Comprehensive assessment of disaster geological risk in Shantou coastal waters in eastern Guangdong
-
摘要:
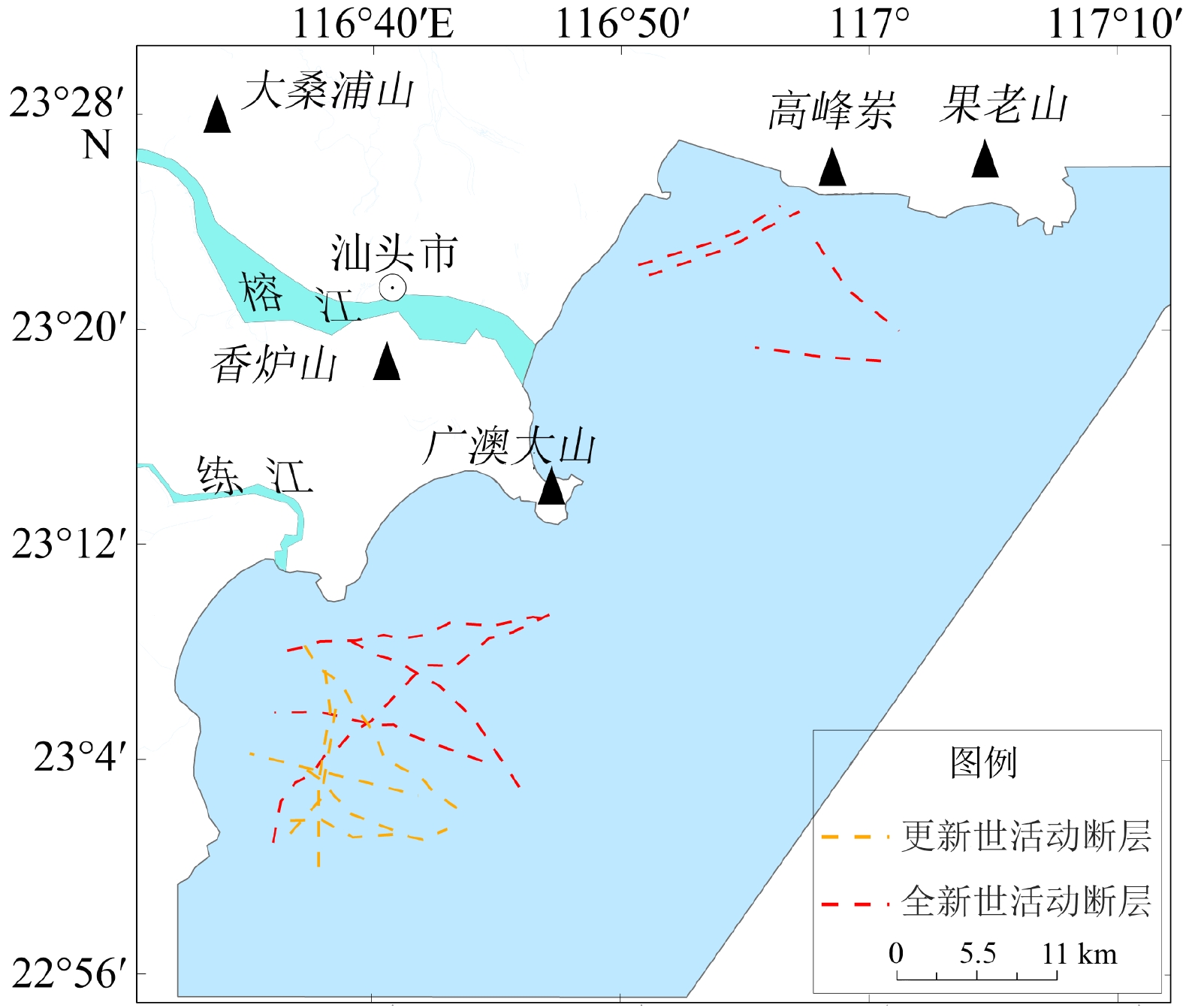
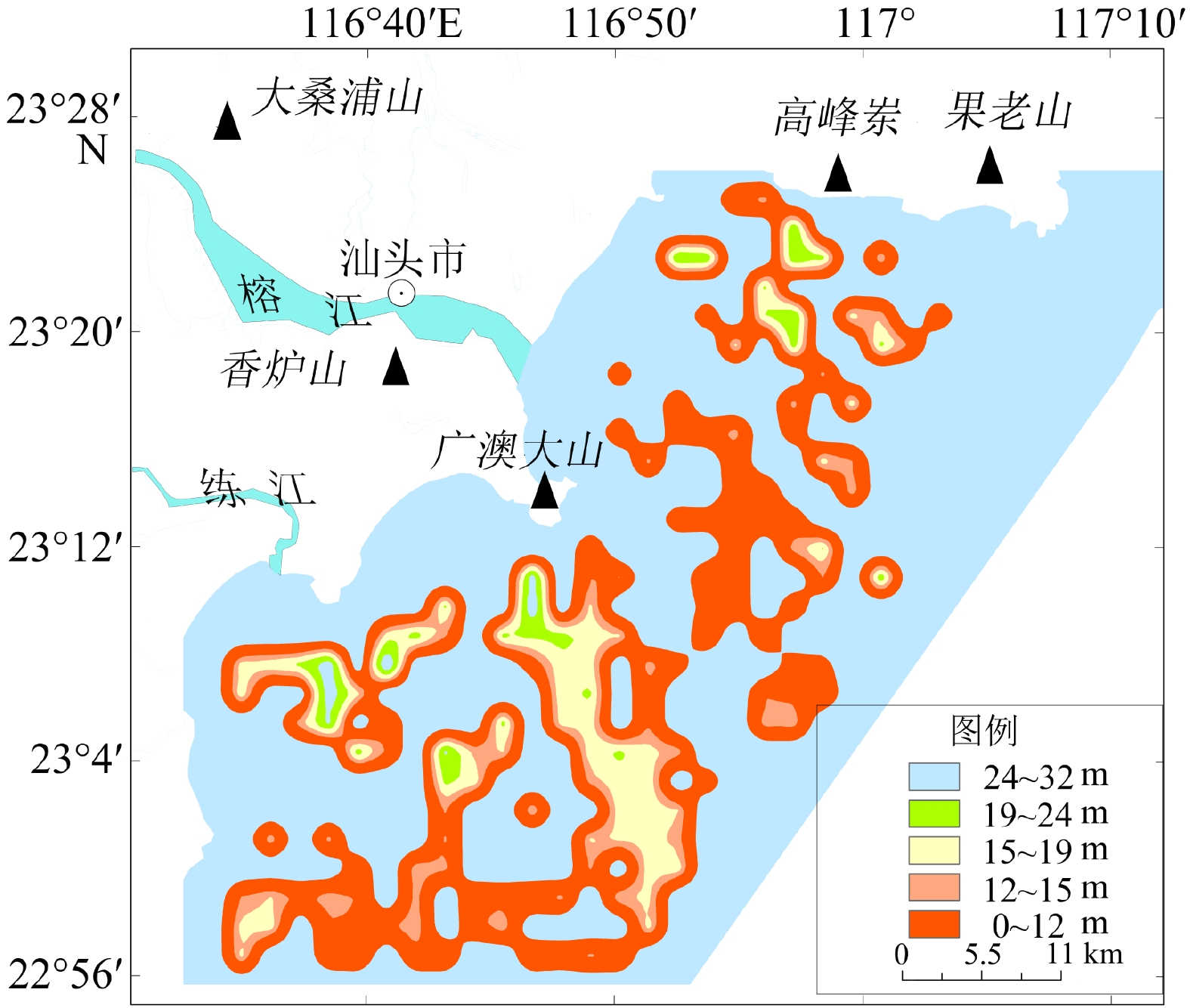
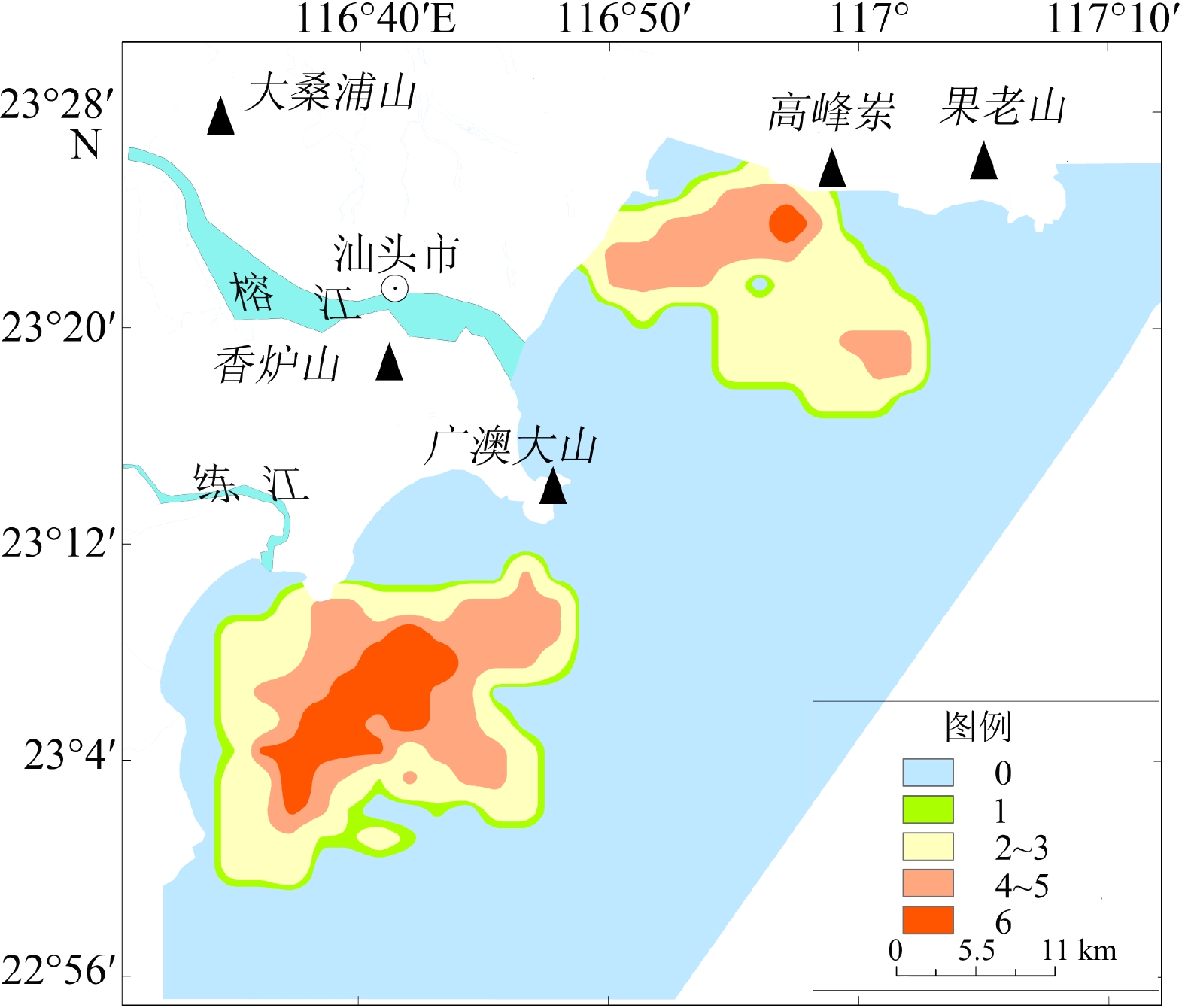
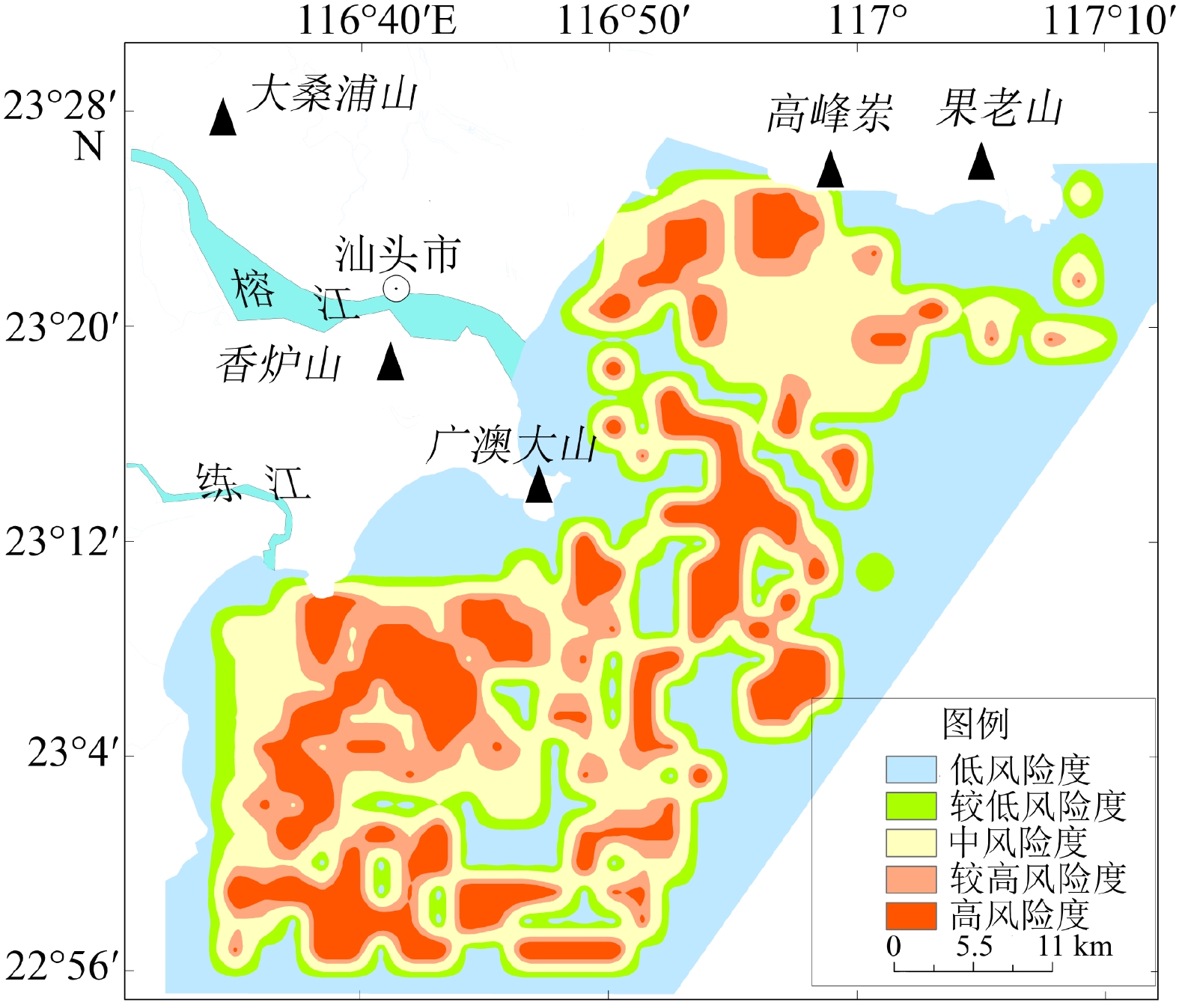
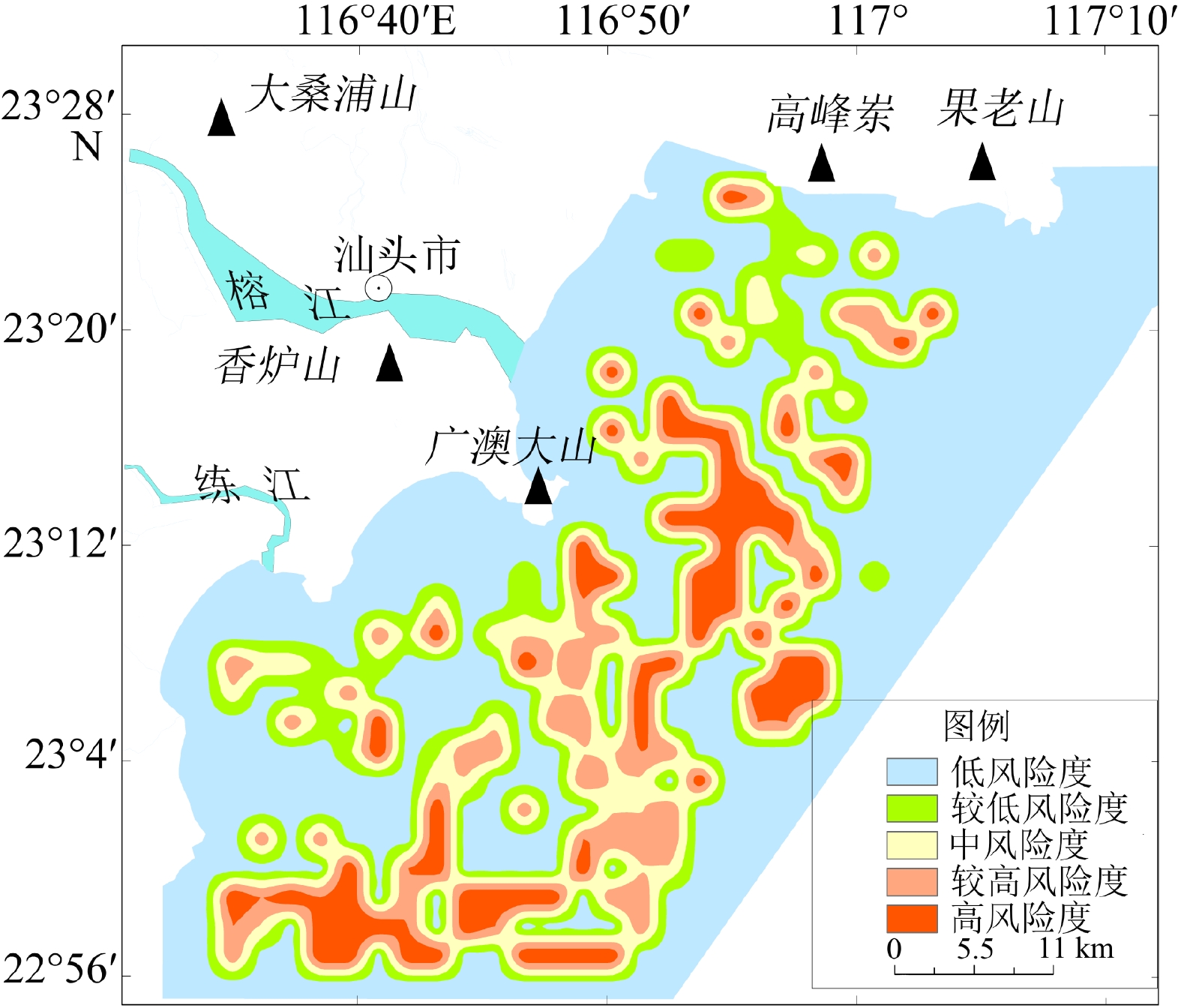
基于粤东汕头近岸海域地质和地球物理资料,通过对物探数据进行解译,查明了该区域内主要有活动断层、埋藏古河道、浅层气、不规则浅埋基岩等灾害地质类型,并结合层次分析法和模糊数学法建立了以断层、埋藏古河道、浅层气、浅埋基岩为评价指标的风险评价体系,得出海域内的不同区块的风险性等级,共分低、较低、中、较高、高5个等级。研究区超过70%的区域灾害风险不高,高风险区分布在榕江外河口、海门湾南部,主要受埋藏古河道和断层影响。较高—高风险区工程地质条件较差,存在的不良地质条件可能会给海上工程建设带来风险,选址时应尽量避开此类区域。评价结果与已查明的灾害分布特点吻合,对以后海上工程项目施工有一定的参考价值。
Abstract:The geological and geophysical data in the coastal area of Shantou, eastern Guangdong were interpreted and analyzed for geohazard assessment. Results show that there are mainly active faults, buried ancient rivers, shallow gas, and irregular shallow bedrock in this area. The geohazard was quantitatively assessed by using the analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy mathematics method. A risk assessment system was built, in which faults, buried ancient rivers, shallow gas, and shallow bedrock were used as assessment indicators, and different weights of them were assigned. According to the principle of maximum membership degree, risk levels of different blocks of the study area were calculated from which five risk levels were divided: very low, low, medium, high, and very high. More than 70% of the study area was in low risk, and the high-risk area was distributed in the Rongjiang River outer estuary and the southern part of Haimen Bay, affected mainly by buried ancient rivers and faults. The engineering geological conditions in the high, and very-high risk areas are poor due to unstable geological setting that should be avoided for site selection. The assessment results are consistent with known distribution of geohazards in the coastal waters of Shantou, indicating that the assessment method is reasonable and feasible, and shall have reference values for future development and disaster prevention in sea areas.
-
Key words:
- hazardous geology /
- risk assessment /
- fuzzy mathematics /
- Shantou coastal waters
-

-
表 1 评价指标权值判别
Table 1. Evaluation index weight discrimination
断层
断距断层活动
时期古河道
埋深古河道
厚度浅层气 浅埋
基岩断层断距 1 3 3 5 8 8 断层活动时期 1/3 1 1 3 6 6 古河道埋深 1/3 1 1 3 6 6 古河道厚度 1/5 1/3 1/3 1 4 4 浅层气 1/8 1/6 1/6 1/4 1 1 浅埋基岩 1/8 1/6 1/6 1/4 1 1 表 2 各项指标权值
Table 2. Weight of each indicator
断层断距 断层活动时期 古河道埋深 古河道厚度 浅层气 浅埋基岩 0.43 0.21 0.21 0.09 0.03 0.03 表 3 评价指标分级
Table 3. Grading of assessment indices
评价指标 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 u1/m 0~2 2~8 8~14 14~24 >24 u2 0 1 2~3 4~5 6 u3/m >24 19~24 15~19 12~15 0~12 u4/m 0~1 1~4 4~7 7~11 >11 u5/km2 0~0.08 0.08~0.28 0.28~0.58 0.58~1.30 >1.30 u6/m >13 12~13 10~12 5~10 <5 表 4 断层活动时期影响因子
Table 4. Influence factors of fault action period
风险级别 V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 2~3 0 0 1 0 0 4~5 0 0 0 1 0 6 0 0 0 0 1 表 5 各风险等级评价单元个数及占比
Table 5. Number and proportion of risk assessment units
风险等级 评价单元/个 百分比/% 低风险 233 46.05 较低风险 19 3.75 中风险 107 21.75 较高风险 72 14.23 高风险 75 14.82 表 6 断距及河道埋深单因子高风险等级单元个数
Table 6. The number of single factor high risk grade units of fault distance and river buried depth
风险等级 断距单因子 河道埋深单因子 高风险等级 16个 68个 与综合评价一致为高风险等级 13个 60个 -
[1] 马胜中. 北部湾广西近岸海洋地质灾害类型及分布规律[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2011
MA Shengzhong. Marine geological disaster factors in Beibu Gulf inshore of Guangxi Province[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011.
[2] Carpenter G B, Mccarthy J C. Hazards analysis on the Atlantic outer continental shelf[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference. Houston: OTC, 1980: 419-424.
[3] 李平. 黄河三角洲近岸海底浅表层典型灾害地质类型发育机制及其分区[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2015
LI Ping. Formation mechanism of typical geological hazards and division in the seabed surface and sub-bottom of the yellow river delta inshore[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[4] 刘守全, 刘锡清, 王圣洁, 等. 南海灾害地质类型及分区[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2000, 11(4):39-44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.04.009
LIU Shouquan, LIU Xiqing, WHANG Shengjie, et al. Kinds of hazardous geology and division in South China Sea [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2000, 11(4): 39-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.04.009
[5] 陈俊仁, 李廷桓. 南海地质灾害类型与分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(1):76-85
CHEN Junren, LI Tinghuan. Types and distribution of geological hazards in the South China Sea [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1993, 67(1): 76-85.
[6] 张虎男, 陈伟光, 黄坤荣, 等. 华南沿海新构造运动与地质环境[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1990: 262-264
ZHANG Hu’nan, CHEN Weiguang, HUANG Kunrong, et al. Neotectonics and Geological Settings of the South China Coasts[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1990: 262-264.
[7] 张虎男. 南海地震活动与区域稳定性评价[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 456-493
ZHANG Hu’nan. Seismicity and Regional Stability Evaluation of South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 456-493.
[8] 詹文欢, 钟建强, 刘以宣. 华南沿海地质灾害[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 24-71
ZHAN Wenhuan, ZHONG Jianqiang, LIU Yixuan. Geological Hazards of South China Coast[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 24-71.
[9] 詹文欢, 张乔民, 孙宗勋, 等. 南澎列岛及邻近海域地质地貌与灾害地质分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2002, 21(1):11-17 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.01.002
ZHAN Wenhuan, ZHANG Qiaomin, SUN Zongxun, et al. Geologic and geomorphologic characteristics and geological hazards of Nanpeng archipelago and adjacent waters, northeastern South China Sea [J]. Journal of the Tropical Oceanography, 2002, 21(1): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2002.01.002
[10] 周英. 汕头市大陆海岸的主要地质灾害[J]. 热带地理, 2008, 28(4):331-337 doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.001168
ZHOU Ying. Primary geological hazards to the continental coast in Shantou [J]. Tropical Geography, 2008, 28(4): 331-337. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.001168
[11] 广东省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查大队. 广东省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1987: 10-108, 140, 379
Guangdong Coast and Coast Resources Survey Team. Comprehensive Investigation Report on Coastal Zone and Marine Resources in Guangdong Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987: 10-108, 140, 379.
[12] 吴正, 黄山, 胡守春, 等. 华南海岸风沙地貌研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995: 31-33
WU Zheng, HUANG Shan, HU Shouchun, et al. Research on the Landforms of the Wind-Drift Sand in South China Coast[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995: 31-33.
[13] 黄镇国, 谢先德, 范锦春, 等. 广东海平面变化及其影响与对策[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2000
HUANG Zhenguo, XIE Xiande, FAN Jinchun, et al. The Sea Level Change in Guangdong and its Influence and Countermeasures[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science and Technology Press, 2000.
[14] 张志忠, 顾兆峰, 刘锡清, 等. 南黄海灾害地质及地质环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5):15-22 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2007.05.007
ZHANG Zhizhong, GU Zhaofeng, LIU Xiqing, et al. Hazardous geology and marine geologic environmental evolution in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(5): 15-22. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2007.05.007
[15] 宋亚娅, 张航泊. 基于加权模糊概率的地质灾害易发性评价模型研究[J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(11):109-115 doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.11.019
SONG Yaya, ZHANG Hangbo. Study on geological hazards susceptibility assessment based on weighted fuzzy probability exponential model [J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(11): 109-115. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2020.11.019
[16] 陈哲锋, 吴静, 郭玉斌, 等. 层次分析与模糊数学综合评价法在矿山环境评价中的应用[J]. 华东地质, 2018, 39(4):305-310
CHEN Zhefeng, WU Jing, GUO Yubin, et al. Application of AHP and fuzzy mathematics in comprehensive assessment of mine environment [J]. East China Geology, 2018, 39(4): 305-310.
[17] 宋玉鹏, 孙永福, 杜星, 等. 渤海海域海底地质灾害危险性区划[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(3):140-146
SONG Yupeng, SUN Yongfu, DU Xing, et al. Risk zonation on the submarine geological hazards in Bohai Sea [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(3): 140-146.
[18] 杨康, 薛喜成, 李识博. 信息量融入GA优化SVM模型下的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(3):109-118 doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20210976
YANG Kang, XUE Xicheng, LI Shibo. Geological hazard susceptibility assessment by incorporating information value into GA optimized SVM model [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(3): 109-118. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20210976
[19] 陈水满, 赵辉龙, 许震, 等. 基于人工神经网络模型的福建南平市滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(2):133-140 doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-16
CHEN Shuiman, ZHAO Huilong, XU Zhen, et al. Landslide risk assessment in Nanping City based on artificial neural networks model [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 133-140. doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2022.02-16
[20] 董津城. 发震断裂的安全距离规定简介:《建筑抗震设计规范》修订简介(五)[J]. 工程抗震, 1999, 4(2):14-16
DONG Jincheng. Brief introduction to the stipulations related safety distance from earthquake causative fault [J]. Earthquake Resistant Engineering, 1999, 4(2): 14-16.
[21] Lv H, Bao D, Wang Z, et al. Identification and characterization of Karst Ancient Channel based on Seismic Multi-attribute[C]//Proceedings of the SPG/SEG Nanjing 2020 International Geophysical Conference. Nanjing: Editorial Department of Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, 2020: 836-839.
[22] Kemp J, Pietsch T, Gontz A, et al. Lacustrine-fluvial interactions in Australia's Riverine Plains [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 352-362. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.02.015
[23] Cserkész-Nagy Á, Thamó-Bozsó E, Tóth T, et al. Reconstruction of a Pleistocene meandering river in East Hungary by VHR seismic images, and its climatic implications [J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 153-154: 205-218. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.02.025
[24] Li G X, Liu Y, Yang Z G, et al. Ancient Changjiang channel system in the East China Sea continental shelf during the last glaciation [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(11): 1972-1978. doi: 10.1360/04yd0053
[25] Mullins H T, Nagel D K. High-frequency seismic data detect shallow hydrocarbons [J]. World Oil, 1983, 197(6): 133-134,136,138.
[26] Boillot G. Géologie de la Manche Occidentale: Fonds Rocheux, Dépôts Quaternaires, Sédiments Actuels[M]. Paris: Masson, 1964.
[27] Ren J F, Cheng C, Xiong P F, et al. Sand-rich gas hydrate and shallow gas systems in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 215: 110630. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110630
[28] Lei Y N, Sun J, Wang G J. Simulation of shallow gas invasion process during deepwater drilling and its control measures [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2022, 21(3): 707-718. doi: 10.1007/s11802-022-4855-z
[29] Marcon L, Sotiri K, Bleninger T, et al. Acoustic mapping of gas stored in sediments of shallow aquatic systems linked to methane production and ebullition patterns [J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 876540. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.876540
[30] 王忆非. 辽东湾北部工程地质条件评价[D]. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2014
WANG Yifei. Assessment on engineering geological suitability in northern Liaodong Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of The First Institute of Oceanography, SOA, 2014.
-




 下载:
下载: