3D seismic characterization and origination of gravity flow geomorphic units on continental slope: A case study of Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
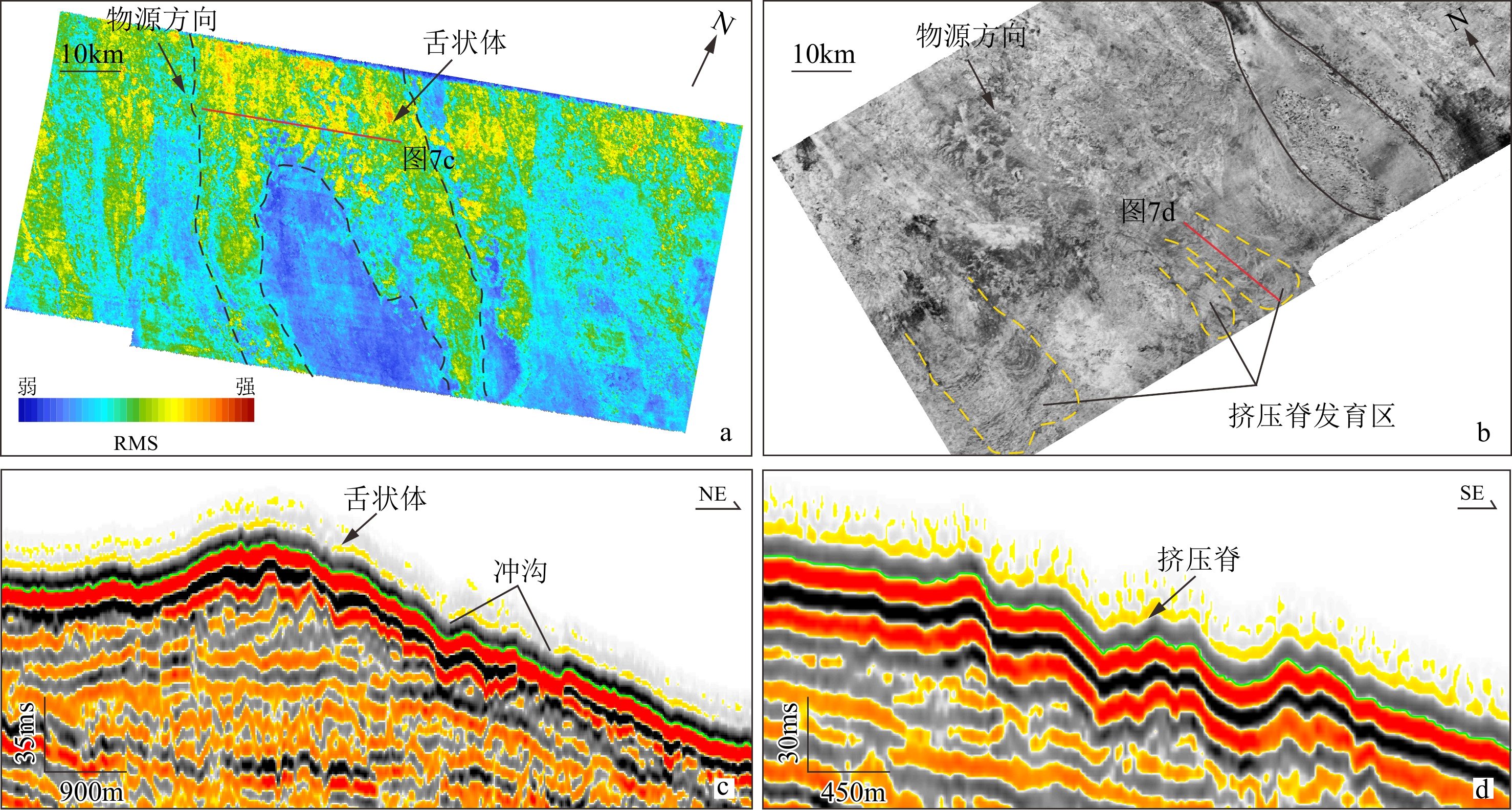
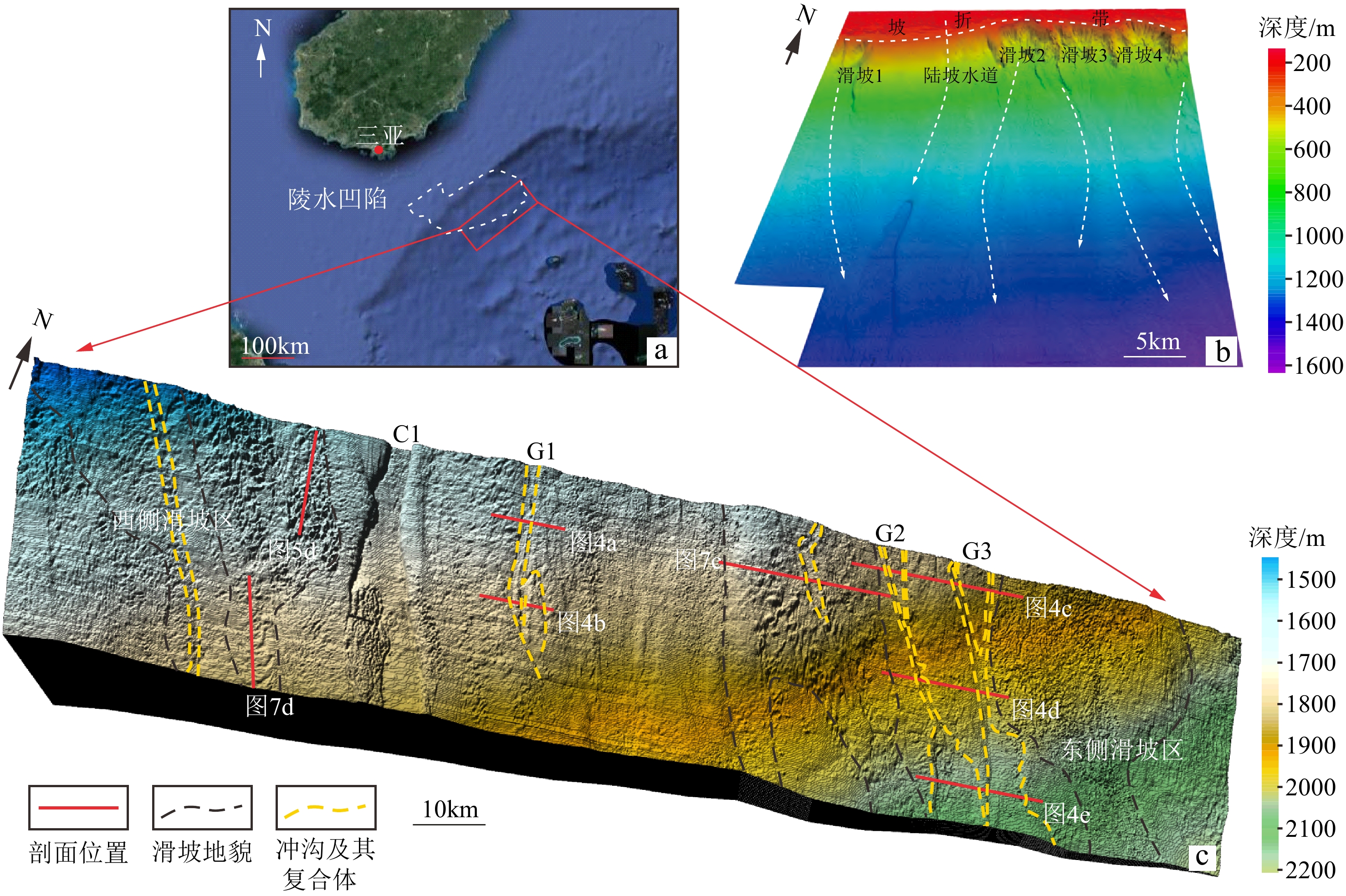
海底地貌一直是国内外学者关注的重点领域。基于琼东南盆地陵水凹陷1000 km2高分辨率三维地震资料,利用GeoFrame综合解释平台、Surfer三维成图等技术,对琼东南盆地陵水凹陷现今海底地貌进行精细刻画。研究结果表明:① 琼东南盆地下陆坡带主要发育水道(大型水道C1和冲沟-朵体复合体G1—G3)、周期阶坎以及滑坡体系3类典型地貌单元。② 水道C1宽深比31.5~232,主要由陆坡水道运输的碎屑物质冲刷而成,冲沟-朵体复合体G1—G3末端可见明显朵体发育;同时,可在水道和滑坡体系内识别到周期阶坎;研究区处于陆坡滑塌的体部-趾部区域,广泛发育挤压脊、舌状体等沉积构造。③ 推测认为研究区海底地貌主要由上陆坡滑坡引起,在物源与海平面升降的加持下,形成如今的综合型地貌。
Abstract:Seafloor topography has always been the key of scientific study. Based on 1000 km2 high-resolution 3D seismic data of Lingshui Sag in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea, the GeoFrame platform, Surfer 3D mapping, and other technologies were applied to characterize the current submarine landform of Lingshui Sag. Results show that the lower slope of Qiongdongnan Basin presented mainly three types of geomorphic units: channels (including large channel C1 and gully-lobe complexes G1-G3), cyclic steps, and submarine landslides. The width-depth ratio of channel C1 that was mainly scoured by debris transported via continental slope channels, is between 31.5 and 232. At the ends of G1-G3 of gully-lobe complex developed obvious lobes. The cyclic steps could be identified in the channel and submarine landslides. Squeeze ridges and underwater tongues were developed widely in the main body and the toes of slumps on continental slope. We speculate that the seafloor topography in the Lingshui Sag was mainly caused by submarine landsliding on the upper continental slope, which was intensified by deposit overload and sea level fluctuation, and finally the modern landform was formed.
-
Key words:
- seafloor topography /
- channel /
- cyclic steps /
- submarine landslide /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-

-
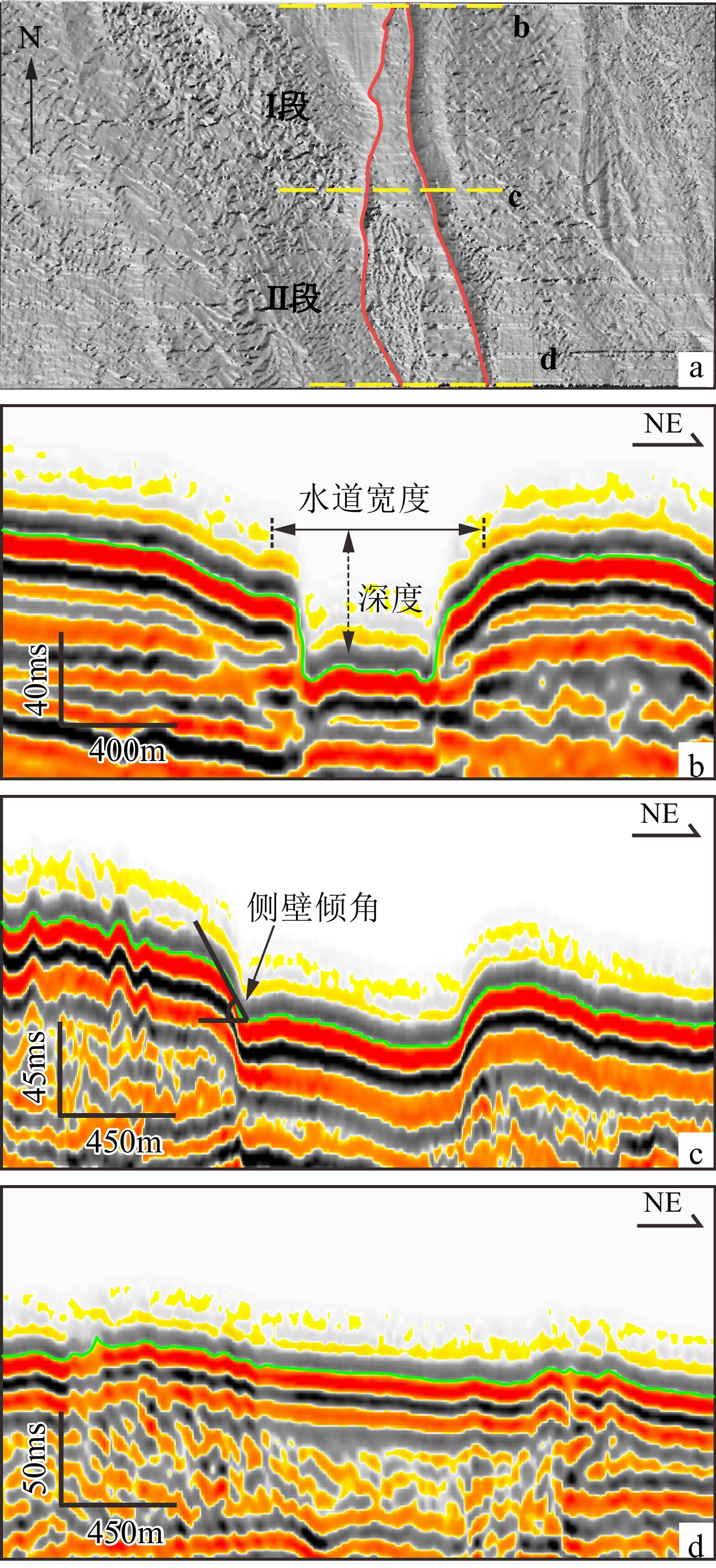
图 1 研究区地理位置(a)及地貌图(b、c)[7]
Figure 1.
表 1 常见海底地貌及特征描述
Table 1. Description and features of typical seafloor topography
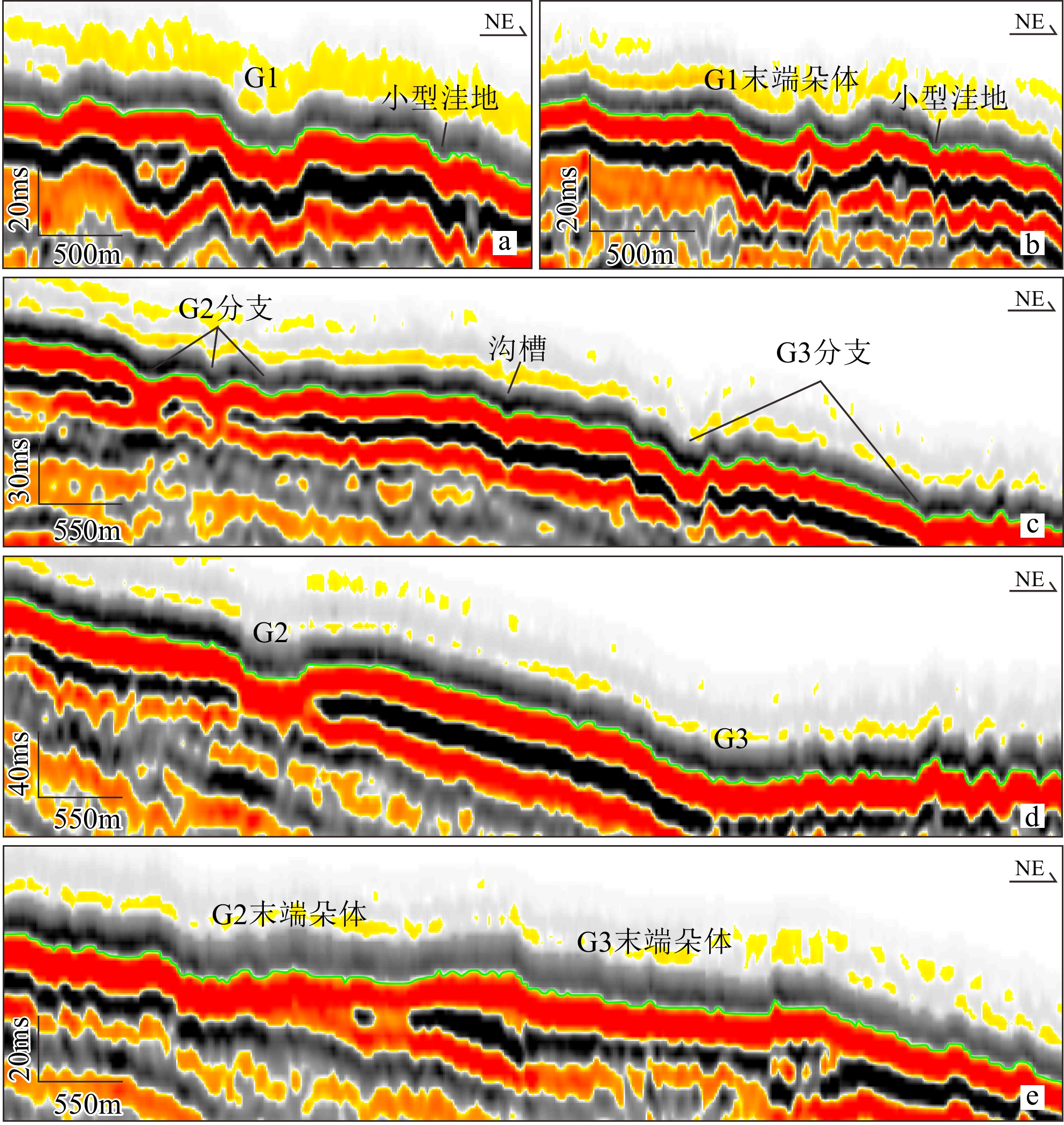
一级分类 二级分类 特征描述 深水水道 单一型水道 深水水道从形态上有弯曲水道(弯曲度>1.2)和顺直水道(弯曲度<1.2)之分[8-9],是沉积物由浅海向
深海搬运的重要通道分支水道 分支水道常发育于海底水道的头部和趾部,似树枝状展布,总体发育规模较小[10] 水道堤岸复合体 外部形态呈“海鸥”翼状展布,由“U”型或“V”型水道和楔状堤岸组成[11] 水道-朵体复合体 头部多为单一水道或者多分支水道,末端常以朵叶状展布 海底滑坡 头部 海底滑坡的头部常可识别出陡崖、滑移块体、侧壁、犁式正断层等沉积构造 体部 体部常见的特征有:滑塌褶皱、剪切槽、滑塌块体 趾部 趾部区域常能识别出逆冲断层、挤压脊、侵蚀擦痕以及外逸块体 冲沟 冲沟是常见的小尺度地貌,相当于深水沉积输送体系的“毛细血管”[12],多由高速冲刷的悬浮颗粒导致 海底峡谷 海底峡谷常呈“V”或“U”型下切,侧壁较陡,主要以侵蚀或沉积为主。深水海底峡谷是良好的油气储层,
同时也可以记录完整的海洋地质环境变迁相关信息[13]海底麻坑 孤立麻坑 孤立麻坑表现为圆形或椭圆形,直径1~300 m[14],是由超压流体溢出海底时侵蚀
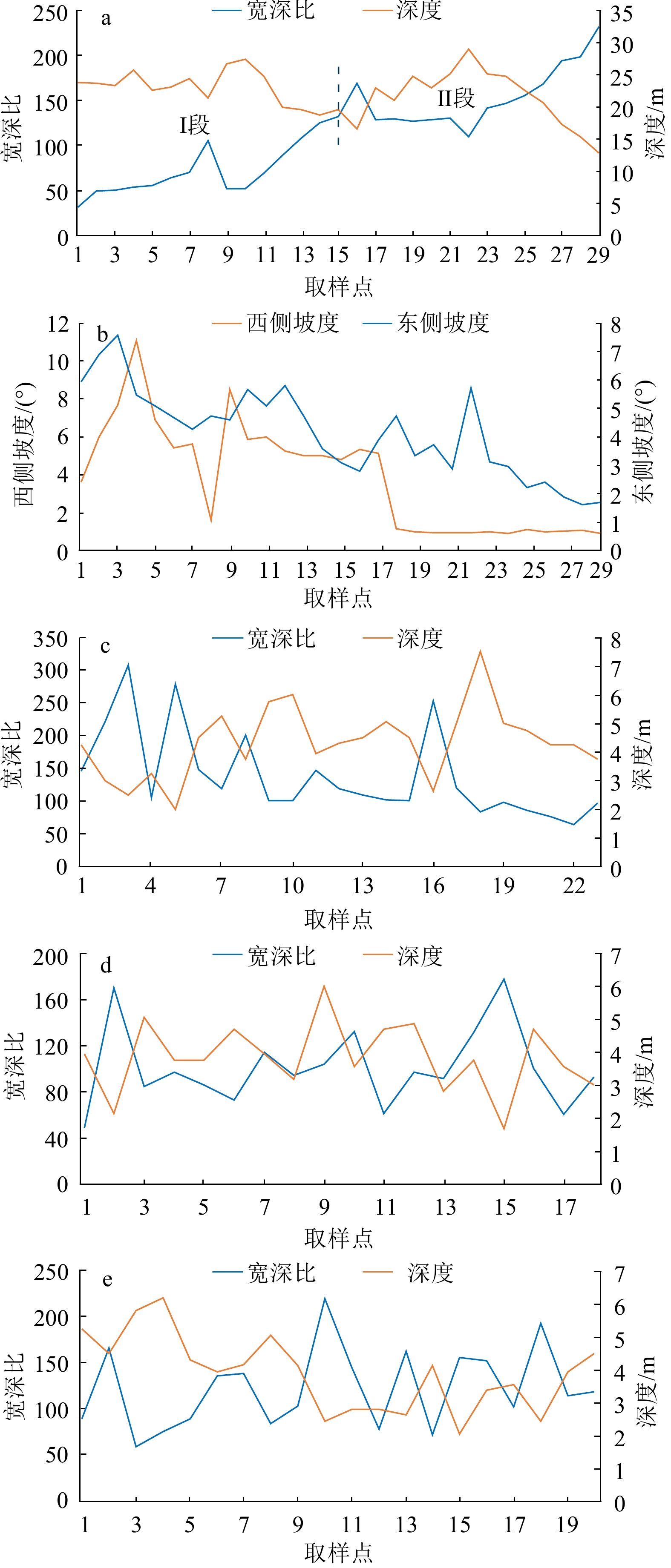
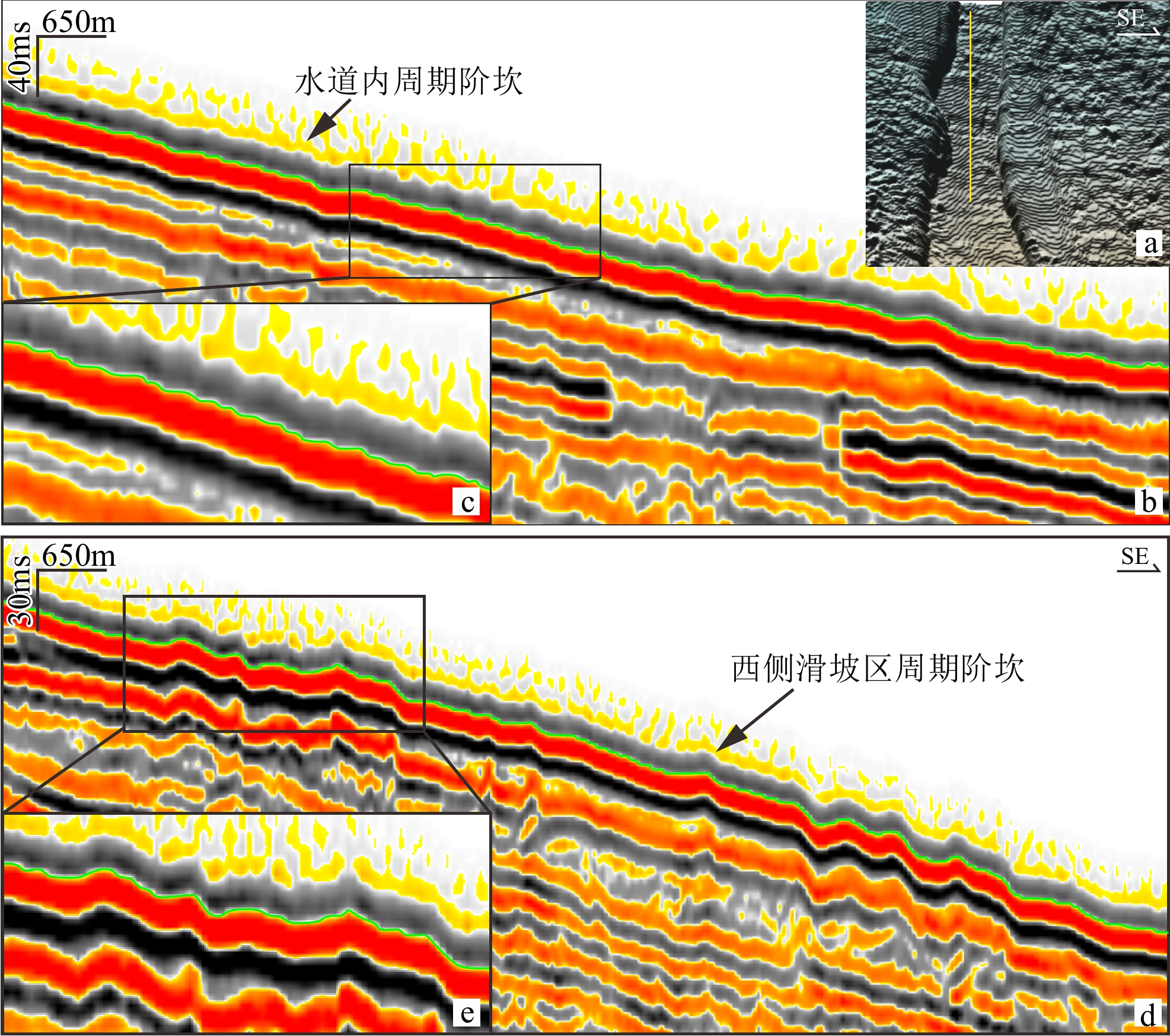
海底沉积物所形成的一种负地形[15]条带状麻坑 由若干个大小不一的麻坑组成的麻坑带,古水道和浅层气的逸散是形成条带状麻坑的主要因素[8,16] 周期阶坎 周期阶坎多为长波形、不对称展布,似正弦曲线多数向上游迁移,部分向下游迁移的新月形[17] 表 2 研究区内周期阶坎发育主要参数
Table 2. Measurements of the cyclic steps in the study area
发育
体系发育位置 沉积区特征 周期阶坎基本特征 面积/km2 坡度/(°) 形态 波长/km 波高/m 水道
体系水道 55.92 1.33 长条状 0.03~3.56 1.2~5.44 冲沟-朵体带 19.18 1.04 叶状 0.05~2.06 1.88~2.06 滑坡
体系西侧滑塌区 87.06 1.41 分散展布 0.38~4.24 2.8~5.36 东侧滑塌区 157.82 1.12 分散展布 0.04~5.14 1.66~4.75 -
[1] Ou X L, Zhu J J, Li S Z, et al. Submarine geomorphological features and their origins analyzed from multibeam bathymetry data in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(12): 1419. doi: 10.3390/jmse9121419
[2] Posamentier H W, Kolla V. Seismic geomorphology and stratigraphy of depositional elements in deep-water settings [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(3): 367-388. doi: 10.1306/111302730367
[3] Francis J M, Daniell J J, Droxler A W, et al. Deep water geomorphology of the mixed siliciclastic-carbonate system, Gulf of Papua [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, 2008, 113(F1): F01S16.
[4] Hogan K A, Dowdeswell J A, Noormets R, et al. Submarine landforms and ice-sheet flow in the Kvitøya Trough, northwestern Barents Sea [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(25-26): 3545-3562. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.015
[5] Serié C, Huuse M, Schødt N H, et al. Subsurface fluid flow in the deep-water Kwanza Basin, offshore Angola [J]. Basin Research, 2017, 29(2): 149-179. doi: 10.1111/bre.12169
[6] 罗进华, 朱培民. 琼东南盆地陆坡区重力流沉积体系超高精度解析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):42-50
LUO Jinhua, ZHU Peimin. Gravity induced deposits in the continental slope of Qiongdongnan Basin based on ultrahigh resolution AUV data [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 42-50.
[7] 朱友生, 王艳秋, 冯湘子, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水17-2深水气田开发区表层沉积物类型及工程地质特性[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):45-56
ZHU Yousheng, WANG Yanqiu, FENG Xiangzi, et al. Surface sediments and their geotechnical characteristics in the development area of deepwater gas field LS17-2 [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 45-56.
[8] 李磊, 李志军, 闫瑞, 等. Rio Muni盆地第四纪陆坡地震地貌学[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(3):485-493
LI Lei, LI Zhijun, YAN Rui, et al. Seismic geomorphology of Quaternary continental slope in Rio Muni Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(3): 485-493.
[9] 尚文亮, 徐少华, 李小刚, 等. 浅述深水水道的形态学特征[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(2):204-209
SHANG Wenliang, XU Shaohua, LI Xiaogang, et al. Brief introduction to morphological characteristics of deep-water channels [J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2020, 35(2): 204-209.
[10] 李华, 何幼斌, 谈梦婷, 等. 深水重力流水道-朵叶体系形成演化及储层分布: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶系拉什仲组露头为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4):917-928
LI Hua, HE Youbin, TAN Mengting, et al. Evolution of and reservoir distribution within deep-water gravity flow channel-lobe system: a case study of the Ordovician Lashenzhong Formation outcrop at western margin of Ordos Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 917-928.
[11] 陈亮, 赵千慧, 王英民, 等. 深水水道沉积单元及演化分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(3):12-19
CHEN Liang, ZHAO Qianhui, WANG Yingmin, et al. Depositional elements of deepwater channels and their evolution [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(3): 12-19.
[12] 王大伟, 曾凡长, 王微微, 等. 海底冲沟: 深水沉积输运系统的“毛细血管”[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(4):331-343
WANG Dawei, ZENG Fanchang, WANG Weiwei, et al. Submarine gullies: the capillary of deep-water sediment transport system [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(4): 331-343.
[13] 杜文波, 聂鑫, 杨楚鹏, 等. 南海北部珠江口外峡谷体系沉积特征、演化及其控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2022, doi:10.3799/dqkx.2022.166.
DU Wenbo, NIE Xin, YANG Chupeng, et al. Sedimentary characteristics, evolution and controlling factors of the Pearl River canyon system in the northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2022, doi:10.3799/dqkx.2022.166.
[14] 杨志鹏, 李磊, 张威, 等. 海底麻坑表征及成因研究: 以尼日尔三角洲为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):61-70
YANG Zhipeng, LI Lei, ZHANG Wei, et al. Characteristics and genesis of submarine pockmarks: a case from the Niger Delta [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 61-70.
[15] 沈奥, 孙启良, 蔡砥柱, 等. 海底麻坑的特征、分类与成因机制[J/OL]. 地质科技通报, 2022: 1-14. [2022-10-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?doi=10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0144.
SHEN Ao, SUN Qiliang, CAI Dizhu, et al. Characteristics, classification and genetic mechanism of pockmarks[J/OL]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022: 1-14. [2022-10-04]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?doi=10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0144.
[16] 李磊, 裴都, 都鹏燕, 等. 海底麻坑的构型、特征、演化及成因: 以西非木尼河盆地陆坡为例[J]. 海相油气地质, 2013, 18(4):53-58
LI Lei, PEI Du, DU Pengyan, et al. Architecture, character, evolution and genesis of seabed pockmarks: a case study to the continental slope in Rio Muni Basin, West Africa [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2013, 18(4): 53-58.
[17] 程琳燕, 李磊, 高毅凡, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷海底周期阶坎底形的特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):37-44
CHENG Linyan, LI Lei, GAO Yifan, et al. The characteristics and genesis of bottom cyclic steps in the Lingshui Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 37-44.
[18] 赵蒙维. 琼东南盆地新生代古海洋环境演变[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2013.
ZHAO Mengwei. Evolution of paleoenvironment in Qiong-Dongnan Basin during Cenozoic[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2013.
[19] 康波. 琼东南盆地新生代沉降—热演化模拟[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2014.
KANG Bo. Cenozoic subsidence and thermal history modelling of Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2014.
[20] 姚根顺, 袁圣强, 吴时国, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区双物源沉积模式及勘探前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(6):685-691 doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(09)60101-4
YAO Genshun, YUAN Shengqiang, WU Shiguo, et al. Double provenance depositional model and exploration prospect in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(6): 685-691. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(09)60101-4
[21] 曾小明, 潘燕, 于佳, 等. 陵水凹陷北坡低密度浊流海底扇沉积特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(33):48-53,78
ZENG Xiaoming, PAN Yan, YU Jia, et al. Low-density turbidity submarine fan sedimentary characteristics in north slope of Lingshui Sag [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(33): 48-53,78.
[22] 何家雄, 陈胜红, 马文宏, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地深水油气成藏条件早期预测与评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(6):780-789
HE Jiaxiong, CHEN Shenghong, MA Wenhong, et al. Early forecast and evaluation on petroleum accumulation conditions in deep basin in northern continental margin of the South China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(6): 780-789.
[23] 冯湘子, 朱友生. 南海北部陵水陆坡重力流沉积调查与分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(5):25-35
FENG Xiangzi, ZHU Yousheng. Investigation of gravity flow deposits on the Lingshui slope of the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(5): 25-35.
[24] Mosher D, Bigg S, LaPierre A. 3D seismic versus multibeam sonar seafloor surface renderings for geohazard assessment: case examples from the central Scotian Slope [J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25(12): 1484-1494. doi: 10.1190/1.2405334
[25] Meng M M, Liang J Q, Kuang Z G, et al. Distribution characteristics of Quaternary channel systems and their controlling factors in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 902517. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.902517
[26] 陈昱瑶, 周江羽, 钟佳, 等. 南海西北缘深水水道体系的地震响应及其演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(2):69-78
CHEN Yuyao, ZHOU Jiangyu, ZHONG Jia, et al. Seismic characteristics of deepwater channel system in northwestern margin of South China Sea and its evolution [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(2): 69-78.
[27] 姚悦, 周江羽, 雷振宇, 等. 西沙海槽盆地强限制性中央峡谷水道地震相与内部结构的分段特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(4):787-795
YAO Yue, ZHOU Jiangyu, LEI Zhenyu, et al. High restriction seismic facies and inner structural segmentation features of the central canyon channel systems in Xisha Trough Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(4): 787-795.
[28] 李爽, 李伟, 詹文欢. 南海东北部陆缘浊流活动的地貌记录及其形成机制分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1):111-121
LI Shuang, LI Wei, ZHAN Wenhuan. Geomorphological records of turbidity current activity in the northeastern margin of the South China Sea and analysis of triggering mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 111-121.
[29] Symons W O, Sumner E J, Talling P J, et al. Large-scale sediment waves and scours on the modern seafloor and their implications for the prevalence of supercritical flows [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 371: 130-148. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.11.009
[30] 李全, 林畅松, 盖海洋, 等. 西非科特迪瓦盆地深水底形样式及成因分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, DOI: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.045.
LI Quan, LIN Changsong, GAI Haiyang, et al. Deep-water bedform patterns and genesis in the Cote D’ Ivoire Basin, west Africa[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, DOI: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.045.
[31] Masson D G, Huggett Q J, Brunsden D. The surface texture of the Saharan debris flow deposit and some speculations on submarine debris flow processes [J]. Sedimentology, 1993, 40(3): 583-598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1993.tb01351.x
[32] Frey-Martínez J, Cartwright J, James D. Frontally confined versus frontally emergent submarine landslides: a 3D seismic characterisation [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(5): 585-604. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.04.002
[33] 何云龙, 解习农, 李俊良, 等. 琼东南盆地陆坡体系发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2):118-122
HE Yunlong, XIE Xinong, LI Junliang, et al. Depositional characteristics and controlling factors of continental slope system in the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(2): 118-122.
[34] 杜浩, 石万忠, 梁金强, 等. 琼东南盆地块体搬运沉积体系成因及其对水合物成藏的影响[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(4):869-881
DU Hao, SHI Wanzhong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Genesis of mass transport deposits and their effect on gas hydrate accumulation in the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(4): 869-881.
[35] 黄维, 汪品先. 南海沉积物总量的统计: 方法与结果[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(5):465-473
HUANG Wei, WANG Pinxian. The statistics of sediment mass in the South China Sea: method and result [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(5): 465-473.
[36] 马畅, 葛家旺, 赵晓明, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地第四系陆架边缘轨迹迁移及深水沉积模式[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4):55-72
MA Chang, GE Jiawang, ZHAO Xiaoming, et al. Quaternary Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea: shelf-edge trajectory migration and deep-water depositional models [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(4): 55-72.
[37] 王菲, 吴艳梅, 丁巍伟. 南海西北与西南次海盆沉积通量及其控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(3):986-1007
WANG Fei, WU Yanmei, DING Weiwei. Sedimentary budget and controlling factors of the northwest and southwest sub-basins, the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(3): 986-1007.
[38] 邵磊, 李昂, 吴国瑄, 等. 琼东南盆地沉积环境及物源演变特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(4):548-552 doi: 10.7623/syxb201004005
SHAO Lei, LI Ang, WU Guoxuan, et al. Evolution of sedimentary environment and provenance in Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(4): 548-552. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004005
[39] Shi X B, Kohn B, Spencer S, et al. Cenozoic denudation history of southern Hainan Island, South China Sea: constraints from low temperature thermochronology [J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 504(1-4): 100-115. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.03.007
[40] Clift P D, Sun Z. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai–Song Hong basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: implications for Xizang uplift and monsoon intensification [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B6): B06405.
[41] 龚再升, 谢泰俊, 张启民, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地分析及油气聚集[R]. 保定: 中国海洋石油勘探开发研究中心, 2002.
GONG Zaisheng, XIE Taijun, ZHANG Qimin, et al. Analysis of continental- margin basins and hydrocarbon accumulation in the northern South China Sea[R]. Baoding: China Offshore Oil Exploration and Development Research Center, 2002.
[42] Smith D E, Harrison S, Jordan J T. Sea level rise and submarine mass failures on open continental margins [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 82: 93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.10.012
[43] Tian J, Zhao Q H, Wang P X, et al. Astronomically modulated Neogene sediment records from the South China Sea [J]. Paleoceanography, 2008, 23(3): PA3210.
[44] 龚承林, 齐昆, 徐杰, 等. 深水源—汇系统对多尺度气候变化的过程响应与反馈机制[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1):231-252
GONG Chenglin, QI Kun, XU Jie, et al. Process-product linkages and feedback mechanisms of deepwater source-to-sink responses to multi-scale climate changes [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1): 231-252.
[45] Peltier W R. On eustatic sea level history: Last Glacial maximum to Holocene [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(1-3): 377-396. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00084-1
[46] 马云, 李三忠, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地海底滑坡特征及其成因机制[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(S3):196-205
MA Yun, LI Sanzhong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of submarine landslides in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(S3): 196-205.
-



 下载:
下载: