Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironmental implications of major elements in sediments from the continental slope of the Ross Sea, Antarctica since late Pleistocene
-
摘要:
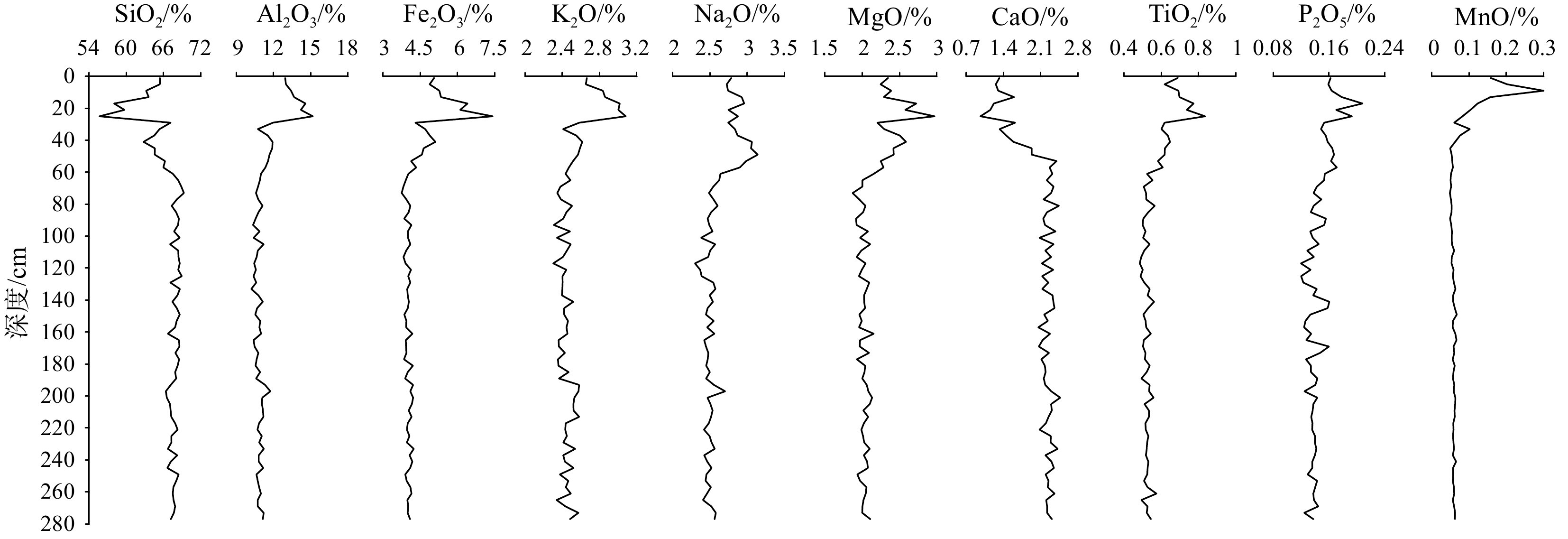
基于中国第32次南极科学考察在罗斯海外陆坡扇区获取的ANT32-RA05C岩芯,开展常量元素地球化学研究,探讨地球化学特征及其古环境意义。结果表明,ANT32-RA05C岩芯以分选差的混合冰海沉积物为主,含有大量的冰筏碎屑(平均29.76%),并含有一定量生物硅(平均4.81%)。化学元素定量测试表明,沉积物常量元素配分模式为SiO2>Al2O3>Fe2O3>Na2O>K2O>MgO>CaO>TiO2>P2O5>MnO,其中含量最高的常量元素为Si,主要来源于陆源碎屑(石英)和硅质生物沉积(生物硅)。对比XRF元素连续扫描与定量测试结果发现,Si、Ca等相关性较高,可用作高分辨率环境研究。结合环境指标研究发现,晚更新世MIS 7末期以来,常量元素含量变化与南极气候具有良好的对应关系,主要反映了气候对物源和环境的控制,气候转暖通常对应于冰山和初级生产力输入增强,气候转冷对应于冰山和初级生产力输入受限。该岩芯对重建罗斯海古气候演变,深化对罗斯海古环境认识有重要意义。
Abstract:Based on the ANT32-RA05C sediment core obtained from the Ross Sea continental slope sector during the 32nd Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition, major-element geochemistry, the geochemical characteristics, and their paleoenvironmental implications were analyzed. Results show that the ANT32-RA05C core is dominated by poorly-sorted compound glacial-marine sediment, containing a large amount of ice-rafted debris (average 29.76%) and a certain amount of biogenic silica (average 4.81%). Quantitative analysis of elements shows that the distribution pattern of major elements in core follows SiO2>Al2O3>Fe2O3>Na2O>K2O>MgO>CaO>TiO2>P2O5>MnO. Clearly, the most abundant major element is Si, coming mainly from terrigenous debris (quartz) and siliceous biogenic deposit (biogenic silica). Data of Si and Ca XRF element scanning show good correlation with quantitative analysis results thus could be used for high-resolution environmental research. Combining with environmental indicators, we found that the changes in element content have a good relationship with the Antarctic climate since the end of MIS 7 of late Pleistocene, reflecting mainly the control of climate on provenance and environment. A warming climate usually causes enhanced iceberg inputs and primary productivity, and vice versa in a cooling climate. This study provides a valuable information to reconstruct the paleoclimate and understand the climate evolution of the Ross Sea in the Antarctic region.
-
Key words:
- geochemistry /
- environmental evolution /
- ice-rafted debris /
- biogenic silica /
- Ross Sea in Antarctica
-

-
表 1 岩芯粒度参数、冰筏碎屑和生物硅含量
Table 1. Statistics of grain size parameters, IRD, and BSi contents
平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 IRD>63 μm/% IRD 63~250 μm/% IRD>250 μm/% BSi/% 最小值 4.35 1.33 1.15 0.57 0.28 1.32 最大值 8.20 2.65 59.96 25.34 51.49 6.79 平均值 6.23 2.04 29.76 12.01 17.75 4.81 标准偏差 0.33 0.33 9.66 3.80 7.75 1.15 表 2 岩芯常量元素含量
Table 2. Statistics of major elements contents in core
% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 Na2O K2O MgO CaO TiO2 P2O5 MnO 最小值 55.65 10.21 3.75 2.30 2.30 1.87 0.97 0.48 0.12 0.05 最大值 69.26 15.16 7.41 3.14 3.08 2.97 2.47 0.84 0.21 0.30 平均值 66.89 11.21 4.26 2.58 2.49 2.11 2.09 0.55 0.14 0.07 标准偏差 2.40 0.99 0.62 0.18 0.15 0.20 0.35 0.07 0.02 0.04 -
[1] Rignot E, Jacobs S, Mouginot J, et al. Ice-shelf melting around Antarctica [J]. Science, 2013, 341(6143): 266-270. doi: 10.1126/science.1235798
[2] Mckay R M, Dunbar G B, Naish T R, et al. Retreat history of the Ross Ice Sheet (Shelf) since the Last Glacial Maximum from deep-basin sediment cores around Ross Island [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2008, 260(1-2): 245-261. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.08.015
[3] Wilson G S, Levy R H, Naish T R, et al. Neogene tectonic and climatic evolution of the Western Ross Sea, Antarctica - Chronology of events from the AND-1B drill hole [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2012, 96-97: 189-203. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.05.019
[4] Brachfeld S, Acton G D, Guyodo Y, et al. High-resolution paleomagnetic records from Holocene sediments from the Palmer Deep, Western Antarctic Peninsula [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 181(3): 429-441.
[5] Yokoyama Y, Anderson J B, Yamane M, et al. Widespread collapse of the Ross Ice Shelf during the late Holocene [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(9): 2354-2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516908113
[6] Anderson J B, Conway H, Bart P J, et al. Ross Sea paleo-ice sheet drainage and deglacial history during and since the LGM [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 100: 31-54. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.08.020
[7] Shipp S, Anderson J. Late Pleistocene-Holocene retreat of the west Antarctic ice-sheet system in the Ross Sea: Part 1-Geophysical results [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1999, 111(10): 1486-1516. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1999)111<1486:LPHROT>2.3.CO;2
[8] Bart P J, Cone A N. Early stall of West Antarctic Ice Sheet advance on the eastern Ross Sea middle shelf followed by retreat at 27500 14C yr BP [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 335-336: 52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.08.007
[9] Domack E W, Jacobson E A, Shipp S, et al. Late Pleistocene-Holocene retreat of the West Antarctic Ice-Sheet system in the Ross Sea: Part 2 – Sedimentologic and stratigraphic signature [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1999, 111(10): 1517-1536. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1999)111<1517:LPHROT>2.3.CO;2
[10] Pudsey C J. Sedimentation on the continental rise west of the Antarctic Peninsula over the last three glacial cycles [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 167(3-4): 313-338. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00039-6
[11] Young G M, Nesbitt H W. Processes controlling the distribution of Ti and Al in weathering profiles, siliciclastic sediments and sedimentary rocks [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1998, 68(3): 448-455. doi: 10.2110/jsr.68.448
[12] Roser B P, Korsch R J. Provenance signatures of sandstone–mudstone suites determined using discriminant function analysis of major-element data [J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 67(1-2): 119-139. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1
[13] Monien D, Kuhn G, Von Eynatten H, et al. Geochemical provenance analysis of fine-grained sediment revealing Late Miocene to recent Paleo-Environmental changes in the Western Ross Sea, Antarctica [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2012, 96-97: 41-58. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.05.001
[14] Damiani D, Giorgetti G. Provenance of glacial-marine sediments under the McMurdo/Ross Ice Shelf (Windless Bight, Antarctica): Heavy minerals and geochemical data [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatoloy, Palaeoecology, 2008, 260(1-2): 262-283. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.08.010
[15] Pistolato M, Quaia T, Marinoni L, et al. Grain size, mineralogy and geochemistry in late quaternary sediments from the Western Ross Sea outer slope as proxies for climate changes[M]//Fütterer D K, Damaske D, Kleinschmidt G, et al. Antarctica. Berlin: Springer, 2006.
[16] 赵仁杰, 陈志华, 刘合林, 等. 15ka以来罗斯海陆架岩心沉积学记录及古海洋学意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(5):78-88
ZHAO Renjie, CHEN Zhihua, LIU Helin, et al. Sedimentary record and paleoceanographic implications of the core on the continental shelf off the Ross Sea since 15 ka [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(5): 78-88.
[17] 崔超, 唐正, REBESCO M, 等. 末次冰消期南大洋深部流通性增强的罗斯海沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(3): 678-690.
CUI Chao, TANG Zheng, REBESCO M, et al. Sedimentary records of enhanced deep ventilation during the last deglaciation in the Ross Sea, Southern Ocean[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 41(3): 678-690.
[18] 李永斌, 王汝建, 武力, 等. 南极罗斯海扇区晚更新世以来冰筏碎屑记录反映的冰川动力学史[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(3): 662-677.
LI Yongbin, WANG Rujian, WU Li, et al. Glacial dynamics evolutions revealed by ice-rafted detritus record from the Ross Sea Sector of the Southern Ocean since Late Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 41(3): 662-677.
[19] Li G, Bu R, Yi L, et al. Geochronology and paleoenvironmental changes of Late Pleistocene sediments in the Ross Sea, Antarctica [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 863336. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.863336
[20] Mosola A B, Anderson J B. Expansion and rapid retreat of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet in Eastern Ross Sea: Possible consequence of over-extended ice streams? [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(17-18): 2177-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.12.013
[21] Smith W O Jr, Sedwick P N, Arrigo K R, et al. The Ross Sea in a sea of change [J]. Oceanography, 2012, 25(3): 90-103. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2012.80
[22] Anderson J B, Brake C F, Myers N C. Sedimentation on the Ross Sea Continental Shelf, Antarctica [J]. Marine Geology, 1984, 57(1-4): 295-333. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(84)90203-2
[23] Cook C P, Hemming S R, Van De Flierdt T, et al. Glacial erosion of East Antarctica in the Pliocene: A comparative study of multiple marine sediment provenance tracers [J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 466: 199-218. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.06.011
[24] Siddoway C S. Tectonics of the West Antarctic Rift System: New light on the history and dynamics of distributed intracontinental extension[R]. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2007: 91-114.
[25] Carter L, McCave I N, Williams M J M. Chapter 4 circulation and water masses of the Southern Ocean: A review [J]. Developments in Earth and Environmental Sciences, 2008, 8: 85-114.
[26] Dotto T S, Garabato A N, Bacon S, et al. Variability of the Ross Gyre, Southern Ocean: Drivers and responses revealed by satellite altimetry [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(12): 6195-6204.
[27] Stewart R A, Mayberry S W, Pickerill M J. Composition of till in the vicinity of the Lake Ellen Kimberlite and implications for the source of diamonds in glacial sediments of eastern Wisconsin [J]. Prospecting in Areas of Glaciated Terrain, 1988, 8(1): 103-120.
[28] Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Cattani O, et al. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800, 000 years [J]. Science, 2007, 317(5839): 793-796. doi: 10.1126/science.1141038
[29] Reimnitz E, McCormick M, Bischof J, et al. Comparing sea-ice sediment load with Beaufort Sea shelf deposits; is entrainment selective? [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1998, 68(5): 777-787. doi: 10.2110/jsr.68.777
[30] 王汝建, 肖文申, 李文宝, 等. 北冰洋西部楚科奇海盆晚第四纪的冰筏碎屑事件[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(4):432-440
WANG Rujian, XIAO Wenshen, LI Wenbao, et al. Late Quaternary ice-rafted detritus events in the Chukchi Basin, western Arctic Ocean [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(4): 432-440.
[31] Röhl U, Abrams L J. High-resolution, downhole, and nondestructive core measurements from Sites 999 and 1001 in the Caribbean Sea: application to the Late Paleocene Thermal Maximum [J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2000, 165: 191-203.
[32] Hobbs W R, Massom R, Stammerjohn S, et al. A review of recent changes in Southern Ocean sea ice, their drivers and forcings [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2016, 143: 228-250. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.06.008
[33] Murray R W, Leinen M. Scavenged excess aluminum and its relationship to bulk titanium in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3869-3878. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00236-0
[34] 吴旻哲, 乔培军, 邵磊. 西太平洋807A孔的元素地球化学特征及其对中更新世气候转型期的记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2):67-74
WU Minzhe, QIAO Peijun, SHAO Lei. Element geochemical record of the Western Pacific Ocean site ODP807A: Implication for the Middle Pleistocene climate transition [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 67-74.
[35] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 李铁刚, 等. 东菲律宾海表层沉积物常量元素组成及地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(6):43-48
XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, LI Tiegang, et al. Major element compositions of surface sediments in the east Philippine Sea and its geological implication [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(6): 43-48.
[36] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[37] Griffin J J, Windom H, Goldberg E D. The distribution of clay minerals in the World Ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1968, 15(4): 433-459. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(68)90051-X
[38] Pedersen T F, Price N B. The geochemistry of manganese carbonate in Panama Basin sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46(1): 59-68. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90290-3
[39] Froelich P N, Klinkhammer G, Bender M L, et al. Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(7): 1075-1090. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90095-4
[40] Leinen M, Cwienk D, Heath G R, et al. Distribution of biogenic silica and quartz in recent deep-sea sediments [J]. Geology, 1986, 14(3): 199-203. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<199:DOBSAQ>2.0.CO;2
[41] Mortlock R A, Froelich P N. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments [J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(9): 1415-1426. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90092-7
[42] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[43] Grobe H, Mackensen A. Late Quaternary climatic cycles as recorded in sediments from the Antarctic continental margin[M]//Kennett J P, Warkne D A. The Antarctic Paleoenvironment: A Perspective on Global Change. Washington, D. C. : American Geophysical Union, 1992, 56: 349-376.
-




 下载:
下载: