Geochemical characteristics and resource significance of polymetallic nodules and cobalt-rich crusts in the southern Kyushu-Palau ridge
-
摘要:
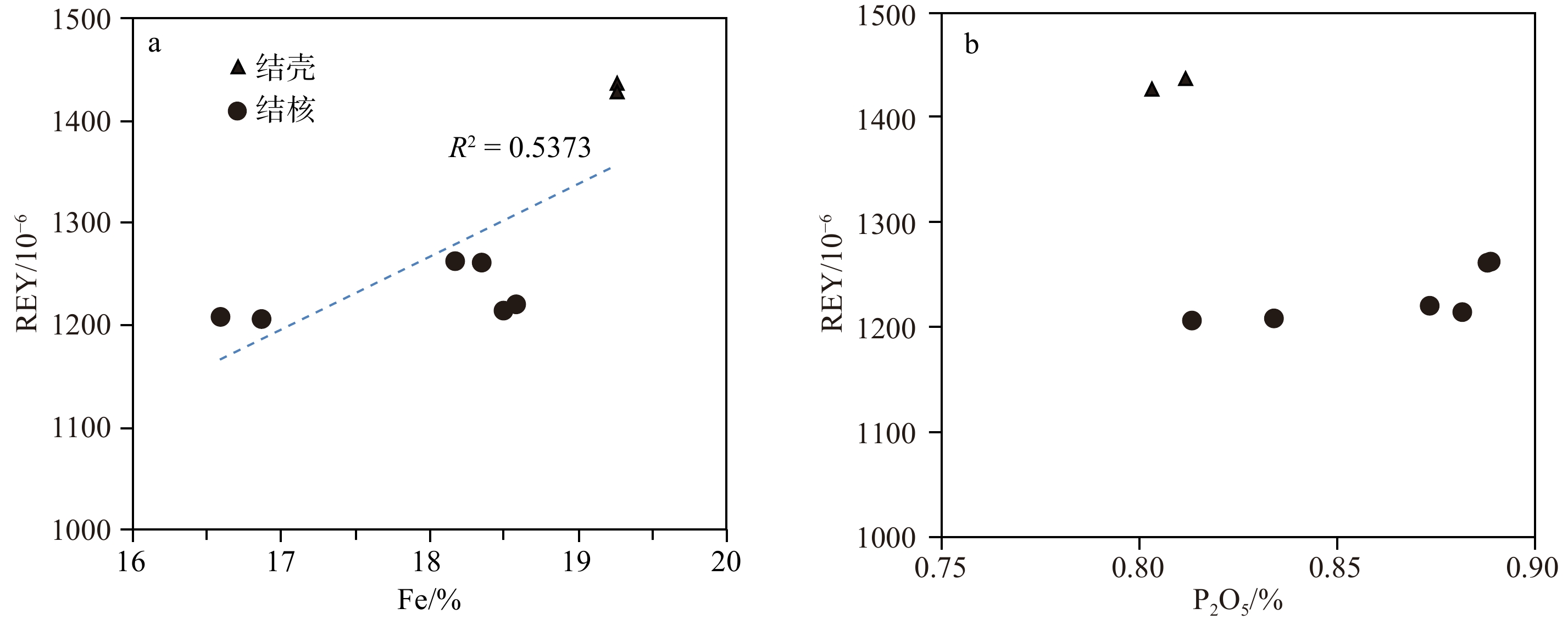
深海多金属结核与富钴结壳富含Mn、Co、Ni、Cu及稀土等元素,极具资源潜力,因而广受关注。选择采集自九州-帕劳海脊南段水深约3 000 m的6个多金属结核和2个富钴结壳样品进行地球化学特征研究。结果显示本区样品Mn/Fe比值为0.88~1.07,Co及稀土元素含量高,与库克群岛多金属结核元素特征相似,表现出典型的水成成因特征。与其他地区水成结核、结壳相比,样品具有较高的Ca含量,可能和其所在位置海脊部位水深较浅、位于碳酸盐补偿深度(CCD)以上有关。样品表现出Y负异常、Nd含量高等水成结核的特点,但微弱的Ce正异常特征与其他地区水成多金属结核/壳的强烈Ce正异常特征不同,这表明其生长于弱氧化环境。本区结核分布在CCD以上,最小溶氧层(OMZ)以下,是一种水成成因、贫氧生长的新型多金属结核,其物质来源、成矿模式将为揭示多金属结核的形成分布规律提供一条全新的认识途径。同时研究区结核、结壳Co及稀土元素含量较高,且分布位置较浅,易于开采,具有一定的资源潜力。
Abstract:Deep-sea polymetallic nodules and cobalt-rich crusts are abundant in a variety of valuable metals with great resource potential. In this paper, 6 polymetallic nodules and 2 cobalt-rich crusts were collected from the southern section of the Kyushu-Palau ridge at a depth of about 3 000 m and their geochemical characteristics were analyzed and revealed. Results show that the Mn/Fe ratios of the samples range from 0.88 to 1.07, and the contents of Co and rare earth elements are high, which is similar to the polymetallic nodules in Cook Islands, showing typical hydrodiagenetic nodules and crusts. Compared to other high potential areas of the global ocean, our samples have higher Ca content, which might be related to the shallow water depth (above the carbonate compensation depth). Negative Y anomaly and high Nd content show characteristics of hydrogenic origin, but the weak positive Ce anomaly makes it different from other hydrogenic nodules/crusts, showing strong negative Ce anomaly, indicating that the samples grew in a weak oxidation environment. Therefore, distribution above CCD, growth in weak oxidation environment, and unique elements characteristics manifested that the nodule in the study area is a new type of polymetallic nodules, and the study of its elements source and mineralization mechanisms will provide a new insight to understand the formation and distribution of polymetallic nodules. In addition, with high Co and rare earth elements content, and shallow distribution, nodules and crusts in this area are easy to exploit with promising resource potential.
-
Key words:
- polymetallic nodules /
- cobalt-rich crusts /
- rare earth elements /
- Kyushu-Palau ridge
-

-
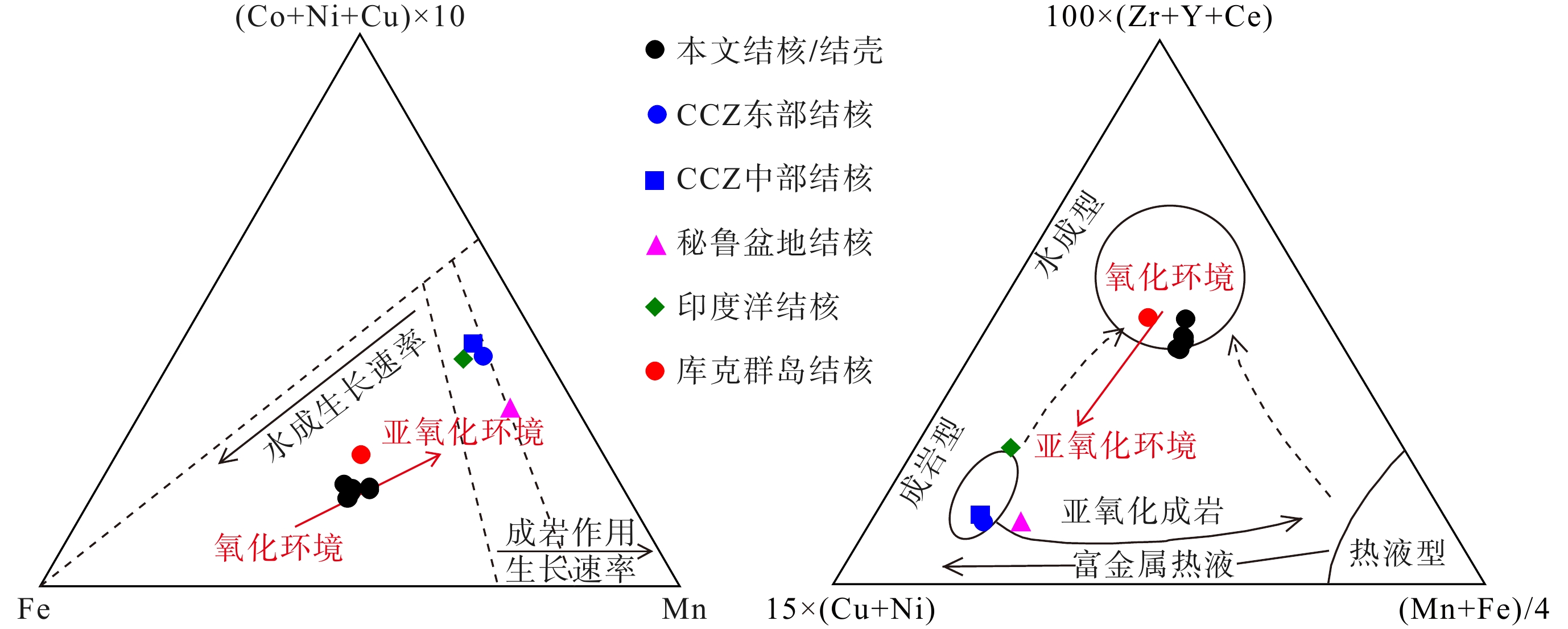
图 2 锰铁沉积物成因三元图解[19]
Figure 2.
图 3 Nd-CeSN/CeSN*(左)与YSN/HoSN-CeSN/CeSN*(右)判别图解[20]
Figure 3.
-
[1] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Kuhn T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(3): 158-169.
[2] 周怀阳. 深海海底铁锰结核的秘密[J]. 自然杂志, 2015, 37(6):397-404
ZHOU Huaiyang. Metallogenetic mystery of deep sea ferromanganese nodules [J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2015, 37(6): 397-404.
[3] Cronan D S. Some controls on the geochemical variability of manganese nodules with particular reference to the tropical South Pacific[M]//Nicholson K, Hein J R, Bühn B, et al. Manganese Mineralization: Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Terrestrial and Marine Deposits. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1997, 119(1): 139-151.
[4] Nicholson K, Hein J R, Bühn B, et al. Manganese Mineralization: Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Terrestrial and Marine Deposits[M]. London: The Geological Society, 1997:370.
[5] Verlaan P A, Cronan D S, Morgan C L. A comparative analysis of compositional variations in and between marine ferromanganese nodules and crusts in the South Pacific and their environmental controls [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2004, 63(3): 125-158. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2004.11.001
[6] Kennett J P, Watkins N D. Deep-sea erosion and manganese nodule development in the Southeast Indian Ocean [J]. Science, 1975, 188(4192): 1011-1013. doi: 10.1126/science.188.4192.1011
[7] 石学法, 符亚洲, 李兵, 等. 我国深海矿产研究: 进展与发现(2011-2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(2):305-318
SHI Xuefa, FU Yazhou, LI Bing, et al. Research on deep-sea minerals in China: Progress and discovery (2011-2020) [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(2): 305-318.
[8] Beiersdorf H. Scientific challenges related to the development of a geological model for the manganese nodule occurrences in the clarion-clipperton zone (Equatorial North Pacific Ocean)[M]//Establishment of a Geological Model of Polymetallic Deposits in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone of the Equatorial North Pacific Ocean. Kingston: International Seabed Authority (ISA), 2003: 175-200.
[9] Hein J R, Schulz M S, Kang J K. Insular and submarine ferromanganese mineralization of the Tonga-Lau region [J]. Marine Mining, 1990, 9(3): 305-354.
[10] Sdrolias M, Roest W R, Müller R D. An expression of Philippine Sea plate rotation: the Parece Vela and Shikoku Basins [J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 394(1-2): 69-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2004.07.061
[11] Okino K, Ohara Y, Fujiwara T, et al. Tectonics of the southern tip of the Parece Vela Basin, Philippine Sea Plate [J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 466(3-4): 213-228. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.017
[12] 殷征欣, 李正元, 沈泽中, 等. 西太平洋帕里西维拉海盆不对称性发育特征及其成因[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(1):218-229
YIN Zhengxin, LI Zhengyuan, SHEN Zezhong, et al. Asymmetric geological developments and their geneses of the Parece Vela Basin in Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(1): 218-229.
[13] 张臻, 李三忠. 雅浦沟-弧体系构造演化过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(5):138-146
ZHANG Zhen, LI Sanzhong. Tectonic evolution of the Yap trench-arc system [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(5): 138-146.
[14] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 20260-2006 海底沉积物化学分析方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006:32.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T20260-2006 Chemcial analysis methods for marine sediment[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006:32.
[15] Halbach P, Friedrich G, von Stackelberg U. The Manganese Nodule Belt of the Pacific Ocean[M]. Stuttgart: Enke, 1988: 254.
[16] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[17] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00122-1
[18] von Stackelberg U. Growth history of manganese nodules and crusts of the Peru Basin[M]//Nicholson K, Hein J R, Biihn B, et al. Manganese Mineralization: Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Terrestrial and Marine Deposits. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1997, 119(1): 153-176.
[19] Halbach P, Hebisch U, Scherhag C. Geochemical variations of ferromanganese nodules and crusts from different provinces of the Pacific Ocean and their genetic control [J]. Chemical Geology, 1981, 34(1-2): 3-17. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(81)90067-X
[20] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[21] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[22] Marcus M A, Toner B M, Takahashi Y. Forms and distribution of Ce in a ferromanganese nodule [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2018, 202: 58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.03.005
[23] 姜学钧, 林学辉, 姚德, 等. 稀土元素在水成型海洋铁锰结壳中的富集特征及机制[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 54(2):197-203 doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4
JIANG Xuejun, LIN Xuehui, YAO De, et al. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 197-203. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4
[24] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045
[25] 黄威, 胡邦琦, 徐磊, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西缘中段铁锰结核的地球化学特征和成因类型[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(1):199-209
HUANG Wei, HU Bangqi, XU Lei, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the ferromanganese nodules in the middle western margin of the Parece Vela Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(1): 199-209.
[26] Cronan D S, Rothwell G, Croudace I. An ITRAX geochemical study of ferromanganiferous sediments from the Penrhyn Basin, South Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2010, 28(3): 207-221.
[27] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine co-rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining. Springer, 2017: 65-141.
[28] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: genetic implications [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[29] Wegorzewski A V, Kuhn T. The influence of suboxic diagenesis on the formation of manganese nodules in the Clarion Clipperton nodule belt of the Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 123-138. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.004
[30] Wegorzewski A V, Kuhn T, Dohrmann R, et al. Mineralogical characterization of individual growth structures of Mn-nodules with different Ni+Cu content from the central Pacific Ocean [J]. American Mineralogist, 2015, 100: 2497-2508. doi: 10.2138/am-2015-5122
[31] Hein J R, Spinardi F, Okamoto N, et al. Critical metals in manganese nodules from the Cook Islands EEZ, abundances and distributions [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 68: 97-116. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.011
[32] Puteanus D, Halbach P. Correlation of Co concentration and growth rate—A method for age determination of ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 69(1-2): 73-85. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90159-3
[33] Paul S A L, Volz J B, Bau M, et al. Calcium phosphate control of REY patterns of siliceous-ooze-rich deep-sea sediments from the central equatorial Pacific [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 251: 56-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.02.019
[34] Liao J L, Sun X M, Li D F, et al. New insights into nanostructure and geochemistry of bioapatite in REE-rich deep-sea sediments: LA-ICP-MS, TEM, and Z-contrast imaging studies [J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 512: 58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.02.039
-




 下载:
下载: