Characteristics of X-ray fluorescence scanning element of modern flood sediments in northern Shandong Province and its geological indicative significance
-
摘要:
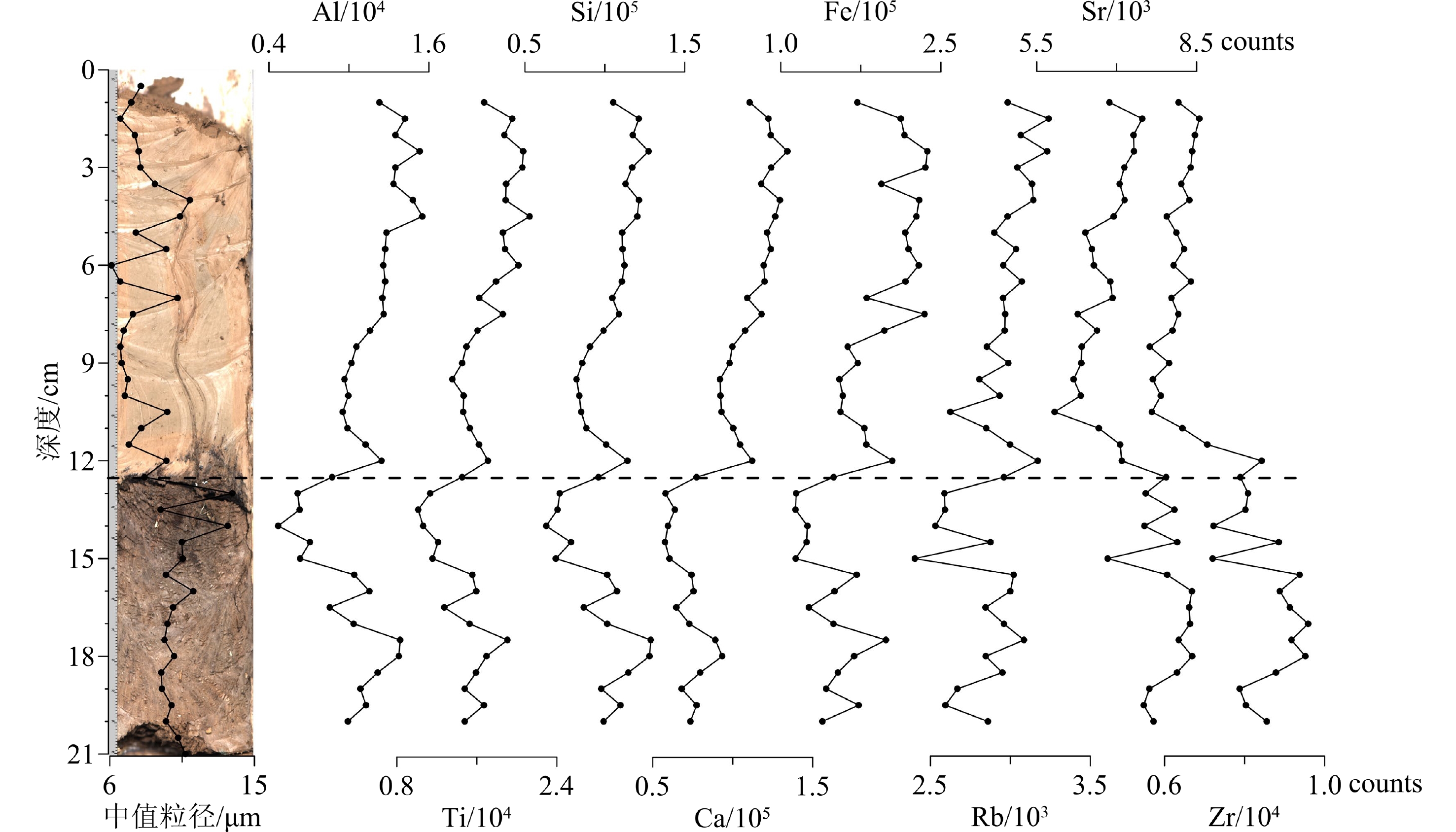
2018年8月山东北部弥河流域受台风暴雨影响发生洪涝灾害,通过对洪水淹没区考察,选择弥河及其支流丹河下游新鲜洪水沉积保存完好的地点,获取两根沉积物浅钻MH1、DH2(长度分别为21.5、21 cm,下段为现代土壤),对沉积岩芯进行X射线荧光光谱(XRF)元素连续扫描,结合粒度指标和其他研究成果,探讨现代洪水沉积物元素特征及其在古洪水事件识别中的指示意义。结果显示,Al、Ti、Si、Ca、Fe等元素具有相似的波动特征,相互之间正相关关系显著,信号强度在细粒洪水沉积层出现峰值;Rb元素信号强度与粒度相关性弱,在钻孔中的变化较为稳定,仅在沉积界面处有所降低,可能与岩芯裂隙造成的实验偏差有关;Sr、Zr两种元素显著正相关,且信号强度在洪水沉积层较低。Zr/Rb和Rb/Sr分析结果表明,两者均受控于粒度特征,风化淋溶作用对其影响有待进一步研究,其中Zr/Rb与粒度呈现较强的正相关性,Rb/Sr则与粒度负相关关系显著,且在其他区域洪水地层研究中具有一致结论。Zr/Rb峰值和Rb/Sr谷值对应黏土质洪水沉积,Zr/Rb谷值和Rb/Sr峰值对应粒度粗组分高值的粉砂质洪水沉积,可在古洪水沉积识别中作为参照指标。本研究结果将为利用XRF技术识别古洪水沉积提供有力参考。
Abstract:In August 2018, a typhoon-storm–induced flood disaster occurred in the Mihe River Basin in the northern Shandong Province of China. By investigating the flood inundated area, the sites were selected where fresh flood deposits in the lower reaches of the Mihe River and its tributary Danhe River were well preserved, and two sediment shallow drills MH1 and DH2 (with the length of 21.5 cm and 21 cm, respectively, including the lower section of modern soil) were obtained. The Avaatech X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy core scanner made in the Netherlands was applied for element analysis, and the characteristics of modern flood sediment elements and its significance in paleoflood layers were discussed in combination with grain size index and other research results. Results show that Al, Ti, Si, Ca, and Fe elements presented similar fluctuation characteristics, and there was a significant positive correlation between them, and the signal intensity of these chemical elements peaked in fine-grained flood sediments sections. The signal intensity of Rb element was weakly correlated with particle size, and the change through the borehole was relatively stable but decreased at sedimentary interface, which might be related to the experimental deviation caused by cracks. The two elements of Sr and Zr were significantly positively correlated, and the signal intensity of them was low in the flood sediment layer. In addition, the Zr/Rb and Rb/Sr ratios were heavily correlated with grain size properties, and the influence of weathering and leaching on them is yet to be studied further. The Zr/Rb ratio was strongly positively correlated with the grain size, while the Rb/Sr ratio was significantly negatively correlated with the grain size, which is consistent with the conclusions obtained from the studies on other regional flood formations. The maximum Zr/Rb and minimum Rb/Sr values occurred in the clayey part of flood deposits, while the minimum Zr/Rb and maximum Rb/Sr values in the silty part of flood deposits with more coarser-grain composition. Therefore, Rb/Sr and Zr/Rb ratios can be used to indicate paleoflood deposits. This study provided a good reference for the identification of paleoflood deposit by using XRF technology.
-
Key words:
- flood deposits /
- X-ray fluorescence /
- Zr/Rb /
- Rb/Sr /
- northern Shandong Province
-

-
图 4 DH2(a)、MH1(b)和DH1(c)[44]钻孔Zr/Rb比和Rb/Sr比变化特征
Figure 4.
表 1 MH1、DH2岩芯不同沉积地层元素平均扫描强度
Table 1. Average scanning intensity of elements in different sedimentary strata of Cores MH1 and DH2
元素强度 Al/104 Ti/104 Si/105 Ca/105 Fe/105 Rb/104 Sr/104 Zr/104 MH1 洪水层 1.35 1.54 1.15 1.44 1.61 0.35 0.62 0.65 土壤层 1.00 1.24 1.09 0.55 1.13 0.32 0.79 1.29 DH2 洪水层 1.23 1.75 1.06 1.13 1.99 0.30 0.68 0.64 土壤层 0.95 1.42 0.95 0.71 1.44 0.28 0.79 0.86 表 2 MH1浅钻元素相关性分析
Table 2. Results of element correlation analysis for Core MH1
Al Ti Si Ca Fe Rb Sr Zr Al 1 Ti 0.884** 1 Si 0.831** 0.773** 1 Ca 0.804** 0.819** 0.437** 1 Fe 0.847** 0.912** 0.605** 0.924** 1 Rb 0.779** 0.765** 0.707** 0.612** 0.704** 1 Sr -0.381* -0.339** 0.128 -0.726** -0.547** -0.061 1 Zr -0.480** -0.480** 0.018 -0.854** -0.663** -0.233 0.927** 1 注:*在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著;**在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 3 DH2岩芯元素相关性分析结果
Table 3. Results of element correlation analysis for Core DH2
Al Ti Si Ca Fe Rb Sr Zr Al 1 Ti 0.950** 1 Si 0.950** 0.912** 1 Ca 0.838** 0.866** 0.694** 1 Fe 0.867** 0.936** 0.787** 0.938** 1 Rb 0.774** 0.747** 0.749** 0.712** 0.727** 1 Sr -0.133 -0.205 0.115 -0.527** -0.387* 0.000 1 Zr -0.214 -0.279 0.052 -0.618** -0.439** -0.084 0.911** 1 注:*在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著;**在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著。 -
[1] Seneviratne S I, Nicholls N, Easterling D, et al. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
[2] Kundzewicz Z W, Kanae S, Seneviratne S I, et al. Flood risk and climate change: global and regional perspectives [J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2014, 59(1): 1-28.
[3] 周成虎, 万庆, 黄诗峰, 等. 基于GIS的洪水灾害风险区划研究[J]. 地理学报, 2000, 55(1):15-24 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.01.003
ZHOU Chenhu, WAN Qing, HUANG Shifeng, et al. A GIS-based approach to flood risk zonation [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2000, 55(1): 15-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.01.003
[4] St. George S, Hefner A M, Avila J. Paleofloods stage a comeback [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13(12): 766-768. doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-00664-2
[5] Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X C, et al. Extraordinary floods related to the climatic event at 4200 a BP on the Qishuihe River, middle reaches of the Yellow River, China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(3-4): 460-468. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.12.007
[6] Lam D, Croke J, Thompson C, et al. Beyond the gorge: palaeoflood reconstruction from slackwater deposits in a range of physiographic settings in subtropical Australia [J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 292: 164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.05.008
[7] Dong G H, Zhang F Y, Liu F W, et al. Multiple evidences indicate no relationship between prehistoric disasters in Lajia site and outburst flood in upper Yellow River valley, China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(4): 441-449. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9079-3
[8] 吴庆龙, 张培震, 张会平, 等. 黄河上游积石峡古地震堰塞溃决事件与喇家遗址异常古洪水灾害[J]. 中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2009, 39(8):1148-1159
WU Qinglong, ZHANG Peizhen, ZHANG Huiping, et al. A palaeo-earthquake induced damming and bursting of Yellow River and the abnormal flood that destroyed Lajia relic [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2009, 39(8): 1148-1159.
[9] 李晓刚, 黄春长. 黄河晋陕峡谷2012年大洪水滞流沉积物性质分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(10):165-171 doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2015.346
LI Xiaogang, HUANG Chunchang. Characteristics of the flood slackwater deposits occurred in 2012 in the Jin-Shaan Gorges of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(10): 165-171. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2015.346
[10] Zhan W, Yang S Y, Liu X L, et al. Reconstruction of flood events over the last 150 years in the lower reaches of the Changjiang River [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(21): 2268-2274. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3263-8
[11] 李华勇, 赵楠, 杨艺萍, 等. 山东丹河2018年洪水沉积特征、物源分析及水文过程重建[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(2):226-236
LI Huayong, ZHAO Nan, YANG Yiping, et al. Sedimentary characterization and provenance analysis of the 2018 flooding along the Dan River, Shandong, and the hydrodynamic process reconstruction [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(2): 226-236.
[12] Kermode S J, Cohen T J, Reinfelds I V, et al. Modern depositional processes in a confined, flood-prone setting: benches on the Shoalhaven River, NSW, Australia [J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 228: 470-485. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.09.022
[13] 张凌华, 张振克. 河漫滩沉积与环境研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):153-163 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2015.05.018
ZHANG Linghua, ZHANG Zhenke. Research progress of river overbank deposits and implications for environment [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 153-163. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2015.05.018
[14] Croudace I W, Rindby A, Rothwell R G. ITRAX: description and evaluation of a new multi-function X-ray core scanner [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2006, 267: 51-63. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2006.267.01.04
[15] Kylander M E, Ampel L, Wohlfarth B, et al. High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning analysis of Les Echets (France) sedimentary sequence: new insights from chemical proxies [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2011, 26(1): 109-117. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1438
[16] Zhang X N, Zhang H C, Chang F Q, et al. Application of corrected methods for high-resolution XRF core scanning elements in lake sediments [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(22): 8012. doi: 10.3390/app10228012
[17] 牛洁, 张文翔, 张虎才, 等. 基于XRF连续扫描的云南抚仙湖沉积物元素特征及环境意义[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(7):2223-2227
NIU Jie, ZHANG Wenxiang, ZHANG Hucai, et al. The characteristics of geochemical elements in Fuxian Lake sediments and its environmental significance based on XRF core scanning [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(7): 2223-2227.
[18] 雷国良, 张虎才, 常凤琴, 等. 湖泊沉积物XRF元素连续扫描与常规ICP-OES分析结果的对比及校正: 以兹格塘错为例[J]. 湖泊科学, 2011, 23(2):287-294 doi: 10.18307/2011.0220
LEI Guoliang, ZHANG Hucai, CHANG Fengqin, et al. Comparison and correction of element measurements in lacustrine sediments using X-ray fluorescence core-scanning with ICP-OES method: a case study of Zigetang Co [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2011, 23(2): 287-294. doi: 10.18307/2011.0220
[19] Yang H F, Zhao Y, Cui Q Y, et al. Paleoclimatic indication of X-ray fluorescence core-scanned Rb/Sr ratios: a case study in the Zoige Basin in the eastern Xizang Plateau [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(1): 80-95. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9667-7
[20] 张晓楠, 张灿, 吴铎, 等. 基于XRF岩心扫描的中国西部湖泊沉积物元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(1):163-174
ZHANG Xiaonan, ZHANG Can, WU Duo, et al. Element geochemistry of lake deposits measured by X-Ray Fluorescencecore scanner in Northwest China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(1): 163-174.
[21] 张喜林, 范德江, 王亮, 等. X-射线岩心扫描系统对海洋沉积物成分测定质量的综合评价和校正[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(6):86-95
ZHANG Xilin, FAN Dejiang, WANG Liang, et al. The calibration and quality evaluation of elemental analysis results of marine sediment measured by an X-ray fluorescence core scanner [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(6): 86-95.
[22] 杨欢, 曾蒙秀, 彭海军, 等. 基于XRF岩芯扫描的贵州喀斯特地区晚全新世泥炭古环境研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(5):1154-1169 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.05.06
YANG Huan, ZENG Mengxiu, PENG Haijun, et al. Application of XRF core scanning method in Late Holocene environment change study derived from a peat core from southwestern Guizhou, Southwestern China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(5): 1154-1169. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.05.06
[23] Li D, Tan L C, Guo F, et al. Application of Avaatech X-ray fluorescence core-scanning in Sr/Ca analysis of speleothems [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(6): 964-973. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9344-2
[24] Bi S B, Bi S J, Lu Y, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of droughts and floods in northern China from 1644 to 1911 [J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2019, 128(4): 98. doi: 10.1007/s12040-019-1121-x
[25] Shen H Y, Yu L P, Zhang H M, et al. OSL and radiocarbon dating of flood deposits and its paleoclimatic and archaeological implications in the Yihe River Basin, East China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 398-404. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.03.005
[26] 栾玉洁, 郭金运, 高永刚, 等. 基于Sentinel-1B SAR数据的2018年寿光洪水遥感监测及灾害分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2021, 30(2):168-175
LUAN Yujie, GUO Jinyun, GAO Yonggang, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of flood and disaster analysis in Shouguang in 2018 from Sentinel-1B SAR data [J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(2): 168-175.
[27] 徐立荣. 气候变化对莱州湾地区水文极端事件的影响研究: 以弥河流域为例[D]. 山东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2001
XU Lirong. Studies on impacts of climate changes on hydrologic extermes in Mihe Basin, Laizhou Bay area of China[D]. Master Dissertation of Shandong Normal University, 2001.
[28] 郭广军, 贺芳丁. 从台风影响谈对水库加固建设与管理的几点反思[J]. 中国水利, 2018(20):66-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.20.017
GUO Guangjun, HE Fangding. Reflections on reservoirs reinforcement under the impact of typhoon [J]. China Water Resources, 2018(20): 66-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.20.017
[29] 李华勇, 于正松. 气候变化和人为活动双重胁迫下山前平原地区洪灾发生机制与防治对策[J]. 陕西水利, 2021(1):75-77,82
LI Huayong, YU Zhengsong. The occurrence mechanism and prevention countermeasures of flood disaster in the piedmont plain area under the dual stress of climate change and human activities [J]. Shaanxi Water Resources, 2021(1): 75-77,82.
[30] 李华勇, 朱佳丽, 张虎才, 等. 鲁北丹河下游洪水决口扇沉积岩芯粒度特征与沉积过程重建[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(2):176-182 doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.057
LI Huayong, ZHU Jiali, ZHANG Hucai, et al. Grain-size characteristics of crevasse splays from the lower reaches of Dan River in northern Shandong province and reconstruction of sedimentary process [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(2): 176-182. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.057
[31] 章桂芳, 郑卓, 乐远福, 等. 福州盆地第四纪钻孔XRF连续扫描的元素特征及沉积相指示意义[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(9):2971-2977
ZHANG Guifang, ZHENG Zhuo, LUE Yuanfu, et al. Continuous XRF element characteristics and significance of sedimentary facies indication of the quaternary core from Fuzhou Basin [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(9): 2971-2977.
[32] 李华勇, 袁俊英, 杨艺萍, 等. 山东弥河流域现代洪水沉积特征与水动力过程反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2):178-189
LI Huayong, YUAN Junying, YANG Yiping, et al. Characteristics of modern flood deposits in the Drainage basin of Mi River, Shandong Province and the reconstruction of hydrodynamic processes [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2): 178-189.
[33] 马雪洋, 陈豆, 阳亚平, 等. 哈拉湖岩芯XRF扫描元素统计分析及其环境意义[J]. 盐湖研究, 2014, 22(4):1-10
MA Xueyang, CHEN Dou, YANG Yaping, et al. Statistical analysis of XRF scanned elements and their environmental significance in Hala Lake, Qinghai, China [J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2014, 22(4): 1-10.
[34] 吴旭东, 沈吉, 汪勇. 湖光岩玛珥湖沉积物反映的全新世以来古环境演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(4):155-162
WU Xudong, SHEN Ji, WANG Yong. Holocene paleoenvironmental evolution of the Huguangyan Maar Lake [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(4): 155-162.
[35] Wünnemann B, Wagner J, Zhang Y Z, et al. Implications of diverse sedimentation patterns in Hala Lake, Qinghai Province, China for reconstructing Late Quaternary climate [J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2012, 48(4): 725-749. doi: 10.1007/s10933-012-9641-2
[36] 金章东. 湖泊沉积物的矿物组成、成因、环境指示及研究进展[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(1):34-44,77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.01.005
JIN Zhangdong. Composition, origin and environmental interpretation of minerals in lake sediments and recent progress [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(1): 34-44,77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.01.005
[37] Cuven S, Francus P, Lamoureux S F. Estimation of grain size variability with micro X-ray fluorescence in laminated lacustrine sediments, Cape Bounty, Canadian High Arctic [J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2010, 44(3): 803-817. doi: 10.1007/s10933-010-9453-1
[38] 岳大鹏, 袁晓宁, 李奎, 等. 陕北子洲黄土洼坝淤地淤积剖面元素分布特征分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2014, 37(5):875-882
YUE Dapeng, YUAN Xiaoning, LI Kui, et al. Distribution features of deposition profile elements on dammed silt land in Huangtuwa of Zizhou County, Northern Shaanxi [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 37(5): 875-882.
[39] 王国平, 刘景双. 向海湿地元素地球化学特征与高分辨沉积记录[J]. 地理科学, 2003, 23(2):208-212 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.02.013
WANG Guoping, LIU Jingshuang. Characteristics of element geochemistry and high-resolution sedimentation records in Xianghai wetlands [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(2): 208-212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.02.013
[40] Wu L, Wilson D J, Wang R J, et al. Evaluating Zr/Rb ratio from XRF scanning as an indicator of grain-size variations of glaciomarine sediments in the Southern Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2020, 21(11): e2020GC009350.
[41] 胡砚泊, Wünnemann B, 张永战, 等. 14 ka以来苦海沉积物地球化学记录及其古环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(1):104-114
HU Yanbo, Wünnemann B, ZHANG Yongzhan, et al. Geochemistry record and their environmental implications during the past 14 ka in Kuhai Lake, NE Xizang Plateau [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(1): 104-114.
[42] 张跞颖, 李长安, 张玉芬, 等. 长江武汉段4.5~2.5 ka沉积地层与古洪水标志识别[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(4):973-982
ZHANG Luoying, LI Chang'an, ZHANG Yufen, et al. Sedimentary strata and paleoflood identification indexes of Wuhan section, Yangtze River, during 4.5~2.5 ka BP [J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(4): 973-982.
[43] 朱诚, 马春梅, 王慧麟, 等. 长江三峡库区玉溪遗址T0403探方古洪水沉积特征研究[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(S1):1-17
ZHU Cheng, MA Chunmei, WANG Huilin, et al. Characteristics of paleoflood deposits archived in unit T0403 of Yuxi Site in the Three Gorges Reservoir areas, China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(S1): 1-17.
[44] 李华勇, 王倩, 张虎才, 等. 鲁北丹河现代洪水沉积物地球化学特征及古洪水识别意义[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 43(3):503-512
LI Huayong, WANG Qian, ZHANG Hucai, et al. Geochemical characteristics of modern flood sediment from Danhe River Basin in northern Shandong Province and its significance of paleoflood identification [J]. Journal of Yunnan University:Natural Sciences Edition, 2021, 43(3): 503-512.
[45] Wang M J, Zheng H B, Xie X, et al. A 600-year flood history in the Yangtze River drainage: comparison between a subaqueous delta and historical records [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(2): 188-195. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4212-2
[46] 韦璐, 范代读, 吴伊婧, 等. 近百年来长江水下三角洲高分辨率洪水沉积记录及其控制机理[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(5):707-720
WEI Lu, FAN Daidu, WU Yijing, et al. High resolution flood records in the Yangtze subaqueous delta during the past century and control mechanism [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(5): 707-720.
[47] 吴霜, 刘倩, 曹向明, 等. 赣北黄茅潭湖泊沉积记录的240年以来古洪水事件[J]. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(11):1413-1422 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.010
WU Shuang, LIU Qian, CAO Xiangming, et al. A 240-year sedimentary record of paleoflood events from the Huangmaotan Lake, northern Jiangxi Province [J]. Progress in Geography, 2017, 36(11): 1413-1422. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.010
[48] 吴立, 朱诚, 李冰, 等. 江汉平原石家河谭家岭遗址新石器时代环境考古[J]. 地球环境学报, 2016, 7(2):140-152 doi: 10.7515/JEE201602004
WU Li, ZHU Cheng, LI Bing, et al. Environmental archaeology of the Tanjialing Neolithic Site in the Shijiahe Ancient City, the Jianghan Plain of Central China [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2016, 7(2): 140-152. doi: 10.7515/JEE201602004
[49] 朱诚, 李兰, 林留根, 等. 江苏全新世灾变事件考古地层学若干问题探讨[J]. 地层学杂志, 2009, 33(4):413-419 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2009.04.009
ZHU Cheng, LI Lan, LIN Liugen, et al. Catastrophic events in archaeological stratigraphy during the Holocene in Jiangsu province [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2009, 33(4): 413-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2009.04.009
[50] 朱诚, 郑朝贵, 马春梅, 等. 长江三峡库区中坝遗址地层古洪水沉积判别研究[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(21):2493-2504 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.20.011
ZHU Cheng, ZHENG Chaogui, MA Chunmei, et al. Identifying paleoflood deposits archived in Zhongba Site, the Three Gorges reservoir region of the Yangtze River, China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(21): 2493-2504. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.20.011
[51] 王浩宇, 张玉柱, 黄春长, 等. 洛阳盆地龙山文化晚期大洪水地球化学特征及其社会影响研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2021, 45(2):168-179 doi: 10.19839/j.cnki.dcxzz.2021.0013
WANG Haoyu, ZHANG Yuzhu, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and social influence of paleoflood events in the late Longshan culture within the Luoyang Basin [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2021, 45(2): 168-179. doi: 10.19839/j.cnki.dcxzz.2021.0013
[52] 李中轩, 孙艳丽, 徐永新, 等. 颍河上游的地貌变迁对新石器晚期聚落分布的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2):174-182 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018122501
LI Zhongxuan, SUN Yanli, XU Yongxin, et al. Impact of fluvial landform changes on the Neolithic settlement distribution in the upper reaches of the Yinghe River [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 174-182. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018122501
[53] 吴立, 朱诚, 李枫, 等. 江汉平原钟桥遗址地层揭示的史前洪水事件[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(7):1149-1164 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201507011
WU Li, ZHU Cheng, LI Feng, et al. Prehistoric flood events recorded at the Zhongqiao Neolithic Site in the Jianghan Plain, Central China [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(7): 1149-1164. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201507011
-



 下载:
下载: