Spatial variation of surface soil color in the eastern Xizang Plateau and its environmental significance
-
摘要:
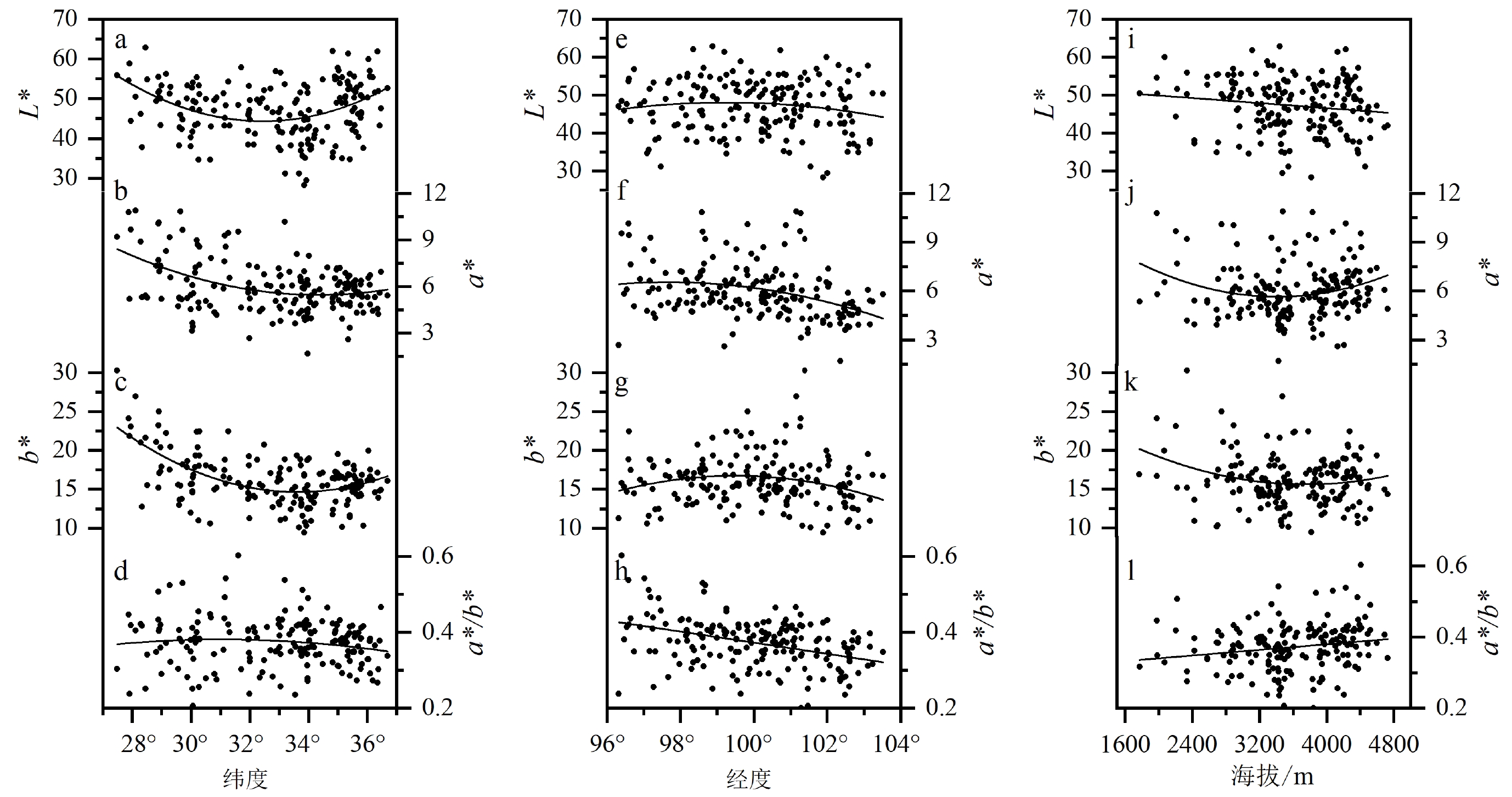
认识青藏高原东部现代表土的色度特征及其空间分布,理解其与现代气候因子之间的联系,对于高原地区黄土-古环境重建和揭示第四纪环境变化历史具有重要意义。通过对研究区表层土壤色度的详细分析,对比现代气候资料,探讨了青藏高原东部表层土壤色度的空间变化特征及其环境意义。结果表明:① 高原东部表土色度参数空间变化特征差异显著,表现为随纬度升高,土壤亮度呈先减小后增大的趋势,而红度和黄度则逐步减小;随经度的升高,黄度先增大后减小,而红度值逐步减小;红度和黄度整体随着海拔上升而呈先减小后升高的特征。这些变化特征和差异是表土色度对高原东部复杂地理环境和水热条件变化响应的结果。② 在高原的干旱-半湿润区,土壤亮度对降水的响应敏感;红度和黄度对大尺度的温度变化响应较敏感,而较冷的环境下,红度对温度响应复杂,但与降水存在一定的联系。红度/黄度比值主要指示了气候控制下的赤铁矿和针铁矿的变化和竞争,对干旱-半湿润区域的降水变化响应较为敏感。青藏高原东部现代表土色度与气候密切相关,其空间变化特征一定程度上反映了该地区现代气候因子的空间变化;另一方面由于该区地形和气候复杂多变,部分色度指标与气候关系复杂,在重建青藏高原东部黄土古环境变化历史时需要谨慎。
Abstract:The color characteristics and spatial variation of surface soil in the eastern Xizang Plateau (ETP) are important for understanding the relationship between soil color and modern climate factors and for reconstructing the Quaternary paleoclimatic environment. We analyzed in detail the spatial variation of surface soil color and its environmental significance. Results show that the spatial variation of surface soil color in the ETP is obvious. The soil brightness decreases first and then increases with latitude increase, and the redness and yellowness decrease with the latitude increase. In addition, the change in yellowness shows a parabolic curve from increase to decrease with longitude increase, and redness decreases with longitude increase. Both redness and yellowness decrease first and then slightly increase with altitude increase. The redness/yellowness ratio does not change significantly with latitude, but decreases with longitude increase, and increases with altitude. The spatial variation of soil color is resulted from the hydrothermal variation in local complicated arid semi-humid environment. In the study region of plateau, brightness decreases with precipitation increase within a certain precipitation range and is sensitive to precipitation. Redness and yellowness are sensitive to large-scale temperature changes. However, the response of redness to temperature is complex in a cold environment, which is related to precipitation. The redness/yellowness ratio indicates mainly the formations of hematite and goethite under special climate conditions, and the ratio is more sensitive to precipitation in arid and semi-humid areas than to temperature. The spatial variation in the color of surface soil reflects the spatial variation of regional climate factors under modern atmospheric circulation to a certain extent. However, due to the complexity of terrain and climate in the ETP, the relationship between color parameters and climate is complex. One should be careful in rebuilding the paleoenvironmental history from loess in the ETP.
-
Key words:
- surface soil /
- color /
- spatial variation /
- environmental significance /
- Eastern Xizang Plateau
-

-
表 1 青藏高原东部表层土壤不同纬度、经度和海拔范围的色度参数
Table 1. The changes in color of surface soil with latitude, longitude, and altitude ranges in the ETP
样品的位置 L* a* b* a*/b* 均值 最大值 最小值 均值 最大值 最小值 均值 最大值 最小值 均值 最大值 最小值 全样 47.22 62.87 28.27 5.95 10.89 1.68 16.07 30.29 9.45 0.37 0.70 0.11 27°~30°N 49.19 62.87 37.78 7.30 10.89 4.54 18.94 26.91 26.91 0.39 0.70 0.24 30°~34°N 45.32 57.91 28.27 5.76 10.15 1.68 15.57 22.45 9.46 0.37 0.60 0.12 34°~37°N 48.61 62.04 34.79 5.60 7.96 2.60 15.41 19.93 10.17 0.36 0.47 0.19 96°~99°E 47.64 62.87 31.19 6.50 10.82 4.34 16.04 22.44 10.61 0.41 0.70 0.25 99°~101°E 47.69 61.88 34.59 6.10 10.10 2.60 16.51 25.02 10.96 0.37 0.47 0.19 101°~104°E 46.32 59.97 28.27 5.30 10.89 1.68 15.56 30.3 9.46 0.34 0.47 0.12 1500~3000 m 49.68 59.97 34.96 6.34 10.77 3.91 17.52 30.29 10.17 0.36 0.51 0.27 3000~4000 m 46.31 62.87 28.27 5.60 10.89 1.68 15.47 26.91 9.46 0.36 0.70 0.11 4000~4600 m 47.30 62.04 31.19 6.34 10.15 2.60 16.19 22.45 10.61 0.39 0.60 0.19 -
[1] 柯夫达 B A. 土壤学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981.
Ковда В А. Principles of Soil Science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981.
[2] 朱鹤健, 何宜庚. 土壤地理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1992.
ZHU Hejian, HE Yigeng. Soil Geography[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1992.
[3] 何柳, 孙有斌, 安芷生. 中国黄土颜色变化的控制因素和古气候意义[J]. 地球化学, 2010, 39(5):447-455
HE Liu, SUN Youbin, AN Zhisheng. Changing color of Chinese loess: Controlling factors and paleocliamtic significances [J]. Geochimica, 2010, 39(5): 447-455.
[4] Sun Y B, He L, Liang L J, et al. Changing color of Chinese loess: Geochemical constraint and paleoclimatic significance [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(6): 1131-1138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.08.006
[5] 杨胜利, 方小敏, 李吉均, 等. 表土颜色和气候定性至半定量关系研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(S1):175-181
YANG Shengli, FANG Xiaomin, LI Jijun, et al. Transformation functions of soil color and climate [J]. Science in China (Series D), 2001, 31(S1): 175-181.
[6] 陈诗越, 方小敏, 王苏民. 川西高原甘孜黄土与印度季风演化关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(3):41-46
CHEN Shiyue, FANG Xiaomin, WANG Sumin. Relation between the loess stratigraphy on the eastern Xizang plateau and Indian monsoon [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(3): 41-46.
[7] Yang S L, Ding Z L. Color reflectance of Chinese loess and its implications for climate gradient changes during the last two glacial-interglacial cycles [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(20): 2058.
[8] 陈一萌, 陈兴盛, 宫辉力, 等. 土壤颜色: 一个可靠的气候变化代用指标[J]. 干旱区地理, 2006, 29(3):309-313 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2006.03.001
CHEN Yimeng, CHEN Xingsheng, GONG Huili, et al. Soil color: a new sensitive indicator for climatic change [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2006, 29(3): 309-313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2006.03.001
[9] 陈杰, 杨太保, 曾彪, 等. 中国帕米尔地区黄土上部色度变化特征及古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(2):333-342
CHEN Jie, YANG Taibao, ZENG Biao, et al. Chroma characteristics and its paleoclimatic significance in Pamir loess section, China [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(2): 333-342.
[10] 杨丹, 庞奖励, 周亚利, 等. 汉中盆地军王村黄土-古土壤剖面的色度特征及机理[J]. 中山大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 57(1):93-101
YANG Dan, PANG Jiangli, ZHOU Yali, et al. Chroma characteristics and its significance of the Junwangcun loess-paleosol profile in the Hanzhong basin [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2018, 57(1): 93-101.
[11] 杜丁丁, Mughal M S, Blaise D, 等. 青藏高原中部色林错湖泊沉积物色度反映末次冰盛期以来区域古气候演化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(3):551-558
DU Dingding, Mughal M S, Blaise D, et al. Paleoclimatic changes reflected by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy since Last Glacial Maximum from Selin Co Lake sediments, central Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2019, 42(3): 551-558.
[12] 崔东, 荣雪, 王晓磊, 等. 中国土壤颜色与气候指标的定量研究[J]. 农业科技与装备, 2011(10):6-7,10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1161.2011.10.005
CUI Dong, RONG Xue, WANG Xiaolei, et al. Quantitative study on the correlation between the redness degree in soil colour and mean annual precipitation in China [J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2011(10): 6-7,10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1161.2011.10.005
[13] 姬红利, 周文君, 张一平, 等. 云南土壤色度与海拔及气候的关系研究[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 35(S2):352-358
JI Hongli, ZHOU Wenjun, ZANG Yiping, et al. Relationship between soil color and climatic factors in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Yunnan University, 2013, 35(S2): 352-358.
[14] 苗运法, 杨胜利, 卓世新, 等. 我国西北干旱区现代地表沉积物颜色指标与降水关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(4):77-85
MIAO Yunfa, YANG Shengli, ZHUO Shixin, et al. Relationship between the color of surface sediments and precipitation in arid northwest China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(4): 77-85.
[15] 严永耀, 安聪荣, 苗运法, 等. 新疆青海地区现代地表沉积物颜色指标与气候参数关系[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(2):355-364
YAN Yongyao, AN Congrong, MIAO Yunfa, et al. Relationship between color index of modern surface sediment and climate parameters in the region of Xinjiang and Qinghai [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(2): 355-364.
[16] 宋瑞卿, 朱芸, 吕镔, 等. 青藏高原表土的色度特征及其环境意义[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2016, 11(1):14-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.01.003
SONG Ruiqing, ZHU Yun, LYU Bin, et al. Topsoil color and its environmental significance in the Xizang Plateau [J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2016, 11(1): 14-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.01.003
[17] 郑兴芬, 吕镔, 陈梓炫, 等. 不同空间范围土壤色度的纬向变化特征及其气候意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(5):1186-1196
ZHENG Xingfen, LÜ Bin, CHEN Zixuan, et al. Latitudinal variation characteristics of soil color in different spatial extents and their climatic significance [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(5): 1186-1196.
[18] 朱丽东, 周尚哲, 李凤全, 等. 庐山JL红土剖面的色度气候意义[J]. 热带地理, 2007, 27(3):193-197,202 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2007.03.001
ZHU Lidong, ZHOU Shangzhe, LI Fengquan, et al. Climatic implication of the chroma of JL red earth section in the Lushan mountain [J]. Tropical Geography, 2007, 27(3): 193-197,202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2007.03.001
[19] Hu X F, Du Y, Guan C L, et al. Color variations of the Quaternary Red Clay in southern China and its paleoclimatic implications [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2014, 303: 15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2014.01.006
[20] 刘峰, 王昊, 秦艺帆, 等. 南京周家山下蜀黄土色度特征及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):143-151
LIU Feng, WANG Hao, QIN Yifan, et al. Chroma characteristics of the Zhoujiashan Xiashu loess profile in Nanjing and its significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 143-151.
[21] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
LIU Tungsheng. Loess and the Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[22] Balsam W, Ji J F, Chen J. Climatic interpretation of the Luochuan and Lingtai loess sections, China, based on changing iron oxide mineralogy and magnetic susceptibility [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(3-4): 335-348. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.04.023
[23] Schaetzl R J, Bettis E A, Crouvi O, et al. Approaches and challenges to the study of loess Introduction to the LoessFest Special Issue [J]. Quaternary Research, 2018, 89(3): 563-618. doi: 10.1017/qua.2018.15
[24] 王攀, 张培新, 杨振京, 等. 靖边黄土剖面记录的末次冰期以来的气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):162-170
WANG Pan, ZHANG Peixin, YANG Zhenjing, et al. Climate change since the last glacial stage recorded in Jingbian loess section [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3): 162-170.
[25] 陈海涛, 孔凡彪, 徐树建, 等. 山东仙境源黄土常量元素特征及其古气候环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):189-197
CHEN Haitao, KONG Fanbiao, XU Shujian, et al. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and their paleoenvironmental significance of the Xianjingyuan loess in Shandong Province [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 189-197.
[26] 王博, 王牛牛, 王志远, 等. MIS13时期黄土高原东西部地区夏季风不对称演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):185-192
WANG Bo, WANG Niuniu, WANG Zhiyuan, et al. Unparallel MIS13 climate evolution between western and eastern Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 185-192.
[27] 李越, 宋友桂, 王千锁. 新疆昭苏黄土剖面色度变化特征及古气候意义[J]. 地球环境学报, 2014, 5(2):67-75 doi: 10.7515/JEE201402003
LI Yue, SONG Yougui, WANG Qiansuo. Chroma characteristics in the Zhaosu loess section and its paleoclimatic significance [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2014, 5(2): 67-75. doi: 10.7515/JEE201402003
[28] Wang Q S, Song Y G, Zhao Z J, et al. Color characteristics of Chinese loess and its paleoclimatic significance during the last glacial-interglacial cycle [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 116: 132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.013
[29] 石培宏, 杨太保, 田庆春, 等. 靖远黄土—古土壤色度变化特征分析及古气候意义[J]. 兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 48(2):15-23
SHI Peihong, YANG Taibao, TIAN Qingchun, et al. Chroma chracteristics in the loess-paleosol at Jingyuan section and its signification to paleocliamete [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 2012, 48(2): 15-23.
[30] Fang X M, Ono Y, Fukusawa H, et al. Asian summer monsoon instability during the past 60, 000 years: magnetic susceptibility and pedogenic evidence from the western Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 168(3-4): 219-232. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00053-9
[31] Chen F H, Zhang J F, Liu J B, et al. Climate change, vegetation history, and landscape responses on the Xizang Plateau during the Holocene: A comprehensive review [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 243: 106444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106444
[32] 潘保田, 王建民. 末次间冰期以来青藏高原东部季风演化的黄土沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999(4):330-335 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.005
PAN Baotian, WANG Jianmin. Loess record of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau monsoon variations in the eastern part of the plateau since the last interglacial [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999(4): 330-335. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.04.005
[33] 方小敏. 青藏高原东部边缘及邻区马兰黄土成因与来源的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(5):539-546
FANG Xiaomin. The origin and provenance of Malan loess along the eastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its adjacent area [J]. Science in China (Series B), 1994, 24(5): 539-546.
[34] 欧先交, 曾兰华, 周尚哲, 等. 四川西部黄土沉积与环境演变研究综述[J]. 地球环境学报, 2012, 3(1):692-704
OU Xianjiao, ZENG Lanhua, ZHOU Shangzhe, et al. A review on research of loess and environmental change in west Sichuan Plateau of the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2012, 3(1): 692-704.
[35] Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Qian G Q, et al. High-altitude Aeolian research on the Xizang Plateau [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2017, 55(4): 864-901. doi: 10.1002/2017RG000585
[36] Huang X, Miao X, Chang Q, et al. Xizang dust accumulation linked to ecological and landscape response to global climate change [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49: e2021GL096615.
[37] 高以信, 李明森. 横断山区土壤[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
GAO Yixin, LI Mingsen. Soils of Hengduan Mountains[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
[38] 熊毅, 李庆逵. 中国土壤[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.
XIONG Yi, LI Qingkui. Chinese Soil[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 1987.
[39] 张荣祖, 郑度, 杨勤业, 等. 横断山区自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.
ZHANG Rongzu, ZHENG Du, YANG Qinye, et al. Physical geography of Hengduan Mountains[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997.
[40] Robertson A R. The CIE 1976 color-difference formulae [J]. Color Research and Application, 1977, 2(1): 7-11. doi: 10.1002/j.1520-6378.1977.tb00104.x
[41] 邱堋星, 叶飞. 武夷山土壤性状及其垂直变化规律[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2008, 36(1):55-57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.01.023
QIU Pengxing, YE Fei. Characteristic and vertical changing regularities of soils in Wuyi Mountain [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2008, 36(1): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2008.01.023
[42] 王海燕, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 郧西县庹家湾黄土剖面色度参数特征及其古气候重建[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(2):151-156
WANG Haiyan, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Chroma characteristics and paleoclimatic reconstruction of the loess-paleosol profile at Tuojiawan in Yunxi County, Hubei Province [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(2): 151-156.
[43] Balsam W L, Deaton B C, Damuth J E. Evaluating optical lightness as a proxy for carbonate content in marine sediment cores [J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 161(2-4): 141-153. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00037-7
[44] 田庆春, 杨太保, 石培宏, 等. 可可西里BDQ0608钻孔沉积物色度环境意义及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):133-140
TIAN Qingchun, YANG Taibao, SHI Peihong, et al. Environmental implication of color reflectance of drill hole BDQ0608, Keke Xili region and its influencing factors [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1): 133-140.
[45] 吴艳宏, 李世杰, 夏威岚. 可可西里苟仁错湖泊沉积物元素地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2004, 26(3):64-68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2004.03.014
WU Yanhong, LI Shijie, XIA Weilan. Element geochemistry of lake sediment from Gourenco Lake, Kekexili, Qinghai-Xizang plateau and its significance for climate variation [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2004, 26(3): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2004.03.014
[46] Torrent J. Iron oxides in Mediterranean soils: properties and influence on soil behavior[C]. Transactions of the 15th World Congress of Soil Science, 1994, 8a: 1-14.
[47] 刘驰, 刘希瑶, 刘澎. 松辽平原典型黑土区有机质的变化及影响因素分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6):550-555
LIU Chi, LIU Xiyao, LIU Peng. Analysis on the changes of organic matters and their influencing factors of typical black soil areas in Songliao Plain [J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 550-555.
[48] Ji J F, Chen J, Balsam W, et al. High resolution hematite/goethite records from Chinese loess sequences for the last glacial-interglacial cycle: Rapid climatic response of the East Asian Monsoon to the tropical Pacific [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(3): L03207.
[49] Schwertmann U. Occurrence and formation of iron oxides in various pedoenvironments[M]//Stucki J W, Goodman B A, Schwertmann U. Iron in Soils and Clay Minerals. Dordrecht: Springer, 1988: 267-308.
[50] 丁敏, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 全新世黄土-古土壤序列色度特征及气候意义: 以关中平原西部梁村剖面为例[J]. 陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 38(5):92-97
DING Min, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Chroma characteristics and its climatic significance in Holocene loess-paleosol sequence: A case study of the Holocene Liangcun profile in the western Guanzhong basin [J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2010, 38(5): 92-97.
[51] 戴霜, 刘俊伟, 张明震, 等. 兰州-民和盆地八盘峡剖面河口群沉积物色度纪录的140.66~124.19Ma间气候变化[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(6):1058-1067
DAI Shuang, LIU Junwei, ZHANG Mingzhen, et al. Climate change during 140.66~124.19 Ma recorded by the color of the sediments of the Hekou group from Lanzhou-Minhe Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(6): 1058-1067.
[52] 高鹏坤, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 陕南丹凤茶房村黄土—古土壤剖面色度参数特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(3):537-542
GAO Pengkun, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Chroma characteristics and its significances of the Chafangcun loess-paleosol profile in southeast Shaanxi, China [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(3): 537-542.
[53] 季峻峰, 陈骏, Balsam W, 等. 黄土剖面中赤铁矿和针铁矿的定量分析与气候干湿变化研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(2):221-229 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.02.007
JI Junfeng, CHEN Jun, Balsam W, et al. Quantitative analysis of hematite and goethite in the Chinese loess-paleosol sequences and its implication for dry and humid variability [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(2): 221-229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.02.007
-




 下载:
下载: