Distribution characteristics and implications of mercury in the surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
-
摘要:
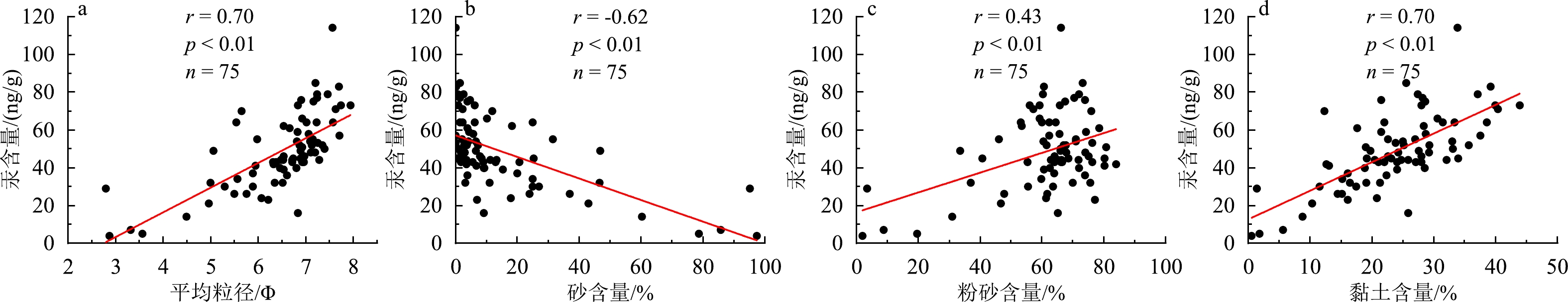
全球变暖导致北极地区冻土退化、海冰消融、河流径流增加及海洋动力发生变化,这些因素连同日益增加的人类活动都影响北冰洋中汞的输入和运移。对取自北极东西伯利亚陆架的87个表层沉积物进行了汞含量测试与分析,发现沉积物中汞含量的分布有显著的空间差异性,可分为近岸低汞区(33 ng/g)、陆架中部汞含量中等区(58 ng/g)和北部深水高汞区(84 ng/g)。总体来看,从近岸向外海,汞含量随水深的增大而升高。结合沉积物粒度、有机碳和比表面积等指标,发现东西伯利亚陆架沉积物中黏土含量与汞含量呈现正相关,显示了沉积物粒度对汞分布的控制作用。近岸由于受河流输入、海岸侵蚀和环流分选等因素的影响,沉积物粒径较粗,导致汞含量较低,而北部陆架深水区的细粒沉积物则吸附了更多的汞。在楚科奇海和拉普捷夫海,沉积汞含量和总有机碳含量有较强的正相关性,而在东西伯利亚海相关性较弱,这可能是因为东西伯利亚海的沉积有机碳来源相对更为复杂。基于沉积汞的富集因子指标,我们认为北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积汞的污染水平整体较低,受人类活动的影响相对较弱。
Abstract:Global warming is leading to permafrost degradation, sea-ice melt, increased river runoff, and changes in ocean dynamics in the Arctic region. These factors, plus the increasing human activities, affects the input and transport of mercury in the Arctic Ocean. We analyzed the mercury content in 87 surface sediments (0~2 cm) sampled in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf in the Chukchi Sea, East Siberian Sea, and Laptev Sea during three Sino-Russian Arctic joint expeditions in 2016, 2018, and 2020 at water depth of 9~2546 m. Results show a significant spatial variability in mercury concentration, which can be divided into the nearshore low-mercury zones (33 ng/g), the middle shelf medium-mercury zone (58 ng/g), and the northern deep water high-mercury zone (84 ng/g). In general, the mercury concentration tended to increase with water depth increasing from nearshore toward offshore. Analyses of sediment grain size, total organic carbon, and specific surface area of sediments show that the mercury concentration was positively correlated with the clay content in the surface sediments, indicating the controlling role of sediment grain size in the distribution of mercury. The coarse sediments in the nearshore showed lower mercury concentration due to the influence of river input, coastal erosion, and hydrodynamic sorting, while the fine-grained sediments in the northern shelf are prone to absorb more mercury. There was a strong positive correlation between mercury and total organic carbon in the Chukchi and Laptev Seas, while the correlation was weaker in the East Siberian Sea due probably to more-complexed source of total organic carbon. The enrichment factor of mercury manifests that the overall level of contamination of sedimentary mercury is low at present in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf area, showing relatively weak influence of human activities.
-

-
图 1 北极东西伯利亚陆架概况[29]及取样站位分布图
Figure 1.
河流 流域面积
/(103 km2)径流量
/(km3/a)输沙量
/(106 t/a)汞通量
/(kg/a)鄂毕河 2990 402.0 15.5 2421 叶尼塞河 2540 580.0 4.7 3642 哈坦加河 437.2 85.3 1.7 − 勒拿河 2460 532.0 20.7 6591 亚纳河 224 31.9 4.0 − 因迪吉尔卡河 329.4 54.2 11.1 − 科雷马河 650 122.0 10.1 1107 表 2 北极东西伯利亚陆架表层沉积汞含量分区
Table 2. Regional-specific Hg concentrations in the surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
区域 平均水深/m 汞含量/(ng/g) 汞含量平均值/(ng/g) 站位数 Ⅰ 区 26 4~50 33 34 Ⅱ 区 89 40~114 58 38 Ⅲ 区 1801 69~119 84 15 -
[1] Selin N E. Global biogeochemical cycling of mercury: a review [J]. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2009, 34: 43-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.environ.051308.084314
[2] Sonke J E, Heimbürger L E. Mercury in flux [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(7): 447-448. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1508
[3] Lindberg S, Bullock R, Ebinghaus R, et al. A synthesis of progress and uncertainties in attributing the sources of mercury in deposition [J]. AMBIO:A Journal of the Human Environment, 2007, 36(1): 19-32. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[19:ASOPAU]2.0.CO;2
[4] Aksentov K I, Astakhov A S, Ivanov M V, et al. Assessment of mercury levels in modern sediments of the East Siberian Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 168: 112426. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112426
[5] Kita I, Kojima M, Hasegawa H, et al. Mercury content as a new indicator of ocean stratification and primary productivity in Quaternary sediments off Bahama Bank in the Caribbean Sea [J]. Quaternary Research, 2013, 80(3): 606-613. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.08.006
[6] Kita I, Yamashita T, Chiyonobu S, et al. Mercury content in Atlantic sediments as a new indicator of the enlargement and reduction of Northern Hemisphere ice sheets [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016, 31(3): 167-177. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2854
[7] Scaife J D, Ruhl M, Dickson A J, et al. Sedimentary mercury enrichments as a marker for submarine large igneous province volcanism? Evidence from the Mid-Cenomanian event and Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (Late Cretaceous) [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(12): 4253-4275. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007153
[8] Font E, Adatte T, Andrade M, et al. Deccan volcanism induced high-stress environment during the Cretaceous-Paleogene transition at Zumaia, Spain: evidence from magnetic, mineralogical and biostratigraphic records [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 484: 53-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.11.055
[9] Grasby S E, Them II T R, Chen Z H, et al. Mercury as a proxy for volcanic emissions in the geologic record [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 196: 102880. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102880
[10] Lim D, Kim J, Xu Z K, et al. New evidence for Kuroshio inflow and deepwater circulation in the Okinawa Trough, East China Sea: sedimentary mercury variations over the last 20 kyr [J]. Paleoceanography, 2017, 32(6): 571-579. doi: 10.1002/2017PA003116
[11] Zou J J, Chang Y P, Zhu A M, et al. Sedimentary mercury and antimony revealed orbital-scale dynamics of the Kuroshio Current [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 265: 107051. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.107051
[12] Krabbenhoft D P, Sunderland E M. Global change and mercury [J]. Science, 2013, 341(6153): 1457-1458. doi: 10.1126/science.1242838
[13] Schuster P F, Striegl R G, Aiken G R, et al. Mercury export from the Yukon River basin and potential response to a changing climate [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9262-9267.
[14] Dastoor A P, Durnford D A. Arctic ocean: is it a sink or a source of atmospheric mercury? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(3): 1707-1717.
[15] Stern G A, Macdonald R W, Outridge P M, et al. How does climate change influence arctic mercury? [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 414: 22-42. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.039
[16] IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021.
[17] Obrist D, Agnan Y, Jiskra M, et al. Tundra uptake of atmospheric elemental mercury drives Arctic mercury pollution [J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7662): 201-204. doi: 10.1038/nature22997
[18] Outridge P M, Macdonald R W, Wang F, et al. A mass balance inventory of mercury in the Arctic Ocean [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 5(2): 89-111. doi: 10.1071/EN08002
[19] Fisher J A, Jacob D J, Soerensen A L, et al. Riverine source of Arctic Ocean mercury inferred from atmospheric observations [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(7): 499-504. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1478
[20] AMAP. AMAP Assessment 2002: Heavy Metals in the Arctic[M]. Oslo: Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme, 2004.
[21] Steffen A, Douglas T, Amyot M, et al. A synthesis of atmospheric mercury depletion event chemistry in the atmosphere and snow [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 8(6): 1445-1482. doi: 10.5194/acp-8-1445-2008
[22] Zhang Y X, Jacob D J, Dutkiewicz S, et al. Biogeochemical drivers of the fate of riverine mercury discharged to the global and Arctic oceans [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2015, 29(6): 854-864. doi: 10.1002/2015GB005124
[23] Kim H, Lee K, Lim D I, et al. Increase in anthropogenic mercury in marginal sea sediments of the Northwest Pacific Ocean [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 654: 801-810. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.076
[24] Darby D A, Polyak L, Bauch H A. Past glacial and interglacial conditions in the Arctic Ocean and marginal seas-a review [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2006, 71(2-4): 129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2006.09.009
[25] Vonk J E, Sánchez-García L, van Dongen B E, et al. Activation of old carbon by erosion of coastal and subsea permafrost in Arctic Siberia [J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7414): 137-140. doi: 10.1038/nature11392
[26] Shakhova N, Semiletov I, Gustafsson O, et al. Current rates and mechanisms of subsea permafrost degradation in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf [J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15872. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15872
[27] Stein R, Fahl K, Schade I, et al. Holocene variability in sea ice cover, primary production, and Pacific‐Water inflow and climate change in the Chukchi and East Siberian Seas (Arctic Ocean) [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2017, 32(3): 362-379. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2929
[28] Opsahl S, Benner R, Amon R M W. Major flux of terrigenous dissolved organic matter through the Arctic Ocean [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1999, 44(8): 2017-2023. doi: 10.4319/lo.1999.44.8.2017
[29] Stein R. Arctic Ocean Sediments: Processes, Proxies, and Paleoenvironment[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008.
[30] Suchet P A, Probst J L, Ludwig W. Worldwide distribution of continental rock lithology: implications for the atmospheric/soil CO2 uptake by continental weathering and alkalinity river transport to the oceans [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2003, 17(2): 1038.
[31] Holmes R M, McClelland J W, Peterson B J, et al. A circumpolar perspective on fluvial sediment flux to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2002, 16(4): 1098.
[32] Guay C K, Falkner K K. Barium as a tracer of Arctic halocline and river waters [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 1997, 44(8): 1543-1569. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(97)00066-0
[33] Dastoor A, Angot H, Bieser J, et al. Arctic mercury cycling [J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(4): 270-286.
[34] Peterson B J, Holmes R M, McClelland J W, et al. Increasing river discharge to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Science, 2002, 298(5601): 2171-2173. doi: 10.1126/science.1077445
[35] Sonke J E, Teisserenc R, Heimbürger-Boavida L E, et al. Eurasian river spring flood observations support net Arctic Ocean mercury export to the atmosphere and Atlantic Ocean [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(50): E11586-E11594.
[36] Zolkos S, Krabbenhoft D P, Suslova A, et al. Mercury export from arctic great rivers [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(7): 4140-4148.
[37] Gordeev V V. Fluvial sediment flux to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 80(1-2): 94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.09.008
[38] Weingartner T J, Danielson S, Sasaki Y, et al. The Siberian coastal current: a wind- and buoyancy-forced Arctic coastal current [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 1999, 104(C12): 29697-29713. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900161
[39] 李日升, 郭跃安, 孙冬娥, 等. 化学蒸气发生-多通道原子荧光光谱法同时测定化探样品中的砷、锑、铋、汞[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2014, 50(5):569-571
LI Risheng, GUO Yuean, SUN Donge, et al. Simultaneous determination of As, Sb, Bi, and Hg in geological samples by Hg-Multi-channel-AFS [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2014, 50(5): 569-571.
[40] Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
[41] Sattarova V, Aksentov K, Astakhov A, et al. Trace metals in surface sediments from the Laptev and East Siberian Seas: levels, enrichment, contamination assessment, and sources [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 173: 112997. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112997
[42] Zhang J, Liu C L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China: weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2002, 54(6): 1051-1070. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2001.0879
[43] Chakraborty P, Sarkar A, Vudamala K, et al. Organic matter: a key factor in controlling mercury distribution in estuarine sediment [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 173: 302-309. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.10.005
[44] 赵一阳. 中国海大陆架沉积物地球化学的若干模式[J]. 地质科学, 1983(4):307-314
ZHAO Yiyang. Some geochemical patterns of shelf sediments of the China seas [J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1983(4): 307-314.
[45] 李秋玲, 乔淑卿, 石学法, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积物物源: 来自黏土矿物和化学元素的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(3):76-89
LI Qiuling, QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, et al. Sediment provenance of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf: evidence from clay minerals and chemical elements [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(3): 76-89.
[46] Thorne L T, Nickless G. The relation between heavy metals and particle size fractions within the severn estuary (U. K. ) inter-tidal sediments [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1981, 19(3): 207-213. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(81)90017-6
[47] Araújo M F D, Bernard P C, Van Grieken R E. Heavy metal contamination in sediments from the Belgian coast and Scheldt estuary [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1988, 19(6): 269-273. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(88)90597-8
[48] 夏逸. 北极拉普捷夫海现代沉积有机碳源汇过程与埋藏记录[D]. 自然资源部第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2022
XIA Yi. Source sink processes and burial records of modern sedimentary organic carbon in the Arctic Laptev Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, 2022.
[49] 叶君, 胡利民, 石学法, 等. 基于木质素示踪北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积有机碳的来源、输运与埋藏[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(3):752-765 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.03.11
YE Jun, HU Limin, SHI Xuefa, et al. Sources, transport and burial of terrestrial organic carbon in the surface sediments across the East Siberian Arctic shelf, insights from lignin [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(3): 752-765. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.03.11
[50] 于文秀, 胡利民, 石学法, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架黑碳的地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(4):50-60 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022022001
YU Wenxiu, HU Limin, SHI Xuefa, et al. Geochemical characteristics of black carbon in surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf and their environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(4): 50-60. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2022022001
[51] Stein R. The great challenges in Arctic Ocean paleoceanography [J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2011, 14: 012001. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/14/1/012001
[52] Stein R, Fahl K. Holocene accumulation of organic carbon at the Laptev Sea continental margin (Arctic Ocean): sources, pathways, and sinks [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2000, 20(1): 27-36. doi: 10.1007/s003670000028
[53] Semiletov I, Dudarev O, Luchin V, et al. The East Siberian Sea as a transition zone between Pacific‐derived waters and Arctic shelf waters [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(10): L10614. doi: 10.1029/2005GL022490
[54] Karlsson E S, Brüchert V, Tesi T, et al. Contrasting regimes for organic matter degradation in the East Siberian Sea and the Laptev Sea assessed through microbial incubations and molecular markers [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 170: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.12.005
[55] Savelieva N I, Semiletov I P, Vasilevskaya L N, et al. A climate shift in seasonal values of meteorological and hydrological parameters for Northeastern Asia [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2000, 47(2-4): 279-297. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6611(00)00039-2
[56] Stroeve J, Barrett A, Serreze M, et al. Using records from submarine, aircraft and satellites to evaluate climate model simulations of Arctic sea ice thickness [J]. The Cryosphere, 2014, 8(5): 1839-1854. doi: 10.5194/tc-8-1839-2014
[57] 胡利民, 石学法, 叶君, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积有机碳的源汇过程研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(10):1073-1086 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.086
HU Limin, SHI Xuefa, YE Jun, et al. Advances in the sources and sink of sedimentary organic carbon in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(10): 1073-1086. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.086
[58] Macdonald R W, Kuzyk Z Z A, Johannessen S C, et al. The vulnerability of Arctic shelf sediments to climate change [J]. Environmental Reviews, 2015, 23(4): 461-479. doi: 10.1139/er-2015-0040
[59] Chen L, Zhang Y X, Jacob D J, et al. A decline in Arctic Ocean mercury suggested by differences in decadal trends of atmospheric mercury between the Arctic and northern midlatitudes [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(14): 6076-6083. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064051
[60] Emmerton C A, Graydon J A, Gareis J A L, et al. Mercury export to the Arctic Ocean from the Mackenzie River, Canada [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(14): 7644-7654.
[61] St. Pierre K A, Zolkos S, Shakil S, et al. Unprecedented increases in total and methyl mercury concentrations downstream of retrogressive thaw slumps in the western Canadian Arctic [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(24): 14099-14109.
[62] Schaefer K, Elshorbany Y, Jafarov E, et al. Potential impacts of mercury released from thawing permafrost [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4650. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18398-5
[63] Søndergaard J, Tamstorf M, Elberling B, et al. Mercury exports from a High-Arctic river basin in Northeast Greenland (74°N) largely controlled by glacial lake outburst floods [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 514: 83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.097
[64] Morel F M M, Kraepiel A M L, Amyot M. The chemical cycle and bioaccumulation of mercury [J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1998, 29: 543-566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.543
[65] Bianchi T S. The role of terrestrially derived organic carbon in the coastal ocean: a changing paradigm and the priming effect [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(49): 19473-19481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017982108
[66] Rontani J F, Charrière B, Sempéré R, et al. Degradation of sterols and terrigenous organic matter in waters of the Mackenzie Shelf, Canadian Arctic [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 75: 61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.06.002
[67] 汪卫国, 方建勇, 陈莉莉, 等. 楚科奇海悬浮体含量分布及其颗粒组分特征[J]. 极地研究, 2014, 26(1):79-88 doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.2014.1.079
WANG Weiguo, FANG Jianyong, CHEN Lili, et al. The distribution and composition of suspended particles in the Chukchi Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2014, 26(1): 79-88. doi: 10.13679/j.jdyj.2014.1.079
[68] 王春娟, 刘焱光, 董林森, 等. 白令海与西北冰洋表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(3):1-9
WANG Chunjuan, LIU Yanguang, DONG Linsen, et al. The distribution pattern of the surface sediments in the Bering Sea and the western Arcric and its environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(3): 1-9.
[69] Nürnberg D, Wollenburg I, Dethleff D, et al. Sediments in Arctic sea ice: implications for entrainment, transport and release [J]. Marine Geology, 1994, 119(3-4): 185-214. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(94)90181-3
[70] Charette M A, Kipp L E, Jensen L T, et al. The transpolar drift as a source of riverine and shelf-derived trace elements to the central Arctic Ocean [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2020, 125(5): e2019JC015920.
[71] Yurco L N, Ortiz J D, Polyak L, et al. Clay mineral cycles identified by diffuse spectral reflectance in Quaternary sediments from the Northwind Ridge: implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation patterns in the Arctic Ocean [J]. Polar Research, 2010, 29(2): 176-197. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-8369.2010.00160.x
[72] Figueiredo T S, Santos T P, Costa K B, et al. Effect of deep Southwestern Subtropical Atlantic Ocean circulation on the biogeochemistry of mercury during the last two glacial/interglacial cycles [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 239: 106368. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106368
[73] Quémerais B, Cossa D, Rondeau B, et al. Mercury distribution in relation to iron and manganese in the waters of the St. Lawrence river [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1998, 213(1-3): 193-201. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00092-8
[74] Shen J, Feng Q L, Algeo T J, et al. Sedimentary host phases of mercury (Hg) and implications for use of Hg as a volcanic proxy [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 543: 116333. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2020.116333
[75] Hasan A B, Kabir S, Reza A H M S, et al. Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index of trace metals in sediments of the ship breaking area of Sitakund Upazilla (Bhatiary-Kumira), Chittagong, Bangladesh [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 125: 130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.12.002
[76] Kim H, Lee K, Lim D I, et al. Widespread anthropogenic nitrogen in northwestern Pacific Ocean sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(11): 6044-6052.
[77] Kim J, Lim D, Jung D, et al. Sedimentary mercury (Hg) in the marginal seas adjacent to Chinese high-Hg emissions: source-to-sink, mass inventory, and accumulation history [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 128: 428-437. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.058
[78] Astakhov A S, Gorbarenko S A, Bakhareva G A, et al. Distribution and accumulation rate of ore elements in Holocene and Late Glacial Sediments of the Deryugin Basin, Sea of Okhotsk [J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2005, 40(2): 97-113. doi: 10.1007/s10987-005-0012-1
[79] Sattarova V V, Aksentov K I. Geochemistry of mercury in surface sediments of the Kuril Basin of the Sea of Okhotsk, Kuril-Kamchatka Trench and adjacent abyssal plain and northwest part of the Bering Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2018, 154: 24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.09.002
[80] Kalinchuk V, Aksentov K, Karnaukh V. Gaseous elemental mercury (Hg (0)) in the surface air over the Sea of Japan, the Sea of Okhotsk and the Kuril-Kamchatka sector of the Pacific Ocean in August-September 2017 [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 224: 668-679. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.185
-




 下载:
下载: