Seabed classification based on sub-bottom profile data in modified geo-acoustic model
-
摘要:
浅地层剖面仪发射的声脉冲能够穿透海底面进入沉积层内部,其回波中携带了丰富的底质信息。地声模型是底质声学与物理性质关系的数学描述,广泛用于海底声学与地声反演研究。本文通过对浅地层剖面数据的处理、解译得到海底反射系数,与考虑底质松密影响的改进Biot-Stoll模型相结合,提出底质反演新方法并开展实例验证。研究结果表明:通过对浅地层剖面原始记录的读取、解译,提取反射波振幅,并结合设备声源级,可有效求取海底反射系数。通过引入相对密度改进孔隙度计算公式,进而在基于Biot-Stoll模型构建海底反射系数和底质平均粒径关系过程中进一步考虑了底质松密的影响。基于山东威海某海域及文献的算例均显示,本文提出的改进地声模型可缩小底质反演与实测结果之间的相对误差、提升基于浅地层剖面数据的海底底质地声反演精度。
-
关键词:
- 浅地层剖面 /
- 底质反演 /
- Biot-Stoll模型 /
- 海底反射系数 /
- 平均粒径
Abstract:The echoes signal of sub-bottom profilers (SBP) carry abundant information of sediment because the acoustic pulses emitted by SBP can penetrate the seafloor surface into the interior of sediment layers and get reflected from different impedance interface. A geoacoustic model describing the relationship between the acoustics and physical properties of sediments mathematically, is widely used in sediment classification and acoustics inversion. We applied the method to obtain the bottom reflection coefficients by decoding the SBP data, and then combined it with a modified Biot-Stoll model considering the influence of sediment’s degree of compaction, based on which a new method of sediment inversion was proposed to evaluate its capacity by examples. Results show that the bottom reflection coefficient of seafloor can be effectively obtained by decoding the original records of SBP, extracting the amplitude of the reflected waves, and combining with the sound source level of the equipment. To build the relationship between bottom reflective coefficient and mean grain size, the degree of sediment compaction was considered based on Biot-Stoll model and the parameter of relative density was introduced into the porosity calculation formula. Examples of both measured data of Weihai sea area and those obtained from available literatures indicate that the presented method could reduce the relative error between the inversion and the measured mean grain sizes, contributing to improve the accuracy of submarine sediment geoacoustic inversion based on SBP data.
-
Key words:
- sub-bottom profile /
- sediment inversion /
- Biot-Stoll model /
- reflection coefficient /
- mean grain size
-

-
表 1 不同平均粒径条件下最大和最小孔隙度取值[34-37]
Table 1. Maximum and minimum porosity values of different mean grain-sizes
平均粒径/Ф 最大孔隙度nmax/% 最小孔隙度nmin/% 0~2 41 29 2~3 53 37 3~4 60 40 4~5 69 40 5~6 75 42 6~7 83 56 7~8 86 57 8~9 90 59 9~10 91 66 表 2 状态可控试验实测数据[33]
Table 2. Measured physical parameters of state-controlled experiments
底质类别 密度ρ/(g·cm−3) 相对密度 孔隙度n /% 饱和度Sr 粉土 2.00 0.67 40.79 0.994 1.99 0.60 41.81 0.995 2.01 0.69 40.45 0.994 2.01 0.70 40.41 0.997 2.03 0.75 39.66 0.998 2.05 0.86 37.97 0.998 2.07 0.92 37.10 0.999 2.04 0.82 38.57 0.999 砂土 2.03 0.39 38.33 0.992 2.16 0.70 30.72 0.994 1.93 0.44 44.18 0.982 2.05 0.67 37.55 0.994 2.00 0.52 40.45 0.992 2.13 0.77 32.64 0.989 1.94 0.33 43.37 0.981 2.00 0.63 39.9 0.978 2.08 0.44 35.55 0.989 2.17 0.74 30.23 0.993 1.92 0.32 44.99 0.986 2.02 0.58 38.8 0.971 表 3 Biot-Stoll模型参数取值
Table 3. The input physical parameters of the Biot-Stoll model
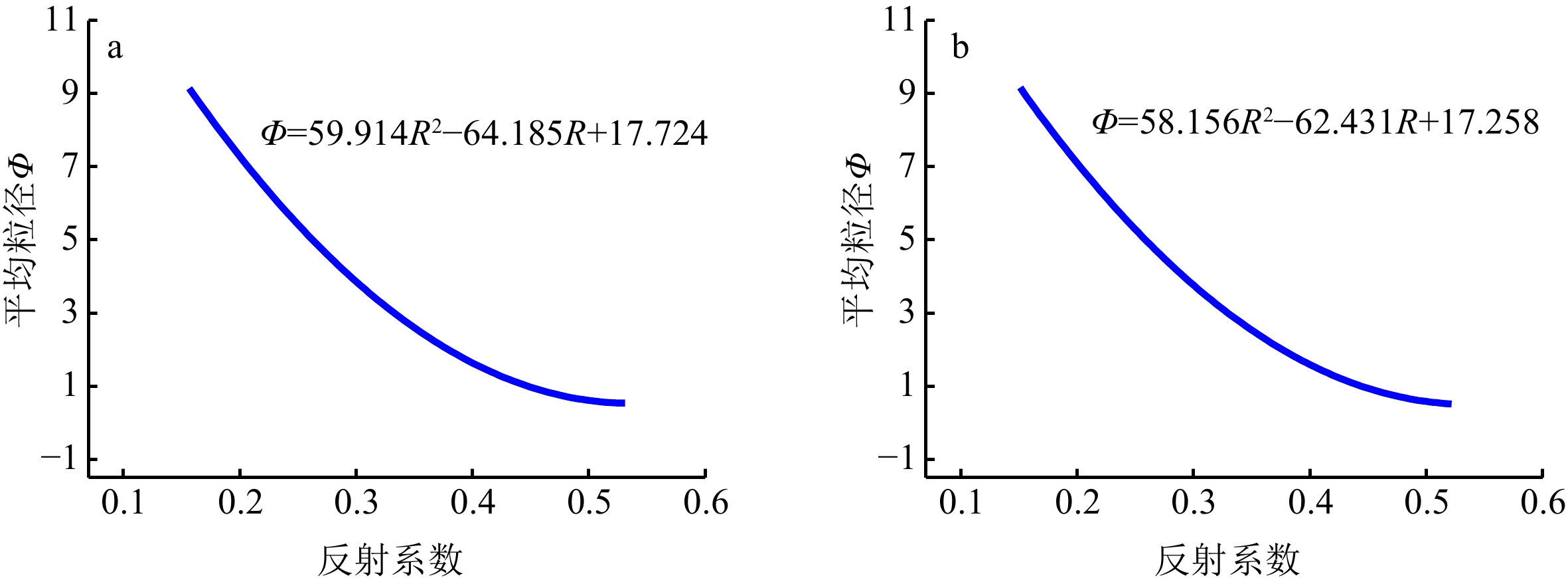
物理参数 参数取值 颗粒密度ρs /kg·m−3 2690 颗粒体积模量Ks /Pa $ 3.2 \times {10^{10}} $ 流体密度ρf /kg·m−3 1023 流体体积模量Kf /Pa $ 2.395 \times {10^9} $ 黏滞系数η/kg·m−1·s−1 0.001 渗透率κ/m2 $ \kappa = \dfrac{{{d^2}{n^3}}}{{180{{\left( {1 - n} \right)}^2}}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {10} }},\;d{\text{为粒径}}({\rm{mm}}) $ 弯曲度Γ $ \Gamma = \left\{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\text{1}}{\text{.35 }}&\varphi {\text{≤}} {\text{4}} \\ {{ - 0}}{\text{.3}} + {\text{0}}{\text{.4125}}\varphi &{\text{ 4}} {\text{<}} \varphi {\text{<}} 8 \\ {\text{3}}{\text{.0 }}&\varphi {\text{≥}}{\text{8}} \\ \end{array} \right. $ 孔隙半径r/m $ r = \dfrac{d}{3}\dfrac{n}{{\left( {1 - n} \right)}}\dfrac{1}{{1.8}} $ 骨架体积模量Kb /Pa $ {K_{\text{b}}} = \dfrac{{2\mu (1 + \sigma )}}{{3(1 - 2\sigma )}} $ ,σ为骨架泊松比,$ \sigma = \left\{ \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\text{0}}{\text{.15 }}&\varphi {\text{≤}} {\text{4}} \\ {{ - 0}}{\text{.05}} + {\text{0}}{\text{.05}}\varphi &{\text{ 4}} {\text{<}} \varphi {\text{<}} 8 \\ {\text{0}}{\text{.35 }}&\varphi {\text{≥}} {\text{8}} \\ \end{array} \right. $ 骨架剪切模量μ/Pa $ 1.3 \times {10^7} $ 表 4 地声反演与实测结果比较
Table 4. Comparison between inversion and measured mean grain-size
实测平均
粒径/ФBiot-Stoll模型反演结果 改进Biot-Stoll模型反演结果 反演值 相对误
差/%平均
值/%反演值 相对误
差/%平均
值/%5.28 5.89 11.70 6.51 5.79 8.87 5.06 5.04 5.50 9.11 5.41 6.34 5.08 5.23 3.02 5.14 0.41 5.12 5.54 8.20 5.44 5.46 5.24 5.29 0.95 5.19 1.61 5.24 5.56 6.06 5.46 3.37 5.20 5.60 7.67 5.50 4.94 5.17 5.51 6.48 5.41 3.79 5.50 5.59 1.63 5.49 0.94 5.56 5.26 5.31 5.17 7.71 1.96 2.06 5.01 2.02 2.20 5.11 4.45 12.93 4.37 15.13 表 5 地声反演与文献结果比较
Table 5. Comparison between inversion results and those from published sources
数据
来源实测平均
粒径/ФBiot-Stoll模型反演结果 改进Biot-Stoll模型反演结果 反演值 相对误
差/%平均
值/%反演值 相对误
差/%平均
值/%周庆杰[20] 5.50 7.31 32.85 29.69 7.12 29.46 27.22 6.20 8.14 31.24 7.93 27.89 8.30 9.87 18.86 9.61 15.81 8.40 10.27 22.22 10.00 19.08 8.70 10.77 23.74 10.49 20.55 黄必桂[40] 6.56 7.38 12.55 7.20 9.68 6.94 7.54 8.65 7.35 5.88 7.49 9.10 21.45 8.86 18.33 7.25 9.40 29.66 9.16 26.33 7.06 10.55 49.48 10.28 45.62 7.48 10.92 45.99 10.64 42.22 6.78 10.46 54.33 10.19 50.35 7.08 10.57 49.33 10.30 45.49 6.81 10.05 47.64 9.80 43.84 6.64 9.95 49.91 9.70 46.05 6.39 9.64 50.90 9.39 47.02 6.08 9.81 61.41 9.56 57.26 6.27 9.81 56.52 9.56 52.49 6.23 9.32 49.59 9.08 45.75 Zheng[19] 6.64 4.45 33.03 4.34 34.73 6.64 7.28 9.63 7.10 6.84 -
[1] 何起祥, 李绍全, 刘健. 海洋碎屑沉积物的分类[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1):115-121
HE Qixiang, LI Shaoquan, LIU Jian. Classification of marine clastic sediments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 115-121.
[2] 赵玉新, 赵廷. 海底声呐图像智能底质分类技术研究综述[J]. 智能系统学报, 2020, 15(3):587-600 doi: 10.11992/tis.202004026
ZHAO Yuxin, ZHAO Ting. Survey of the intelligent seabed sediment classification technology based on sonar images [J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2020, 15(3): 587-600. doi: 10.11992/tis.202004026
[3] 徐超, 李海森, 王川, 等. 基于合成核SVM的多波束海底声图像底质分类研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(5):2437-2442 doi: 10.6038/pg20140567
XU Chao, LI Haisen, WANG Chuan, et al. Seabed classification of multibeam seabed acoustic image based on composite kernel SVM [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(5): 2437-2442. doi: 10.6038/pg20140567
[4] 金绍华, 肖付民, 边刚, 等. 利用多波束反向散射强度角度响应曲线的底质特征参数提取算法[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2014, 39(12):1493-1498
JIN Shaohua, XIAO Fumin, BIAN Gang, et al. A method for extracting seabed feature parameters based on the angular response curve of multibeam backscatter strength [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(12): 1493-1498.
[5] 卜英勇, 周木荣. 基于连续小波变换和分形理论的水下回波特征提取[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2008, 27(11):44-46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2008.11.014
BU Yingyong, ZHOU Murong. Feature extraction of underwater echoes based on continuous wavelet transform and fractal theories [J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2008, 27(11): 44-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9787.2008.11.014
[6] Hasan R C, Ierodiaconou D, Laurenson L. Combining angular response classification and backscatter imagery segmentation for benthic biological habitat mapping [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 97: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.10.004
[7] Alevizos E, Snellen M, Simons D G, et al. Acoustic discrimination of relatively homogeneous fine sediments using Bayesian classification on MBES data [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 370: 31-42. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.10.007
[8] Snellen M, Eleftherakis D, Amiri-Simkooei A, et al. An inter-comparison of sediment classification methods based on multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter and sediment natural radioactivity data [J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2013, 134(2): 959-970. doi: 10.1121/1.4812858
[9] 唐秋华, 纪雪, 丁继胜, 等. 多波束声学底质分类研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(1):1-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.001
TANG Qiuhua, JI Xue, DING Jisheng, et al. Research progress and prospect of acoustic seabed classification using multibeam echo sounder [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.01.001
[10] 罗宇, 郑旭, 施剑, 等. 基于浅地层回波信号的底质分类技术研究[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2020, 39(6):42-47
LUO Yu, ZHENG Xu, SHI Jian, et al. Study on the seabed classification approach based on echo signal of sub-bottom profiler [J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2020, 39(6): 42-47.
[11] 张同伟, 秦升杰, 王向鑫, 等. 深海浅地层剖面探测系统现状及展望[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2018, 15(5):547-554
ZHANG Tongwei, QIN Shengjie, WANG Xiangxin, et al. Technical status and development trend of deep sea sub-bottom profiler [J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2018, 15(5): 547-554.
[12] 李平, 杜军. 浅地层剖面探测综述[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(3):344-350 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.018
LI Ping, DU Jun. Review on the probing of sub-bottom profiler [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(3): 344-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.018
[13] Stevenson I R, McCann C, Runciman P B. An attenuation-based sediment classification technique using Chirp sub-bottom profiler data and laboratory acoustic analysis [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2002, 23(4): 277-298. doi: 10.1023/A:1025708024518
[14] Theuillon G, Stephan Y, Pacault A. High-resolution geoacoustic characterization of the seafloor using a subbottom profiler in the gulf of lion [J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2009, 33(3): 240-254.
[15] 郑江龙, 童思友, 许江. 基于Chirp源浅地层剖面资料计算海底反射损失[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(3):1256-1261 doi: 10.6038/pg2019DD0067
ZHENG Jianglong, TONG Siyou, XU Jiang. Estimating seabed reflection loss from Chirp sub-bottom profile [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(3): 1256-1261. doi: 10.6038/pg2019DD0067
[16] 刘玉萍, 丁龙翔, 杨志成, 等. 利用浅剖资料进行海底底质分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):66-72
LIU Yuping, DING Longxiang, YANG Zhicheng, et al. Seabed sediment analysis using sub-bottom profile data [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1): 66-72.
[17] Saleh M, Rabah M. Seabed sub-bottom sediment classification using parametric sub-bottom profiler [J]. NRIAG Journal of Astronomy and Geophysics, 2016, 5(1): 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.nrjag.2016.01.004
[18] Schock S G. A method for estimating the physical and acoustic properties of the sea bed using chirp sonar data [J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(4): 1200-1217. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.841421
[19] Zheng H B, Yan P, Chen J, et al. Seabed sediment classification in the northern South China Sea using inversion method [J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2013, 39: 131-136. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2012.11.002
[20] 周庆杰, 李西双, 刘乐军, 等. 基于Chirp数据和Biot-Stoll模型反演南海北部陆坡海底表层沉积物物理性质[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(3):72-82
ZHOU Qingjie, LI Xishuang, LIU Lejun, et al. Physical properties of the seabed inversed based on Chirp data and the Biot-Stoll model in the northern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(3): 72-82.
[21] Biot M A. Mechanics of deformation and acoustic propagation in porous media [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1962, 33(4): 1482-1498. doi: 10.1063/1.1728759
[22] Stoll R D. Acoustic waves in ocean sediments [J]. Geophysics, 1977, 42(4): 715-725. doi: 10.1190/1.1440741
[23] 王景强, 郭常升, 刘保华, 等. 基于Buckingham模型和Biot-Stoll模型的南沙海域沉积物声速分布特征[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(3):359-367 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.13
WANG Jingqiang, GUO Changsheng, LIU Baohua, et al. Sound speed distribution of seafloor sediments in Nansha Islands Sea based on Buckingham model and Biot-Stoll model [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 359-367. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.13
[24] 陈静, 吕修亚, 陈亮, 等. 基于Chirp数据反演琼州海峡海底沉积物物性[J]. 热带地理, 2017, 37(6):874-879 doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002943
CHEN Jing, LYU Xiuya, CHEN Liang, et al. Physical properties of the seabed inversed by Chirp data in the Qiongzhou Strait [J]. Tropical Geography, 2017, 37(6): 874-879. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002943
[25] Kimura M. Study on the Biot-Stoll model for porous marine sediments [J]. Acoustical Science and Technology, 2007, 28(4): 230-243. doi: 10.1250/ast.28.230
[26] Kan G M, Meng X M, Wang J Q, et al. Shear wave speed dispersion characteristics of seafloor sediments in the northern south China sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2022, 21(1): 91-100. doi: 10.1007/s11802-022-4774-z
[27] 孟祥梅, 刘保华, 阚光明, 等. 南黄海海底沉积物声学特性及其影响因素试验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6):74-83
MENG Xiangmei, LIU Baohua, KAN Guangming, et al. An experimental study on acoustic properties and their influencing factors of marine sediment in the southern Huanghai Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(6): 74-83.
[28] 郑红波, 阎贫, 王彦林, 等. 基于希尔伯特变换的Chirp信号浅地层剖面数据分析及转换[J]. 海洋技术, 2012, 31(1):91-95
ZHENG Hongbo, YAN Pin, WANG Yanlin, et al. Sub-bottom profile data analysis and transformation for the Chirp signal based on Hilbert transform [J]. Ocean Technology, 2012, 31(1): 91-95.
[29] Li C Z, Yang Y, Wang R, et al. Inversion of river-bottom sediment parameters using mechanically sampled specimens and subbottom profiling data [J]. Applied Geophysics, 2017, 14(2): 225-235. doi: 10.1007/s11770-017-0621-1
[30] 张志军, 周东红, 孙成禹, 等. 基于三维模型数据的地震振幅补偿处理技术的保幅性分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(3):621-626
ZHANG Zhijun, ZHOU Donghong, SUN Chengyu, et al. An analysis of the amplitude preservation of seismic amplitude compensation processing technology based on 3D model data [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(3): 621-626.
[31] Hamilton E L. Reflection coefficients and bottom losses at normal incidence computed from Pacific sediment properties [J]. Geophysics, 1970, 35(6): 995-1004. doi: 10.1190/1.1440149
[32] 卢博, 刘强. 海底沉积物声学响应中的颗粒与孔隙因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2008, 27(3):23-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2008.03.005
LU Bo, LIU Qiang. Grain and pore factors in acoustic response of seafloor sediments [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2008, 27(3): 23-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2008.03.005
[33] 吴涛. 无黏性海底沉积物声传播规律研究[D]. 天津大学硕士学位论文, 2021
WU Tao. Study on Sound Propagation law of cohesiveless seabed sediments[D]. Master Thesis of Tianjin University, 2021.
[34] Hamilton E L, Bachman R T. Sound velocity and related properties of marine sediments [J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1982, 72(6): 1891-1904. doi: 10.1121/1.388539
[35] 潘国富, 叶银灿, 来向华, 等. 海底沉积物实验室剪切波速度及其与沉积物的物理性质之间的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(5):64-68
PAN Guofu, YE Yincan, LAI Xianghua, et al. Shear wave velocity of seabed sediment from laboratory measurements and its relationship with physical properties of sediment [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2006, 28(5): 64-68.
[36] Kirca V S O. Sinking of irregular shape blocks into marine seabed under wave-induced liquefaction [J]. Coastal Engineering, 2013, 75: 40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2013.01.006
[37] 《工程地质手册》编委会. 工程地质手册[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2007
Editorial Boards of Engineering Geological Manual. Engineering Geology Manual[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2007.
[38] 陈静, 阎贫, 王彦林, 等. 基于Biot-Stoll模型声速反演中的参数选择: 以南海南部沉积物为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(1):50-54
CHEN Jing, YAN Pin, WANG Yanlin, et al. Choice of parameters for Biot-Stoll model-based inversion of sound velocity of seafloor sediments in the southern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(1): 50-54.
[39] Rayleigh J W S. The Theory of Sound[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 1945.
[40] 黄必桂, 李家钢, 周庆杰, 等. 基于浅地层剖面的海底浅表层沉积物物理性质参数反演技术研究: 以渤海海底管线路由区为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(9):156-164
HUANG Bigui, LI Jiagang, ZHOU Qingjie, et al. Research on inversion technology of physical properties parameters of seafloor sediments based on sub-bottom profile: Taking the Bohai Sea submarine pipeline route as an example [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(9): 156-164.
-




 下载:
下载: