Assessment on geological condition for carbon dioxide sequestration and source-sink matching in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
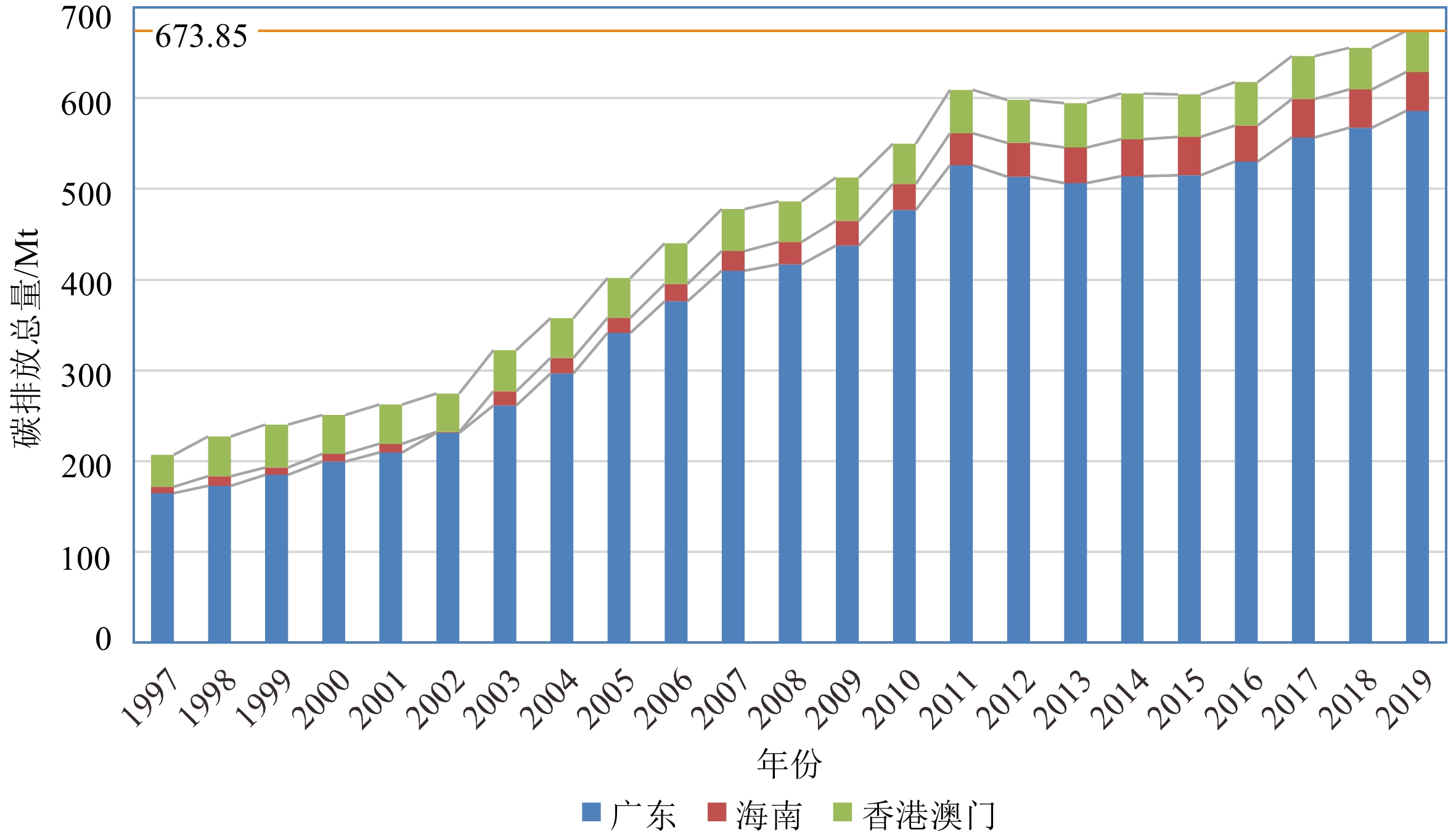
当今全球气候突变,极端天气频发,温室气体过量排放造成的温室效应是其形成原因之一。我国正值经济转型,又受限于能源结构,继续大量使用化石能源是不可避免的。通过收集有关珠江口盆地的公开地质资料,与前人所提出的E级和D级碳封存适宜性评价指标对比,得知珠江口盆地具有巨大的碳封存潜力和较高的适宜性。分析了粤港澳琼四地区碳排放情况及变化趋势,认为四地区碳排放源与珠江口盆地碳封存区构成良好的源汇匹配关系,在珠江口盆地实施碳封存,不仅可以使四地区达成碳中和,而且可以使盆地内油气田开发最大效益化。因此,对珠江口盆地碳封存地质条件及源汇匹配性的研究具有重要意义。
Abstract:Abrupt global climate change and extreme weather occur frequently in recent decades, for which the greenhouse effect caused by excessive greenhouse gas emission shall be one of the responsible reasons. China is in the midst of economic transformation but is constrained by the energy structure, thus continuous use of fossil energy in large quantities is inevitable in the foreseeable future. Available geological data about the Pearl River Mouth Basin were collected and the evaluation indicators of carbon sequestration suitability in the E and D levels proposed by previous researchers were compared. Results show that the Pearl River Mouth Basin has a huge carbon sequestration potential and high suitability. Moreover, the carbon emission status quo and variation trend in Guangdong, Hong Kong, Macao, and Hainan were analyzed, by which we believed that the carbon emission sources in the four regions formed a good source-sink matching relationship with the carbon sequestration area in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. The implementation of carbon sequestration in the Pearl River Mouth Basin can not only achieve carbon neutrality in the four regions, but also maximize the benefits of oil and gas field development of the basin. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the geological conditions and source-sink matching of carbon sequestration in the Pearl River Mouth Basin.
-

-
表 1 珠江口盆地碳封存地质条件对比[38]
Table 1. Comparison of geological conditions for carbon sequestration in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[38]
碳封存地质条件 研究区 适宜 较适宜 一般适宜 较不适宜 不适宜 地
质
安
全
性区域
地壳
稳定
性地震动峰值加速度 <0.05g <0.05g 0.05g (0.05~0.10)g (0.10~0.15)g ≥0.20g 历史地震震级(M) 北部隆起带1次M6.75级 历史地震围空区 M<5(1/2) 5(1/2)<M<6.0 6.0<M<7.0 M>7(1/2) 活动断裂发育情况 远离活动断裂带 远离活动断裂带 距活动断裂近但
未通过有新近纪断裂通过但在
全新世活动不明显有规模较小、活动
较弱断裂通过位于强烈的活动断裂带 区域性盖层特征 主力盖层埋深(d)/m 珠江组平均埋深1179 800~1200 1200~1700 1700~3500 3500以上 800以下 盖层岩性 海相泥岩 膏岩、泥岩、
钙质泥岩含砂泥岩、
含粉砂泥岩粉砂质泥岩、
砂质泥岩泥质粉砂岩、
泥质砂岩裂缝发育灰岩、
粗碎屑砂岩主力盖层的单层厚度/m 400~800 >100 100~50 50~30 30~10 <10 盖层分布的连续性 连续,稳定 连续,稳定 较连续,较稳定 连续性中等,较稳定 连续性较差,
较不稳定连续性差,不稳定 盖层渗透率/10−3μm2 0.002~0.2,平均<0.02 <0.0001 0.0001~0.001 0.001~0.01 0.01~0.1 >0.1 地热地质条件 地热流值/(mW·m−2) 平均值69.9 30~50 50~70 70~90 90~150 >150 地温梯度/(℃/100 m) 2.9~11.3/4.2 <2.0冷盆地 2.0~3.0次冷盆地 3.0~4.0中等 4.0~5.0次热盆地 >5.0热盆 海底温度/℃ 2.5~15,平均8.2 ≤2 2~3 3~10 10~25 >25 沉积盆地性质 张扭性 压性 压扭性 扭性 张扭性 张性 水动力作用 水力封闭和封堵作用 水力封闭作用 水力封堵作用 水力运移逸散作用 火山活动 较弱 弱 较弱 中等 强 较强 储
存
规
模储层属性 沉积盆地面积/km2 200000 >10000 10000~5000 5000~1000 1000~500 <500 沉积地层厚度/m 7000~14000 ≥3500 3500~1600 1600~800 适宜区带构造单元面积/104 km2 珠一坳陷4 ≥5000 5000~1000 1000~500 珠三坳陷3.6 珠二坳陷3 东沙隆起3 储层厚度/m 韩江组308~370
珠海组450~800>80 50~80 20~50 10~20 <10 储集层岩性 砂岩 碎屑岩 碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩混合 碳酸盐岩 岩浆岩、变质岩、岩丘等特殊储层 无 储层砂厚比/% 49.9~54.2 >60 60~40 40~20 20~10 <10 储层孔隙度/% 15~31 ≥25 25~20 20~10 10~5 <5 储层渗透率/10−3μm2 珠江组1.71
珠海组4~85≥50 50~10 10~1 1~0.1 <0.1 储存潜力 资源潜力(油气规模) 大,D级29.1×108t 大 较大 一般 较小 小 E级预测潜力/108t 3080 >1000 1000~100 100~5 5~0.5 <0.5 单位面积E级预测潜力/(104 t·km−2) 152 >500 500~100 100~50 50~5 <5 D级推定潜力/108t 珠一坳陷1030 >50 50~25 25~0.5 0.5~0.02 <0.02 珠三坳陷153 珠二坳陷466 东沙坳陷417 单位面积D级预测潜力/(104 t·km−2) 珠一坳陷257.5 >20 20~10 10~5 5~0.1 <0.1 珠三坳陷42.5 珠二坳陷155.3 东沙坳陷139.0 经济适宜性和社会环境风险 勘探开发程度 开发后期 开发中 勘探程度高 勘探程度一般 勘探程度低 未勘探过 数据支持情况 499口钻井、69个油藏,勘探开发数据详实 数据充分可靠 数据较充分较可靠 数据一般充分一般可靠 数据不太充分 数据不充分 碳源密度 北部沿岸排放源
很多高 较高 中 低 零 离岸距离/km 150~300 0~50 50~100 100~200 200~500 >500 海水深度/m 0~200,平均93 0~50 50~100 100~200 200~500 >500 土地利用现状 未利用土地 沙漠等未利用土地 牧草地 林地 耕地、园地 居民点、工矿交通用地、水域 人口密度/(人/km2) 无人区 ≤25
极端稀疏区25~50
绝对稀疏区50~100
相对稀疏区100~200
一般过渡区≥200
集聚区基础工程条件 油气工程条件成熟 大规模 较多 一般 较少 无 -
[1] Shan Y L, Liu J H, Liu Z, et al. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 184: 742-750. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.073
[2] Shan Y L, Guan D B, Zheng H R, et al. China CO2 emission accounts 1997-2015 [J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5: 170201. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017.201
[3] Shan Y L, Huang Q, Guan D B, et al. China CO2 emission accounts 2016-2017 [J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(1): 54. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0393-y
[4] Guan Y R, Shan Y L, Huang Q, et al. Assessment to China’s recent emission pattern shifts [J]. Earth’s Future, 2021, 9(11): e2021EF002241.
[5] 李晓江, 何舸, 罗彦, 等. 粤港澳大湾区碳排放空间特征与碳中和策略[J]. 城市规划学刊, 2022(1):27-34 doi: 10.16361/j.upf.202201004
LI Xiaojiang, HE Ge, LUO Yan, et al. Spatial characteristics of carbon emissions and carbon neutralization strategies for Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area [J]. Urban Planning Forum, 2022(1): 27-34. doi: 10.16361/j.upf.202201004
[6] Wang J, Feng L, Palmer P I, et al. Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data [J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7831): 720-723. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2849-9
[7] Zhou D, Zhao Z X, Liao J, et al. A preliminary assessment on CO2 storage capacity in the Pearl River Mouth Basin offshore Guangdong, China [J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2011, 5(2): 308-317. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.09.011
[8] 刘雪雁. 南海北部珠江口盆地惠州21-1油田CO2-EOR与碳封存潜力评价研究[D]. 中国科学院大学
LIU Xueyan. Research on CO2-EOR and carbon sequestration potential evaluation of Huizhou 21-1 Oilfield in the the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[D]. University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[9] 白冰, 李小春, 刘延锋, 等. 中国CO2集中排放源调查及其分布特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(S1):2918-2923
BAI Bing, LI Xiaochun, LIU Yanfeng, et al. Preliminary study on CO2 industrial point sources and their distribution in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(S1): 2918-2923.
[10] 彭佳龙, 陈广浩, 周蒂, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州21-1构造二氧化碳地质封存数值模拟[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(9):59-70 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2013.09.007
PENG Jialong, CHEN Guanghao, ZHOU Di, et al. Numerical simulation for offshore storage of carbon dioxide in Huizhou 21-1 trap, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(9): 59-70. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2013.09.007
[11] 姚伯初. 南海新生代的构造演化与沉积盆地[J]. 南海地质研究(十), 1998: 1-17
YAO Bochu. The tectonic evolution and sedimentary basins of South China Sea in Cenozoic[J]. Geological Research of the South China Sea (Memoir 10), 1998: 1-17.
[12] 冯志强, 缪宛岑. 南海珠江口盆地地质构造特征和含油气远景[J]. 石油实验地质, 1982, 4(1):19-25 doi: 10.11781/sysydz198201019
FENG Zhiqiang, MIAO Wancen. The geological structures and the oil and gas potential of the Zhujiangkou Basin, the South China Sea [J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1982, 4(1): 19-25. doi: 10.11781/sysydz198201019
[13] 杜家元, 施和生, 丁琳, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)地层岩性油气藏勘探有利区域分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):30-36,55
DU Jiayuan, SHI Hesheng, DING Lin, et al. An analysis of favorable exploration areas for stratigraphic-lithologic hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 30-36,55.
[14] 王善书. 珠江口盆地地质构造的基本特征[J]. 石油学报, 1982(S1):1-13 doi: 10.7623/syxb1982S1001
WANG Shanshu. Basic geological structural features of the basin at the mouth of Pearl River [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1982(S1): 1-13. doi: 10.7623/syxb1982S1001
[15] 钟建强. 珠江口盆地的构造特征与盆地演化[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1994, 94(1):1-8 doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.1994.01.001
ZHONG Jianqiang. Characteristics of geologic structure and basin evolution in Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 1994, 94(1): 1-8. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.1994.01.001
[16] 崔莎莎, 何家雄, 陈胜红, 等. 珠江口盆地发育演化特征及其油气成藏地质条件[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(3):384-391
CUI Shasha, HE Jiaxiong, CHEN Shenghong, et al. Development characteristics of pearl river mouth basin and its geological conditions for oil and gas accumulation [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(3): 384-391.
[17] 陈建文, 梁杰, 张银国, 等. 中国海域油气资源潜力分析与黄东海海域油气资源调查进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6):1-29 doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019112001
CHEN Jianwen, LIANG Jie, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Regional evaluation of oil and gas resources in offshore China and exploration of marine Paleo-Mesozoic oil and gas in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6): 1-29. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019112001
[18] 詹诚, 卢绍平, 方鹏高. 汇聚背景下的多幕裂陷作用及其迁移机制: 以南海北部珠江口盆地为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4):307-318
ZHAN Cheng, LU Shaoping, FANG Penggao. Multiphase rift and migration mechanism in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(4): 307-318.
[19] 王宁, 张铜耀, 明承栋, 等. 珠江口盆地东部珠一坳陷古近系不同类型烃源岩和原油热裂解生气特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(8):67-76 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2022.044
WANG Ning, ZHANG Tongyao, MING Chengdong, et al. Different types of Paleogene source rocks and characteristics of pyrolysis gas generation of crude oil in Zhuyi Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(8): 67-76. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2022.044
[20] 刘富强. 利用卫星重力资料研究珠江口盆地北部边界及构造区划[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2014
LIU Fuqiang. Study on the northern border and tectonic division of Pearl River Mouth Basin By using satellite gravity data[D]. Master Dissertation of Chang’an University, 2014.
[21] 贺勇, 邱欣卫, 雷永昌, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰13东洼新生代构造演化与油气成藏特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(1):74-82 doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230107
HE Yong, QIU Xinwei, LEI Yongchang, et al. Tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of Cenozoic in eastern Lufeng 13 subsag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(1): 74-82. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230107
[22] 吕炳全, 李平鲁, 简馨秀. 珠江口盆地构造应力场与油气聚集[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1991, 5(1):25-37
LÜ Bingquan, LI Pinglu, JIAN Xinxiu. Tectonic stress field & oil & gas accumulation of pearl river Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1991, 5(1): 25-37.
[23] 陈长民. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003
CHEN Changmin. Formation Conditions of Tertiary Oil and Gas Reservoirs in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (East)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003.
[24] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 18306-2015 中国地震动参数区划图[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB 18306-2015 Seismic ground motion parameters zonation map of China[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[25] 米立军, 袁玉松, 张功成, 等. 南海北部深水区地热特征及其成因[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(1):27-32 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.01.005
MI Lijun, YUAN Yusong, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Characteristics and genesis of geothermal field in deep-water area of the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(1): 27-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.01.005
[26] 胡圣标, 龙祖烈, 朱俊章, 等. 珠江口盆地地温场特征及构造-热演化[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1):178-187 doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1015
HU Shengbiao, LONG Zulie, ZHU Junzhang, et al. Characteristics of geothermal field and the tectonic-thermal evolution in Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 178-187. doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1015
[27] 唐晓音, 黄少鹏, 张功成, 等. 南海北部陆缘珠江口盆地岩石圈热结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(9):3749-3759
TANG Xiaoyin, HUANG Shaopeng, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Lithospheric thermal structure of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(9): 3749-3759.
[28] 唐晓音, 黄少鹏, 杨树春, 等. 南海珠江口盆地钻井BHT温度校正及现今地温场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(8):2911-2921
TANG Xiaoyin, HUANG Shaopeng, YANG Shuchun, et al. Correcting on logging-derived temperatures of the Pearl River Mouth Basin and characteristics of its present temperature field [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(8): 2911-2921.
[29] 唐晓音, 胡圣标, 张功成, 等. 珠江口盆地大地热流特征及其与热岩石圈厚度的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(6):1857-1867
TANG Xiaoyin, HU Shengbiao, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Characteristic of surface heat flow in the Pearl River Mouth Basin and its relationship with thermal lithosphere thickness [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(6): 1857-1867.
[30] 饶春涛, 李平鲁. 珠江口盆地热流研究[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1991, 5(6):7-18
RAO Chuntao, LI Pinglu. Study of heat flow in pearl river Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1991, 5(6): 7-18.
[31] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴. 珠江口盆地新生代岩浆活动与盆地演化, 油气聚集的关系[J]. 广东地质, 1994, 9(2):23-24
LI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian. The relationship between Cenozoic magmatic activity and basin evolution, oil and gas accumulation in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Guangdong Geology, 1994, 9(2): 23-24.
[32] 《中国油气田开发志》总编纂委员会. 中国油气田开发志(卷二十七): 南海东部油气区卷[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011
China Oil and Gas Field Development Journal, General Compilation Committee. China Oil and Gas Field Development Journal, Volume 27, East South China Sea Oil and Gas Region Volume[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011.
[33] 《中国油气田开发志》总编纂委员会. 中国油气田开发志: 南海东部油气区油气田卷[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011
Editorial Committee of China's Oil and Gas Field Development Journal. China's Oil and Gas Field Development Journal: Oil and Gas Fields in the Eastern South China Sea Oil and Gas Region Volume[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011.
[34] 叶建平, 武强, 王子和. 水文地质条件对煤层气赋存的控制作用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2001, 26(5):459-462 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.05.003
YE Jianping, WU Qiang, WANG Zihe. Controlled characteristics of hydrogeological conditions on the coalbed methane migration and accumulation [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2001, 26(5): 459-462. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.05.003
[35] Schrag D P. Storage of carbon dioxide in offshore sediments [J]. Science, 2009, 325(5948): 1658-1659. doi: 10.1126/science.1175750
[36] 郭建强, 文冬光, 张森琦, 等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存适宜性评价与示范工程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014
GUO Jianqiang, WEN Dongguang, ZHANG Senqi, et al. China's Carbon Dioxide Geological Storage Suitability Evaluation and Demonstration Project[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2014.
[37] 陈建亮, 施和生, 舒誉, 等. 测井盖层评价方法在珠一坳陷的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2007, 19(3):157-161 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.03.004
CHEN Jianliang, SHI Hesheng, SHU Yu, et al. The application of seal evaluation method with log data in Zhu I depression, Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2007, 19(3): 157-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2007.03.004
[38] 郭建强. 全国二氧化碳地质储存潜力评价与示范工程总成果报告[R]. 中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心, 2013
GUO Jianqiang. Report on the overall results of the national carbon dioxide geological storage potential evaluation and demonstration project[R]. Hydrogeological Environmental Geological Survey Center of the China Geological Survey, 2013.
[39] 朱俊章, 朱明, 史玉玲, 等. 珠一坳陷油气成藏组合划分及有利成藏组合预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(5):67-75 doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.072
ZHU Junzhang, ZHU Ming, SHI Yuling, et al. Division of hydrocarbon accumulation assemblage and prediction of favorable accumulation assemblage in Zhu I Depression [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(5): 67-75. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.072
[40] 廖成基, 廖明光. 珠江口盆地珠三坳陷地层及沉积演化特征分析[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(2):232,242 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.02.154
LIAO Chengji, LIAO Mingguang. Analysis on the strata and sedimentary evolution characteristics of Zhusan depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2020, 46(2): 232,242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.02.154
[41] 吕彩丽, 张功成, 杨东升. 珠江口盆地珠二坳陷文昌组构造差异性与动力学成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(6):333-341 doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2016-11-56
LÜ Caili, ZHANG Gongcheng, YANG Dongsheng. Differential structure and dynamic mechanism of Wenchang Formation in the Zhu II depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(6): 333-341. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2016-11-56
[42] 曾清波, 张功成, 廖宗宝, 等. 珠江口盆地东沙隆起早中新世台缘带特征及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2015, 20(1):17-24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.01.003
ZENG Qingbo, ZHANG Gongcheng, LIAO Zongbao, et al. Geological feature and prospecting potential of early Miocene platform margin belt in Dongsha Uplift, Zhujiangkou Basin [J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2015, 20(1): 17-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.01.003
[43] 霍传林. 我国近海二氧化碳海底封存潜力评估和封存区域研究[D]. 海事大学博士学位论文, 2014
HUO Chuanlin. Study on the potential evaluation and the storage areas of the carbon dioxide seabed storage in offshore China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Maritime University, 2014.
[44] 周泽兴. 火电厂排放CO2的分离回收和固定技术的研究开发现状[J]. 环境科学进展, 1993, 1(1):56-73
ZHOU Zexing. Present R&D status of technological development for CO2 capture and fixation from thermal power plant flue gas [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1993, 1(1): 56-73.
-




 下载:
下载: