Prediction of favorable reservoir in granite weathering-crust buried-hill type—A case study of the Baoyunting area on Pinghu slope
-
摘要:
平湖斜坡是东海盆地西湖凹陷的油气重点勘探区域,随着勘探开发的不断深入,深部和基底潜山油气藏成为重要的油气勘探接替领域。为进一步指导该区油气勘探,综合利用录井、测井、地震、岩心与实验分析等多种资料,对平湖斜坡宝云亭油气区花岗岩潜山储层发育主控因素及有效储层分布开展研究。结果表明,矿物成分为花岗岩储层的形成提供物质基础,风化淋滤控制溶蚀孔隙形成,构造活动形成大量裂缝提升储层物性,三者共同控制着花岗岩潜山储层展布。利用古地貌恢复、蚂蚁体属性提取等手段,预测风化溶蚀强度和裂缝发育程度,对宝云亭油气区花岗岩潜山储层进行了综合评价。
Abstract:Pinghu slope is the key exploration area of oil and gas in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea basin. With the deepening of exploration and development, buried-hill-typed reservoirs in deep and basement have become an important target. To promote the exploration, the main controlling factors and favorable reservoir distribution of granite weathering-crust buried-hill reservoirs in the Baoyunting area of Pinghu slope were studied comprehensively using various data including logging, seismic, core, and experimental analysis. Results show that the mineral composition provided material bases for the formation of the granite weathering-crust buried-hill–typed reservoir; leaching controlled the formation of dissolution pores; and tectonic activities generated many fractures. These factors improved the physical properties of the reservoir, and jointly controlled the distribution of reservoirs in the buried-hill type. In addition, using paleogeomorphic restoration and ant body attribute extraction, the weathering and dissolution intensity and fracture development degree were predicted, and finally the granite buried hill reservoirs in the Baoyunting oil-gas area was evaluated in overall.
-
Key words:
- granite buried hill /
- favorable reservoir /
- weathering crust /
- Pinghu slope
-

-
表 1 宝云亭潜山风化壳型花岗岩储层分类评价
Table 1. Classification and evaluation of weathering-crust–typed granite reservoir in the Baoyunting buried hill
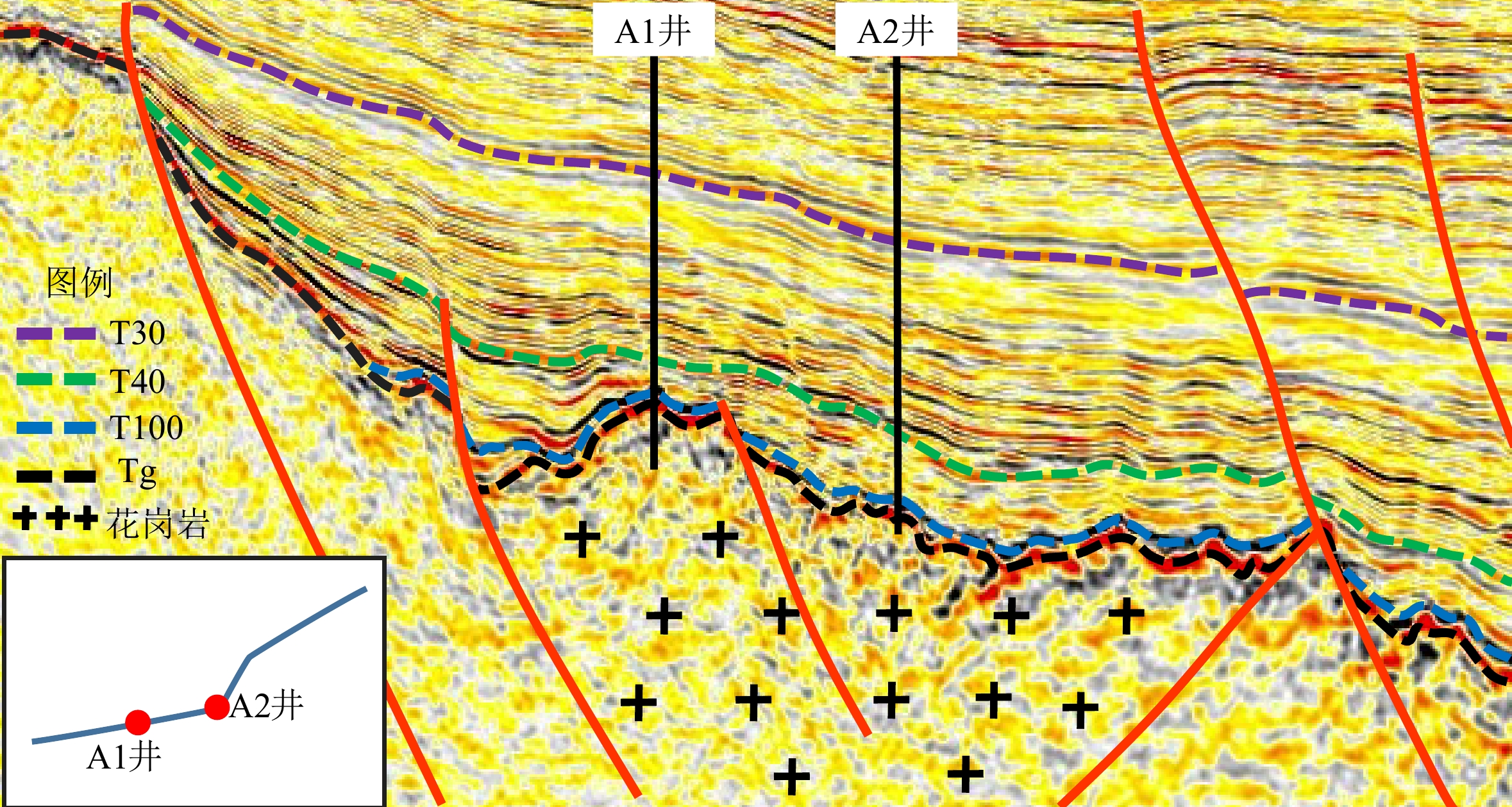
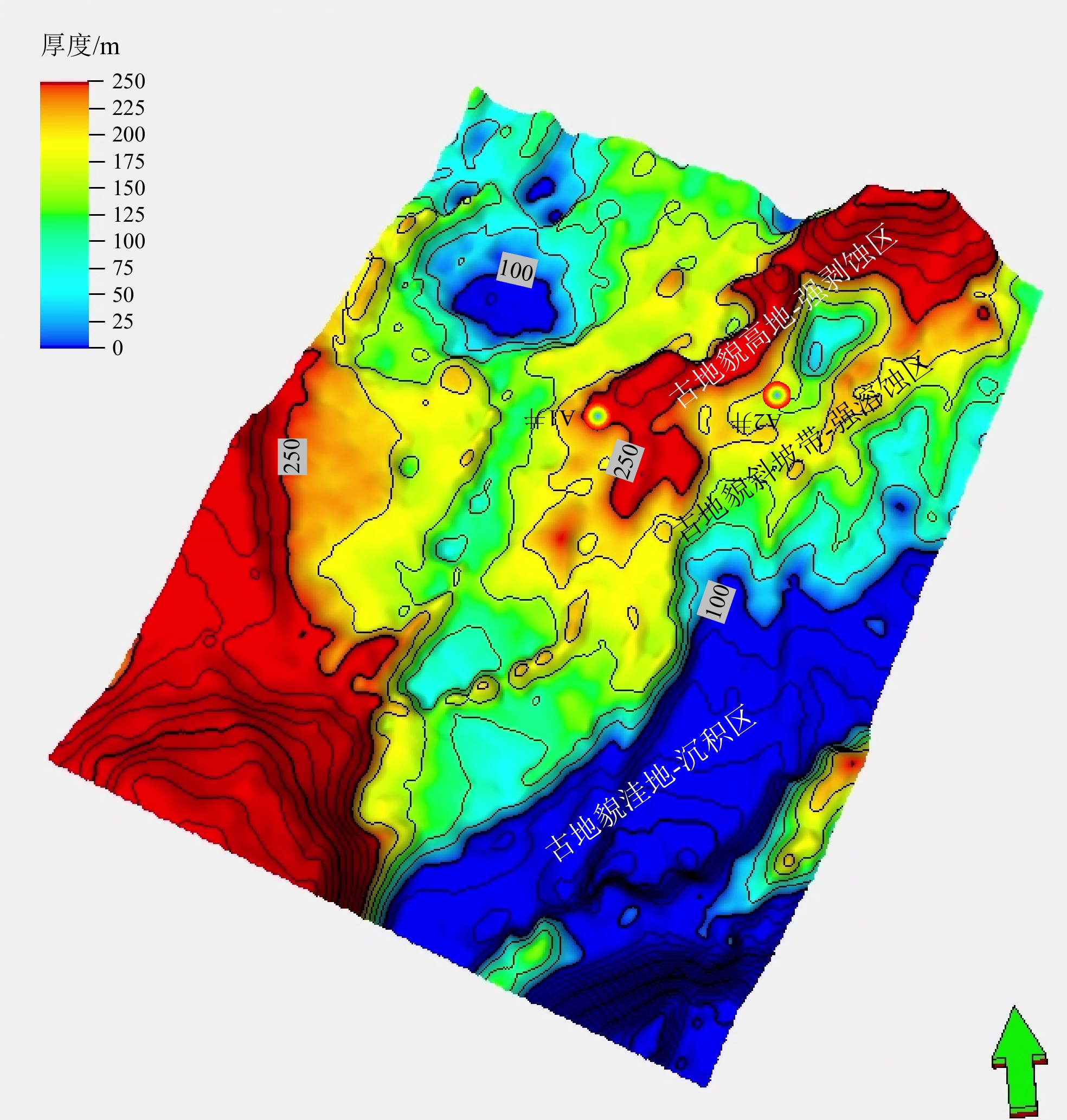
储层类型 储集空间类型 储层定性特征 储层定量表征 已钻井特征 一类储层 孔隙-裂缝型 古地貌斜坡带+裂缝发育区 古地貌高度100~250 m,
蚂蚁体属性值大于0.2A2井潜山岩芯发育裂缝,
出后效气约1万m3二类储层 裂缝型 古地貌高地+裂缝发育区 古地貌高度大于250 m,
蚂蚁体属性值大于0.2A1井潜山井段发育裂缝,
见气测异常显示孔隙型 古地貌斜坡带+裂缝不发育区 古地貌高度100~250 m,
蚂蚁体属性值小于0.2暂无 三类储层 无有效储集空间 古地貌高地/洼地+裂缝不发育区 古地貌高度大于250 m或小于100 m,
蚂蚁体属性值小于0.2暂无 -
[1] 沈澈, 蒋有录, 苏圣民, 等. 二连盆地乌兰花凹陷花岗岩潜山储层特征及发育模式[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(6):12-19
SHEN Che, JIANG Youlu, SU Shengmin, et al. Characteristics and development modes of the granite buried-hill reservoir in Wulanhua Sag of Erlian Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(6): 12-19.
[2] 闫林辉, 常毓文, 田中元, 等. 乍得Bongor盆地潜山基岩储集层特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):60-68 doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0608
YAN linhui, CHANG Yuwen, TIAN Zhongyuan, et al. Characteristics of basement rock reservoirs in Bongor Basin, Chad [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 60-68. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2019.0608
[3] 伍劲, 高先志, 周伟, 等. 柴达木盆地东坪地区基岩风化壳与油气成藏[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(6):666-672 doi: 10.7657/XJPG20180606
WU Jin, GAO Xianzhi, ZHOU Wei, et al. Base rock weathering crusts and petroleum accumulation in Dongping Area, Qaidam Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(6): 666-672. doi: 10.7657/XJPG20180606
[4] 胡志伟, 徐长贵, 杨波, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱9-1油田花岗岩潜山储层成因机制及石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(3):274-285 doi: 10.7623/syxb201703004
HU Zhiwei, XU Changgui, YANG Bo, et al. Reservoir forming mechanism of Penglai 9-1 granite buried-hills and its oil geology significance in Bohai Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 274-285. doi: 10.7623/syxb201703004
[5] 徐守立, 尤丽, 毛雪莲, 等. 琼东南盆地松南低凸起周缘花岗岩潜山储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8):2717-2728
XU Shouli, YOU Li, MAO Xuelian, et al. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of granite buried hill in Songnan low uplift, Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8): 2717-2728.
[6] 宋爱学, 杨金海, 胡斌, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区古潜山裂缝性储层展布特征及有利区含油气性预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(7):60-67
SONG Aixue, YANG Jinhai, HU Bin, et al. Distribution patterns of fracture reservoirs in the buried-hills in deep water areas of Qiongdongnan Basin and prediction of favorable areas for hydrocarbon exploration [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(7): 60-67.
[7] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等. 东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J]. 上海地质, 2003(3):1-6
LIU Jinshui, LIAO Zongting, JIA Jianyi, et al. The geological structure and tectonic evolution of the East China Sea shelf basin [J]. Shanghai Geology, 2003(3): 1-6.
[8] 魏恒飞, 陈践发, 陈晓东. 东海盆地西湖凹陷凝析气藏成藏特征及分布控制因素[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2019, 49(6):1507-1517
WEI Hengfei, CHEN Jianfa, CHEN Xiaodong. Characteristics and controlling factors of condensate reservoir accumulation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2019, 49(6): 1507-1517.
[9] 侯国伟, 李帅, 秦兰芝, 等. 西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组源-汇体系特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):29-39
HOU Guowei, LI Shuai, QIN Lanzhi, et al. Source-to-sink system of Pinghu Formation in west slope belt of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(3): 29-39.
[10] 苏奥, 陈红汉. 东海盆地西湖凹陷宝云亭气田油气成藏史: 来自流体包裹体的证据[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(3):300-309 doi: 10.7623/syxb201503005
SU Ao, CHEN Honghan. Accumulation history of Baoyunting gas field in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin: from evidence of fluid inclusions [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(3): 300-309. doi: 10.7623/syxb201503005
[11] 黄建红, 谭先锋, 程承吉, 等. 花岗质基岩风化壳结构特征及油气地质意义: 以柴达木盆地东坪地区基岩风化壳为例[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(12):2041-2060
HUANG Jianhong, TAN Xianfeng, CHENG Chengji, et al. Structural features of weathering crust of granitic basement rock and its petroleum geological significance: a case study of basement weathering crust of Dongping Area in Qaidam Basin [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(12): 2041-2060.
[12] 刘震, 朱茂林, 刘惠民, 等. 花岗岩风化壳储层形成机理及分布特征: 以东营凹陷北带西段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(2):163-175
LIU Zhen, ZHU Maolin, LIU Huimin, et al. Formation mechanism and distribution characteristics of granitic weathering crust reservoir: a case study of the western segment of the northern belt of Dongying Sag [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 163-175.
[13] 王德英, 王清斌, 刘晓健, 等. 渤海湾盆地海域片麻岩潜山风化壳型储层特征及发育模式[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4):1181-1193 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.13
WANG Deying, WANG Qingbin, LIU Xiaojian, et al. Characteristics and developing patterns of gneiss buried hill weathering crust reservoir in the sea area of the Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1181-1193. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.04.13
[14] 华仁民, 李晓峰, 张开平, 等. 金山金矿热液蚀变黏土矿物特征及水-岩反应环境研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2003, 23(1):23-30 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2003.01.005
HUA Renmin, LI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Kaiping, et al. Characteristics of clay minerals derived from hydrothermal alteration in Jinshan gold deposit: implication for the environment of water-rock interaction [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2003, 23(1): 23-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2003.01.005
[15] 张乃娴. 黏土矿物与风化作用[J]. 建材地质, 1992(6):1-6
ZHANG Naixian. Clay minerals and weathering [J]. China Non-Metallic Minerals Industry, 1992(6): 1-6.
[16] 王昕, 周心怀, 徐国胜, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱9-1花岗岩潜山大型油气田储层发育特征与主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(2):262-270 doi: 10.11743/ogg20150211
WANG Xin, ZHOU Xinhuai, XU Guosheng, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of reservoirs in Penglai 9-1 large-scale oilfield in buried granite hills, Bohai Sea [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(2): 262-270. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150211
[17] 胡修棉. 白垩纪"温室"气候与海洋[J]. 中国地质, 2004, 31(4):442-448 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.04.017
HU Xiumian. Greenhouse climate and ocean during the Cretaceous [J]. Geology in China, 2004, 31(4): 442-448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.04.017
[18] 易泽军, 王伟锋, 李飞, 等. 构造古地貌对石炭系火山岩风化壳型储层物性的控制作用[J]. 中国矿业, 2015, 24(S2):153-157 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.z2.034
YI Zejun, WANG Weifeng, LI Fei, et al. Tectonic geomorphology control factors on properties of weathering reservoirs of carboniferous volcanic rocks [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2015, 24(S2): 153-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.z2.034
[19] 左丽群. 古地貌恢复方法综述[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2019, 33(3):12-16,21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2019.03.003
ZUO Liqun. Review on methods of paleo-geomorphologic restoration [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2019, 33(3): 12-16,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2019.03.003
[20] 陈亮, 张珂嘉, 张振平, 等. 裂缝型储层预测技术优选: 以涪陵地区侏罗系大安寨段为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2013, 27(5):43-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2013.05.012
CHEN Liang, ZHANG Kejia, ZHANG Zhenping, et al. Optimization of fracture reservoir prediction technology: with reservoir of Daanzhai member of Jurassic in Fulin region as an example [J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2013, 27(5): 43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2013.05.012
[21] 姜晓宇, 张研, 甘利灯, 等. 花岗岩潜山裂缝地震预测技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(3):694-704
JIANG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Yan, GAN Lideng, et al. Seismic techniques for predicting fractures in granite buried hills [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(3): 694-704.
[22] 刘厚彬, 于兴川, 张震, 等. 长宁页岩地层井下复杂及裂缝三维展布规律研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 43(4):208-218
LIU Houbin, YU Xingchuan, ZHANG Zhen, et al. A study on downhole complex and three dimensional distribution of fractures in Changning shale formation [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University:Science & Technology Edition, 2021, 43(4): 208-218.
[23] 李楠, 王龙颖, 黄胜兵, 等. 利用高清蚂蚁体精细解释复杂断裂带[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(1):182-190
LI Nan, WANG Longying, HUANG Shengbing, et al. 3D seismic fine structural interpretation in complex fault zones based on the high-definition ant-tracking attribute volume [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(1): 182-190.
[24] 张欣. 蚂蚁追踪在断层自动解释中的应用: 以平湖油田放鹤亭构造为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(2):278-281
ZHANG Xin. Application of ant tracing algorithm in fault automatic interpretation: a case study on Fangheting structure in Pinghu oilfield [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 45(2): 278-281.
[25] 刘慧楠, 李婷婷, 张幸兴, 等. 蚂蚁体属性断裂解释技术及在苏德尔特地区的应用[J]. 中国锰业, 2019, 37(6): 38-41, 47.
LIU Huinan, LI Tingting, ZHANG Xingxing, et al. Fracture interpretation technology on ant attribute and its application in suddelt area[j]. China’s Mangasnese Industry, 2019, 37(6): 38-41, 47.
-




 下载:
下载: