Integrated reconstruction of fire history and climatic changes in Northwest China since mid-late Holocene
-
摘要:
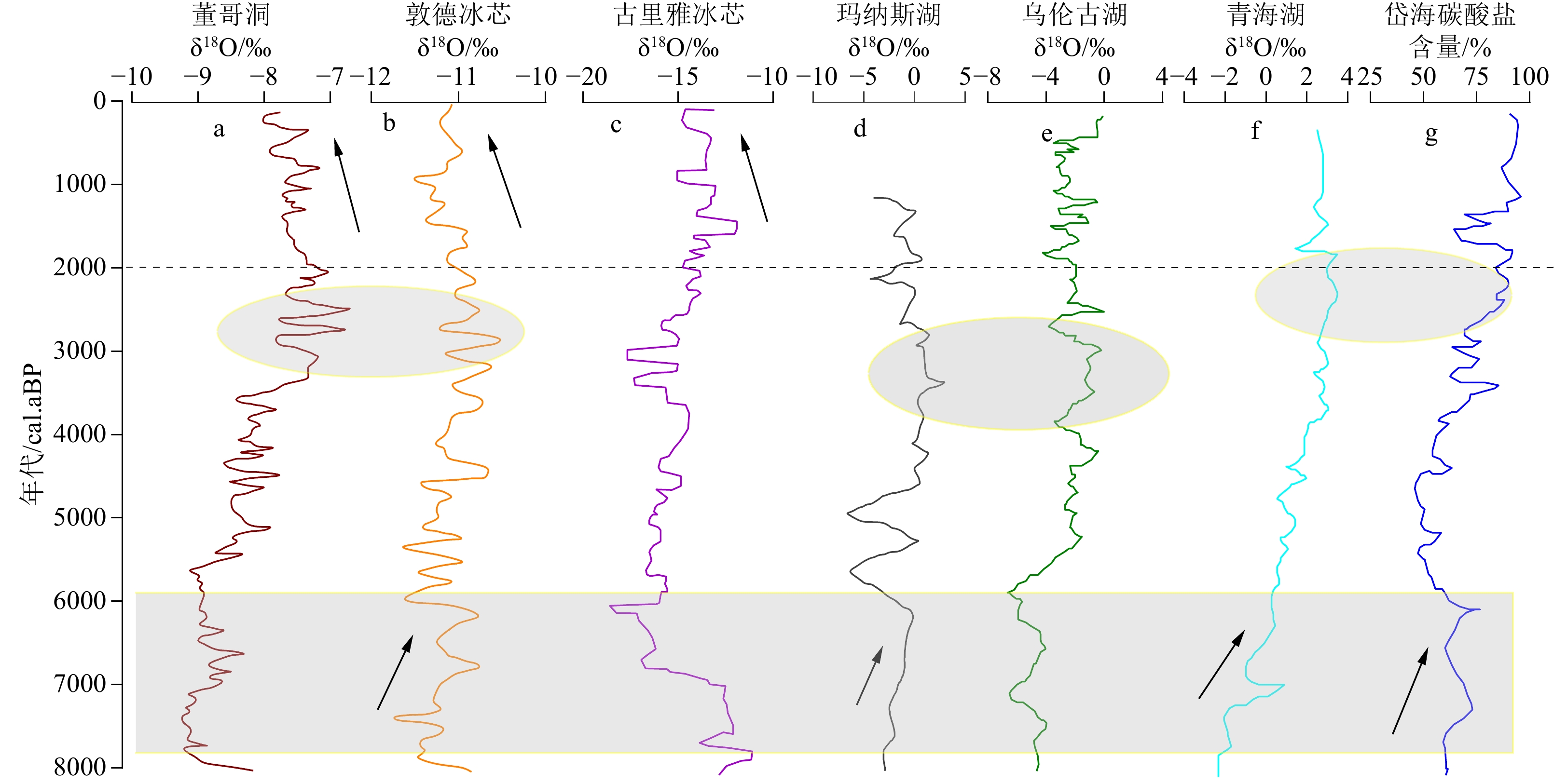
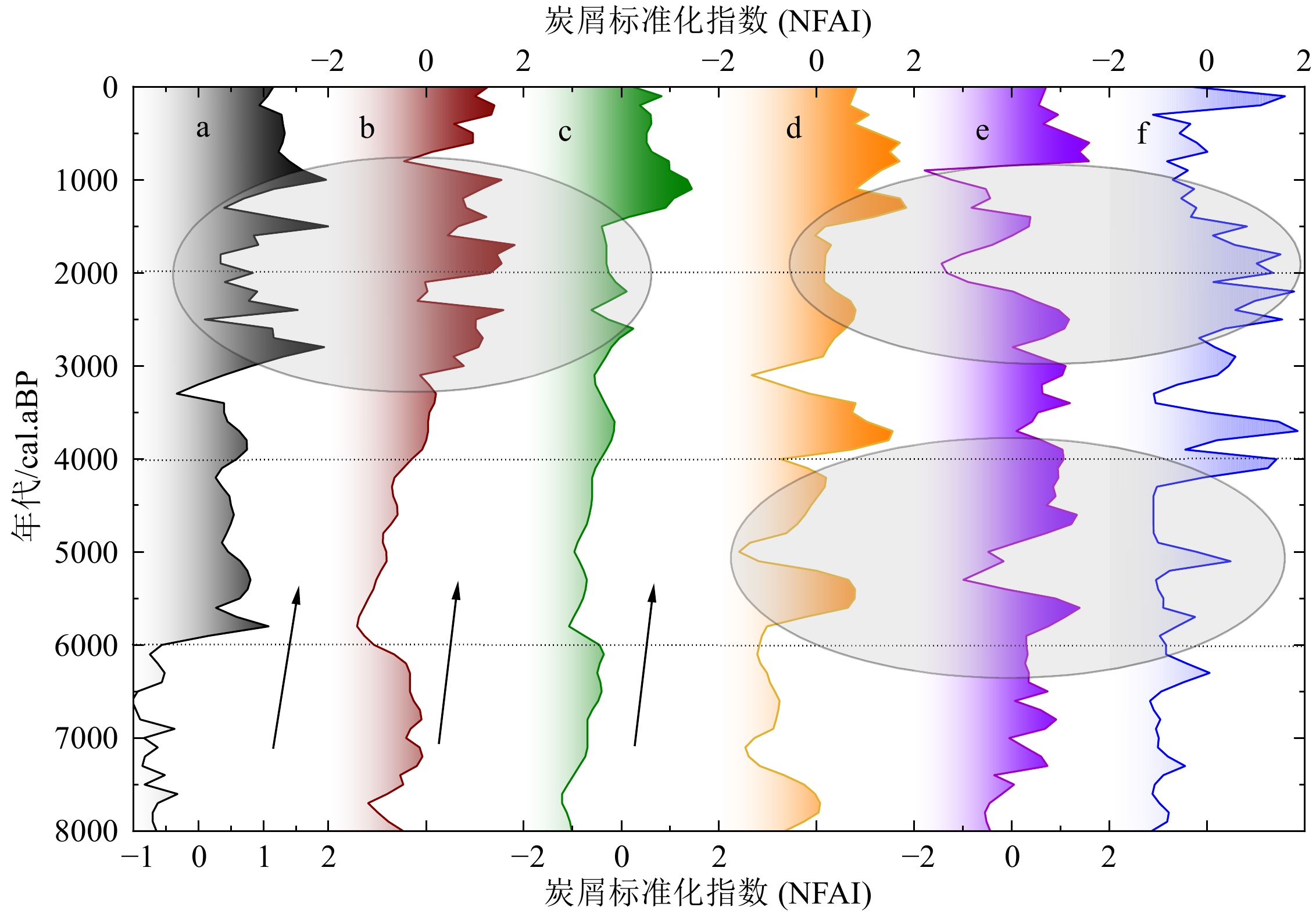
为了探讨西北地区古火演化及其驱动机制,基于28个样点的炭屑和黑碳记录,集成重建该区8 kaBP的古火变化序列;同时结合古植被、古气候、历史文献等记录,分析了古火活动与气候变化和人类活动之间的关系。结果表明:西北地区中晚全新世火历史可以划分为4个阶段;① 火活动波动阶段(8~6 kaBP),古火事件发生频繁,主要受气候变化的影响;② 火活动平稳阶段(6~4 kaBP),气候趋于暖湿化,植被有所发展,贮藏了一定的燃烧质;③ 火活动快速上升阶段(4~2 kaBP),人类活动成为火事件的主要影响因素,古火活动频率呈现不断上升的趋势;④ 火活动大范围发生阶段(2~0 kaBP),气候由湿冷向干冷转化,生物质干燥易燃,农业快速发展,朝代更替和战争频繁,火活动异常剧烈。
Abstract:A total of 28 records of charcoal and black carbon were used to reconstruct the evolution and driving mechanism of paleofire events in Northwest China in the past 8 ka. Combined with paleovegetation, paleoclimate, and historical records, relationship among paleofire activity, climate change, and human impact was analyzed. Results show that during the middle and late Holocene, fire history in Northwest China can be divided into four stages: (1) the fluctuation stage of fire activity (8~6 kaBP), paleofire events occurred frequently and were mainly affected by climate change; (2) the stable stage of fire activity (6~4 kaBP), when the climate tended to be warm and humid, vegetation developed and stored a certain amount of combustible material; (3) the rapid rise stage of fire activity (4~2 kaBP), human activities became the main influencing factor for fire events, and the frequency of fire activities showed a rising trend; (4) the stage of large-scale fire activity (2~0 kaBP), the climate changed from wet-cold to dry-cold, biomass was dry and flammable, agriculture developed rapidly, dynasty changed and frequent wars occurred, and the fire activity was exceptionally intense.
-
Key words:
- charcoal /
- black carbon /
- paleofire /
- climate evolution /
- human activities /
- Northwest China
-

-
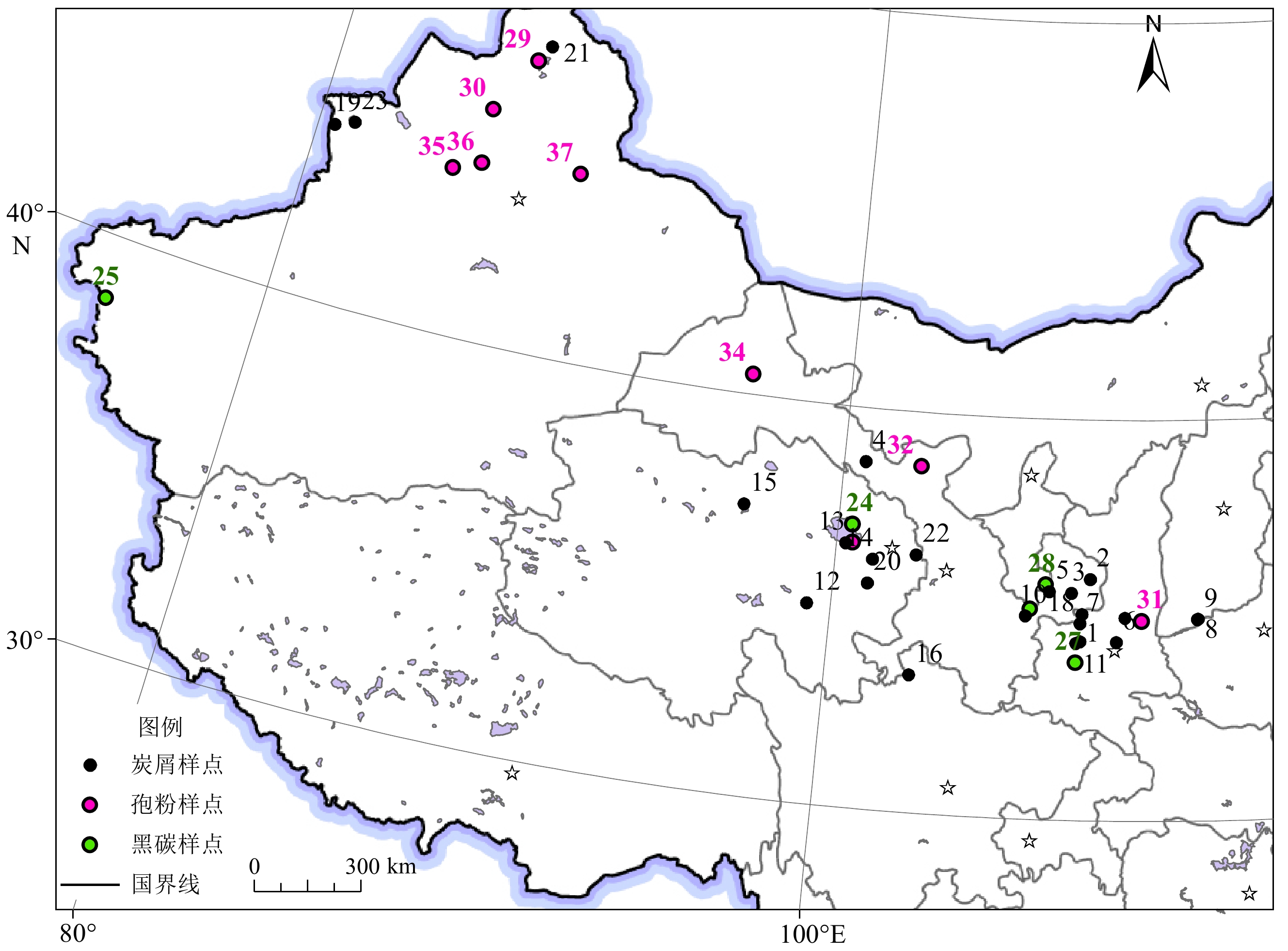
表 1 中国西北地区中晚全新世火记录不完全统计
Table 1. Statistics of the Middle and Late Holocene fire records (incomplete) in Northwest China
序号 点位 地点 位置 指标 研究方法 测年 文献 1 JYC 扶风蒋阳村 34°28′N、107°53′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [21] 2 MJY 甘肃合水马家塬 36°2′N、108°10′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [22] 3 HGZ 陇东后官寨 35°41′N、107°35′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [23] 4 QC 陇东桥村 38°39'N、100°43′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [23] 5 ZJC 甘肃平凉赵家村 35°41′51.9″N、106°52′57.8″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [24] 6 YGZ 高陵杨官寨 34°28′13″N、109°0′59″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [25] 7 ETC 黄土高原二塘村 34°55′12″N、107°52′12″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [26] 8 DXF-N 黄土高原东夏丰北 35°2′24″N、111°34′48″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [26] 9 DXF-S 黄土高原东夏丰南 35°1′48″N、111°34′12″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [26] 10 XJN 黄土高原徐建遗址 35°4′48″N、106°9′0″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [26] 11 WLP 岐山五里铺 34°26′N、107°45′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [27] 12 XDW 青藏高原下大武地区 35°0′6.9″N、99°15′37.7″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [28] 13 JXG 青海湖江西沟 36°35′25″N、100°17′47″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [29] 14 QLB 青海湖盆地 36°14′58″N、101°12′16″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [27] 15 HL-1 青海可鲁克湖 37°16′N、96°54′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [30] 16 ZB08-C1 若尔盖盆地 33°27′N、102°38'E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [31] 17 YHC 陕西白水尧禾村 35°4′27″N、109°16′45″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 OSL [24] 18 XHC 咸阳长武 35°08′50″N、107°55′55.5″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [32] 19 WQ-1 新疆天山 44°97′N、80°11′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [33] 20 KE 青海共和盆地 35°38.7′N、101°06′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [34] 21 ALHK 新疆阿拉哈克盐湖 47°41′37″N、87°32′40.5″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [35] 22 DZP 青海高庙盆地 36°26′28″N、102°34′51″E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [19] 23 SLMH 新疆赛里木湖 44°35′N、81°15′E 炭屑 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [36] 24 CCC 宁夏彭阳 35°52′N、106°46′E 黑碳 化学氧化法 AMS 14C [37] 25 CDL12A 青海草褡裢湖 37°3′50.4″N、100°27′43.2″E 黑碳 化学氧化法 AMS 14C [38] 26 PG1950 新疆卡拉库里湖 38°26′20.4″N、75°3′25.2″E 黑碳 化学氧化法 AMS 14C [38] 27 GSA07 六盘山天池 35°15′0″N、106°18′0″E 黑碳 化学氧化法 AMS 14C [38] 28 YHC16A 陕西玉皇池 33°56′24″N、107°45′36″E 黑碳 化学氧化法 AMS 14C [38] 29 HLGU 新疆乌伦古湖 47°15′43.2″N、87°9′21.6″E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [39] 30 ML-1 新疆玛纳斯湖 45°48′10.44″N、85°57′33.84″E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [40] 31 WN 陕西渭南 34°59′17.7″N、109°48′44.3″E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [41] 32 SJC 青海三角城 38°38′49.2″N、102°33′7.2″E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [42] 33 QJ-2000 青海湖 36°37′N、100°31′E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [43] 34 JDG 甘肃九道沟 40°30′N、96°39′E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [44] 35 MGH 新疆蘑菇湖湿地 44°25′39.3″N、85°54′35.6″E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [45] 36 CTHC 新疆草滩湖村湿地 44°25′06″N、86°01.26′E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [46] 37 DDHZ 新疆东道海子 44°41.7′N、89°33.5′E 孢粉 薄片计数法 AMS 14C [47] -
[1] 张健平, 吕厚远 . 现代植物炭屑形态的初步分析及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2006 ,26 (5 ):857 -863 ZHANG Jianping, LÜ Houyuan . Preliminary study of charcoal morphology and its environmental significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2006 ,26 (5 ):857 -863 .[2] Zhang Z Q, Zhong J J, Lv X G, et al . Climate, vegetation, and human influences on late-Holocene fire regimes in the Sanjiang plain, northeastern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,2015 ,438 :1 -8 .[3] 李宜垠, 侯树芳, 赵鹏飞 . 微炭屑的几种统计方法比较及其对人类活动的指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2010 ,30 (2 ):356 -363 LI Yiyin, HOU Shufang, ZHAO Pengfei . Comparison of different quantification methods for microfossil charcoal concentration and the implication for human activities[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2010 ,30 (2 ):356 -363 .[4] Xue J B, Zhong W, Li Q, et al . Holocene fire history in eastern monsoonal region of China and its controls[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,2018 ,496 :136 -145 .[5] Miao Y F, Song Y G, Li Y, et al . Late Pleistocene fire in the Ili Basin, Central Asia, and its potential links to paleoclimate change and human activities[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,2020 ,547 :109700 .[6] Ji P P, Chen J H, Zhou A F, et al . Biofuels reserve controlled wildfire regimes since the last deglaciation: a record from Gonghai Lake, North China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2021 ,48 (16 ):e2021GL094042 .[7] 占长林, 曹军骥, 韩永明, 等 . 古火灾历史重建的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2011 ,26 (12 ):1248 -1259 ZHAN Changlin, CAO Junji, HAN Yongming, et al . Research progress on reconstruction of paleofire history[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2011 ,26 (12 ):1248 -1259 .[8] 江鸿, 饶志国 . 火的历史重建及其与气候变化和人类活动关系研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018 ,38 (2 ):185 -197 JIANG Hong, RAO Zhiguo . Research progress on fire history reconstruction and its implications for climate change and human activities[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2018 ,38 (2 ):185 -197 .[9] 穆燕, 秦小光, 刘嘉麒, 等 . 黑碳的研究历史与现状[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011 ,31 (1 ):143 -155 MU Yan, QIN Xiaoguang, LIU Jiaqi, et al . A review of black carbon study: history and current status[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2011 ,31 (1 ):143 -155 .[10] 吕静, 王宇飞, 李承森 . 古炭屑与古森林火[J]. 古地理学报,2002 ,4 (2 ):71 -76 LÜ Jing, WAMG Yufei, LI Chengsen . Fossil charcoal and ancient forest fire[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2002 ,4 (2 ):71 -76 .[11] 徐鑫, 李宜垠 . 基于3种不同类型的炭屑数据定量重建大兴安岭火历史的结果对比[J]. 第四纪研究,2015 ,35 (4 ):960 -966 XU Xin, LI Yiyin . Comparison of the fire history reconstructions from three different kinds of charcoal data on the same site, Daxing’an Mountain[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2015 ,35 (4 ):960 -966 .[12] 杜建峰, 王宁练, 李建勇, 等 . 洛阳盆地全新世炭屑记录及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2022 ,42 (2 ):383 -396 DU Jianfeng, WANG Ninglian, LI Jianyong, et al . Charcoal records of Holocene loess-soil sequences and palaeoenvironmental significance in the Luoyang Basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2022 ,42 (2 ):383 -396 .[13] Novenko E Y, Rudenko O V, Mazei N G, et al . Late-Holocene vegetation and fire history in Western Putorana Plateau (subarctic Siberia, Russia)[J]. The Holocene,2022 ,32 (5 ):433 -441 .[14] 庞洋, 周斌, 徐向春, 等 . 中国东部季风区全新世火历史及其影响因素[J]. 第四纪研究,2022 ,42 (2 ):368 -382 PANG Yang, ZHOU Bin, XU Xiangchun, et al . Holocene fire history and its influencing factors in the monsoon region of East China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2022 ,42 (2 ):368 -382 .[15] 裴文强. 中国边缘海黑碳记录的长江、珠江流域火历史[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2020 PEI Wenqiang. Fire history in the Yangtze River and Pearl River Basins: black carbon records from the China seas[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanography, China Academy of Sciences, 2020. [16] 李明, 孙洪泉, 苏志诚 . 中国西北气候干湿变化研究进展[J]. 地理研究,2021 ,40 (4 ):1180 -1194 LI Ming, SUN Hongquan, SU Zhicheng . Research progress in dry/wet climate variation in Northwest China[J]. Geographical Research,2021 ,40 (4 ):1180 -1194 .[17] 徐国昌, 姚辉 . 中国西部全新世历史气侯的变化[J]. 水科学进展,1991 ,2 (4 ):277 -288 XU Guochang, YAO Hui . Historical climate changes of the West China in the Holocene[J]. Advances in Water Science,1991 ,2 (4 ):277 -288 .[18] 姚轶锋, 王霞, 谢淦, 等 . 新疆地区全新世植被演替与气候环境演变[J]. 科学通报,2015 ,60 (31 ):2963 -2976 YAO Yifeng, WANG Xia, XIE Gan, et al . Holocene vegetation succession and climate-environment change in Xinjiang Region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2015 ,60 (31 ):2963 -2976 .[19] 刘瑾. 内蒙古中东部湖泊沉积记录的全新世以来的气候变化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2017 LIU Jin. Paleoclimate changes during Holocene recorded by lake sediment in central East Inner Mongolia[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017. [20] 王晾晾. 多种代用气候指标揭示的西部干旱区全新世气候环境变化[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2009 WANG Liangliang. Multi-proxy data analysis on Holocene climate changes in western arid China[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2009. [21] 谭志海, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等 . 渭河流域全新世土壤剖面木炭屑记录及其古环境意义[J]. 中国生态农业学报,2010 ,18 (1 ):25 -30 TAN Zhihai, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al . Charcoal records of Holocene loess-soil sequences and its palaeoenvironmental significance in Weihe River Drainage[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2010 ,18 (1 ):25 -30 .[22] 谭志海, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等 . 陇东黄土高原北部全新世野火历史的木炭屑记录[J]. 第四纪研究,2008 ,28 (4 ):733 -738 TAN Zhihai, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al . Charcoal recorded Holocene fire history in the northern part of the Longdong Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2008 ,28 (4 ):733 -738 .[23] 周新郢, 李小强, 赵克良, 等 . 陇东地区新石器时代的早期农业及环境效应[J]. 科学通报,2011 ,56 (4-5): 318 -326ZHOU Xinying, LI Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Keliang, et al . Early agricultural development and environmental effects in the Neolithic Longdong basin (eastern Gansu)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2011 ,56 (8 ):762 -771 .[24] 谭志海, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等 . 渭河流域全新世以来野火历史与人类土地利用的炭屑记录[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版,2014 ,44 (4 ):1297 -1306 TAN Zhihai, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al . Wildfire history and human land use over Weihe River Basin Since Holocene: evidence from charcoal records[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition,2014 ,44 (4 ):1297 -1306 .[25] 范汇晨. 高陵杨官寨遗址剖面全新世火历史的黑碳记录与人类活动[D]. 西安工程大学硕士学位论文, 2017 FAN Huichen. The black carbon record of Holocene fire history and human activities in the Yangguanzhai archeological site of Gaoling[D]. Master Dissertation of Xi’an Polytechnic University, 2017. [26] Huang C C, Pang J L, Chen S E, et al . Charcoal records of fire history in the Holocene loess-soil sequences over the southern Loess Plateau of China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,2006 ,239 (1-2 ):28 -44 .[27] Tan Z H, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al . Holocene wildfires related to climate and land-use change over the Weihe River Basin, China[J]. Quaternary International,2011 ,234 (1-2 ):167 -173 .[28] 赵亚娟, 候光良, 鄂崇毅, 等 . 青藏高原下大武地区炭屑浓度所反映的环境演变与人类活动[J]. 地球环境学报,2016 ,7 (1 ):19 -26 ZHAO Yajuan, HOU Guangliang, E Chongyi, et al . Charcoal concentration reflect of environment change and human activities in Xiadawu Relic, Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2016 ,7 (1 ):19 -26 .[29] 姜莹莹, 鄂崇毅, 侯光良, 等 . 青海湖江西沟2号遗址炭屑浓度反映的环境变化与人类活动[J]. 地球环境学报,2015 ,6 (2 ):98 -105 JIANG Yingying, E Chongyi, HOU Guangliang, et al . Charcoal concentration reflect of environment change and human activities in Qinghai-Lake JXG2 relic[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2015 ,6 (2 ):98 -105 .[30] 余英浩, 金映豫, 徐德克, 等 . 青海可鲁克湖孢粉记录的14 cal. ka B. P. 以来植被和气候演化历史[J]. 第四纪研究,2021 ,41 (5 ):1229 -1243 YU Yinghao, JIN Yingyu, XU Deke, et al . Vegetational and climatic changes in the Hurleg Lake, Qinghai, during the last 14000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2021 ,41 (5 ):1229 -1243 .[31] 赵文伟. 若尔盖泥炭地孢粉和炭屑记录的全新世环境变化[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2012 ZHAO Wenwei. Holocene environmental changes inferred by pollen and charcoal records from the Zoige Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2012. [32] 邓琴. 宝鸡地区全新世的气候环境变迁[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2011 DENG Qin. The climatic evolution during the Holocene in the Baoji region[D]. Master Dissertation of Chang'an University, 2011. [33] Li J Y, Wang N L . Holocene grassland fire dynamics and forcing factors in continental interior of China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2020 ,47 (13 ):e2020GL088049 .[34] Miao Y F, Zhang D J, Cai X M, et al . Holocene fire on the northeast Xizang Plateau in relation to climate change and human activity[J]. Quaternary International,2017 ,443 :124 -131 .[35] 李玉梅. 新疆北部典型湿地4700年以来环境和植被演变研究[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2019 LI Yumei. Vegetation and environment changes of the typical wetland since 4700 yr BP in the northern part of Xinjiang[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Jilin University, 2019. [36] 蒋庆丰, 季峻峰, 沈吉, 等 . 赛里木湖孢粉记录的亚洲内陆西风区全新世植被与气候变化[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学,201 , 43(2): 243-2553 JIANG Qingfeng, JI Junfeng, SHEN Ji, et al . Holocene vegetational and climatic variation in westerly-dominated areas of Central Asia inferred from the Sayram Lake in northern Xinjiang, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2013 ,56 (3 ):339 -353 .[37] 孙斌. 陇东地区全新世土壤剖面的黑碳记录及环境变化[D]. 西安工程大学硕士学位论文, 2016 [SUN Bin. Holocene records of Black Carbon in the loess and paleo-soil profiles and it’s environmental changes in Longdong region[D]. Master Dissertation of Xi'an Polytechnic University, 2016. [38] 张山佳. 丝绸之路中—东段中晚全新世古火历史时空差异及影响因素研究[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2016 ZHANG Shanjia. Temporal-spatial differences and influencing factors of paleo-fire history during middle and late Holocene in northwest China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2016. [39] 肖霞云, 蒋庆丰, 刘兴起, 等 . 新疆乌伦古湖全新世以来高分辨率的孢粉记录与环境变迁[J]. 微体古生物学报,2006 ,23 (1 ):77 -86 XIAO Xiayun, JIANG Qingfeng, LIU Xingqi, et al . High resolution sporopollen record and environmental change since Holocene in the Wulungu Lake, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica,2006 ,23 (1 ):77 -86 .[40] 孙湘君, 杜乃秋, 翁成郁, 等 . 新疆玛纳斯湖盆周围近14000年以来的古植被古环境[J]. 第四纪研究,1994 ,14 (3 ):239 -248 SUN Xiangjun, DU Naiqiu, WENG Chengyu, et al . Paleovegetation and paleoenvironment of Manasi Lake, Xinjiang, N. W. China during the last 14000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences,1994 ,14 (3 ):239 -248 .[41] 王芳. 渭南地区全新世以来的孢粉组合与古环境[D]. 石家庄经济学院硕士学位论文, 2015 WANG Fang. Research of structural geology and genesis of Pollen assemblages and Paleoenvironment since Holocene in the Weinan region[D]. Master Dissertation of Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2015. [42] 靳立亚, 陈发虎, 朱艳 . 西北干旱区湖泊沉积记录反映的全新世气候波动周期性变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004 ,24 (2 ):101 -108 JIN Liya, CHEN Fahu, ZHU Yan . Holocene climatic periodicities recorded from lake sediments in the arid-semiarid areas of Northwestern China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2004 ,24 (2 ):101 -108 .[43] Shen J, Liu X Q, Wang S M, et al . Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18, 000 years[J]. Quaternary International,2005 ,136 (1 ):131 -140 .[44] 毛洪亮, 赵华, 卢演俦, 等 . 甘肃疏勒河冲积扇绿洲全新世孢粉组合和环境演化[J]. 地球学报,2007 ,28 (6 ):528 -534 MAO Hongliang, ZHAO Hua, LU Yanchou, et al . Pollen assemblages and environment evolution in Shule River alluvial fan oasis of Gansu[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica,2007 ,28 (6 ):528 -534 .[45] 段晓红, 张芸, 杨振京, 等 . 新疆石河子蘑菇湖湿地4800年以来的环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018 ,38 (4 ):203 -211 DUAN Xiaohong, ZHANG Yun, YANG Zhenjing, et al . Environmental evolution of the Moguhu Wetland of Shihezi City in Xinjiang since 4800 cal. a BP[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2018 ,38 (4 ):203 -211 .[46] 张芸, 孔昭宸, 倪健, 等 . 新疆草滩湖村湿地4550年以来的孢粉记录和环境演变[J]. 科学通报,2008 ,53 (3): 306-316ZHANG Yun, KONG Zhaochen, NI Jian, et al . Pollen record and environmental evolution of Caotanhu wetland in Xinjiang since 4550 cal. a BP[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2008 ,53 (7 ):1049 -1061 .[47] 阎顺, 李树峰, 孔昭宸, 等 . 乌鲁木齐东道海子剖面的孢粉分析及其反映的环境变化[J]. 第四纪研究,2004 ,24 (4 ):463 -468 YAN Shun, LI Shufeng, KONG Zhaochen, et al . The pollen analyses and environment changes of the Dongdaohaizi area in Ürümqi, Xinjiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2004 ,24 (4 ):463 -468 .[48] Carcaillet C, Richard P J H . Holocene changes in seasonal precipitation highlighted by fire incidence in eastern Canada[J]. Climate Dynamics,2000 ,16 (7 ):549 -559 .[49] Carcaillet C, Bouvier M, Fréchette B, et al . Comparison of pollen-slide and sieving methods in lacustrine charcoal analyses for local and regional fire history[J]. The Holocene,2001 ,11 (4 ):467 -476 .[50] Carcaillet C, Almquist H, Asnong H, et al . Holocene biomass burning and global dynamics of the carbon cycle[J]. Chemosphere,2002 ,49 (8 ):845 -863 .[51] 狄丽颖, 孙仁义 . 中国森林火灾研究综述[J]. 灾害学,2007 ,22 (4 ):118 -123 DI Liying, SUN Renyi . Summarization of research on forest fire in China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2007 ,22 (4 ):118 -123 .[52] Xu Q H, Tian F, Bunting M J, et al . Pollen source areas of lakes with inflowing rivers: modern pollen influx data from Lake Baiyangdian, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2012 ,37 :81 -91 .[53] 张恩源. 中国西北全新世湿度时空变化集成及区域史前人类活动[D]. 兰州大学硕士学位论文, 2020 ZHANG Enyuan. Spatiotemporal changes of Holocene moisture across northwestern China and regional prehistoric human activities[D]. Master Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2020. [54] Zhang D L, Huang X Z, Liu Q, et al . Holocene fire records and their drivers in the westerlies-dominated Central Asia[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022 ,833 :155153 .[55] 郭超, 马玉贞, 胡彩莉, 等 . 中国内陆区湖泊沉积所反映的全新世干湿变化[J]. 地理科学进展,2014 ,33 (6 ):786 -798 GUO Chao, MA Yuzhen, HU Caili, et al . Holocene humidity changes in inland China inferred from lake sediments[J]. Progress in Geography,2014 ,33 (6 ):786 -798 .[56] 侯光良, 方修琦 . 中国全新世分区气温序列集成重建及特征分析[J]. 古地理学报,2012 ,14 (2 ):243 -252 HOU Guangliang, FANG Xiuqi . Characteristics analysis and synthetical reconstruction of regional temperature series of the Holocene in China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2012 ,14 (2 ):243 -252 .[57] 侯光良, 方修琦 . 中国全新世气温变化特征[J]. 地理科学进展,2011 ,30 (9 ):1075 -1080 HOU Guangliang, FANG Xiuqi . Characteristics of Holocene temperature change in China[J]. Progress in Geography,2011 ,30 (9 ):1075 -1080 .[58] 方修琦, 侯光良 . 中国全新世气温序列的集成重建[J]. 地理科学,2011 ,31 (4 ):385 -393 FANG Xiuqi, HOU Guangliang . Synthetically reconstructed Holocene temperature change in China[J]. Scientia Geographical Sinica,2011 ,31 (4 ):385 -393 .[59] 葛全胜, 王顺兵, 郑景云 . 过去5000年中国气温变化序列重建[J]. 自然科学进展,2006 ,16 (6 ):689 -696 GE Quansheng, WANG Shunbing, ZHENG Jingyun . Reconstruction of temperature change sequence in China in the past 5000 years[J]. Progress in Natural Science,2006 ,16 (6 ):689 -696 .[60] 谭志海, 龙艳侠, 范汇晨, 等 . 史前关中盆地土壤剖面的黑碳与炭屑记录[J]. 土壤通报,2016 ,47 (3 ):518 -524 TAN Zhihai, LONG Yanxia, FAN Huichen, et al . Records of charcoal and black carbon in Holocene loess-paleosol profiles from Guanzhong Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2016 ,47 (3 ):518 -524 .[61] 施雅风, 孔昭宸, 王苏民, 等 . 中国全新世大暖期的气候波动与重要事件[J]. 中国科学: B辑,1992 (12 ):1300 -1308 SHI Yafeng, KONG Zhaochen, WANG Sumin, et al . Climate fluctuations and important events during the Holocene great warm period in China[J]. Scientia Sinica: Chimica,1992 (12 ):1300 -1308 .[62] 王绍武, 闻新宇, 黄建斌 . 五帝时代(距今6-4千年)中国的气候[J]. 中国历史地理论丛,2011 ,26 (2 ):5 -13 WANG Shaowu, WEN Xinyu, HUANG Jianbin . Climate in China during the Five-Emperor Period: 6-4 kaBP[J]. Journal of Chinese Historical Geography,2011 ,26 (2 ):5 -13 .[63] 侯小青, 侯光良, 王芳芳, 等 . 中国北方全新世降水分区对比分析[J]. 青海环境,2017 ,27 (3 ):126 -130, 139HOU Xiaoqing, HOU Guangliang, WANG Fangfang, et al . Comparative analysis of Holocene precipitation zoning in northern China[J]. Journal of Qinghai Environment,2017 ,27 (3 ):126 -130, 139.[64] 李小强, 安芷生, 周杰, 等 . 全新世黄土高原塬区植被特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2003 ,23 (3 ):109 -114 LI Xiaoqiang, AN Zhisheng, ZHOU Jie, et al . Characteristics of vegetation in the Loess plateau area since Holocene[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2003 ,23 (3 ):109 -114 .[65] 李小强, 赵宏丽, 闫敏华, 等 . 东北三江平原全新世火演化及其与植被和气候的关系[J]. 地理科学,2005 ,25 (2 ):177 -182 LI Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Hongli, YAN Minhua, et al . Fire variations and Relationship among Fire and Vegetation and Climate during Holocene at Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2005 ,25 (2 ):177 -182 .[66] 李小强 . 中国全新世气候和农业活动研究新进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学,2013 , 43(12 ): 1919-1928LI Xiaoqiang . New progress in the Holocene climate and agriculture research in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2013 ,56 (12 ):2027 -2036 .[67] 吴文祥, 刘东生 . 4000aB. P. 前后东亚季风变迁与中原周围地区新石器文化的衰落[J]. 第四纪研究,2004 ,24 (3 ):278 -284 WU Wenxiang, LIU Dongsheng . Variations in east Asia monsoon around 4000. B. P. and the collapse of neolithic cultures around central plain[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2004 ,24 (3 ):278 -284 .[68] 吴文祥, 刘东生 . 4000aB. P. 前后降温事件与中华文明的诞生[J]. 第四纪研究,2001 ,21 (5 ):443 -451 WU Wenxiang, LIU Dongsheng . 4000a B. P. event and its implications for the origin of Ancient Chinese civilization[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2001 ,21 (5 ):443 -451 .[69] 吴文祥, 周扬, 胡莹 . 甘青地区全新世环境变迁与新石器文化兴衰[J]. 中原文物,2009 (4 ):31 -37 WU Wenxiang, ZHOU Yang, HU Ying . Holocene climate change and the rise and fall of Neolithic cultures in the Ganqing areas[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China,2009 (4 ):31 -37 .[70] 陈发虎, 黄小忠, 杨美临, 等 . 亚洲中部干旱区全新世气候变化的西风模式: 以新疆博斯腾湖记录为例[J]. 第四纪研究,2006 ,26 (6 ):881 -887 CHEN Fahu, HUANG Xiaozhong, YANG Meilin, et al . Westerly dominated Holocene climate model in arid central Asia: case study on Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2006 ,26 (6 ):881 -887 .[71] 赵凯华. 艾比湖地区中全新世以来孢粉组合与古气候定量重建[D]. 石家庄经济学院硕士学位论文, 2013 ZHAO Kaihua. Palynological assemblages and Paleoclimate quantitative reconstruction in the Ebinur Lake region since the Holocene[D]. Master Dissertation of Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2013. [72] 安成邦, 陈发虎, 冯兆东 . 甘青地区中晚全新世植被变化与人类活动[J]. 干旱区地理,2002 ,25 (2 ):160 -164 AN Chengbang, CHEN Fahu, FENG Zhaodong . Study on the relationship between the vegetation change and the human activities in the Gansu-Qinghai region during the period from mid-to late-Holocene[J]. Arid Land Geography,2002 ,25 (2 ):160 -164 .[73] 马琴玉. 北宋对黄河流域植被的破坏及影响[D]. 西北师范大学硕士学位论文, 2019 MA Qinyu. Destruction and influence of Northern Song dynasty on vegetation in Yellow River Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Northwest Normal University, 2019. [74] 尚雪, 张鹏程, 周新郢, 等 . 陕西下河遗址新石器时代早期农业活动初探[J]. 考古与文物,2012 (4 ):55 -59, 103SHANG Xue, ZHANG Pengcheng, ZHOU Xinying, et al . A preliminary study on early agricultural activities at the Neolithic site of Xiahe in Shaanxi Province[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics,2012 (4 ):55 -59, 103.[75] 樊志民, 冯风 . 关于历史上的旱灾与农业问题研究[J]. 中国农史,1988 (1 ):33 -39, 49FAN Zhimin, FENG Feng . Study on drought and agricultural problems in history[J]. Agricultural Archaeology,1988 (1 ):33 -39, 49.[76] 方修琦, 刘翠华, 侯光良 . 中国全新世暖期降水格局的集成重建[J]. 地理科学,2011 ,31 (11 ):1287 -1292 FANG Xiuqi, LIU Cuihua, HOU Guangliang . Reconstruction of precipitation pattern of China in the Holocene Megathermal[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2011 ,31 (11 ):1287 -1292 .[77] 王菊婵. 关中东部全新世黄土序列记录的气候变化[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2011 WANG Juchan. A record on the climate change during Holocene in the eastern of Guanzhong[D]. Master Dissertation of Chang'an University, 2011. [78] 唐领余, 李春海, 安成邦, 等 . 黄土高原西部4万多年以来植被与环境变化的孢粉记录[J]. 古生物学报,2007 ,46 (1 ):45 -61 TANG Lingyu, LI Chunhai, AN Chengbang, et al . Vegetation history of the western loess plateau of China during the last 40ka based on pollen record[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica,2007 ,46 (1 ):45 -61 .[79] 黄春长 . 黄土高原南部晚更新世黄土古土壤与气候变迁[J]. 地理学报,1989 ,44 (1 ):1 -10 HUANG Chunchang . Loss-palaeosoil and climatic changes on southern loess plateau in late Pleistocene[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,1989 ,44 (1 ):1 -10 .[80] 黄春长 . 渭河流域3100年前资源退化与人地关系演变[J]. 地理科学,2001 ,21 (1 ):30 -35 HUANG Chunchang . The deterioration of land resources and the change in Human-Earth relationships in the Weihe River Basin at 3100 a B. P. [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2001 ,21 (1 ):30 -35 .[81] 莫多闻, 李非, 李水城, 等 . 甘肃葫芦河流域中全新世环境演化及其对人类活动的影响[J]. 地理学报,1996 ,51 (1 ):59 -69 MO Duowen, LI Fei, LI Shuicheng, et al . A preliminary study on the paleoenvironment of the middle Holocene in the Hulu river area in Gansu province and its effects on human activity[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,1996 ,51 (1 ):59 -69 .[82] 方修琦, 章文波, 张兰生 . 全新世暖期我国土地利用的格局及其意义[J]. 自然资源学报,1998 ,13 (1 ):16 -22 FANG Xiuqi, ZHANG Wenbo, ZHANG Lansheng . The land use arrangement of china in the Holocene Megathermal period and its significance[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,1998 ,13 (1 ):16 -22 .[83] 赵景波, 侯甬坚, 杜娟, 等 . 关中平原全新世环境演变[J]. 干旱区地理,2003 ,26 (1 ):17 -22 ZHAO Jingbo, HOU Yongjian, DU Juan, et al . Holocene environmental changes in the Guanzhong Plain[J]. Arid Land Geography,2003 ,26 (1 ):17 -22 .[84] 金勇强. 宋夏战争与黄土高原地区生态环境关系研究[D]. 陕西师范大学硕士学位论文, 2007 JIN Yongqiang. Song and the tangut war and the loess plateau area ecological environment relations studies[D]. Master Dissertation of Shaanxi Normal University, 2007. [85] 尹君, 罗玉洪, 方修琦, 等 . 西汉至五代中国盛世及朝代更替的气候变化和农业丰歉背景[J]. 地球环境学报,2014 ,5 (6 ):400 -409 YIN Jun, LUO Yuhong, FANG Xiuqi, et al . The climatic and harvest backgrounds of dynastic flourishing ages and transitions in China during 210 BC to 960 AD[J]. Journal of Earth Environment,2014 ,5 (6 ):400 -409 .[86] 刘璐, 苏筠, 方修琦 . 中国西汉至清代北方农牧民族战争及其与温度变化的关联[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版,2016 ,52 (4 ):450 -457 LIU Lu, SU Yun, FANG Xiuqi . Wars between farming and nomadic groups from Western Han Dynasty to Qing Dynasty in north China and relationship with temperature change[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University: Natural Science,2016 ,52 (4 ):450 -457 .[87] Tan L C, Cai Y J, An Z S, et al . Centennial-to decadal-scale monsoon precipitation variability in the semi-humid region, northern China during the last 1860 years: records from stalagmites in Huangye Cave[J]. The Holocene,2011 ,21 (2 ):287 -296 .[88] 刘俊霞. 秦汉时期西北农业开发与生态环境问题研究[D]. 西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文, 2008 LIU Junxia. A study on northwest agricultural development and ecological environment problems in Qin and Han dynasties[D]. Master Dissertation of Northwest A&F University, 2008. [89] 杜娟 . 秦汉时期关中农业土地利用区域特征及影响因素[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版,2014 ,44 (1 ):150 -155 DU Juan . The regional characteristics and influence factors of agricultural land use in Guanzhong area during Qin and Han Dynasties[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition,2014 ,44 (1 ):150 -155 .[90] 杨保, 施雅风, 李恒鹏 . 过去2 ka气候变化研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2002 ,17 (1 ):110 -117 YANG Bao, SHI Yafeng, LI Hengpeng . Some advances in climatic change over the past two millennia[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2002 ,17 (1 ):110 -117 .[91] 任国玉, 姜大膀, 燕青 . 古气候演化特征、驱动与反馈及对现代气候变化研究的启示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2021 ,41 (3 ):824 -841 REN Guoyu, JIANG Dabang, YAN Qing . Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of paleo-climatic variations and the implications for modern climate change research[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2021 ,41 (3 ):824 -841 .[92] 王岳, 李育, 张成琦 . 河西走廊东西段全新世古湖泊演化对比研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2017 ,37 (3 ):581 -596 WANG Yue, LI Yu, ZHANG Chengqi . The comparative study of paleolakes evolution between the eastern and western parts of the Hexi Corridor in Holocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2017 ,37 (3 ):581 -596 .[93] 陶士臣. 新疆东部湖泊沉积花粉记录的全新世植被与环境[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2011 TAO Shichen. Pollen record of vegetation and environmental changes from lakes’ sediment in eastern Xinjiang China, during the Holocene[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Lanzhou University, 2011. [94] 宋姝瑶. 新疆艾比湖湿地全新世以来环境演变研究[D]. 河北地质大学硕士学位论文, 2016 SONG Shuyao. Holocene climate change in the Ebinur Lake wetland, Xinjiang, China[D]. Master Dissertation of Hebei Geo University, 2016. [95] 韩淑媞, 袁玉江 . 新疆巴里坤湖35000年来古气候变化序列[J]. 地理学报,1990 ,45 (3 ):350 -362 HAN Shuti, YUAN Yujiang . The sequence of paleoclimatic variation of Balikun lake of Xinjiang in the part 35000 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,1990 ,45 (3 ):350 -362 .[96] 薛积彬, 钟巍 . 新疆巴里坤湖全新世环境记录及区域对比研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2008 ,28 (4 ):610 -620 XUE Jibin, ZHONG Wei . Holocene climate change recorded by lacustrine sediments in Barkol Lake and its regional comparison[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2008 ,28 (4 ):610 -620 .[97] 徐和阳 . 历史气候变迁对中国古代社会影响的研究综述[J]. 哈尔滨学院学报,2013 ,34 (9 ):99 -101 XU Heyang . Research summary on historical climate change impact on ancient Chinese society[J]. Journal of Harbin University,2013 ,34 (9 ):99 -101 .[98] 刘家坤 . 火攻在中国历代战争中的运用和发展[J]. 军事历史研究,2001 (4 ):99 -103 LIU Jiakun . The application and development of fire attack in the feudal dynasties of past ages[J]. Military Historical Research,2001 (4 ):99 -103 .[99] 钟茂华 . 中国火灾史(秦朝~1949年)简析[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2004 ,14 (5 ):67 -71 ZHONG Maohua . Brief analysis on history of fire in China (221 B. C. ∽ 1949 A. D. )[J]. China Safety Science Journal,2004 ,14 (5 ):67 -71 .[100] 杨铭, 柳春鸣 . 西周时期的气候变化与民族迁徙[J]. 中原文物,1997 (2 ):77 -83 YANG Ming, LIU Chunming . Climate change and ethnic migration in the Western Zhou Dynasty[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China,1997 (2 ):77 -83 .[101] Tan L C, Cai Y J, Cheng H, et al . Centennial-to decadal-scale monsoon precipitation variations in the upper Hanjiang River region, China over the past 6650 years[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2018 ,482 :580 -590 . -



 下载:
下载: