Concentration of suspended particulate matter and magnetic minerals from surface seawater in Russian Arctic Seas: Distribution and influencing factors
-
摘要:
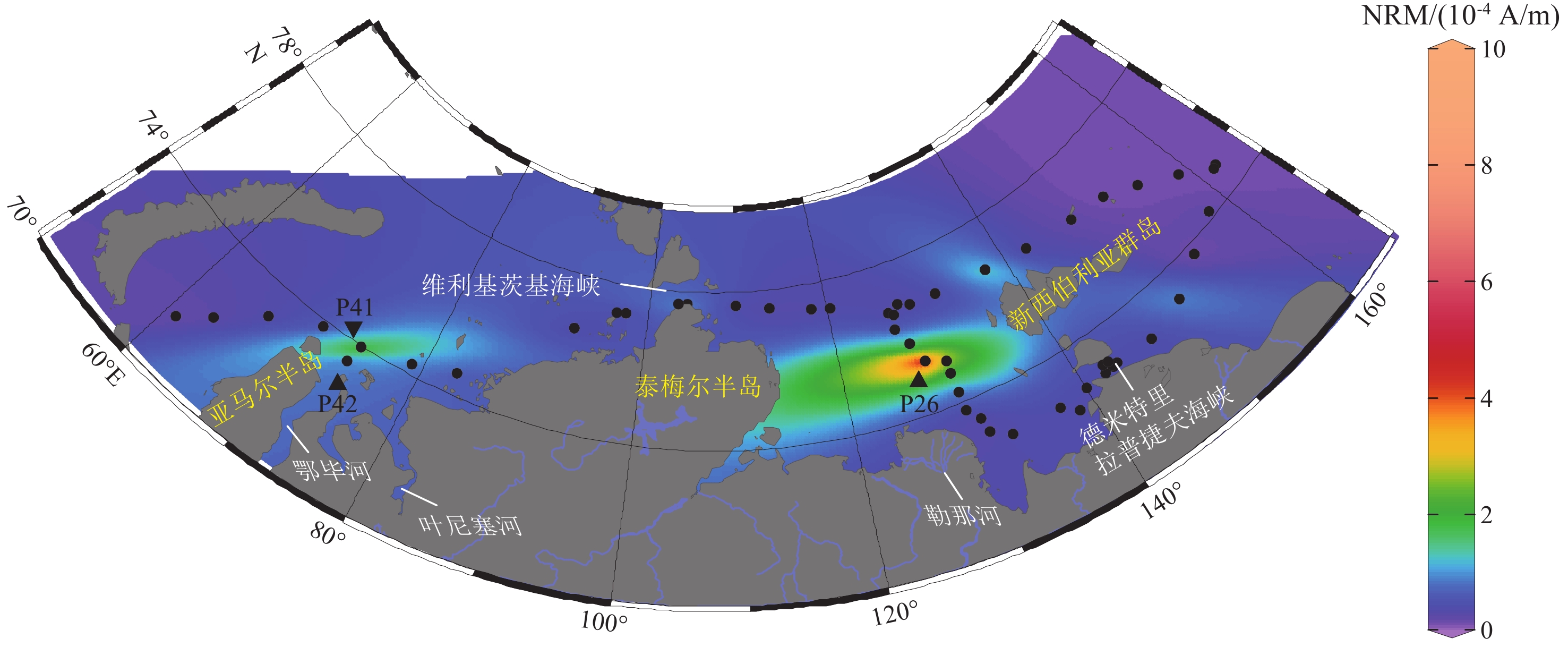
为了解俄罗斯极地海悬浮体颗粒物(Suspended Particulate Matter,SPM)的分布特征及其沉积学意义,对2019年中俄北极联合考察(AMK78航次)在喀拉海-拉普捷夫海-东西伯利亚海表层海水采集的SPM样品开展了颗粒浓度、组成和岩石磁学分析。研究发现,SPM主要由陆源碎屑和硅质浮游生物碎屑组成。悬浮体浓度在德米特里拉普捷夫海峡及其东侧海域最高,鄂毕河和叶尼塞河河口外侧次之,其他海域整体较低。悬浮体中携磁矿物为单畴、多畴磁铁矿。陆源碎屑集中分布在近岸和河流入海口附近海域,离海岸和河口较远海域悬浮体中硅质生物碎屑占比升高。SPM浓度主要受到河流搬运入海的陆源碎屑通量和海岸侵蚀的影响,而SPM中磁性矿物与流域内岩石类型有关,并受西伯利亚沿岸流的影响,磁性矿物集中在洋流流速缓慢的区域,粒径粗的磁性矿物分布在沿岸地区,可能与海岸侵蚀有关。
Abstract:To understand the distribution characteristics and sedimentological significance of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in the Russian Arctic Seas, the particle concentration, composition, and rock magnetism of SPM samples collected in the surface seawater of the Kara Sea-Laptev Sea-Eastern Siberia Sea during the Sino-Russian joint Arctic expedition (AMK78 voyage) were analyzed. Results show that the SPM was mainly composed of terrigenous detritus and siliceous plankton debris. The SPM concentration was the highest in the Dmitry Laptev Strait and its eastern sea areas, followed by the outer sides of the Ob and Yenisei estuaries, and were generally lower in the other sea areas. The magnetic minerals in the SPM were single-domain and multi-domain magnetite. The terrigenous detritus was concentrated in the waters near the coast and the estuary of the river, and the proportion of siliceous bioclasts in the SPM in the sea farther from the coast and the estuary increases. The SPM concentration was mainly affected by the flux of terrigenous debris transported into the sea by rivers and coastal erosion, while the magnetic minerals in SPM were related to the rock types in the watershed and were affected by the Siberian Coastal Current. Coarse magnetic minerals were distributed in the coastal areas, which might be related to coastal erosion.
-

-
[1] Kravchishina M D, Lisitsyn A P, Klyuvitkin A A, et al. Suspended particulate matter as a main source and proxy of the sedimentation processes[M]//Lisitsyn A P, Demina L L. Sedimentation Processes in the White Sea. Cham: Springer, 2018: 13-48.
[2] 胡吉连, 杜晓琴. 舟山海域悬浮体的特征及输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):39-48 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019111304
HU Jilian, DU Xiaoqin. Characteristics and transport mechanism of suspended particles in offshore area of Zhoushan Islands [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 39-48. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019111304
[3] 李文建, 王珍岩, 黄海军. 夏季南黄海悬浮体粒度分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):49-60
LI Wenjian, WANG Zhenyan, HUANG Haijun. Grain size distribution pattern and influencing factors of suspended matters in the southern Yellow Sea during summer season [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 49-60.
[4] Stein R. The Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic arctic ocean climate and sea ice history: a challenge for past and future scientific ocean drilling [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2019, 34(12): 1851-1894. doi: 10.1029/2018PA003433
[5] Larkin C S, Piotrowski A M, Hindshaw R S, et al. Constraints on the source of reactive phases in sediment from a major Arctic river using neodymium isotopes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 565: 116933. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2021.116933
[6] 汪卫国, 方建勇, 陈莉莉, 等. 楚科奇海悬浮体含量分布及其颗粒组分特征[J]. 极地研究, 2014, 26(1):79-88
WANG Weiguo, FANG Jianyong, CHEN Lili, et al. The Distribution and composition of suspended particles in the Chukchi Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2014, 26(1): 79-88.
[7] Kravchishina M, Lein A, Burenkov V, et al. Distribution and sources of suspended particulate matter in the Kara Sea[C]//Complex Interfaces Under Change: Sea-River-Groundwater-Lake. Gothenburg: IAHS, 2014: 42-48.
[8] Wegner C, Hölemann J A, Dmitrenko I, et al. Suspended particulate matter on the Laptev Sea shelf (Siberian Arctic) during ice-free conditions [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(1-2): 55-64. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00328-1
[9] Rachold V, Eisenhauer A, Hubberten H W, et al. Sr isotopic composition of suspended particulate material (SPM) of east Siberian rivers: sediment transport to the arctic ocean [J]. Arctic and Alpine Research, 1997, 29(4): 422-429. doi: 10.2307/1551990
[10] Stein R, Dittmers K, Fahl K, et al. Arctic (palaeo) river discharge and environmental change: evidence from the Holocene Kara Sea sedimentary record [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(11-13): 1485-1511. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.12.004
[11] Matul A G, Khusid T A, Mukhina V V, et al. Recent and Late Holocene environments on the southeastern shelf of the Laptev Sea as inferred from microfossil data [J]. Oceanology, 2007, 47(1): 80-90. doi: 10.1134/S0001437007010110
[12] 李秋玲, 乔淑卿, 石学法, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积物物源: 来自黏土矿物和化学元素的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(3):76-89
LI Qiuling, QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, et al. Sediment provenance of the East Siberian arctic shelf: evidence from clay minerals and chemical elements [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(3): 76-89.
[13] Lien V S, Trofimov A G. Formation of Barents sea branch water in the north-eastern Barents Sea [J]. Polar Research, 2013, 32(1): 18905. doi: 10.3402/polar.v32i0.18905
[14] Schauer U, Loeng H, Rudels B, et al. Atlantic water flow through the Barents and Kara seas [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2002, 49(12): 2281-2298. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(02)00125-5
[15] Rozhkova A Y, Dmitrenko I A, Baukh D, et al. Variations in characteristics of the Barents branch of the Atlantic Water in the Nansen Basin under the influence of atmospheric circulation over the Barents Sea [J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2008, 418(1): 149-154. doi: 10.1134/S1028334X08010339
[16] Weingartner T J, Danielson S, Sasaki Y, et al. The Siberian coastal current: a wind- and buoyancy-forced arctic coastal current [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 1999, 104(C12): 29697-29713. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900161
[17] 贾福福, 沙龙滨, 李冬玲, 等. 西伯利亚极地海域第四纪以来古海洋环境研究进展[J]. 极地研究, 2020, 32(2):250-263 doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20190074
JIA Fufu, SHA Longbin, LI Dongling, et al. Review of research on Quaternary paleoceanography of the Siberian arctic seas [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2020, 32(2): 250-263. doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20190074
[18] 田引, 白学志, 黄颖祺. 北冰洋穿极流强度和源头位置变动机制分析[J]. 极地研究, 2021, 33(4):529-544 doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20210034
TIAN Yin, BAI Xuezhi, HUANG Yingqi. Analysis of the variation in intensity and source region of the arctic transpolar drift [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2021, 33(4): 529-544. doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.20210034
[19] Deng C, Zhu R, Jackson M J, et al. Variability of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of the Holocene Eolian deposits in the Chinese loess plateau: a Pedogenesis indicator [J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2001, 26(11-12): 873-878. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00135-1
[20] Verwey E J W. Electronic conduction of magnetite (Fe3O4) and its transition point at low temperatures [J]. Nature, 1939, 144(3642): 327-328.
[21] Tauxe L, Bertram H N, Seberino C. Physical interpretation of hysteresis loops: micromagnetic modeling of fine particle magnetite [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2002, 3(10): 1-22.
[22] Roberts A P, Tauxe L, Heslop D, et al. A critical appraisal of the “day” diagram [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2018, 123(4): 2618-2644. doi: 10.1002/2017JB015247
[23] Dunlop D J. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 1. Theoretical curves and tests using titanomagnetite data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2002, 107(B3): 2056. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000486
[24] Dunlop D J. Theory and application of the day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 2. Application to data for rocks, sediments, and soils [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2002, 107(B3): 2057. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000487
[25] Thompson R, Oldfield F. Environmental Magnetism[M]. London: Allen & Unwin, 1986.
[26] 敖红, 邓成龙. 磁性矿物的磁学鉴别方法回顾[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(2):432-442 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.02.015
AO Hong, DENG Chenglong. Review in the identification of magnetic minerals [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(2): 432-442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.02.015
[27] Rudenko О, Taldenkova Е, Ovsepyan Y, et al. A multiproxy-based reconstruction of the mid- to Late Holocene paleoenvironment in the Laptev Sea off the Lena River Delta (Siberian Arctic) [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 540: 109502. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109502
-




 下载:
下载: