Characteristics of submarine landslides and their implications for petroleum geology
-
摘要:
海底滑坡是一种由于重力失稳导致的广泛发生在外陆架-上陆坡-深海平原的沉积物搬运体,是海底沉积物重要的搬运过程,具有较强的侵蚀能力和搬运能力,可将大量陆架沉积物搬运至深海,为深海带来丰富的沉积物。再沉积后的滑坡体因其特殊的内部结构,对海洋油气成藏有重要影响。综合国内外研究,对海底滑坡空间展布特征和垂向结构特征进行总结,对滑坡体岩石物理特征进行梳理,揭示海底滑坡边界特征、内部结构以及岩石物理特征。结合海底滑坡特征,从提供物源、储层、盖层、改变海底温压等方面分析海底滑坡对海底油气藏的积极意义,从破坏盖层、改变海底土体温压环境等方面分析海底滑坡对海底油气藏的负面影响。最后结合国内外研究现状,指出未来应对海底滑坡微尺度特征识别、进一步开展海底滑坡与海底油气藏联系以及加强海洋油气开发致灾风险等方面进行深入研究。
Abstract:Submarine landslide is a type of sediment transport body that occurs widely in the regions from outer continental shelf to upper continental slope and to deep-sea plain due to gravity instability. It is an important transport process of seafloor sediments. Its strong power of erosion could transport a huge amount of sediments from continental shelf to deep sea. A landslide event has an important impact on submarine hydrocarbon accumulation and distribution because of its special internal structure. This mini-review summarizes studies on submarine landslide and its role in shaping and re-working marine hydrocarbon resources, specified the characteristics in spatial distribution and vertical structure of submarine landslides, and revealed preliminarily the petrophysical characteristics of landslides. Based on the above-mentioned works, the roles of submarine landslides in both positive and negative manner, on submarine oil and gas reservoirs was analyzed in terms of provenance, reservoir, caprock, and variations in seafloor temperature and pressure. Finally, combined with the current research progresses, we pointed out that the future direction of research shall focus on the microscale characteristics of submarine landslides, on the relationship between submarine landslides and submarine oil and gas reservoirs, and on the prevention in submarine-landslide–risk regions against possible disaster from trigging during offshore operation of oil and gas development.
-

-
图 1 Storegga滑坡多波束测深图像[14]
Figure 1.
图 3 滑坡陡壁及滑坡滑动方向[14]
Figure 3.
图 4 海底滑坡头部地震反射特征[15]
Figure 4.
图 5 滑坡侧缘和挤压脊[31]
Figure 5.
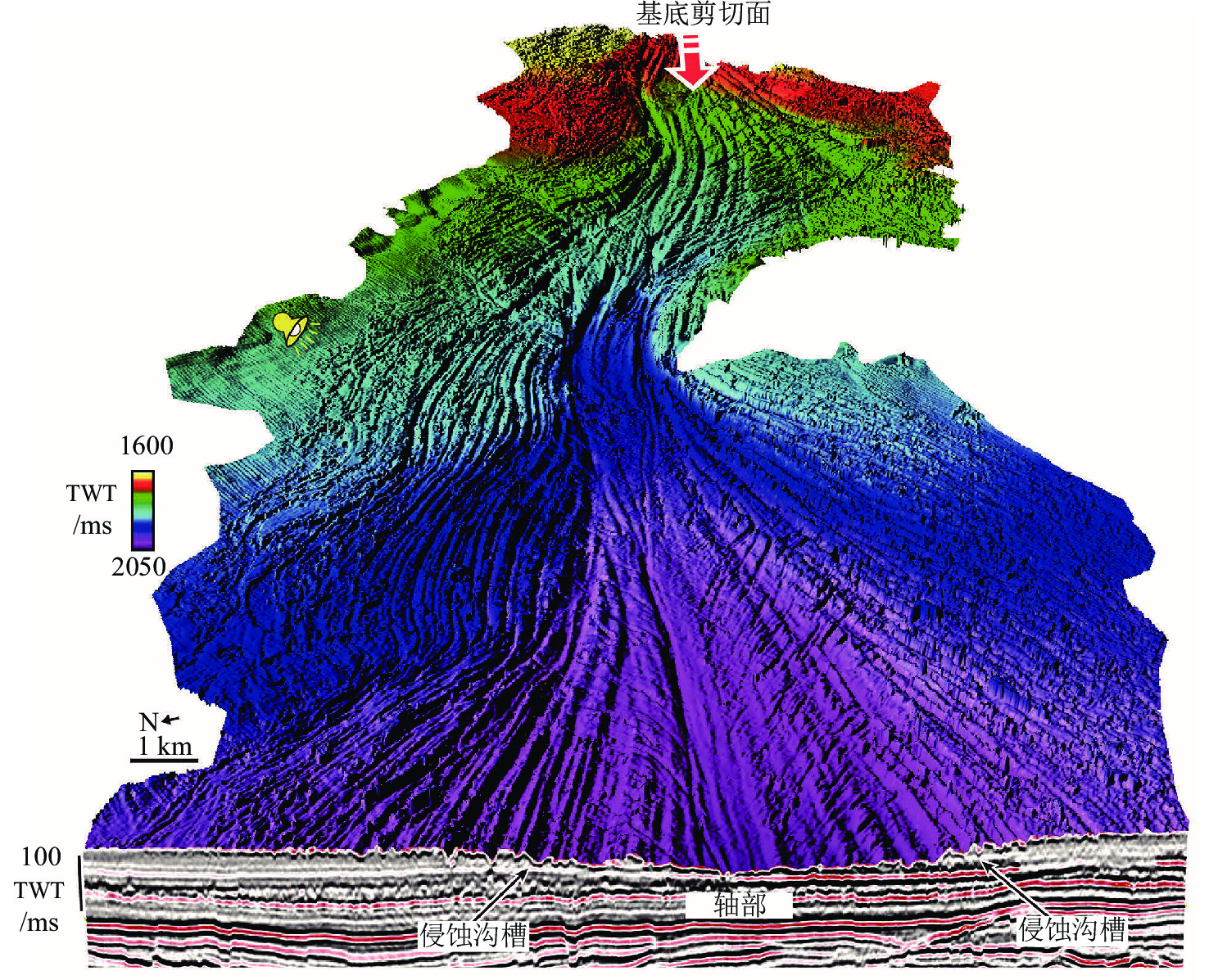
图 6 海底滑坡基底剪切面及其侵蚀特征[33]
Figure 6.
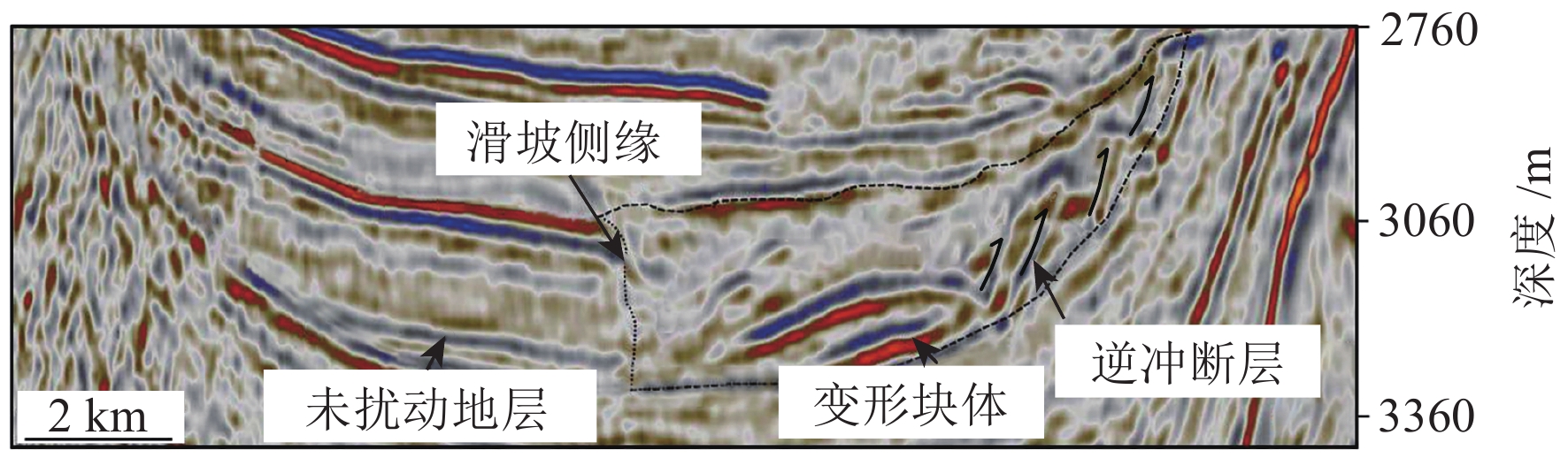
图 7 滑坡内部逆冲断层[38]
Figure 7.
图 8 海底滑坡内部可作为储层的富砂块体[37]
Figure 8.
图 9 海底滑坡的盖层作用[54]
Figure 9.
图 10 海底滑坡构造天然气水合物成藏模式[56]
Figure 10.
表 1 全球海底滑坡陡壁坡度统计
Table 1. Slope of global submarine landslide headwall
滑坡名称 位置 陡壁坡度 中国南海北部陆坡滑坡[16] 中国南海北部陆坡 5°~35° The Israel Slump Complex[18] 以色列近海大陆边缘 2°~15° The Gorgon Slide[19] 澳大利亚西北部边缘 30° The Gebra Slide[21] 南极布兰斯菲尔德盆地 16° The Storegga Slide[22] 挪威近海大陆架 25°~35° The Hinlopen Slide[23] 北冰洋斯瓦尔巴群岛边缘 20°~35° The Goleta Slope[24] 美国圣巴巴拉海峡西部边坡 40°~45° The 44-North Slide[25] 美国俄勒冈州近海边缘 22° Submarine landslides along the Israeli continental-slope[26] 以色列大陆坡 5°~26° 白云滑坡[27] 中国南海珠江口盆地 6°~14.5° -
[1] Hampton M A, Lee H J, Locat J. Submarine landslides [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1996, 34(1): 33-59. doi: 10.1029/95RG03287
[2] Locat J, Lee H, Ten Brink U S, et al. Geomorphology, stability and mobility of the Currituck slide [J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 264(1-2): 28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.12.005
[3] 朱超祁, 贾永刚, 刘晓磊, 等. 海底滑坡分类及成因机制研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(6):153-163
ZHU Chaoqi, JIA Yonggang, LIU Xiaolei, et al. Classification and genetic machanism of submarine landslide: a review [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(6): 153-163.
[4] 贾永刚, 王振豪, 刘晓磊, 等. 海底滑坡现场调查及原位观测方法研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(10):61-72
JIA Yonggang, WANG Zhenhao, LIU Xiaolei, et al. The research progress of field investigation and in-situ observation methods for submarine landslide [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(10): 61-72.
[5] 宋晓帅, 孙志文, 朱超祁, 等. 深海滑坡研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):222-235 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021062701
SONG Xiaoshuai, SUN Zhiwen, ZHU Chaoqi, et al. A review on deepwater landslide [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 222-235. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021062701
[6] 潘继平, 张大伟, 岳来群, 等. 全球海洋油气勘探开发状况与发展趋势[J]. 中国矿业, 2006, 15(11):1-4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2006.11.001
PAN Jiping, ZHANG Dawei, YUE Laiqun, et al. Status quo of global offshore oil and gas exploration and development and its trends [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2006, 15(11): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2006.11.001
[7] Randolph M F, Gaudin C, Gourvenec S M, et al. Recent advances in offshore geotechnics for deep water oil and gas developments [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2011, 38(7): 818-834. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2010.10.021
[8] 苏丕波, 梁金强, 张伟, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏系统[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):77-89 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.006
SU Pibo, LIANG Jinqiang, ZHANG Wei, et al. Natural gas hydrate accumulation system in the Shenhu sea area of the northern South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 77-89. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.006
[9] 宁伏龙, 梁金强, 吴能友, 等. 中国天然气水合物赋存特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(8):1-24 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.001
NING Fulong, LIANG Jinqiang, WU Nengyou, et al. Reservoir characteristics of natural gas hydrates in China [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(8): 1-24. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.08.001
[10] Gee M J R, Masson D G, Watts A B, et al. The Saharan debris flow: an insight into the mechanics of long runout submarine debris flows [J]. Sedimentology, 1999, 46(2): 317-335. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00215.x
[11] Solheim A, Berg K, Forsberg C F, et al. The Storegga Slide complex: repetitive large scale sliding with similar cause and development [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22(1-2): 97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.10.013
[12] 年廷凯, 沈月强, 郑德凤, 等. 海底滑坡链式灾害研究进展[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(6):1657-1675 doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0815
NIAN Tingkai, SHEN Yueqiang, ZHENG Defeng, et al. Research advances on the chain disasters of submarine landslides [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(6): 1657-1675. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0815
[13] 贾永刚, 陈天, 李培英, 等. 海洋地质灾害原位监测技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(3):1-14 doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-01
JIA Yonggang, CHEN Tian, LI Peiying, et al. Research progress on the in-situ monitoring technologies of marine geohazards [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 1-14. doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.03-01
[14] Micallef A, Masson D G, Berndt C, et al. Submarine spreading in the Storegga Slide, Norwegian Sea [J]. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 2016, 46(1): 411-412. doi: 10.1144/M46.88
[15] Bull S, Cartwright J, Huuse M. A review of kinematic indicators from mass-transport complexes using 3D seismic data [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(7): 1132-1151. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.09.011
[16] Wang W W, Wang D W, Wu S G, et al. Submarine landslides on the north continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(1): 83-100. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3491-0
[17] Wu N. Multi-scale, multidisciplinary analysis of mass-transport complex (MTC) emplacement and structure[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Imperial College London, 2020.
[18] Frey Martinez J, Cartwright J, Hall B. 3D seismic interpretation of slump complexes: examples from the continental margin of Israel [J]. Basin Research, 2005, 17(1): 83-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2005.00255.x
[19] Nugraha H D, Jackson C A L, Johnson H D, et al. How erosive are submarine landslides[J]. Geology, 2019.
[20] 何叶, 钟广法. 海底滑坡及其反射地震识别综述[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(1):116-125 doi: 10.11759/hykx20130714001
HE Ye, ZHONG Guangfa. Current status of submarine landslides and their seismic recognition [J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(1): 116-125. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130714001
[21] Imbo Y, De Batist M, Canals M, et al. The Gebra Slide; a submarine slide on the Trinity Peninsula margin, Antarctica[J]. Marine geology, 2003, 193(3-4): 235-252.
[22] Bryn P, Berg K, Forsberg C F, et al. Explaining the Storegga slide [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22(1-2): 11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.12.003
[23] Vanneste M, Mienert J, Bunz S. The Hinlopen Slide; a giant, submarine slope failure on the northern Svalbard margin, Arctic Ocean[J]. Earth and planetary science letters, 2006, 245(1-2): 373-388.
[24] Jared W Kluesner D S B A. Structural controls on slope failure within the western Santa Barbara Channel based on 2D and 3D seismic imaging [J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics, Geosystems, 2020, 8(21):1-34.
[25] Lenz B L, Sawyer D E, Phrampus B, et al. Seismic imaging of seafloor deformation induced by impact from large submarine landslide blocks, offshore Oregon[J]. Geosciences (Basel), 2019, 9(1): 10.
[26] Katz O, Reuven E, Aharonov E. Submarine landslides and fault scarps along the eastern Mediterranean Israeli continental slope[J]. Marine geology, 2015, 369: 100-115.
[27] 孙运宝, 吴时国, 王志君, 等. 南海北部白云大型海底滑坡的几何形态与变形特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(6):69-77
SUN Yunbao, WU Shiguo, WANG Zhijun, et al. The geometry and deformation characteristics of Baiyun submarine landslide [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(6): 69-77.
[28] Alves T M, Kurtev K, Moore G F, et al. Assessing the internal character, reservoir potential, and seal competence of mass-transport deposits using seismic texture: A geophysical and petrophysical approach [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(4): 793-824. doi: 10.1306/09121313117
[29] Scarselli N. Submarine landslides: architecture, controlling factors and environments. A summary[M]//Scarselli N, Adam J, Chiarella D, et al. Regional Geology and Tectonics. Volume 1: Principles of Geologic Analysis. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 417-439.
[30] 吴时国, 马林伟, 孙金, 等. 海上丝绸之路大型地质灾害: 特点与现状[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(1):401-411 doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0316
WU Shiguo, MA Linwei, SUN Jin, et al. Characteristic and current status of some large-scale geological disasters along the Maritime Silk Road [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(1): 401-411. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0316
[31] Nugraha H D, Jackson C A L, Johnson H D, et al. Evolution of flow cells within a mass-transport complex: Insights from the Gorgon Slide, offshore NW Australia[Z]. EarthArXiv, 2020.
[32] Le Goff J, Slootman A, Mulder T, et al. On the architecture of intra-formational mass-transport deposits; insights from the carbonate slopes of Great Bahama Bank and the Apulian carbonate platform[J]. Marine geology, 2020, 427: 106205.
[33] Scarselli N, McClay K, Elders C. Submarine slide and slump complexes, Exmouth Plateau, NW Shelf of Australia[C]//Western Australian Basins Symposium 2013. Perth: Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia, 2013.
[34] Gee M J R, Gawthorpe R L, Friedmann J S. Giant striations at the base of a submarine landslide [J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 214(1-3): 287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.09.003
[35] Lastras G, De Blasio F V, Canals M, et al. Conceptual and numerical modeling of the BIG'95 debris flow, Western Mediterranean Sea [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2005, 75(5): 784-797. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2005.063
[36] Wu N, Jackson C A L, Johnson H D, et al. The formation and implications of giant blocks and fluid escape structures in submarine lateral spreads [J]. Basin Research, 2021, 33(3): 1711-1730. doi: 10.1111/bre.12532
[37] Wu N, Jackson C A L, Johnson H D, et al. Lithological, petrophysical, and seal properties of mass-transport complexes, northern Gulf of Mexico [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2021, 105(7): 1461-1489. doi: 10.1306/06242019056
[38] Gafeira J, Bulat J, Evans D. The southern flank of the Storegga Slide: imaging and geomorphological analyses using 3D seismic[M]//Lykousis V, Sakellariou D, Locat J. Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences. Dordrecht: Springer, 2007, 27: 57-65.
[39] Gee M J R, Gawthorpe R L, Friedmann S J. Triggering and evolution of a giant submarine landslide, offshore Angola, revealed by 3D seismic stratigraphy and geomorphology[J]. Journal of sedimentary research, 2006, 76(1): 9-19.
[40] Kneller B, Dykstra M, Fairweather L, et al. Mass-transport and slope accommodation: Implications for turbidite sandstone reservoirs [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(2): 213-235. doi: 10.1306/09011514210
[41] 姚哲, 朱继田, 左倩媚, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区重力流沉积体系及油气勘探前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(10):21-30 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.003
YAO Zhe, ZHU Jitian, ZUO Qianmei, et al. Gravity flow sedimentary system and petroleum exploration prospect of deep water area in the Qiongdongnan Basin South, China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(10): 21-30. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.003
[42] Zabanbark A, Lobkovsky L I. Continental slopes of the West Africa Region: A unique treasure of hydrocarbons [J]. Oceanology, 2018, 58(5): 727-736. doi: 10.1134/S000143701805017X
[43] Le A N. Mass-transport deposit in deep water setting, offshore Cameroon, West Africa [J]. Indonesian Journal on Geoscience, 2021, 8(2): 213-219.
[44] Lisitsyn A P. Patterns of rapid and extremely rapid (avalanche) sedimentation: implications for marine oil and gas generation [J]. Russian Geology & Geophysics, 2009, 50(4): 278-298.
[45] Allen J, Schwartz K, Desantis J, et al. Integration of structure and stratigraphy in bone spring tight oil sandstones using 3D seismic in the Delaware Basin, TX[C]//Unconventional Resources Technology Conference. Denver, Colorado: SEG, 2013: 2521-2527.
[46] Bhatnagar P, Verma S, Bianco R. Characterization of mass transport deposits using seismic attributes: Upper Leonard Formation, Permian Basin [J]. Interpretation, 2019, 7(4): SK19-SK32. doi: 10.1190/INT-2019-0036.1
[47] Qin Y P, Alves T M, Constantine J, et al. The role of mass wasting in the progressive development of submarine channels (Espírito Santo Basin, Se Brazil) [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2017, 87(5): 500-516. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2017.18
[48] Henry L C, Wadsworth J A, Hansen B, et al. Erosion and ponding of Thunder Horse deepwater turbidites by mass transport complexes in Mississippi Canyon based on image log sedimentology [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 639-658. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.006
[49] 姚根顺, 袁圣强, 马玉波, 等. 琼东南华光凹陷深水重力搬运沉积体系及其油气勘探[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(3):471-476 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.052
YAO Genshun, YUAN Shengqiang, MA Yubo, et al. Deepwater mass transport deposition system of Huaguang depression, Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance for hydrocarbon exploration [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(3): 471-476. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.052
[50] 陈珊珊, 孙运宝, 吴时国. 南海北部神狐海域海底滑坡在地震剖面上的识别及形成机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(6):40-45 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2012.06.008
CHEN Shanshan, SUN Yunbao, WU Shiguo. Sea bottom landslide in the Shenhu area on the north margin of South China Sea and triggering mechanisms [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(6): 40-45. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2012.06.008
[51] Posamentier H W, Martinsen O J, Shipp R C, et al. The character and genesis of submarine mass-transport deposits: insights from outcrop and 3D seismic data[M]//Mass-Transport Deposits in Deepwater Settings. Special Publication, Society for Sedimentary Geology, 2011, 96: 7-38.
[52] Alves T M, Kurtev K, Moore G F, et al. Assessing the internal character, reservoir potential, and seal competence of mass-transport deposits using seismic texture: A geophysical and petrophysical approach[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(4): 793-824.
[53] Cardona S, Wood L J, Day-Stirrat R J, et al. Fabric development and pore-throat reduction in a mass-transport deposit in the Jubilee Gas Field, eastern Gulf of Mexico: consequences for the sealing capacity of MTDs[M]//Lamarche G, Mountjoy J, Bull S, et al. Submarine Mass Movements and their Consequences. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016, 41: 27-37.
[54] Cardona S, Wood L, Moscardelli L, et al. Cannibalization and sealing of deepwater reservoirs by mass-transport complexes: The Jubilee field, Gulf of Mexico [J]. Interpretation, 2020, 8(4): SV17-SV30. doi: 10.1190/INT-2019-0274.1
[55] 赵芳. 南海北部陆缘裂后期岩浆活动及海底滑坡事件研究[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2016.
ZHAO Fang. Post-rift magmatism and submarine landslides on the northern South China Sea continental margin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016.
[56] 杨木壮, 潘安定, 沙志彬. 陆缘地区天然气水合物成藏地质模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(6):85-90
YANG Muzhuang, PANG Anding, SHA Zhibin. Geological models of gas hydrates deposits along the continental margin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(6): 85-90.
[57] 郭依群, 梁金强, 王宏斌, 等. 南海北部海底滑坡与天然气水合物的关系[C]//海洋地质、矿产资源与环境学术研讨会论文摘要集. 广州, 2006
GUO Yiqun, LIANG Jinqiang, WANG Hongbin, et al. Relationship between submarine landslides and gas hydrate in the northern South China Sea[C]//Abstracts of Seminar on Marine Geology, Mineral Resources & Environment. Guangzhou, 2006.
[58] 吴时国, 姚根顺, 董冬冬, 等. 南海北部陆坡大型气田区天然气水合物的成藏地质构造特征[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(3):324-328 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.03.002
WU Shiguo, YAO Genshun, DONG Dongdong, et al. Geological structures for forming gas hydrate reservoir in the huge deepwater gas field of the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(3): 324-328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.03.002
[59] 蔡峰, 闫桂京, 梁杰, 等. 大陆边缘特殊地质体与水合物形成的关系[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(6):11-15 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2011.06.001
CAI Feng, YAN Guijing, LIANG Jie, et al. The relationship between special geological bodies and hydrate formation at continental margin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(6): 11-15. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2011.06.001
[60] Bünz S, Mienert J, Berndt C. Geological controls on the Storegga gas-hydrate system of the mid-Norwegian continental margin [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 209(3-4): 291-307. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00097-9
[61] 吴时国, 董冬冬, 杨胜雄, 等. 南海北部陆坡细粒沉积物天然气水合物系统的形成模式初探[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(7):1849-1857 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.019
WU Shiguo, DONG Dongdong, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Genetic model of the hydrate system in the fine grain sediments in the northern continental slope of South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(7): 1849-1857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.019
[62] 张丙坤, 李三忠, 夏真, 等. 南海北部海底滑坡与天然气水合物形成与分解的时序性[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(2):434-440 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2014.02.001
ZHANG Bingkun, LI Sanzhong, XIA Zhen, et al. Time sequence of submarine landslides and gas hydrates in the northern South China Sea [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014, 38(2): 434-440. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2014.02.001
[63] 杜浩, 石万忠, 梁金强, 等. 琼东南盆地块体搬运沉积体系成因及其对水合物成藏的影响[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(4):869-881 doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2021.04.020
DU Hao, SHI Wanzhong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Genesis of mass transport deposits and their effect on gas hydrate accumulation in the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(4): 869-881. doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2021.04.020
[64] Alves T M. Megablocks and the stratigraphic record of continental margins: how large an event do they materialise?[C]//STRATI 2013. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 775-780.
[65] Talling P, Clare M, Urlaub M, et al. Large submarine landslides on continental slopes: Geohazards, methane release, and climate change [J]. Oceanography, 2014, 27(2): 32-45. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2014.38
[66] 刘杰, 杨睿, 邬黛黛, 等. 琼东南盆地华光凹陷天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8):13-25
LIU Jie, YANG Rui, WU Daidai, et al. Factors affecting the thickness of gas hydrate stability zones in the Huaguang Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 13-25.
[67] 刘杰, 刘丽华, 吴能友, 等. 南海东沙海域深水区末次冰期以来天然气水合物稳定带演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(2):146-155 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020061801
LIU Jie, LIU Lihua, WU Nengyou, et al. Evolution of gas hydrate stability zone in the deep water of Dongsha sea area since the Last Glaciation Maximum [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(2): 146-155. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020061801
[68] Riboulot V, Ker S, Sultan N, et al. Freshwater lake to salt-water sea causing widespread hydrate dissociation in the Black Sea [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 117. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02271-z
[69] Maslin M, Owen M, Betts R, et al. Gas hydrates: past and future geohazard? [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2010, 368(1919): 2369-2393. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2010.0065
[70] Eldholm O, Bungum H. Potential secondary events caused by early Holocene paleoearthquakes in Fennoscandia: a climate-related review [J]. Norwegian Journal of Geology, 2021, 101: 202108.
[71] Paull C K, Brewer P G, Ussler W, et al. An experiment demonstrating that marine slumping is a mechanism to transfer methane from seafloor gas-hydrate deposits into the upper ocean and atmosphere [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2002, 22(4): 198-203. doi: 10.1007/s00367-002-0113-y
[72] Maslin M, Owen M, Day S, et al. Linking continental-slope failures and climate change: testing the clathrate gun hypothesis [J]. Geology, 2004, 32(1): 53-56. doi: 10.1130/G20114.1
[73] Brothers D S, Luttrell K M, Chaytor J D. Sea-level-induced seismicity and submarine landslide occurrence [J]. Geology, 2013, 41(9): 979-982. doi: 10.1130/G34410.1
[74] Yelisetti S, Spence G D, Riedel M. Role of gas hydrates in slope failure on frontal ridge of northern Cascadia margin [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 199(1): 441-458. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu254
-




 下载:
下载: