Geochemical characteristics of sediment pore water in Haima area of the South China Sea: An indication of cold seeps
-
摘要:
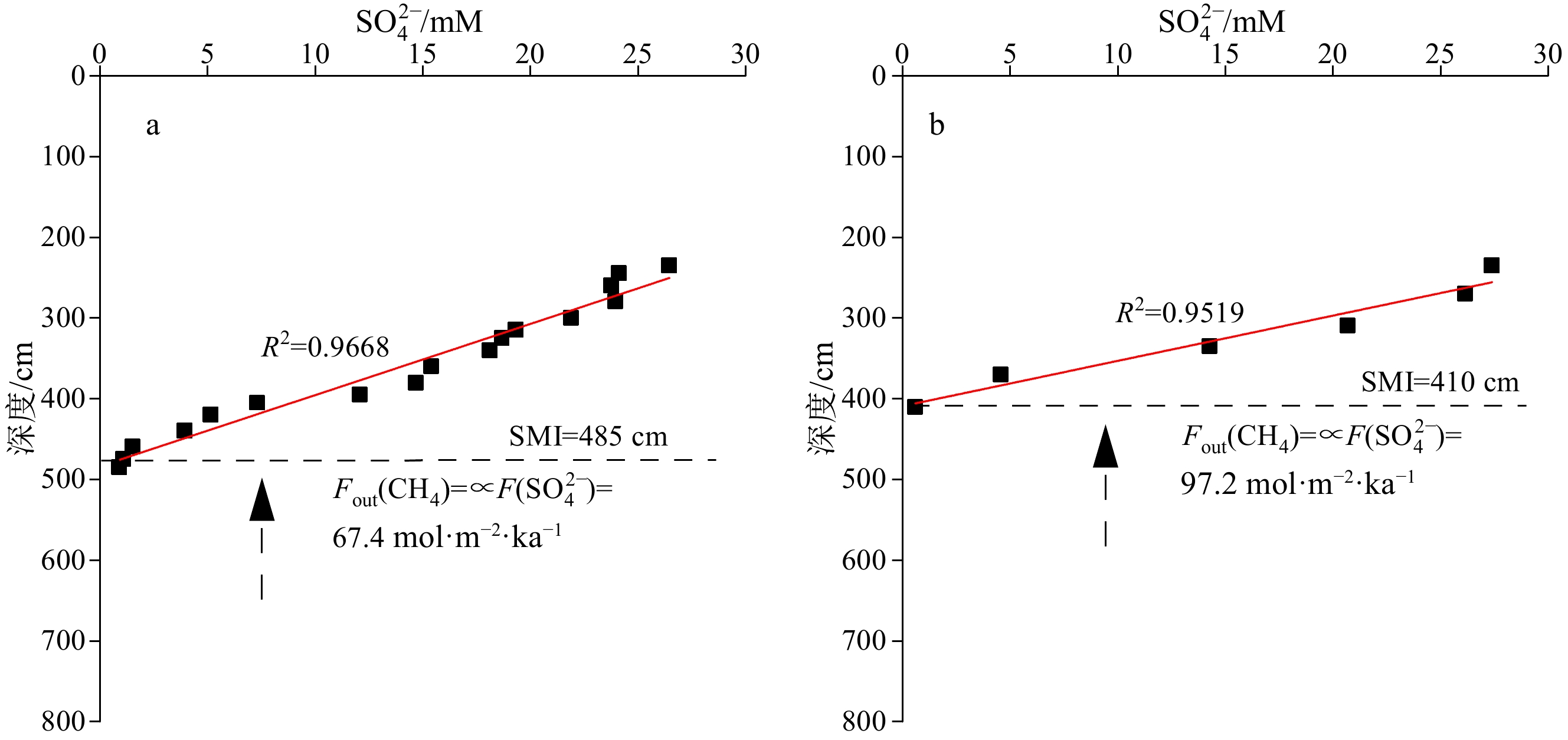
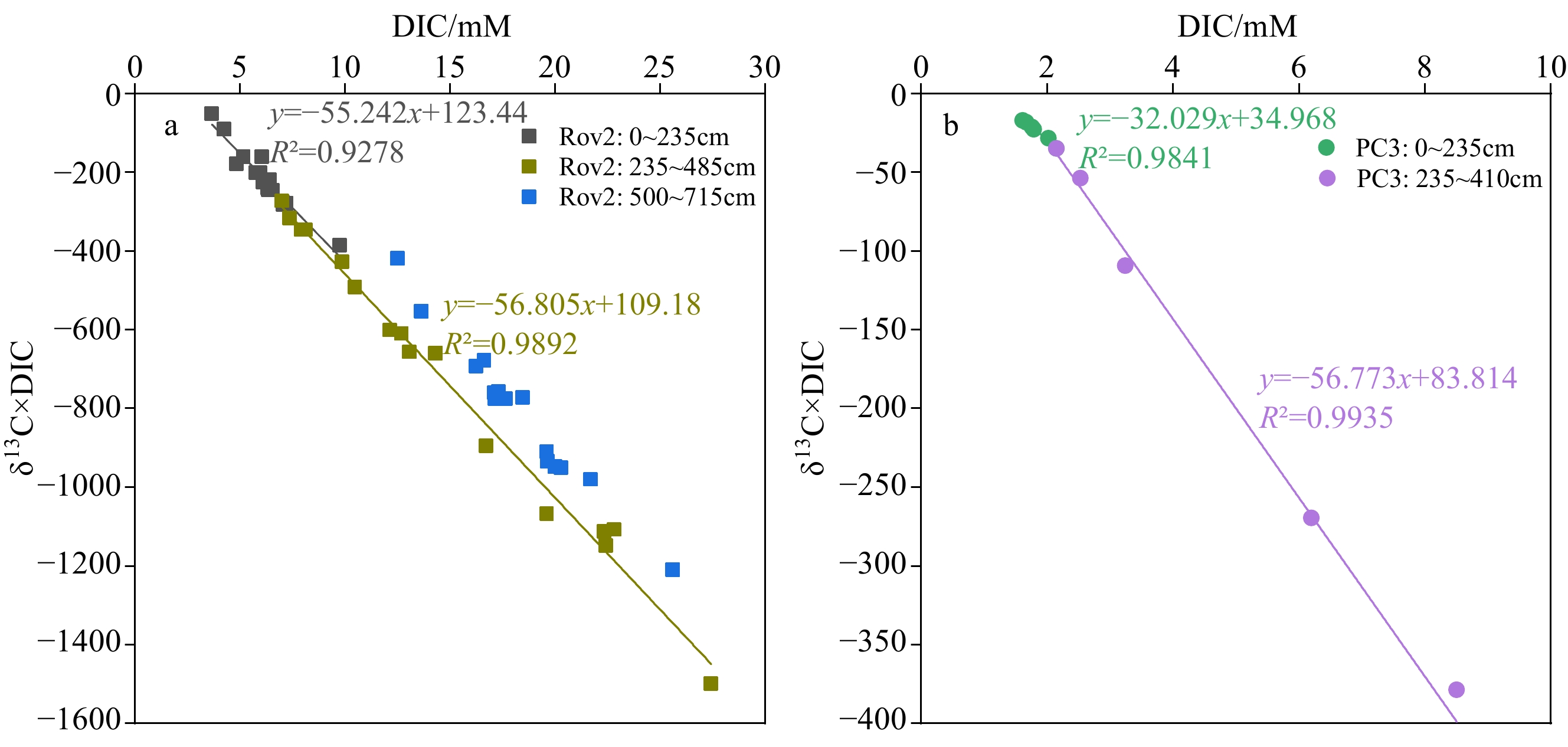
海马冷泉位于南海琼东南海域,是南海迄今发现的两个活动冷泉之一。我们对海马冷泉Rov2和PC3站位两个活塞重力柱沉积物孔隙水的阴阳离子、溶解无机碳(DIC)及其碳同位素组成和Sr、Ba含量等进行了分析。结果表明,两个站位孔隙水DIC含量(Rov2和PC3最大DIC含量分别为27.4 、8.5 mM)和δ13CDIC(Rov2和PC3站位最低值分别为−54.63‰和−48.93‰)具有明显的镜像关系。结合孔隙水硫酸盐浓度的变化特征,Rov2和PC3站位的硫酸盐-甲烷界面(SMI)分别位于约485和410 cm。通过模拟估算,Rov2和PC3站位向上甲烷通量分别为67.4和97.2 mol·m−2·ka−1,较浅的SMI深度与相对较高的甲烷通量相一致。SMI附近极低的孔隙水δ13CDIC值指示了AOM作用的发生及其对DIC的贡献。在Rov2站位,自生碳酸盐矿物以高镁方解石为主,阳离子Ca2+、Mg2+和Sr2+含量随深度增加并表现出与SO42−阴离子含量相似的变化特征。在SMI附近,随着SO42−的消耗、有机质的矿化将大量的Ba2+和PO43−释放进入孔隙水。因此,冷泉孔隙水地球化学特征的变化能帮助我们有效识别渗漏活动过程,对AOM作用下物质的迁移与转化具有重要的指示意义。
Abstract:The Haima cold seeps are located in the southeastern part of Qiongdongnan Basin, which is one of the two active cold seeps found in the South China Sea. We analyzed the contents of anions and cations, dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and its carbon isotopic composition, and Sr and Ba contents of sediment pore water in two piston gravity columns at the Rov2 and PC3 cores in Haima Cold Seeps. Results show that the DIC contents and δ13CDIC values of pore water in the two cores had a significant "mirror" relationship. With the increase of depth, the DIC contents of the two cores gradually increased (Maximum DIC content of Rov2 and PC3: 27.4 and 8.5 mM, respectively). In contrast, the δ13CDIC values had a negative excursion (Minimum values for the two cores: −54.63‰ and −48.93‰, respectively). Combined with the sulfate depth profile characteristics of pore water, the sulfate-methane interface (SMI) in Rov2 and PC3 cores was located at ~485 and ~410 cm, respectively. The upward methane fluxes in Rov2 and PC3 cores were estimated to be 67.4 and 97.2 mol m−2 ka−1, respectively. The very low δ13CDIC values in pore water near SMI are indicative of the occurrence of AOM (anaerobic oxidation of methane) interaction and its contribution to DIC. In Rov2 core, authigenic carbonate minerals are dominated by high-Mg calcite, and the Ca2+, Mg2+ and Sr2+ showed similar trends to those of SO42−. Near the SMI, with the depletion of SO42−, the mineralization of organic matter released large amounts of Ba2+ and PO43− into the pore water. The geochemical characteristics of pore water could help us effectively identify the early diagenesis in seepage activity area, and are indicative of migration and transformation of materials under the influence of AOM.
-
Key words:
- anaerobic oxidation of methane /
- cold seeps /
- pore water /
- South China Sea
-

-
[1] Campbell K A. Hydrocarbon seep and hydrothermal vent paleoenvironments and paleontology: past developments and future research directions [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 232(2-4): 362-407. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.018
[2] Peckmann J, Thiel V. Carbon cycling at ancient methane–seeps [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 205(3-4): 443-467. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.025
[3] 陈多福, 陈先沛, 陈光谦. 冷泉流体沉积碳酸盐岩的地质地球化学特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(1):34-40
CHEN Duofu, CHEN Xianpei, CHEN Guangqian. Geology and geochemistry of cold seepage and venting-related carbonates [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(1): 34-40.
[4] Dickens G R, O’Neil J R, Rea D K, et al. Dissociation of oceanic methane hydrate as a cause of the carbon isotope excursion at the end of the Paleocene [J]. Paleoceanography, 1995, 10(6): 965-971. doi: 10.1029/95PA02087
[5] Kastner M, Claypool G, Robertson G. Geochemical constraints on the origin of the pore fluids and gas hydrate distribution at Atwater Valley and Keathley Canyon, northern Gulf of Mexico [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(9): 860-872. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.01.022
[6] Cicerone R J, Oremland R S. Biogeochemical aspects of atmospheric methane [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1988, 2(4): 299-327. doi: 10.1029/GB002i004p00299
[7] Niu M Y, Liang W Y, Wang F P. Methane biotransformation in the ocean and its effects on climate change: a review [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(12): 1697-1713. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9299-4
[8] Reeburgh W S. Oceanic methane biogeochemistry [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(2): 486-513. doi: 10.1021/cr050362v
[9] Regnier P, Dale A W, Arndt S, et al. Quantitative analysis of anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM) in marine sediments: a modeling perspective [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 106(1-2): 105-130. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.01.002
[10] Joye S B, Boetius A, Orcutt B N, et al. The anaerobic oxidation of methane and sulfate reduction in sediments from Gulf of Mexico cold seeps [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 205(3-4): 219-238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.019
[11] Hensen C, Zabel M, Pfeifer K, et al. Control of sulfate pore-water profiles by sedimentary events and the significance of anaerobic oxidation of methane for the burial of sulfur in marine sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(14): 2631-2647. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00199-6
[12] Chen Y F, Ussler III W, Haflidason H, et al. Sources of methane inferred from pore-water δ13C of dissolved inorganic carbon in Pockmark G11, offshore Mid-Norway [J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 275(3-4): 127-138. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.04.013
[13] Malinverno A, Pohlman J W. Modeling sulfate reduction in methane hydrate-bearing continental margin sediments: does a sulfate-methane transition require anaerobic oxidation of methane? [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(7): Q07006.
[14] Luo M, Chen L Y, Wang S H, et al. Pockmark activity inferred from pore water geochemistry in shallow sediments of the pockmark field in southwestern Xisha Uplift, northwestern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48: 247-259. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.08.018
[15] Hu Y, Luo M, Chen L Y, et al. Methane source linked to gas hydrate system at hydrate drilling areas of the South China Sea: porewater geochemistry and numerical model constraints [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.028
[16] Masuzawa T, Handa N, Kitagawa H, et al. Sulfate reduction using methane in sediments beneath a bathyal "cold seep" giant clam community off Hatsushima Island, Sagami Bay, Japan [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1992, 110(1-4): 39-50. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(92)90037-V
[17] Borowski W S, Paull C K, Ussler III W. Marine pore-water sulfate profiles indicate in situ methane flux from underlying gas hydrate [J]. Geology, 1996, 24(7): 655-658. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0655:MPWSPI>2.3.CO;2
[18] Dickens G R. Sulfate profiles and barium fronts in sediment on the Blake Ridge: present and past methane fluxes through a large gas hydrate reservoir [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(4): 529-543. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00556-1
[19] Wang X D, Li N, Feng D, et al. Using chemical compositions of sediments to constrain methane seepage dynamics: a case study from Haima cold seeps of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.11.011
[20] Boetius A, Ravenschlag K, Schubert C J, et al. A marine microbial consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane [J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6804): 623-626. doi: 10.1038/35036572
[21] Peckmann J, Reimer A, Luth U, et al. Methane-derived carbonates and authigenic pyrite from the northwestern Black Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(1-2): 129-150. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00128-1
[22] Haese R R, Meile C, Van Cappellen P, et al. Carbon geochemistry of cold seeps: methane fluxes and transformation in sediments from Kazan mud volcano, eastern Mediterranean Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 212(3-4): 361-375. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00226-7
[23] Feng D, Roberts H H. Initial results of comparing cold-seep carbonates from mussel- and tubeworm-associated environments at Atwater Valley lease block 340, northern Gulf of Mexico [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(21-23): 2030-2039. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2010.05.004
[24] Chen D F, Cathles III L M, Roberts H H. The geochemical signatures of variable gas venting at gas hydrate sites [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(3): 317-326. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.12.003
[25] Yang T, Jiang S Y, Yang J H, et al. Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and its carbon isotopic composition in sediment pore waters from the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2008, 64(2): 303-310. doi: 10.1007/s10872-008-0024-2
[26] Ussler III W, Paull C K. Rates of anaerobic oxidation of methane and authigenic carbonate mineralization in methane-rich deep-sea sediments inferred from models and geochemical profiles [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 266(3-4): 271-287. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.10.056
[27] Treude T, Niggemann J, Kallmeyer J, et al. Anaerobic oxidation of methane and sulfate reduction along the Chilean continental margin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(11): 2767-2779. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.002
[28] Snyder G T, Hiruta A, Matsumoto R, et al. Pore water profiles and authigenic mineralization in shallow marine sediments above the methane-charged system on Umitaka Spur, Japan Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54(11-13): 1216-1239. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.04.001
[29] Nöthen K, Kasten S. Reconstructing changes in seep activity by means of pore water and solid phase Sr/Ca and Mg/Ca ratios in pockmark sediments of the Northern Congo Fan [J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 287(1-4): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.008
[30] 邬黛黛, 吴能友, 付少英, 等. 南海北部东沙海域水合物区浅表层沉积物的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(5):41-51
WU Daidai, WU Nengyou, FU Shaoying, et al. Geochemical characteristics of shallow sediments in the gas hydrate distribution area of Dongsha, the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(5): 41-51.
[31] Sassen R, Roberts H H, Carney R, et al. Free hydrocarbon gas, gas hydrate, and authigenic minerals in chemosynthetic communities of the northern Gulf of Mexico continental slope: relation to microbial processes [J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 205(3-4): 195-217. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.032
[32] Yang T, Jiang S Y, Ge L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of pore water in shallow sediments from Shenhu area of South China Sea and their significance for gas hydrate occurrence [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(8): 752-760. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0312-2
[33] 杨涛, 蒋少涌, 杨竞红, 等. 孔隙水中NH4+和HPO42-浓度异常: 一种潜在的天然气水合物地球化学勘查新指标[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(1):55-60
YANG Tao, JIANG Shaoyong, YANG Jinghong, et al. Anomaly of ammonia and phosphate concentration in pore waters: a potential geochemical indicator for prospecting marine gas hydrate [J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(1): 55-60.
[34] Torres M E, Brumsack H J, Bohrmann G, et al. Barite fronts in continental margin sediments: a new look at barium remobilization in the zone of sulfate reduction and formation of heavy barites in diagenetic fronts [J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 127(1-3): 125-139. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(95)00090-9
[35] Castellini D G, Dickens G R, Snyder G T, et al. Barium cycling in shallow sediment above active mud volcanoes in the Gulf of Mexico [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 226(1-2): 1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.08.008
[36] McQuay E L, Torres M E, Collier R W, et al. Contribution of cold seep barite to the barium geochemical budget of a marginal basin [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2008, 55(6): 801-811. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2008.03.001
[37] Torres M E, McManus J, Huh C A. Fluid seepage along the San Clemente Fault scarp: basin-wide impact on barium cycling [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 203(1): 181-194. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00800-2
[38] Riedinger N, Kasten S, Gröger J, et al. Active and buried authigenic barite fronts in sediments from the Eastern Cape Basin [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 876-887. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.10.032
[39] 赵静, 梁前勇, 尉建功, 等. 南海北部陆坡西部海域“海马”冷泉甲烷渗漏及其海底表征[J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49(1):108-118
ZHAO Jing, LIANG Qianyong, WEI Jiangong, et al. Seafloor geology and geochemistry characteristic of methane seepage of the “Haima” cold seep, northwestern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Geochimica, 2020, 49(1): 108-118.
[40] Lin Q, Wang J S, Taladay K, et al. Coupled pyrite concentration and sulfur isotopic insight into the paleo sulfate–methane transition zone (SMTZ) in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 115: 547-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.001
[41] 吴庐山, 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部琼东南海域HQ-48PC站位地球化学特征及对天然气水合物的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3):534-544
WU Lushan, YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediments at Site HQ-48PC in Qiongdongnan Area, the north of the South China Sea, and their implication for gas hydrates [J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 534-544.
[42] 孙甜甜, 邬黛黛, 潘梦迪, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地浅表层沉积物的地球化学特征及对沉积环境的指示[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4):70-80
SUN Tiantian, WU Daidai, PAN Mengdi, et al. Geochemical characteristics of surface sediments in the southern Qiongdongnan Basin of the northern South China Sea and its implication for sedimentary environment [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 70-80.
[43] Wang J L, Wu S G, Kong X, et al. Subsurface fluid flow at an active cold seep area in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.06.001
[44] Wang X, Wu S, Yuan S, et al. Geophysical signatures associated with fluid flow and gas hydrate occurrence in a tectonically quiescent sequence, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea [J]. Geofluids, 2010, 10(3): 351-368. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00292.x
[45] Feng D, Chen D F. Authigenic carbonates from an active cold seep of the northern South China Sea: new insights into fluid sources and past seepage activity [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.02.003
[46] Feng D, Qiu J W, Hu Y, et al. Cold seep systems in the South China Sea: an overview [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 3-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.09.021
[47] 何家雄, 夏斌, 孙东山, 等. 琼东南盆地油气成藏组合、运聚规律与勘探方向分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(1):53-58 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.012
HE Jiaxiong, XIA Bin, SUN Dongshan, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation, migration and play targets in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(1): 53-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.01.012
[48] 邬黛黛. 南海天然气水合物的早期成岩作用和地球化学特性研究[D]. 浙江大学博士学位论文, 2008
WU Daidai. Early diagenesis records and geochemical characteristics of gas hydrate in the South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Zhejiang University, 2008.
[49] Zhu W L, Huang B J, Mi L J, et al. Geochemistry, origin, and deep-water exploration potential of natural gases in the Pearl River Mouth and Qiongdongnan basins, South China Sea [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(6): 741-761. doi: 10.1306/02170908099
[50] 张启明, 胡忠良. 莺-琼盆地高温高压环境及油气运移机制[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1992, 6(1):1-9
ZHANG Qiming, HU Zhongliang. Hot, geopressured Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, its hydrocarbon migration [J]. China Offshore oil and Gas (Geology), 1992, 6(1): 1-9.
[51] 刘建章, 王存武. 莺-琼盆地热流体及油气地质意义[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2004, 27(1):12-15,7
LIU Jianzhang, WANG Cunwu. Thermal fluid in Ying-Qiong Basin and its significance of oil-gas geology [J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2004, 27(1): 12-15,7.
[52] Ye J L, Wei J G, Liang J Q, et al. Complex gas hydrate system in a gas chimney, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 104: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.03.023
[53] 拜阳, 宋海斌, 关永贤, 等. 利用反射地震和多波束资料研究南海西北部麻坑的结构特征与成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(7):2208-2222
BAI Yang, SONG Haibin, GUAN Yongxian, et al. Structural characteristics and genesis of pockmarks in the northwest of the South China Sea derived from reflective seismic and multibeam data [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(7): 2208-2222.
[54] 刘斌, 刘胜旋. 南海北部陆坡气泡羽状流的发现: 多波束水体数据[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(9):83-89
LIU Bin, LIU Shengxuan. Gas bubble plumes observed at north slope of South China Sea from multi-beam water column data [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(9): 83-89.
[55] 杨力, 刘斌, 徐梦婕, 等. 南海北部琼东南海域活动冷泉特征及形成模式[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(7):2905-2914 doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0374
YANG Li, LIU Bin, XU Mengjie, et al. Characteristics of active cold seepages in Qiongdongnan Sea area of the northern South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(7): 2905-2914. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0374
[56] 赵斌, 刘胜旋, 李丽青, 等. 南海冷泉分布特征及油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(10):32-43
ZHAO Bin, LIU Shengxuan, LI Liqing, et al. Distribution pattern of cold seeps in South China Sea and its geological significance [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(10): 32-43.
[57] Huang Y Y, Feng J C, Xie Y, et al. Phase equilibrium characteristics of natural gas hydrate formation at the deep-water environment of “Haima” cold seep [J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 5501-5509. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.04.011
[58] Liang Q Y, Hu Y, Feng D, et al. Authigenic carbonates from newly discovered active cold seeps on the northwestern slope of the South China Sea: constraints on fluid sources, formation environments, and seepage dynamics [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 124: 31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2017.04.015
[59] Fang Y X, Wei J G, Lu H L, et al. Chemical and structural characteristics of gas hydrates from the Haima cold seeps in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 182: 103924. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103924
[60] 陈多福, 李绪宣, 夏斌. 南海琼东南盆地天然气水合物稳定域分布特征及资源预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(3):483-489
CHEN Duofu, LI Xuxuan, XIA Bin. Distribution of gas hydrate stable zones and resource prediction in the Qiongdongnan basin of the South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(3): 483-489.
[61] 杨涛, 蒋少涌, 赖鸣远, 等. 海洋沉积物孔隙水中溶解无机碳(DIC)的碳同位素分析方法[J]. 地球学报, 2005, 26(S1):51-52
YANG Tao, JIANG Shaoyong, LAI Mingyuan, et al. An analytical method for carbon isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in pore waters from marine sediments [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26(S1): 51-52.
[62] 杨涛, 蒋少涌, 赖鸣远, 等. 连续流同位素质谱测定水中溶解无机碳含量和碳同位素组成的方法研究[J]. 地球化学, 2006, 35(6):675-680
YANG Tao, JIANG Shaoyong, LAI Mingyuan, et al. Analytical method for concentration and carbon isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) by continuous flow-isotope ratio mass spectrometer [J]. Geochimica, 2006, 35(6): 675-680.
[63] Schulz H D. Quantification of early diagenesis: dissolved constituents in pore water and signals in the solid phase[M]//Schulz H D, Zabel M. Marine Geochemistry. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2006.
[64] Hu Y, Luo M, Liang Q Y, et al. Pore fluid compositions and inferred fluid flow patterns at the Haima cold seeps of the South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103: 29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.01.007
[65] Feng J X, Yang S X, Wang H B, et al. Methane source and turnover in the shallow sediments to the west of Haima cold seeps on the northwestern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Geofluids, 2019, 2019: 1010824.
[66] Hu Y, Feng D, Peckmann J, et al. The impact of diffusive transport of methane on pore-water and sediment geochemistry constrained by authigenic enrichments of carbon, sulfur, and trace elements: a case study from the Shenhu area of the South China Sea [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 553: 119805. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119805
[67] Borowski W S, Paull C K, Ussler III W. Global and local variations of interstitial sulfate gradients in deep-water, continental margin sediments: sensitivity to underlying methane and gas hydrates [J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 159(1-4): 131-154. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00004-3
[68] Thomas C J, Blair N E, Alperin M J, et al. Organic carbon deposition on the North Carolina continental slope off Cape Hatteras (USA) [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2002, 49(20): 4687-4709. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00135-2
[69] Feng J X, Yang S X, Liang J Q, et al. Methane seepage inferred from the porewater geochemistry of shallow sediments in the Beikang Basin of the southern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 168: 77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.02.005
[70] Hu Y, Feng D, Liang Q Y, et al. Impact of anaerobic oxidation of methane on the geochemical cycle of redox-sensitive elements at cold-seep sites of the northern South China Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.06.012
[71] Liu W N, Wu Z J, Xu S N, et al. Pore-water dissolved inorganic carbon sources and cycling in the shallow sediments of the Haima cold seeps, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 201: 104495. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104495
[72] Wu L S, Yang S X, Liang J Q, et al. Variations of pore water sulfate gradients in sediments as indicator for underlying gas hydrate in Shenhu Area, the South China Sea [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(4): 530-540. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4545-6
[73] Borowski W S, Hoehler T M, Alperin M J, et al. Significance of anaerobic methane oxidation in methane-rich sediments overlying the Blake Ridge gas hydrates[M]//Paull C K, Matsumoto R, Wallace P J, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 164. College Station: Ocean Drilling Program, 2000: 87-99.
[74] Chatterjee S, Dickens G R, Bhatnagar G, et al. Pore water sulfate, alkalinity, and carbon isotope profiles in shallow sediment above marine gas hydrate systems: a numerical modeling perspective [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B9): B09103.
[75] Hong W L, Torres M E, Kim J H, et al. Towards quantifying the reaction network around the sulfate–methane-transition-zone in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea, with a kinetic modeling approach [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 140: 127-141. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.05.032
[76] 陈法锦, 陈建芳, 金海燕, 等. 南海表层沉积物与沉降颗粒物中有机碳的δ13C对比研究及其古环境再造意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(2):340-345
CHEN Fajin, CHEN Jianfang, JIN Haiyan, et al. Correlation of δ13Corg in surface sediments with sinking particulate matter in South China Sea and implication for reconstructing Paleo-environment [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(2): 340-345.
[77] Huang B J, Xiao X M, Li X X. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, offshore South China Sea [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(7): 1009-1025. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(03)00036-6
[78] Whiticar M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1-3): 291-314. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3
[79] 苏新, 陈芳, 于兴河, 等. 南海陆坡中新世以来沉积物特性与气体水合物分布初探[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(1):1-13
SU Xin, CHEN Fang, YU Xinghe, et al. A pilot study on miocene through Holocene sediments from the continental slope of the South China Sea in correlation with possible distribution of gas hydrates [J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(1): 1-13.
[80] Hu X P, Cai W J, Wang Y C, et al. Pore-water geochemistry of two contrasting brine-charged seep sites in the northern Gulf of Mexico continental slope [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2010, 118(3-4): 99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2009.11.006
[81] Martin W R, McNichol A P, McCorkle D C. The radiocarbon age of calcite dissolving at the sea floor: estimates from pore water data [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(8): 1391-1404. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00424-X
[82] Hu X P, Burdige D J. Enriched stable carbon isotopes in the pore waters of carbonate sediments dominated by seagrasses: evidence for coupled carbonate dissolution and reprecipitation [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(1): 129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.08.043
[83] Cangemi M, Di Leonardo R, Bellanca A, et al. Geochemistry and mineralogy of sediments and authigenic carbonates from the Malta Plateau, Strait of Sicily (Central Mediterranean): relationships with mud/fluid release from a mud volcano system [J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3-4): 294-308. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.06.014
[84] Gontharet S, Pierre C, Blanc-Valleron M M, et al. Nature and origin of diagenetic carbonate crusts and concretions from mud volcanoes and pockmarks of the Nile deep-sea fan (eastern Mediterranean Sea) [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54(11-13): 1292-1311. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.04.007
[85] Haas A, Peckmann J, Elvert M, et al. Patterns of carbonate authigenesis at the Kouilou pockmarks on the Congo deep-sea fan [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 268(1-4): 129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.10.027
[86] Hovland M, Svensen H, Forsberg C F, et al. Complex pockmarks with carbonate-ridges off mid-Norway: products of sediment degassing [J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 218(1-4): 191-206. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.04.005
[87] Kastner M, Elderfield H, Martin J B, et al. 25. Diagenesis and interstitial-water chemistry at the peruvian continental margin-major constituents and strontium isotopes[M]//Suess E, von Huene R. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results vol. 112. College Station: Ocean Drilling Porgramm, 1990.
[88] Meister P, Mckenzie J A, Vasconcelos C, et al. Dolomite formation in the dynamic deep biosphere: results from the Peru Margin [J]. Sedimentology, 2007, 54(5): 1007-1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2007.00870.x
[89] Burton E A. Controls on marine carbonate cement mineralogy: review and reassessment [J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 105(1-3): 163-179. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90124-2
[90] Mazzini A, Svensen H, Hovland M, et al. Comparison and implications from strikingly different authigenic carbonates in a Nyegga complex pockmark, G11, Norwegian Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 231(1-4): 89-102. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.05.012
[91] Monnin C, Wheat C G, Dupre B, et al. Barium geochemistry in sediment pore waters and formation waters of the oceanic crust on the eastern flank of the Juan de Fuca Ridge (ODP Leg 168) [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(1): 2000GC000073.
[92] 冯东, 陈多福. 海底沉积物孔隙水钡循环对天然气渗漏的指示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(1):49-57 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.01.007
FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. Barium cycling in pore water of seafloor sediment: indicator of methane fluxes [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(1): 49-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.01.007
[93] 冯俊熙, 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部神狐东南海域沉积物孔隙水地球化学特征及其对天然气水合物的指示[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(7):32-44
FENG Junxi, YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Pore water geochemistry in shallow sediments from southeastern Shenhu Area of northern South China Sea and their implications for gas hydrate occurrence [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(7): 32-44.
[94] Paull C K, Matsumoto R, Wallace P J. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program[R]. College Station: Ocean Drilling Program, 1996.
[95] 邬黛黛, 叶瑛, 吴能友, 等. 琼东南盆地与甲烷渗漏有关的早期成岩作用和孔隙水化学组分异常[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(2):86-96
WU Daidai, YE Ying, WU Nengyou, et al. Early diagenesis records and chemical composition abnormalities in pore water for methane-seep in sediments from the southern Qiongdong Basin [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(2): 86-96.
-




 下载:
下载: