANG Ying. Seasonal variation of hypoxic zone in the central eastern Indian Ocean[D]. Master Dissertation of the First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2018.
[7] Bé A W H. An ecological, zoogeographic and taxonomic review of recent planktonic foraminifera [J]. Oceanic Micropaleontology, 1977, 1: 1-100.
[8] Fairbanks R G, Sverdlove M, Free R, et al. Vertical distribution and isotopic fractionation of living planktonic foraminifera from the Panama Basin [J]. Nature, 1982, 298(5877): 841-844. doi: 10.1038/298841a0
[9] Jian Z M, Wang P X, Saito Y, et al. Holocene variability of the Kuroshio Current in the Okinawa Trough, northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 184(1): 305-319. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00321-6
[10] 吴永华, 程振波, 石学法, 等. 琉球群岛东部海区表层沉积物中浮游有孔虫分布及指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):1-7
WU Yonghua, CHENG Zhenbo, SHI Xuefa, et al. Distribution of planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments from sea area East of the Ryukyu Islands and their indications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(6): 1-7.
[11] 张玲芝, 向荣, 唐灵刚, 等. 安达曼海浮游有孔虫群落对全新世海洋环境变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6):51-61
ZHANG Lingzhi, XIANG Rong, TANG Linggang, et al. Response of planktonic foraminifera to Holocene marine environmental changes in the Andaman Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 51-61.
[12] Thunell R C. Distribution of recent planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments of the Mediterranean Sea [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1978, 3(2): 147-173. doi: 10.1016/0377-8398(78)90003-8
[13] Fairbanks R G, Wiebe P H, Bé A W H. Vertical distribution and isotopic composition of living planktonic foraminifera in the western North Atlantic [J]. Science, 1980, 207(4426): 61-63. doi: 10.1126/science.207.4426.61
[14] 郑执中, 郑守仪. 南海北部的浮游有孔虫[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1964, 6(1):38-73
ZHENG Zhizhong, ZHENG Shouyi. The planktonic foraminifera of the northern South China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1964, 6(1): 38-73.
[15] 赵泉鸿, 汪品先. 南海第四纪古海洋学研究进展[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 19(6):481-501 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.06.001
ZHAO Quanhong, WANG Pinxian. Progress in quaternary paleoceanography of the South China sea: A review [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 19(6): 481-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.06.001
[16] 涂霞. 南海东北部海区有孔虫的分布及其与海洋环境的关系[J]. 热带海洋, 1983, 2(1):11-19
TU Xia. Distribution and habitats of foraminifera in bottom sediments of the northeastern South China Sea [J]. Tropical Oceanography, 1983, 2(1): 11-19.
[17] 孙荣涛, 李铁刚, 曹奇原, 等. 冲绳海槽北部表层沉积物中浮游有孔虫的分布与海洋环境[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(5):511-518 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.006
SUN Rongtao, LI Tiegang, CAO Qiyuan, et al. Planktonic Foraminifera distributions in surface sediments of the northern Okinawa trough and their marine environment interpretation [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(5): 511-518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.006
[18] Berger W H. Planktonic Foraminifera: selective solution and paleoclimatic interpretation [J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1968, 15(1): 31-43. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(68)90027-2
[19] 齐泽坤, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等. 热带西太平洋碳酸盐溶跃深度及其变化规律[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(12):3852-3863 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.12.022
QI Zekun, XU Jishang, LI Guangxue, et al. The variation of carbonate lysocline depth in the western tropical Pacific Ocean [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(12): 3852-3863. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.12.022
[20] 郑连福, 陈荣华. 浮游有孔虫与深海碳酸盐溶解作用[J]. 海洋石油, 1982, 2(5):41-49
ZHENG Lianfu, CHEN Ronghua. Planktonic foraminifera and deep-sea carbonate dissolution [J]. Offshore Oil, 1982, 2(5): 41-49.
[21] 张江勇, 赵利, 李波, 等. 南海与台湾岛东部海域浅地层碳酸盐旋回[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5):1486-1500
ZHANG Jiangyong, ZHAO Li, LI Bo, et al. Carbonate cycle in sub-bottom strata in the South China Sea and the East Sea area of Taiwan Island [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1486-1500.
[22] 丁旋, 方念乔, 陈萍. 等. 孟加拉湾深海氧同位素2、3期上升流活动: 北印度洋冬季风的实证[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(1):53-59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.01.006
DING Xuan, FANG Nianqiao, CHEN Ping, et al. Upwelling actions in the Bay of Bengal during marine isotope stages 2 and 3: evidence for Indian winter monsoon [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2003, 23(1): 53-59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.01.006
[23] Ding X, Bassinot F, Guichard F, et al. Distribution and ecology of planktonic foraminifera from the seas around the Indonesian Archipelago [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2006, 58(2): 114-134. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2005.10.003
[24] 魏华玲, 方念乔, 丁旋, 等. 赤道东经90°海岭3.5Ma以来远洋记录反映的重大环境事件[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12):1627-1632 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.016
WEI Hualing, FANG Nianqiao, DING Xuan, et al. Major environmental events reflected by pelagic records since 3.5 Ma BP in the Ninetyeast Ridge at the equator [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(12): 1627-1632. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.016
[25] 刘勇勤. 晚中新世以来东北印度洋赤道海岭的远洋沉积记录及其环境意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2003.
LIU Yongqin. Pelagic sedimentary records and its palaeoenvironmental implication in Ninetyeast Ridge of the NE Indian Ocean since Middle Miocene[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2003.
[26] Symphonia T, Nathan D S. Planktonic Foraminifera from the Offshore segment between Chennai and Cuddalore, Bay of Bengal, India [J]. International Journal of Science and Research, 2014, 3(8): 1222-1225.
[27] Gandhi M S, Solai A. Statistical studies and ecology of benthic foraminifera from the depositional environment; a case study between Mandapam and Tuticorin, South East Coast of India [J]. International Journal of Research and Reviews, 2010, 5(1): 86-94.
[28] 李日辉, 孙荣涛, 陈晓辉. 渤海南部表层沉积物有孔虫埋藏群组合特征与海洋环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(3):17-27
LI Rihui, SUN Rongtao, CHEN Xiaohui. Comparison of foraminiferal taphocoenose assemblages with marine environmental parameters of the surface sediments from southern Bohai sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(3): 17-27.
[29] 张洁. 西南印度洋晚更新世以来的浮游有孔虫组合及其环境意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2017.
ZHANG Jie. Foraminiferal Assemblages in the Southwest Indian ocean sediments and their paleoenrivonmental implications since Late Pleistocene[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017.
[30] Anbuselvan N, Senthil Nathan D. Distribution and environmental implications of planktonic foraminifera in the surface sediments of southwestern part of Bay of Bengal, India [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Environments, 2021, 6(2): 213-235. doi: 10.1007/s43217-021-00053-8
[31] Kennet J P, Srinivasan M S. Neogene Planktonic Foraminifera: A Phylogenetic Atlas[M]. Hutchinson Ross Publishing Company, 1983: 265.
[32] Le J N, Shackleton N J. Carbonate dissolution fluctuations in the western equatorial Pacific during the Late Quaternary [J]. Paleoceanography, 1992, 7(1): 21-42. doi: 10.1029/91PA02854
[33] Oda M, Takemoto A. Planktonic foraminifera and paleoceanography in the domain of the Kuroshio current around Japan during the last 20, 000 years [J]. The Quaternary Research (Daiyonki Kenkyu), 1992, 31(5): 341-357. doi: 10.4116/jaqua.31.341
[34] Kawahata H, Nishimura A, Gagan M K. Seasonal change in foraminiferal production in the western equatorial Pacific warm pool: evidence from sediment trap experiments [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2002, 49(13-14): 2783-2800. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00058-9
[35] 李两全, 涂霞, 罗又郎, 等. 南海表层沉积物中浮游有孔虫的定量分析[J]. 中国科学B辑, 1992(9):966-971
LI Liangquan, TU Xia, LUO Youlang, et al. Quantitative analysis of planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments of the South China Sea [J]. Scientia Sinica(Series B), 1992(9): 966-971.
[36] 刘志学. 印度洋东经90°海岭更新世晚期的上层海水性质及其古气候意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2016
LIU Zhixue. Charateristic of the upper sea water in Ninetyeast Ridge and Paleoclimatic implication in the Late Pleistocene[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016.
[37] 张振芳. 孟加拉湾上新世以来沉积记录及古气候演化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2003.
ZHANG Zhenfang. Sedimentary records and paleoclimate evolution of bay of Bengal since Pliocene Time[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2003.
[38] Huber B T. Modern planktonic foraminifera [J]. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 1990, 20(1): 90-91. doi: 10.2113/gsjfr.20.1.90
[39] 赵其渊. 海洋地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989.
ZHAO Qiyuan. Marine Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1989.
[40] 刘振尤. 中印度洋海盆南部中新世以来CCD的演变及意义: 来自微体化石组合和元素地球化学的证据[D]. 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2020.
LIU Zhenyou. CCD evolution and implications since the Miocene: evidence from nannofossils assemblage and element geochemistry in the south part of Central Indian Ocean Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2020.
-



 下载:
下载: