Application of two heavy mineral analysis methods in the provenance study of Irrawaddy River sediments on the southeastern margin of Xizang Plateau
-
摘要:
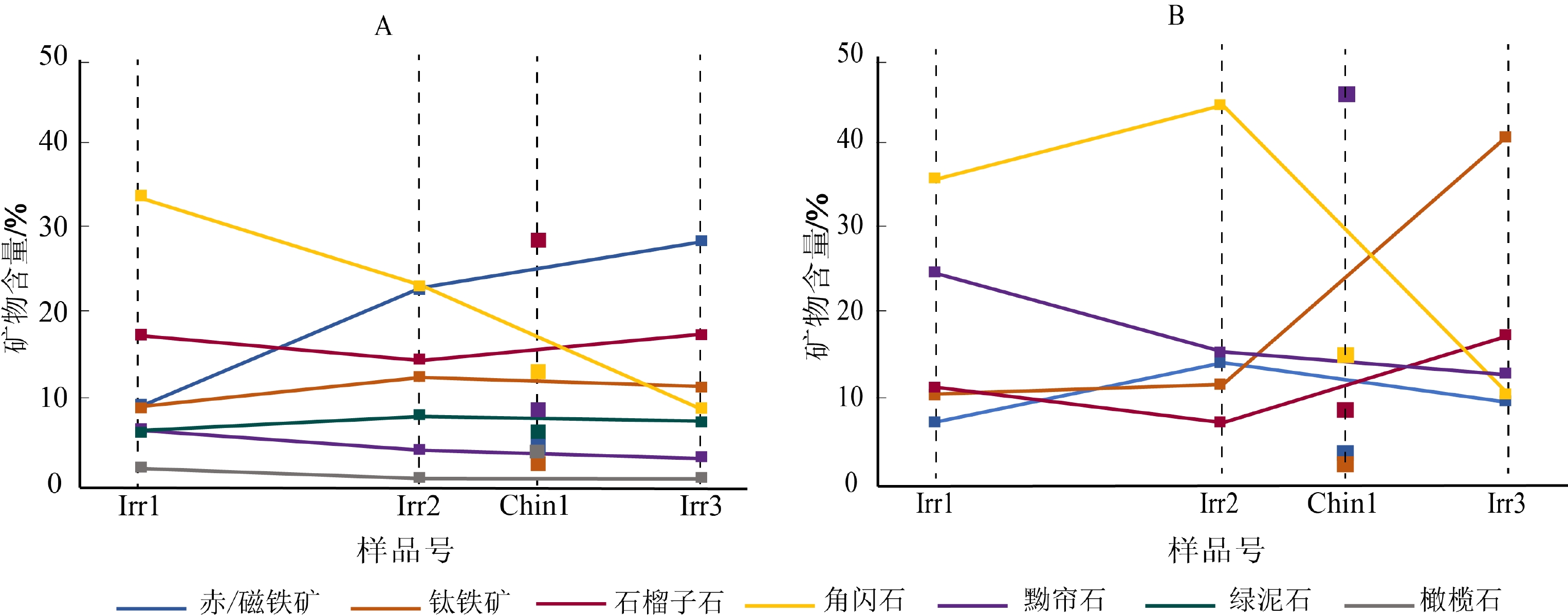
伊洛瓦底江是亚洲大型河流之一,其沉积物记录了青藏高原周缘造山带的剥蚀风化信息,对该流域沉积物的溯源研究是探究高原隆升对水系演化影响的重要课题。沉积物的重矿物种类与源岩联系紧密,是物源分析的重要手段之一。重矿物鉴定分析手段层出不穷,但不同鉴定手段之间缺乏对比分析。采用自动矿物分析系统TIMA与光学显微镜鉴定(optical microscope, OM)两种方法对伊洛瓦底江沉积物重矿物进行了鉴定分析,结果表明:伊洛瓦底江上游主要重矿物是角闪石-石榴子石-赤/磁铁矿、钛铁矿;伊洛瓦底江下游主要重矿物是赤/磁铁矿、钛铁矿-石榴子石-黝帘石-角闪石;支流钦敦江主要重矿物组合是黝帘石-角闪石-石榴子石。两种方法的结果都指示了伊洛瓦底江沉积物主要来自上游流经的缅甸北部构造单元的变质岩以及中/基性岩,太公-密支那带对伊洛瓦底江沉积物贡献量最大,钦敦江流域对伊洛瓦底江下游沉积物贡献量有限。但是两种方法对重矿物种类以及单个重矿物含量鉴定结果有着明显差异:TIMA方法的鉴定种类更加丰富,且其分析结果与伊洛瓦底江流域地质岩性分布的耦合程度更高,但TIMA无法区分化学性质相同的矿物;OM法对光学性质相近的矿物鉴定结果不准确。因此建议对重矿物分类程度或精确性要求更高的研究使用TIMA进行精确分析,同时辅助OM法区分化学性质相同的矿物。
Abstract:The Irrawaddy River is one of the large rivers in Asia, and its sediments record the denudation and weathering information of the orogenic belt around the Xizang Plateau. Tracing the sediments in this basin is an important topic to explore the impact of plateau uplift on the evolution of river system. The types of heavy minerals in sediments are closely related to source rocks, which is one of the important means for provenance analysis. There are a variety of methods to identify and analyze heavy minerals, but there is a lack of comparative analysis among different methods. This paper adopted TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer (TIMA) and Optical Microscope (OM) to identify and analyze heavy minerals of Irrawaddy River sediments. The main heavy minerals in the upper reaches of the Irrawaddy are amphibole-garnet- hematite/magnetite, ilmenite. The main heavy minerals in the lower reaches of the Irrawaddy are hematite/magnetite, ilmenite-garnet-zoisite-hornblende. The main heavy mineral combination of the tributary Chindwin River is zoisite-hornblende-garnet. The results of both methods indicate that the Irrawaddy sediments are mainly derived from metamorphic and intermediate or mafic rocks of tectonic units in northern Myanmar, with the Tagaung-Myitkyina Belt contributing the most to the Irrawaddy sediments and the Chindwin River basin contributing a limited amount to the lower reaches of the Irrawaddy sediments. However, there are significant differences in the identification results of heavy mineral species and individual heavy mineral contents between the two methods. The identification species of TIMA method are more abundant, and its analysis results are more coupled with the geological lithological distribution of Irrawaddy River basin. It’s also found that TIMA cannot distinguish the minerals with the same chemical properties, and OM method is not accurate in identifying the minerals with similar optical properties. Therefore, it is promoted in this paper that TIMA should be used for accurate analysis in studies requiring more precise and accurate classification of heavy minerals, while the OM method should be supplemented to distinguish minerals with the same chemical properties.
-
Key words:
- TIMA /
- optical microscope /
- heavy minerals source analysis /
- Irrawaddy River /
- Xizang Plateau
-

-
表 1 伊洛瓦底江沉积物样品信息
Table 1. Sample information of Irrawaddy sediments
样品号 纬度(N) 经度(E) 样品量/g 重矿物/mg 重矿物占比/% Irr1 23°51'25.03'' 96°13'49.00'' 900 21814 2.42 Irr2 22°26'42.23'' 96°1'00.23'' 1350 58694 4.35 Irr3 20°08'59.83'' 94°53'32.46'' 500 11747 2.35 Chin1 22°11'43.27'' 95°04'27.83'' 1100 5088 0.46 表 2 TIMA及OM法测得的伊洛瓦底江沉积物重矿物含量
Table 2. Heavy mineral content of Irrawaddy River sediments by TIMA and OM methods
% 矿物名称
Irr1
Irr2
Chin1
Irr3TIMA OM TIMA OM TIMA OM TIMA OM 角闪石 / 35.75 / 44.35 / 14.60 / 10.68 普通角闪石 21.45 / 16.23 / 6.68 / 6.03 / 韭闪石 2.55 / 1.75 / 1.51 / 1.09 / 阳起石 9.88 / 5.70 / 5.32 / 2.04 / 赤铁矿 / 1.54 / 5.20 / 0.81 / 0.82 磁铁矿 / 5.98 / 9.19 / 1.70 / 8.94 赤/磁铁矿 9.48 / 23.36 / 4.79 / 28.74 / 钛铁矿 9.49 10.75 12.88 11.88 3.38 1.62 11.83 40.90 铬铁矿 0.42 — 0.61 — 1.84 △ 4.34 0.87 石榴子石 / 11.52 / 7.42 / 8.11 / 17.53 钙铝榴石 13.42 / 10.23 / 23.89 / 10.59 / 铁铝榴石 3.60 / 4.06 / 3.77 / 6.11 / 钙铁榴石 0.40 / 0.19 / 0.90 / 0.67 / 锰铝榴石 0.12 / 0.21 / 0.29 / 0.45 / 镁铝榴石 0.24 / 0.19 / 0.15 / 0.11 / 黝帘石 6.69 24.74 4.38 15.64 9.02 45.60 3.41 12.96 褐帘石 1.13 / 1.66 / 1.47 / 1.70 / 锆石 0.03 1.73 0.25 0.25 0.01 0.43 1.73 1.84 金红石 0.98 0.41 1.49 0.29 2.92 0.27 3.09 1.46 锐钛矿 / — / 0.02 / 0.02 / 0.57 白钛石 / — / — / 0.01 / 0.22 榍石 0.96 0.46 1.47 1.42 1.48 0.64 1.13 1.81 绿泥石 6.68 / 8.34 / 6.33 / 7.8 / 橄榄石 2.26 / 1.07 / 4.31 / 1.04 / 磷灰石 0.08 0.04 0.16 0.03 0.09 — 0.07 0.06 十字石 0.17 △ 0.15 — 1.74 0.05 0.96 0.05 电气石 0.39 0.14 0.22 0.07 0.88 1.06 0.29 0.05 蓝晶石 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.06 1.48 0.97 0.50 0.19 独居石 0.02 0.07 0.22 0.04 0.01 △ 0.00 △ 尖晶石 — △ 0.04 △ 0.83 * 0.25 △ 辉石 / △ / △ / △ / △ 白云母 0.59 / 0.28 / 0.50 / 0.14 / 黑云母 0.33 / 0.10 / 0.03 / 0.02 / 钡锰闪叶石 — / — / 0.08 / — / 刚玉 — / — / 0.07 / — / 方铁锰矿 — / — / 0.04 / — / 重晶石 — / — / — / 0.05 / 霓石 — / 0.03 / — / — / 其他 8.62 6.81 4.68 3.32 16.22 24.09 5.81 1.04 注:“—”表示矿物含量小于0.01%;“/”表示未发现该矿物;“△”代表0~500粒;“*”代表500~700粒;OM指光学显微镜法。 表 3 TIMA与OM法鉴定的伊洛瓦底江沉积物重矿物统一分类
Table 3. Unified classification of heavy mineral identification of Irrawaddy River sediments by TIMA and OM methods
% 矿物种类
Irr1
Irr2
Chin1
Irr3TIMA OM TIMA OM TIMA OM TIMA OM 稳定
重矿物赤/磁铁矿 9.48 7.52 23.36 14.39 4.79 2.51 28.74 9.76 钛铁矿 9.49 10.75 12.88 11.88 3.38 1.62 11.83 40.90 铬铁矿 0.42 — 0.61 — 1.84 △ 4.34 0.87 石榴子石 17.78 11.52 14.87 7.42 28.98 8.11 17.94 17.53 锆石 0.03 1.73 0.25 0.25 0.01 0.43 1.73 1.84 TiO2 0.98 0.41 1.49 0.31 2.92 0.30 3.09 2.25 十字石 0.17 △ 0.15 — 1.74 0.05 0.96 0.05 电气石 0.39 0.14 0.22 0.07 0.88 1.06 0.29 0.05 榍石 0.96 0.46 1.47 1.42 1.48 0.64 1.13 1.81 蓝晶石 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.06 1.48 0.97 0.50 0.19 独居石 0.02 0.07 0.22 0.04 0.01 △ 0.00 △ 尖晶石 — △ 0.04 △ 0.83 * 0.25 △ 不稳定
重矿物角闪石 33.88 35.75 23.68 44.35 13.51 14.60 9.16 10.68 黝帘石 6.69 24.74 4.38 15.64 9.02 45.60 3.41 12.96 褐帘石 1.13 / 1.66 / 1.47 / 1.70 / 绿泥石 6.68 / 8.34 / 6.33 / 7.8 / 橄榄石 2.26 / 1.07 / 4.31 / 1.04 / 磷灰石 0.08 0.04 0.16 0.03 0.09 — 0.07 0.06 注:“—”表示矿物含量小于0.01%;“/”表示未发现该矿物;“△”代表0~500粒;“*”代表500~700粒;OM指光学显微镜法。 -
[1] Clark M K, Schoenbohm L M, Royden L H, et al. Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Xizang from large-scale drainage patterns [J]. Tectonics, 2004, 23(1): TC1006.
[2] Brookfield M E. The evolution of the great river systems of southern Asia during the Cenozoic India-Asia collision: rivers draining southwards [J]. Geomorphology, 1998, 22(3-4): 285-312. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(97)00082-2
[3] 郑洪波, 王平, 何梦颖, 等. 长江东流水系建立的时限及其构造地貌意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4):621-630 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.01
ZHENG Hongbo, WANG Ping, HE Mengying, et al. Timing of the establishment of the east-flowing Yangtze River and tectonic-geomorphic implications [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(4): 621-630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.01
[4] Robinson R A J, Bird M I, Oo N W, et al. The irrawaddy river sediment flux to the Indian ocean: the original nineteenth‐century data revisited [J]. The Journal of Geology, 2007, 115(6): 629-640. doi: 10.1086/521607
[5] Robinson R A J, Brezina C A, Parrish R R, et al. Large rivers and orogens: The evolution of the Yarlung Tsangpo-Irrawaddy system and the eastern Himalayan syntaxis [J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(1): 112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.002
[6] Liang Y H, Chung S L, Liu D Y, et al. Detrital zircon evidence from Burma for reorganization of the eastern Himalayan river system [J]. American Journal of Science, 2008, 308(4): 618-638. doi: 10.2475/04.2008.08
[7] Licht A, Reisberg L, France-Lanord C, et al. Cenozoic evolution of the central Myanmar drainage system: insights from sediment provenance in the Minbu Sub-Basin [J]. Basin Research, 2016, 28(2): 237-251. doi: 10.1111/bre.12108
[8] Zhang P, Najman Y, Mei L F, et al. Palaeodrainage evolution of the large rivers of East Asia, and Himalayan-Xizang tectonics [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 601-630. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.003
[9] Licht A, France-Lanord C, Reisberg L, et al. A palaeo Xizang-Myanmar connection? Reconstructing the Late Eocene drainage system of central Myanmar using a multi-proxy approach [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2013, 170(6): 929-939. doi: 10.1144/jgs2012-126
[10] Licht A, Dupont-Nivet G, Win Z, et al. Paleogene evolution of the Burmese forearc basin and implications for the history of India-Asia convergence [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2019, 131(5-6): 730-748. doi: 10.1130/B35002.1
[11] Van Hoang L, Wu F Y, Clift P D, et al. Evaluating the evolution of the Red River system based on in situ U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis of zircons [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2009, 10(11): Q11008.
[12] Garzanti E, Wang J G, Vezzoli G, et al. Tracing provenance and sediment fluxes in the Irrawaddy River basin (Myanmar) [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 440: 73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.010
[13] 杨仁超, 李进步, 樊爱萍, 等. 陆源沉积岩物源分析研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(1):99-107
YANG Renchao, LI Jinbu, FAN Aiping, et al. Research progress and development tendency of provenance analysis on terrigenous sedimentary rocks [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(1): 99-107.
[14] Pettijohn F J, Potter P E, Siever R. Sand and Sandstone[M]. New York: Springer, 1972.
[15] Mange M A, Maurer H F W. Heavy Minerals in Colour[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1992.
[16] Morton A C, Hallsworth C R. Processes controlling the composition of heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 124(1-4): 3-29. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00118-3
[17] Morton A C, Hallsworth C. Identifying provenance-specific features of detrital heavy mineral assemblages in sandstones [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3-4): 241-256. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(94)90041-8
[18] Zuffa G G, Serra F. Chapter 9 effects of hydrothermal fluids on the heavy mineral assemblage of a late pleistocene succession deposited in an oceanic ridge valley (Escanaba trough, Juan De Fuca Plate) [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58: 263-276.
[19] Sylvester P. Quantitative Mineralogy and Microanalysis of Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks[M]. St. John’s NL: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2012: 25-26.
[20] 任迎新, 朱宝华. 重砂矿物分选及鉴定[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1987.
ZHU Yingxin, ZHU Baohua. Heavy Placer Mineral Separation and Identification[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1987.
[21] Sylvester P J. Use of the Mineral Liberation Analyzer (MLA) for Mineralogical Studies of Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks[M]. St. John’s NL: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2012: 1-16.
[22] Hrstka T, Gottlieb P, Skála R, et al. Automated mineralogy and petrology - applications of TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer (TIMA) [J]. Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 63(1): 47-63.
[23] 陈倩, 宋文磊, 杨金昆, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统的基本原理及其在岩矿研究中的应用: 以捷克泰思肯公司TIMA为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(2):345-368
CHEN Qian, SONG Wenlei, YANG Jinkun, et al. Principle of automated mineral quantitative analysis system and its application in petrology and mineralogy: An example from TESCAN TIMA [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(2): 345-368.
[24] Dunkl I, Von Eynatten H, Andò S, et al. Comparability of heavy mineral data – The first interlaboratory round robin test [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 211: 103210. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103210
[25] 崔颖颖, 周亚利, 陈国祥, 等. 毛乌素沙地样品扫描电镜的矿物定量分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(6):1505-1513
CUI Yingying, ZHOU Yali, CHEN Guoxiang, et al. Mineral quantitative analysis of Mu Us Sandy Land with QEMSCAN [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(6): 1505-1513.
[26] 刘冬英, 陈玺, 黄燕, 等. 缅甸伊洛瓦底江流域水文资料初步复核评价[J]. 人民长江, 2018, 49(22):112-117
LIU Dongying, CHEN Xi, HUANG Yan, et al. Preliminary recheck and evaluation of hydrological data in Irrawaddy River Basin, Myanmar [J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(22): 112-117.
[27] Furuichi T, Win Z, Wasson R J. Discharge and suspended sediment transport in the Ayeyarwady River, Myanmar: centennial and decadal changes [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2010, 23(11): 1631-1641.
[28] Mitchell A H G, Htay M T, Htun K M, et al. Rock relationships in the Mogok metamorphic belt, Tatkon to Mandalay, central Myanmar [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29(5-6): 891-910. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.05.009
[29] 刘锋, 赵越, 宋立才, 等. 伊洛瓦底江上游水系形成时代研究: 以滇西龙川江为例[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1):199-206 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.016
LIU Feng, ZHAO Yue, SONG Licai, et al. Time of the upper Irrawaddy streams: A case study of the Longchuan River, western Yunnan [J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(1): 199-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.016
[30] Chapman H, Bickle M, Thaw S H, et al. Chemical fluxes from time series sampling of the Irrawaddy and Salween Rivers, Myanmar [J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 401: 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.012
[31] Zin W W, Nestmann F, Ihringer J. Flood forecasting using FGM model in Chindwin river basin [J]. Malaysian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2009, 21(2): 135-151.
[32] UNDGSE. Mineral exploration in selected areas, Burma[R]. New York: United Nations, 1979: 86.
[33] UNDGSE. Geological mapping and geochemical exploration in Mansi-Manhton, Indaw-Tigyaing, Kyindwe-Longyi, Patchaung-Yane and Yezin areas, Burma[R]. New York: United Nations, 1979: 13.
[34] Searle M P, Noble S R, Cottle J M, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Mogok metamorphic belt, Burma (Myanmar) constrained by U-Th-Pb dating of metamorphic and magmatic rocks [J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26(3): TC3014.
[35] Bender F. Geology of Burma[M]. Berlin: Gebrüder Borntraeger, 1983.
[36] Mitchell A H G. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic events in the western Myanmar(Burma)-Assam region [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1993, 150(6): 1089-1102. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.150.6.1089
[37] Thein M L. The lower paleozoic stratigraphy of western part of the Southern Shan State, Burma [J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 1973, 6: 143-163. doi: 10.7186/bgsm06197310
[38] Mitchell A, Chung S L, Oo T, et al. Zircon U–Pb ages in Myanmar: Magmatic–metamorphic events and the closure of a neo-Tethys ocean? [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 56: 1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.019
[39] Brunnschweiler R O. On the geology of the Indoburman ranges [J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 1966, 13(1): 137-194. doi: 10.1080/00167616608728608
[40] Acharyya S K, Ray K K, Sengupta S. Tectonics of the ophiolite belt from Naga Hills and Andaman Islands, India [J]. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1990, 99(2): 187.
[41] Acharyya S K. Indo-Burma Range: a belt of accreted microcontinents, ophiolites and Mesozoic–Paleogene flyschoid sediments [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104(5): 1235-1251. doi: 10.1007/s00531-015-1154-6
[42] 和钟铧, 刘招君, 郭巍. 柴达木盆地北缘大煤沟剖面重矿物分析及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2001, 20(3):279-284,312 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2001.03.012
HE Zhonghua, LIU Zhaojun, GUO Wei. The heavy mineral analysis and its geological significance of Dameigou section in northern Caidam Basin [J]. World Geology, 2001, 20(3): 279-284,312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2001.03.012
[43] Mitchell A. Mogok metamorphic belt[M]//Mitchell A. Geological Belts, Plate Boundaries, and Mineral Deposits in Myanmar. Barcelona: Elsevier, 2018: 201-251.
[44] Mitchell A. Kumon range[M]//Mitchell A. Geological Belts, Plate Boundaries, and Mineral Deposits in Myanmar. Barcelona: Elsevier, 2018: 461-465.
[45] Enami M, Ko Z W, Win A, et al. Eclogite from the Kumon range, Myanmar: Petrology and tectonic implications [J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21(2-3): 548-558. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.018
[46] Mitchell A. Popa-loimye magmatic arc[M]//Mitchell A. Geological Belts, Plate Boundaries, and Mineral Deposits in Myanmar. Barcelona: Elsevier, 2018: 277-323.
[47] 吴良士. 缅甸区域成矿地质特征及其矿产资源(一)[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(1):176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.016
WU Liangshi. Regional metallogenic geological characteristics and mineral resources in Myanmar [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(1): 176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.016
[48] Amidon W H, Burbank D W, Gehrels G E. Construction of detrital mineral populations: insights from mixing of U-Pb zircon ages in Himalayan rivers [J]. Basin Research, 2005, 17(4): 463-485. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2005.00279.x
[49] Xu C, Kynický J, Tao R B, et al. Recovery of an oxidized majorite inclusion from Earth's deep asthenosphere [J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(4): e1601589. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601589
[50] 李胜荣, 许虹, 申俊峰, 等. 结晶学与矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008.
LI Shengrong, XU Hong, SHEN Junfeng, et al. Crystallography and Mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2008.
[51] Morton A C. Influences of provenance and diagenesis on detrital garnet suites in the Paleocene Forties sandstone, central North Sea [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1987, 57(6): 1027-1032.
-




 下载:
下载: