Provenance and environmental response of terrigenous debris in the southeastern continental shelf of Hainan Island since 7.8 kaBP
-
摘要:
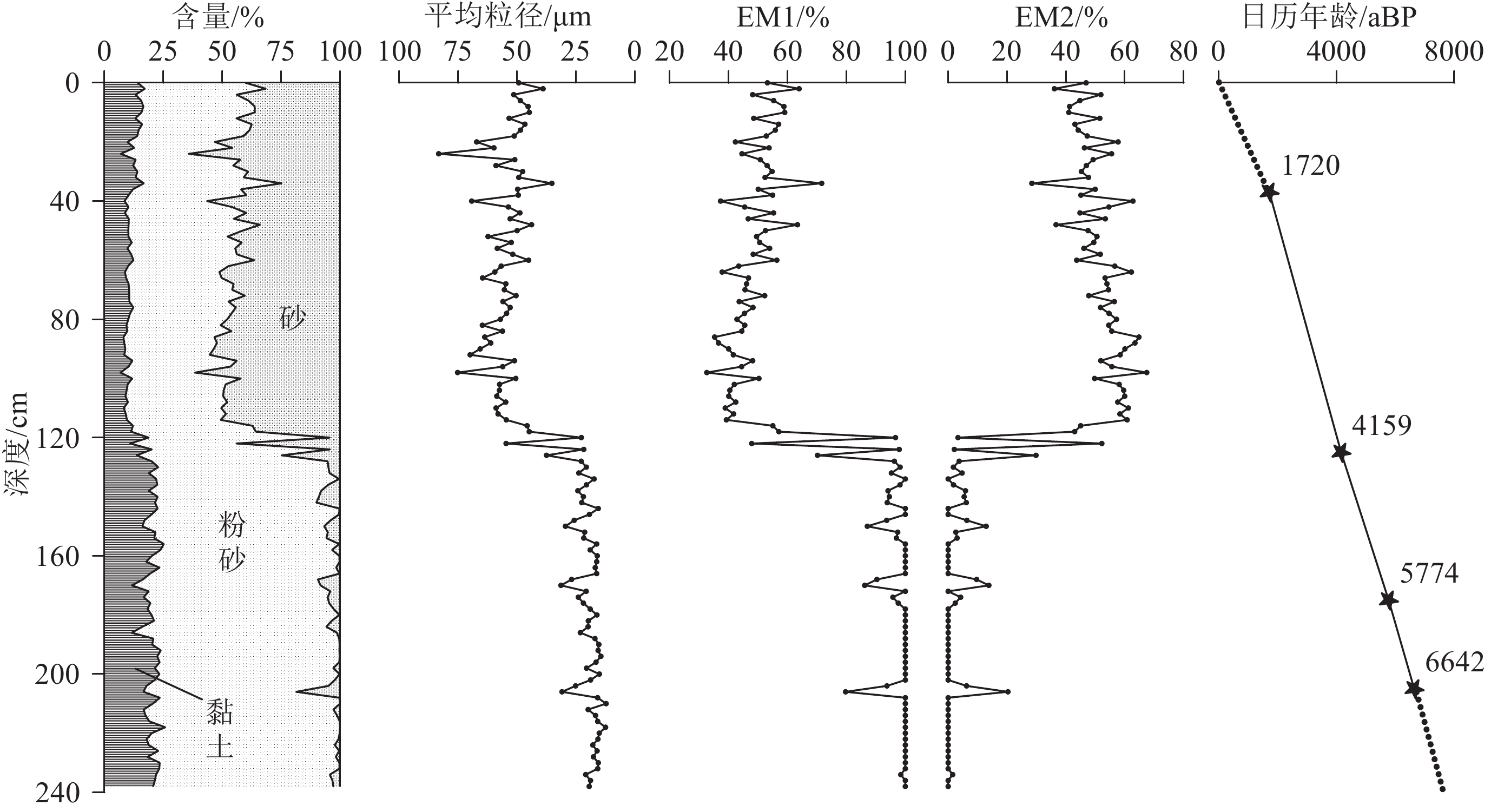
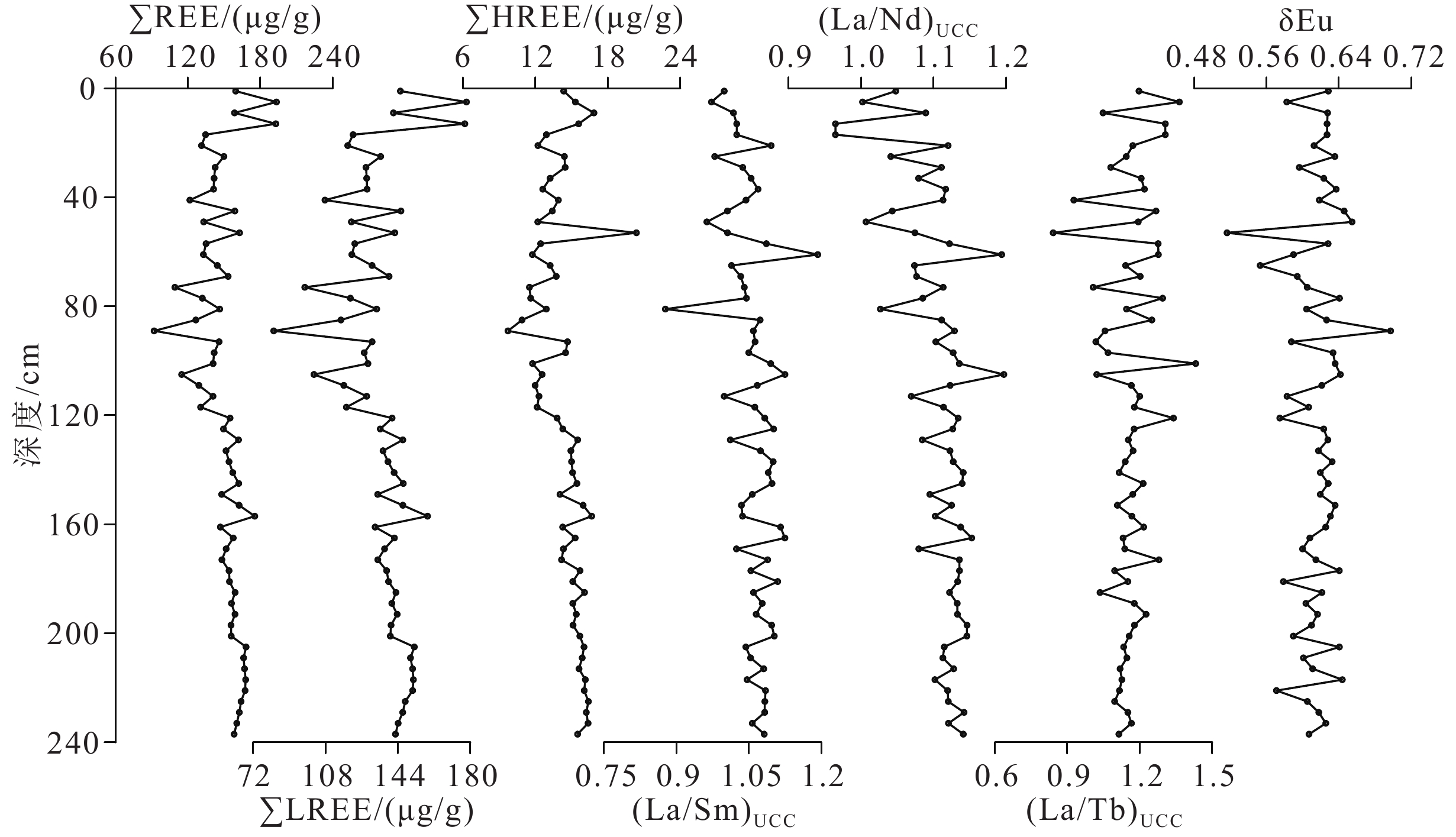
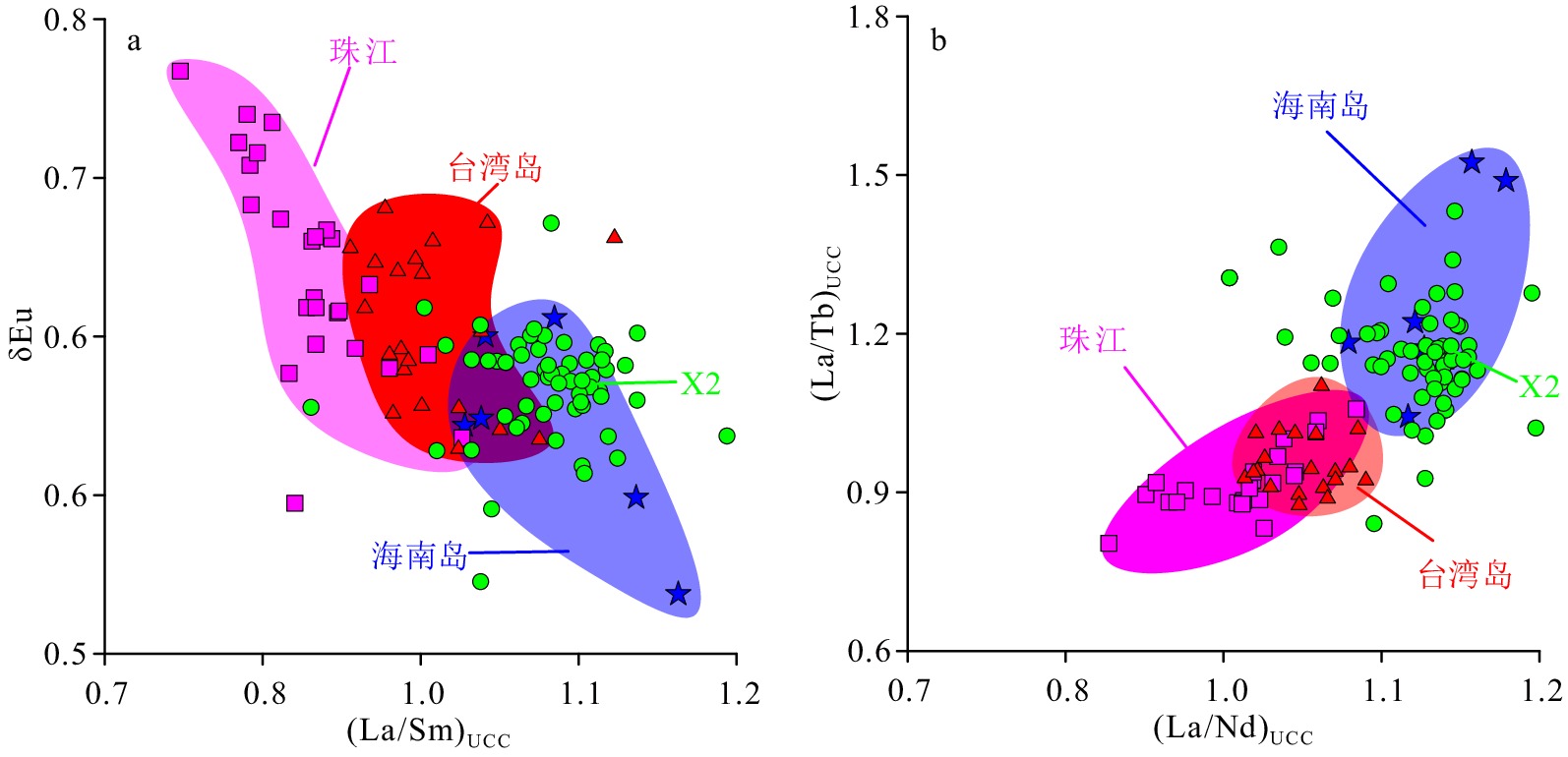
对取自海南岛东南部的X2站柱状样品进行了粒度、全岩稀土元素和重矿物分析,探讨了7.8 kaBP以来海南岛东南陆架陆源碎屑来源及其环境响应。粒度端元模拟识别出了两个端元,EM1端元对应的是海洋流系搬运的近源与远源细粒物质的混合沉积,EM2对应的主要是近源海南岛河流输入的粗粒物质,两个端元代表着两个不同的输运机制。物源分析结果表明,7.8 kaBP以来X2站陆源碎屑来源较为稳定,主要来源于海南岛。4 kaBP以来,X2站粒度、稀土元素和重矿物特征参数发生了显著改变,与El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)事件开始增强有很好的对应关系,推测频繁的ENSO事件导致降雨量增加是研究区风化程度增强的主要原因。与全岩稀土元素特征指标相比,X2站重矿物组合受源区风化剥蚀的影响更为显著,后期在环境演化研究中,应适当关注重矿物这一指标。
Abstract:Grain-size, bulk Rare Earth Element (REE), and heavy mineral analysis of Core X2 at southeastern Hainan Island were carried out. The provenances of terrigenous clasts and their environmental responses of this study area since 7.8 kaBP were discussed. Two endmembers were identified by grain-size endmember simulation. The EM1 endmember corresponded to the fine-grained material transported by the ocean current system, while the EM2 endmember corresponded to the coarse-grained material input from nearby rivers in Hainan Island; therefore, the two endmembers represented two different transport mechanisms. Results show that since 7.8 kaBP, the provenance of terrigenous detrital of Core X2 was relatively stable, mainly from Hainan Island. After 4 kaBP, the grain size, REE, and heavy mineral characteristic parameters of Core X2 had changed significantly, which has a good correspondence to the intensification of El Nino and Southern Oscillation (ENSO). It is speculated that the increase of rainfall caused by frequent ENSO events is the main reason for the enhancement of weathering degree in the study area. Compared with the characteristics of REE, the heavy mineral assemblages of Core X2 were more significantly affected by weathering and denudation in the source area. Therefore, study on heavy mineral index is suggested in the future study of environmental evolution.
-
Key words:
- continental shelf /
- rare earth element /
- heavy mineral /
- provenance /
- Hainan Island
-

-
[1] Wang S H, Zhang N, Chen H, et al. The surface sediment types and their rare earth element characteristics from the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 88: 185-202. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.08.005
[2] Xu F J, Hu B Q, Dou Y G, et al. Sediment provenance and paleoenvironmental changes in the northwestern shelf mud area of the South China Sea since the mid-Holocene [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 144: 21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.06.013
[3] 田成静, 欧阳婷萍, 朱照宇, 等. 海南岛周边海域表层沉积物磁化率空间分布特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 热带地理, 2013, 33(6):666-673 doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002477
TIAN Chengjing, OUYANG Tingping, ZHU Zhaoyu, et al. Spatial distribution of magnetic susceptibility and its provenance implication of surface sediments in the sea areas around the Hainan Island [J]. Tropical Geography, 2013, 33(6): 666-673. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002477
[4] Hu B Q, Li J, Cui R Y, et al. Clay mineralogy of the riverine sediments of Hainan Island, South China Sea: Implications for weathering and provenance [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96: 84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.036
[5] Xu F J, Tian X, Yin X B, et al. Trace metals in the surface sediments of the eastern continental shelf of Hainan Island: Sources and contamination [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 99(1-2): 276-283. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.055
[6] 高为利, 张富元, 章伟艳, 等. 海南岛周边海域表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 海洋通报, 2009, 28(2):71-80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2009.02.011
GAO Weili, ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Weiyan, et al. Characteristics of grain size distributions of surface sediments in the Hainan Island offshore area [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2009, 28(2): 71-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2009.02.011
[7] Sahoo P K, Souza-Filho P W M, Guimarães J T F, et al. Use of multi-proxy approaches to determine the origin and depositional processes in modern lacustrine sediments: Carajás Plateau, Southeastern Amazon, Brazil [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 52: 130-146. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.010
[8] Prajith A, Rao V P, Kessarkar P M. Controls on the distribution and fractionation of Yttrium and rare earth elements in core sediments from the Mandovi estuary, Western India [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 92: 59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.11.003
[9] 赵德博, 万世明. 南海沉积物中黏土矿物及其在古气候中的应用研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(4):163-171
ZHAO Debo, WAN Shiming. Research progress of clay minerals in sediments of the South China Sea and its application to paleoclimatic reconstruction [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(4): 163-171.
[10] 李正刚, 初凤友, 张富元, 等. 南海西北部内陆架表层沉积物的重矿物分布及其控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(4):89-96
LI Zhenggang, CHU Fengyou, ZHANG Fuyuan, et al. Distribution pattern of heavy minerals in the surface sediments on inner shelf, northwest South China Sea and its controlling factors [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(4): 89-96.
[11] Qin Y C, Xue C T, Jiang X J. Tidal current-dominated depositional environments in the central-northern Yellow Sea as revealed by heavy-mineral and grain-size dispersals [J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 398: 59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.01.004
[12] Cheng L Q, Song Y G, Chang H, et al. Heavy mineral assemblages and sedimentation rates of eastern central Asian loess: Paleoenvironmental implications [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 551: 109747. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109747
[13] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海西北部陆架表层沉积物重矿物组合及其沉积环境指示[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6):114-125
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. The heavy mineral assemblages of the surface sediments on the northeast shelf of the East China Sea and their environmental implication [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(6): 114-125.
[14] Li M K, Ouyang T P, Zhu Z Y, et al. Rare earth element fractionations of the northwestern South China Sea sediments, and their implications for East Asian Monsoon reconstruction during the last 36 kyr [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 525: 16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.09.007
[15] Walsh E, Caracciolo L, Ravidà D, et al. Holocene fluvial depositional regimes of the Huab River, Skeleton Coast, Namibia [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2022, 47(7): 1820-1844. doi: 10.1002/esp.5349
[16] 张凯棣, 李安春, 董江, 等. 东海表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5):902-911 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2016.05.009
ZHANG Kaidi, LI Anchun, DONG Jiang, et al. Detrital mineral distributions in surface sediments of the East China Sea: Implications for sediment provenance and sedimentary environment [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 902-911. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2016.05.009
[17] Chen Q, Liu Z F, Kissel C. Clay mineralogical and geochemical proxies of the East Asian summer monsoon evolution in the South China Sea during Late Quaternary [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 42083. doi: 10.1038/srep42083
[18] Liu Z F, Colin C, Li X J, et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: Source and transport [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 277(1-4): 48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.08.010
[19] Xu F J, Hu B Q, Zhao J T, et al. Topographic and climatic control on chemical weathering of mountainous riverine sediments of Hainan Island, South China Sea [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 9: 7702369.
[20] 周娇, 杨楚鹏, 孙桂华, 等. 海南岛西南浅海域有用重砂资源潜力分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2):89-96 doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0212
ZHOU Jiao, YANG Chupeng, SUN Guihua, et al. Potential analysis of valuable heavy minerals in surface sediments in the shallow waters of the southwest of Hainan Island [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 89-96. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0212
[21] 韩念龙, 张伟璇, 张亦清. 基于InVEST模型的海南岛产水量的时空变化研究[J]. 海南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 39(3):280-287
HAN Nianlong, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Yiqing. Spatio-temporal analysis of water yield in Hainan Island based on InVEST model [J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 2021, 39(3): 280-287.
[22] Liu Y L, Gao S, Wang Y P, et al. Distal mud deposits associated with the Pearl River over the northwestern continental shelf of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 347: 43-57. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.10.012
[23] Zhang X D, Wang H M, Xu S M, et al. A basic end-member model algorithm for grain-size data of marine sediments [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 236: 106656. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106656
[24] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[25] 高爱国, 韩国忠, 刘峰, 等. 楚科奇海及其邻近海域表层沉积物的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(2):132-139
GAO Aiguo, HAN Guozhong, LIU Feng, et al. The elemental geochemistry of the surface sediments in the Chukchi Sea and its adjacent areas [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(2): 132-139.
[26] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 208-219
LIU Dungsheng. Loessand Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 208-219.
[27] 曾方侣, 姜楷, 黄超, 等. 砂岩中重矿物的成因意义[J]. 四川地质学报, 2020, 40(1):26-29,50 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2020.01.006
ZENG Fanglü, JIANG Kai, HUANG Chao, et al. Genetic significance of heavy minerals in sandstone [J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2020, 40(1): 26-29,50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2020.01.006
[28] 王昆山, 石学法, 李珍, 等. 东海DGKS9617岩心重矿物及自生黄铁矿记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(4):41-45
WANG Kunshan, SHI Xuefa, LI Zhen, et al. Records of heavy mineral and authigenous pyrite in core DGKS9617 from the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(4): 41-45.
[29] Song H Y, Liu J Q, Yin P, et al. Characteristics of heavy minerals and quantitative provenance identification of sediments from the muddy area outside the Oujiang Estuary since 5.8 kyr [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(6): 1325-1335. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3684-6
[30] Liu J Q, Yin P, Zhang Y, et al. Distribution and provenance of detrital minerals in southern coast of Shandong Peninsula [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2017, 16(5): 747-756. doi: 10.1007/s11802-017-3196-9
[31] 仝长亮, 黎刚, 陈飞, 等. 海南岛东北部海域海砂资源特征及成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(1):12-19 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.01003
TONG Changliang, LI Gang, CHEN Fei, et al. Geological characteristics and origin of marine sands in the northeast sea off Hainan Island [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(1): 12-19. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.01003
[32] 潘燕俊, 崔汝勇, 林明坤, 等. 海南岛周边浅海砂矿资源潜力浅析[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(4):458-467 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.04.013
PAN Yanjun, CUI Ruyong, LIN Mingkun, et al. Preliminary analysis of placer resources potential in Hainan Island offshore area [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(4): 458-467. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.04.013
[33] 叶翔, 徐勇航, 王爱军, 等. 海南岛东南部陆架晚全新世以来海洋沉积物来源与环境变化特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(1):18-30 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.02
YE Xiang, XU Yonghang, WANG Aijun, et al. Variations in sediment source and marine environment characteristics during the Late Holocene on the continental shelf off southeastern Hainan Island [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1): 18-30. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.02
[34] 周娇, 蔡观强, 邹俪琦, 等. 海南岛东南部海域有用重砂的资源潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(12):58-65
ZHOU Jiao, CAI Guanqiang, ZOU Liqi, et al. Resource potential of valuable heavy minerals in the southeast water off Hainan Island [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(12): 58-65.
[35] Ge Q, Xu D, Ye L M, et al. Linking Monsoon activity with river-derived sediments deposition in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2019, 18(5): 1098-1104. doi: 10.1007/s11802-019-4155-4
[36] 文启忠, 刁桂仪, 潘景瑜, 等. 黄土高原黄土的平均化学成分与地壳克拉克值的类比[J]. 土壤学报, 1996, 33(3):225-231 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1996.03.001
WEN Qizhong, DIAO Guiyi, PAN Jingyu, et al. Comparison of average chemical composition of loess in Loess Plateau with clark values of crust [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1996, 33(3): 225-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1996.03.001
[37] Cui Z N, Schulz-Bull D E, Hou Y M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and provenance of Holocene sediments (Core STAT22) in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2016, 32(5): 1105-1115.
[38] Liu J G, Xiang R, Chen M H, et al. Influence of the Kuroshio current intrusion on depositional environment in the northern South China Sea: Evidence from surface sediment records [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 285(1-4): 59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.05.010
[39] Xu K H, Milliman J D, Li A C, et al. Yangtze- and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2009, 29(18): 2240-2256. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.017
[40] Ge Q, Liu J P, Xue Z, et al. Dispersal of the Zhujiang River (Pearl River) derived sediment in the Holocene [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(8): 1-9. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0407-8
[41] 仝长亮, 孙龙飞, 黄仕锐. 海南省海洋地质调查主要进展与成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(1):60-70 doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2020.01.09
TONG Changliang, SUN Longfei, HUANG Shirui. Main progress and achievements of marine geological survey in Hainan Province [J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(1): 60-70. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2020.01.09
[42] Xu Z F, Han G L. Rare earth elements (REE) of dissolved and suspended loads in the Xijiang River, South China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(9): 1803-1816. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.06.001
[43] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.001
[44] Cao L C, Jiang T, Wang Z F, et al. Provenance of upper miocene sediments in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins, northwestern South China Sea: Evidence from REE, heavy minerals and zircon U–Pb ages [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 361: 136-146. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.007
[45] 仝长亮, 陈飞, 张匡华. 海南岛东北部海域海砂资源分布特征及开发前景分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(1):58-65 doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2019.01.002
TONG Changliang, CHEN Fei, ZHANG Kuanghua. Analysis of the distribution and development of marine sand resources in the northeast sea of Hainan Island [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019, 28(1): 58-65. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2019.01.002
[46] 曹立成. 莺歌海—琼东南盆地区新近纪物源演化研究: 来自稀土元素、重矿物和锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)硕士学位论文, 2014
CAO Licheng. Provenance evolution since Neogene in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins: Evidence from REE, heavy mineral and zircon U-Pb ages[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2014.
[47] 张娜. 北部湾海底沉积物的矿物学特征及其对环境的响应[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2015
ZHANG Na. The mineralogical characteristics of the sediments and its environmental significance in the Beibuwan Gulf[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[48] Andersen T, Kristoffersen M, Elburg M A. How far can we trust provenance and crustal evolution information from detrital zircons? A South African case study [J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 34: 129-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.003
[49] 程瑜, 李向前, 赵增玉, 等. 苏北盆地TZK9孔磁性地层及重矿物组合特征研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4):994-1003 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.017
CHENG Yu, LI Xiangqian, ZHAO Zengyu, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and heavy minerals records of TZK9 core in Subei Basin [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(4): 994-1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.017
[50] 田豹. 重矿物物源分析研究进展[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(1):107-109,115 doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2017.01.032
TIAN Bao. A research progress in provenance analysis of heavy minerals [J]. China's Manganese Industry, 2017, 35(1): 107-109,115. doi: 10.14101/j.cnki.issn.1002-4336.2017.01.032
[51] 董江, 李安春, 徐方建, 等. 东海内陆架EC2005孔重矿物组合特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(6):1292-1303
DONG Jiang, LI Anchun, XU Fangjian, et al. Heavy mineral assemblages in core EC2005 in the inner shelf of East China Sea and the origin [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(6): 1292-1303.
[52] Wu W X, Liu T S. Possible role of the “Holocene Event 3” on the collapse of Neolithic Cultures around the Central Plain of China [J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117(1): 153-166. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00125-3
[53] Yang X Q, Wei G J, Yang J, et al. Paleoenvironmental shifts and precipitation variations recorded in tropical Maar Lake sediments during the Holocene in Southern China [J]. The Holocene, 2014, 24(10): 1216-1225. doi: 10.1177/0959683614540962
[54] 汤文坤. 7ka以来海南双池玛珥湖气候环境演变的高分辨率沉积记录[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院硕士学位论文, 2017
TANG Wenkun. High revolution sedimentary record of environmental evolution since 7 cal ka BP in Shuangchi Maar Lake, north Hainan Island[D]. Master Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2017.
[55] Fu Y H, Lin Z D, Wang T. Simulated relationship between wintertime ENSO and east Asian summer rainfall: From CMIP3 to CMIP6 [J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 38(2): 221-236. doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0147-y
[56] Drever J I, Clow D W. Weathering rates in catchments [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1995, 31(1): 463-483.
[57] 黄向青, 崔振昂, 林海, 等. 北部湾全新世气候与古生态环境演进特征及其驱动因素[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(2):129-143 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2021.042501
HUANG Xiangqing, CUI Zhen’ang, LIN Hai, et al. The driving factors on climatic and palaeo-ecological evolution of Beibu Gulf since Holocene [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(2): 129-143. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2021.042501
[58] Moy C M, Seltzer G O, Rodbell D T, et al. Variability of El Niño/Southern Oscillation activity at millennial timescales during the Holocene epoch [J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6912): 162-165. doi: 10.1038/nature01194
[59] Dykoski C, Edwards R, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1-2): 71-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.01.036
[60] Berger A, Loutre M F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(4): 297-317. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q
-




 下载:
下载: