Enrichment and constraints of critical metals in ferromanganese crusts from 13°20'N seamount of the southern Kyushu-Palau Ridge
-
摘要:
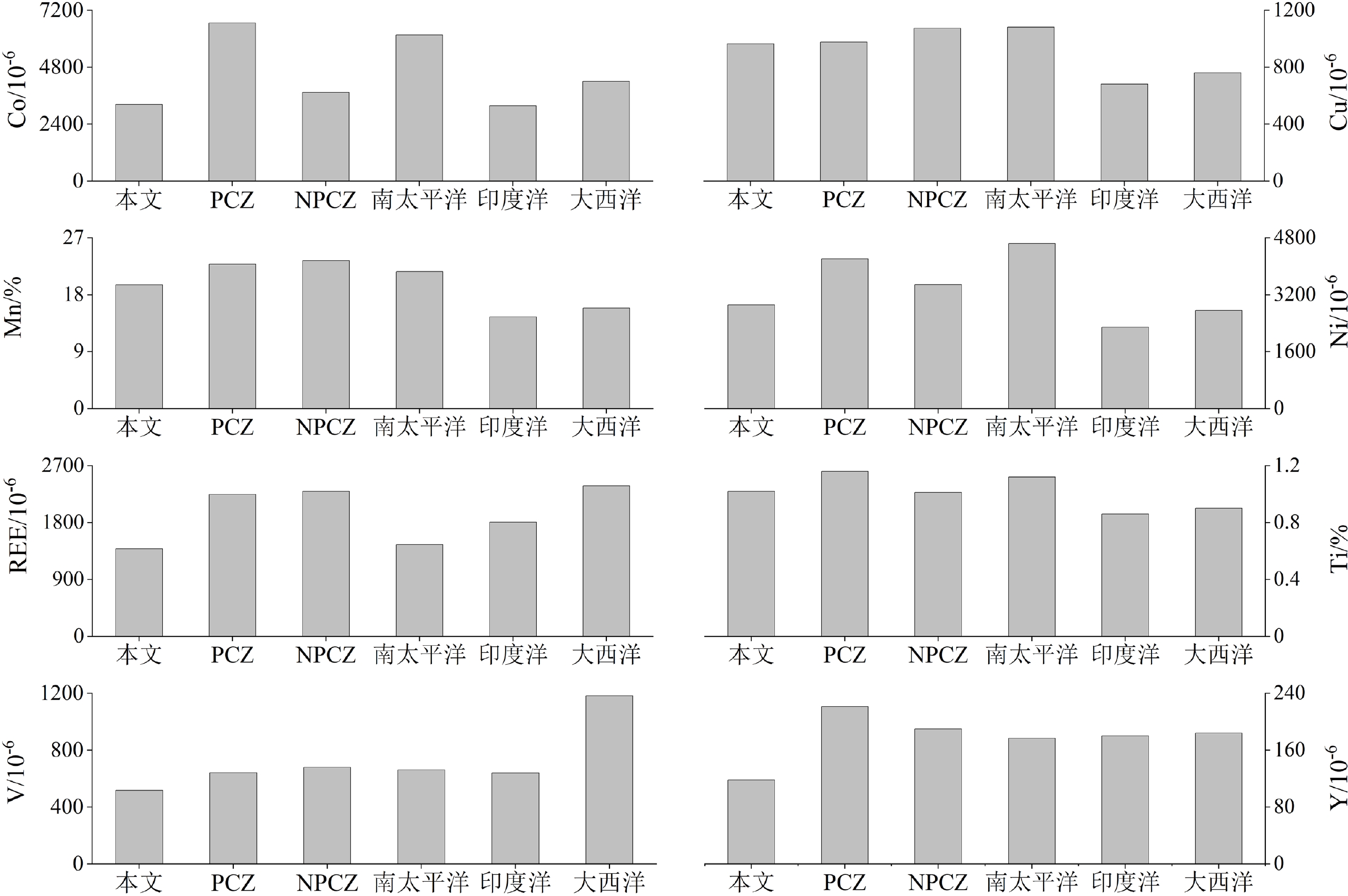
铁锰结壳富集Co、Cu、Mn、Ni、Ti、V、REE、Y和Zn等关键金属,研究其富集于结壳的规律以及相关地质环境制约因素对于未来开发利用这些海底金属资源十分重要。本文对九州-帕劳海脊南部13°20′N新发现的铁锰结壳样品进行了矿物学、元素地球化学和电子探针微区分析,发现其成分较为均一,未遭受明显的磷酸盐化作用,属于单层型水生成因结壳。Co、Ni等高含量关键金属主要富集在水羟锰矿内,其中主要以晶格态形式存在的Co所经历的表面氧化还原反应是其累积富集的关键;而Ni除了与Co一样通过置换Mn或占据晶格空位而呈现富集特征外,还大量以吸附态形式存在。Ti、V和REY等通过表面络合、晶格进入以及共沉淀作用富集在以六方纤铁矿为主的铁羟基氧化物组分内。Cu、Zn的晶格进入能力不足,加之海水Cu含量偏低,Zn的弱吸附作用共同导致它们以相对低含量形式分散分布。基于Co经验公式揭示结壳的形成起始于晚中新世,未出现明显生长间断,但持续生长时间不足导致结壳的关键金属累积富集程度低于全球主要结壳成矿区。不过,研究区理想的水深条件、较低的沉积速率、稳定的构造环境、合适的最小含氧带水深分布和远离非成矿物质的大规模稀释影响,都是本区结壳未来持续性增生和进一步富集关键金属的有利条件。
Abstract:Ferromanganese crusts are highly enriched in a wide variety of critical metals including Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Ti, V, REE, Y, and Zn. Study of their enrichment in the crusts and the geological constraints is important for future development and utilization of them at seafloor. Recently, ferromanganese crust samples were acquired from 13°20′N seamount of the southern Kyushu-Palau Ridge, and analyzed in mineralogy and element geochemistry, as well as for electron probe microanalysis. Results show that the mineralogical and chemical composition of the samples are relatively uniform, and the crusts have not suffered from obvious phosphatization, which indicates that the crusts are characterized by one hydrogenetic crustal layer. Critical metals with high content such as Co and Ni are mainly enriched in vernadite. Co mainly exists in the lattice of vernadite due mainly to surface oxidation of vernadite. Ni is enriched in the crusts by replacing and occupying lattice vacancies of Mn as Co does, and a large amount of Ni exists in the form of adsorption. Ti, V, and REY are enriched in the iron oxyhydroxide components dominated by feroxyhyte by surface complexation, crystal lattice entry, and co-precipitation. Cu and Zn are lack of crystal lattice entry ability; the Cu content in seawater is very low and the adsorption of Zn is weak, thus resulting in their dispersed distribution and low content in the samples. This study reveals that the crusts started growing in the late Miocene and show no obvious growth break; the accumulated enrichment degree of critical metals in these samples is lower than that in the highest potential areas of the global ocean due to insufficient continuous growth time. However, the ideal water depth conditions, low deposition rate, stable tectonic environment, suitable water depth distribution of the oxygen minimum zone, and long distance from macroscale input of the non-metallogenic material into the study area are favorable for continuous growth and enrichment of critical metals in these crusts in the future.
-
Key words:
- ferromanganese crusts /
- critical metals /
- enrichment principles /
- constraints /
- Kyushu-Palau Ridge
-

-
表 1 结壳样品元素含量特征
Table 1. Chemical composition of the ferromanganese crusts
元素 外层 中间层 内层 基质 Al/% 1.58 1.69 1.98 7.97 Ca/% 2.31 2.36 2.41 4.26 Fe/% 17.70 18.78 18.52 11.20 Mn/% 20.68 19.44 18.67 1.35 P/% 0.23 0.23 0.22 0.09 Si/% 5.92 6.47 7.01 21.29 Ti/% 0.94 1.08 1.03 0.76 Ce/10−6 692 764 717 94 Co/10−6 3400 3220 3090 156 Cu/10−6 1120 853 927 373 Ni/10−6 3400 2620 2720 291 V/10−6 547 515 491 261 Zn/10−6 512 463 491 276 LREY/10−6 1230 1322 1202 173 HREY/10−6 274 258 229 60 REY/10−6 1503 1579 1431 233 表 2 样品不同层位铁锰氧化物的电子探针微区成分数据
Table 2. Element contents in the ferromanganese oxides layers from different parts of the sample revealed in electron probe microanalysis
元素 Al Ca Ce Co Cu Fe Mn Ni P Si Ti V Zn 外层
(n=13)最大值/% 1.62 3.04 0.16 0.73 0.18 24.37 28.61 1.10 0.45 3.70 1.32 0.13 0.10 最小值/% 0.43 1.62 0.05 0.24 0.09 16.84 22.98 0.42 0.30 2.07 0.64 0.07 0.05 平均值/% 0.64 2.47 0.13 0.59 0.14 19.25 26.81 0.65 0.36 2.62 1.16 0.09 0.08 离散系数/% 45.98 16.64 21.87 23.60 19.89 10.58 6.06 24.58 12.97 17.90 14.80 17.29 17.38 中间层
(n=20)最大值/% 1.22 2.89 0.16 0.74 0.22 24.81 32.27 0.82 0.47 4.93 1.38 0.12 0.11 最小值/% 0.34 2.05 0.09 0.26 0.07 17.01 22.72 0.40 0.30 1.59 1.00 0.07 0.01 平均值/% 0.67 2.54 0.13 0.50 0.14 21.06 26.50 0.58 0.38 2.92 1.21 0.10 0.07 离散系数/% 29.34 7.88 14.57 25.34 24.59 11.22 9.67 23.00 14.48 26.75 8.97 13.66 33.77 内层
(n=20)最大值/% 1.77 2.61 0.19 0.75 0.20 35.47 30.66 0.75 0.48 6.40 3.14 0.14 0.14 最小值/% 0.49 1.05 0.10 0.20 0.08 16.36 11.02 0.15 0.28 1.88 1.13 0.07 0.06 平均值/% 0.85 2.24 0.15 0.42 0.13 23.71 23.83 0.43 0.39 3.62 1.44 0.11 0.09 离散系数/% 41.40 17.22 16.12 27.84 22.63 15.34 15.92 29.60 13.75 25.83 29.81 15.91 25.82 表 3 微区铁锰氧化物纹层内各元素间的相关系数矩阵(n=53)
Table 3. Pearson correlation coefficient matrix for major and valuable metal elements contained in the ferromanganese oxide layers (n=53)
Al Ca Ce Co Cu Fe Mn Ni P Si Ti V Ca −0.78 Ce 0.12 −0.07 Co −0.67 0.57 −0.21 Cu −0.01 0.18 −0.13 −0.04 Fe 0.49 −0.43 0.60 −0.69 −0.06 Mn −0.72 0.67 −0.41 0.75 0.06 −0.90 Ni −0.48 0.45 −0.45 0.65 0.13 −0.82 0.77 P 0.09 0.08 0.35 −0.47 −0.01 0.68 −0.52 −0.64 Si 0.78 −0.64 0.38 −0.72 −0.04 0.87 −0.94 −0.76 0.52 Ti 0.53 −0.55 0.53 −0.37 −0.04 0.76 −0.76 −0.55 0.18 0.72 V −0.03 0.06 0.41 −0.30 0.11 0.68 −0.49 −0.50 0.63 0.46 0.40 Zn 0.17 −0.10 0.12 −0.45 0.15 0.44 −0.39 −0.47 0.50 0.40 0.12 0.45 -
[1] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. 13. 11 - Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 273-291.
[2] Petersen S, Krätschell A, Augustin N, et al. News from the seabed – geological characteristics and resource potential of deep-sea mineral resources [J]. Marine Policy, 2016, 70: 175-187. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2016.03.012
[3] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine Co-Rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining. Cham: Springer, 2017: 65-141.
[4] Li Y H, Schoonmaker J E. 9.1 - Chemical composition and mineralogy of marine sediments [M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 1-32.
[5] White W M, Klein E M. 4.13 - Composition of the oceanic crust[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 457-496.
[6] Mizell K, Hein J R, Au M, et al. Estimates of metals contained in abyssal manganese nodules and ferromanganese crusts in the global ocean based on regional variations and genetic types of nodules [M]//Sharma R. Perspectives on Deep-Sea Mining: Sustainability, Technology, Environmental Policy and Management. Cham: Springer, 2022: 53-80.
[7] 李三忠, 赵淑娟, 索艳慧, 等. 区域海底构造-上册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.
LI Sanzhong, ZHAO Shujian, SUO Yanhui, et al. Regional Submarine Tectonics-Volume One[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021.
[8] Ishizuka O, Taylor R N, Yuasa M, et al. Making and breaking an island arc: A new perspective from the Oligocene Kyushu-Palau arc, Philippine Sea [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(5): Q05005.
[9] 张洁, 李家彪, 丁巍伟. 九州-帕劳海脊地壳结构及其形成演化的研究综述[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(4):595-607 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.04.016
ZHANG Jie, LI Jiabiao, DING Weiwei. Reviews of the study on crustal structure and evolution of the Kyushu-Palau ridge [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(4): 595-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.04.016
[10] Yamazaki T, Takahashi M, Iryu Y, et al. Philippine Sea Plate motion since the Eocene estimated from paleomagnetism of seafloor drill cores and gravity cores [J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2010, 62(6): 495-502. doi: 10.5047/eps.2010.04.001
[11] Party Shipboard Scientific. Initial reports of the deep sea drilling project leg 59. Part I: introduction, site reports, 2, site 447: east side of the West Philippine Basin[R]. 1981.
[12] 何良彪. 马里亚纳海脊-西菲律宾海盆铁锰结核的地球化学[J]. 科学通报, 1991, 36(14):1190-1193
HE Liangbiao. Geochemical characteristics of Fe-Mn nodules and crusts from the Mariana ridge and the West Philippine Basin [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1991, 36(14): 1190-1193.
[13] 陈穗田, Stüben D. 菲律宾海的锰结壳和锰结核[J]. 海洋学报, 1997, 19(4):109-116
CHEN Suitian, Stüben D. Manganese crusts and nodules in the Philippine Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1997, 19(4): 109-116.
[14] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 于心科, 等. 东菲律宾海新型铁锰结壳中元素的赋存状态[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2008, 33(3):329-336 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.043
XU Zhaokai, LI Anchun, YU Xinke, et al. Elemental occurrence phases of the new-type ferromanganese crusts from the east Philippine Sea [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 33(3): 329-336. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2008.043
[15] Usui A, Graham I J, Ditchburn R G, et al. Growth history and formation environments of ferromanganese deposits on the Philippine Sea Plate, northwest Pacific Ocean [J]. Island Arc, 2007, 16(3): 420-430. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.2007.00592.x
[16] Wegorzewski A V, Kuhn T. The influence of suboxic diagenesis on the formation of manganese nodules in the Clarion Clipperton nodule belt of the Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 123-138. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.004
[17] Heller C, Kuhn T, Versteegh G J M, et al. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018, 142: 16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.09.008
[18] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[19] Josso P, Lusty P, Chenery S, et al. Controls on metal enrichment in ferromanganese crusts: Temporal changes in oceanic metal flux or phosphatisation? [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 308: 60-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.06.002
[20] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[21] Deng Y N, Ren J B, Guo Q J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater from deep sea in western Pacific [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 16539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16379-1
[22] Zhang J, Nozaki Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji basins of the western South Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23): 4631-4644. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00276-1
[23] Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003
[24] Bonatti E, Kraemer T F, Rydell H. Classification and genesis of submarine iron-manganese deposits[M]//Horn D R. Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. New York: Arden House, 1972.
[25] 黄威, 胡邦琦, 徐磊, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西缘中段铁锰结核的地球化学特征和成因类型[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(1):199-209 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020101501
HUANG Wei, HU Bangqi, XU Lei, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the ferromanganese nodules in the middle western margin of the Parece Vela Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(1): 199-209. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020101501
[26] Peacock C L, Sherman D M. Vanadium(V) adsorption onto goethite (α-FeOOH) at pH 1.5 to 12: a surface complexation model based on ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(8): 1723-1733. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.018
[27] Millero F J, Woosley R, Ditrolio B, et al. Effect of ocean acidification on the speciation of metals in seawater [J]. Oceanography, 2009, 22(4): 72-85. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2009.98
[28] GEOTRACES Intermediate Data Product Group. The GEOTRACES intermediate data product 2021 (IDP2021). NERC EDS British Oceanographic Data Centre NOC, 2021.
[29] Bruland K W, Middag R, Lohan M C. 8.2 - controls of trace metals in seawater[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 19-51.
[30] Gong G C, Liu K K, Liu C T, et al. The chemical hydrography of the South China Sea West of Luzon and a comparison with the West Philippine Sea [J]. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 1992, 3(4): 587-602. doi: 10.3319/TAO.1992.3.4.587(O)
[31] Behrens M K, Pahnke K, Schnetger B, et al. Sources and processes affecting the distribution of dissolved Nd isotopes and concentrations in the West Pacific [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 222: 508-534. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.11.008
[32] Manceau A, Drits V A, Silvester E, et al. Structural mechanism of Co2+ oxidation by the phyllomanganate buserite [J]. American Mineralogist, 1997, 82(11-12): 1150-1175. doi: 10.2138/am-1997-11-1213
[33] Manceau A, Lanson M, Takahashi Y. Mineralogy and crystal chemistry of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu in a deep-sea Pacific polymetallic nodule [J]. American Mineralogist, 2014, 99(10): 2068-2083. doi: 10.2138/am-2014-4742
[34] Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer, 2017: 23-63.
[35] Nozaki Y. A fresh look at element distribution in the North Pacific Ocean [J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1997, 78(21): 221-221.
[36] Hens T, Brugger J, Etschmann B, et al. Nickel exchange between aqueous Ni(II) and deep-sea ferromanganese nodules and crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 528: 119276. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119276
[37] Peacock C L. Physiochemical controls on the crystal-chemistry of Ni in birnessite: Genetic implications for ferromanganese precipitates [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(12): 3568-3578. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.020
[38] Peacock C L, Sherman D M. Crystal-chemistry of Ni in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules [J]. American Mineralogist, 2007, 92(7): 1087-1092. doi: 10.2138/am.2007.2378
[39] Wegorzewski A V, Grangeon S, Webb S M, et al. Mineralogical transformations in polymetallic nodules and the change of Ni, Cu and Co crystal-chemistry upon burial in sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 282: 19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.04.012
[40] Sherman D M, Peacock C L. Surface complexation of Cu on birnessite (δ-MnO2): Controls on Cu in the deep ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(23): 6721-6730. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.08.042
[41] Little S H, Sherman D M, Vance D, et al. Molecular controls on Cu and Zn isotopic fractionation in Fe–Mn crusts [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 396: 213-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.04.021
[42] Yang P, Post J E, Wang Q, et al. Metal adsorption controls stability of layered manganese oxides [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(13): 7453-7462.
[43] Grangeon S, Manceau A, Guilhermet J, et al. Zn sorption modifies dynamically the layer and interlayer structure of vernadite [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 85: 302-313. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.02.019
[44] Hinkle M A G, Dye K G, Catalano J G. Impact of Mn(II)-manganese oxide reactions on Ni and Zn speciation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(6): 3187-3196.
[45] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Kuhn T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(3): 158-169.
[46] Wu F, Owens J D, Tang L M, et al. Vanadium isotopic fractionation during the formation of marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 265: 371-385. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.09.007
[47] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10): 1709-1725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00063-4
[48] Bau M. Scavenging of dissolved yttrium and rare earths by precipitating iron oxyhydroxide: experimental evidence for Ce oxidation, Y-Ho fractionation, and lanthanide tetrad effect [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(1): 67-77. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00014-9
[49] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045
[50] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[51] Marcus M A, Toner B M, Takahashi Y. Forms and distribution of Ce in a ferromanganese nodule [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2018, 202: 58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.03.005
[52] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[53] Josso P, Parkinson I, Horstwood M, et al. Improving confidence in ferromanganese crust age models: A composite geochemical approach [J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 513: 108-119. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.003
[54] Puteanus D, Halbach P. Correlation of Co concentration and growth rate — A method for age determination of ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 69(1-2): 73-85. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90159-3
[55] Manheim F T, Lane-Bostwick C M. Cobalt in ferromanganese crusts as a monitor of hydrothermal discharge on the Pacific sea floor [J]. Nature, 1988, 335(6185): 59-62. doi: 10.1038/335059a0
[56] Mcmurtry G M, Vonderhaar D L, Eisenhauer A, et al. Cenozoic accumulation history of a Pacific ferromanganese crust [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125(1-4): 105-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90209-7
[57] Hein J R, Konstantinova N, Mikesell M, et al. Arctic deep water ferromanganese-oxide deposits reflect the unique characteristics of the Arctic Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(11): 3771-3800. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007186
[58] Dutkiewicz A, Müller R D, Wang X, et al. Predicting sediment thickness on vanished ocean crust since 200 Ma [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(12): 4586-4603. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007258
-




 下载:
下载: