-
摘要:
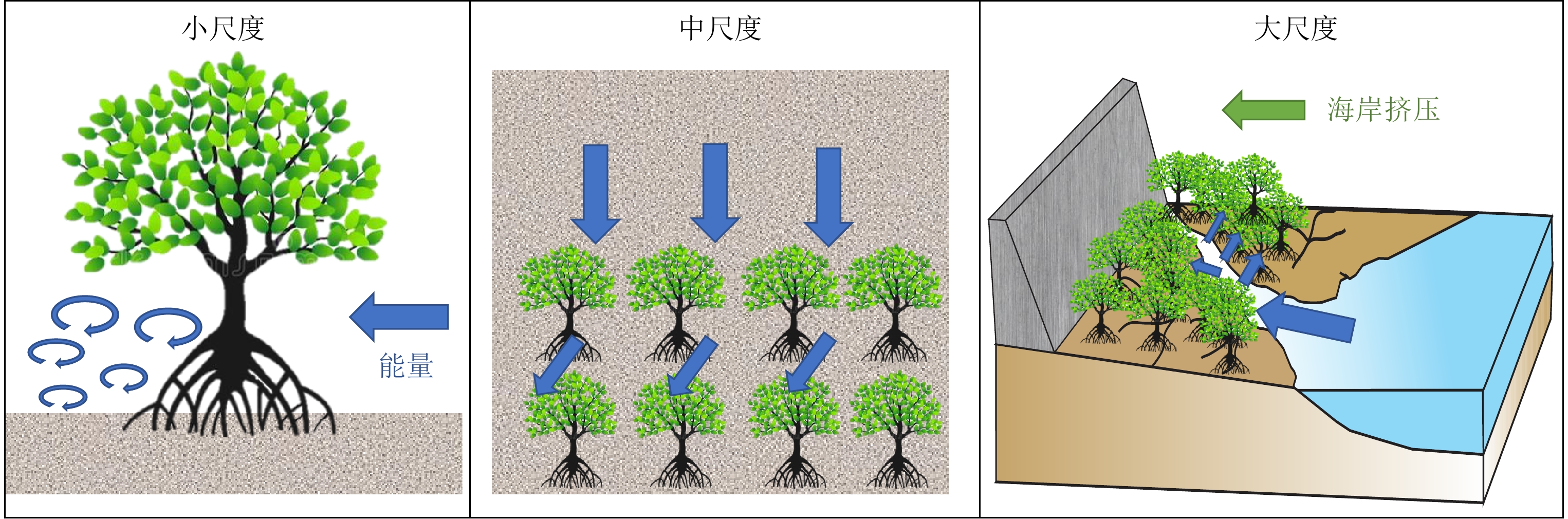
能量耗散是海岸带沉积地貌学的重要研究方向。地貌系统中的能量耗散往往存在极值,但是关于地貌演化的能量耗散趋向是最大值还是最小值,一直存在争议。本文试图从文献梳理入手,回顾海岸带地貌过程中的能量耗散问题,并用阻抗匹配概念来解释能量耗散的极值问题:当地貌系统的机械储能效率最大而热力学耗散最小时,表现为“共振阻抗匹配”,反之则表现为“梯度阻抗匹配”。基于无量纲沉降速度Ω的海滩地貌分类体系,正是表现从“共振阻抗匹配”到“梯度阻抗匹配”的典型谱系。在此基础上,从能量耗散的视角,对红树林生态系统的沉积地貌过程进行了文献综述,总结了潮沟-潮滩-红树林界面上的阻抗匹配和能量耗散问题,讨论了界面能量耗散行为如何通过水动力学和热力学过程反馈到红树林的生长过程,指出了红树林生态系统中潮沟-潮滩三维地形结构的重要性,并建议在红树林生态修复工程中应用这种结构来更好地维持系统的稳定性。
Abstract:Energy dissipation has been widely studied in coastal sedimentary geomorphology. It has been assumed that thresholds in energy dissipation may exist in geomorphological evolution; however, whether energy dissipation evolves towards a minimum, maximum, or both, aroused a big debate in a long history. We summarized the previous publications to revisit the energy dissipation problem in coastal geomorphology, and proposed a concept of ‘impedance matching’ to explain the problem regarding minimum and maximum values of energy dissipation. Once the geomorphological system showed a maximal mechanical energy storage but a minimal thermal energy dissipation, it could be a ‘resonance impedance matching’ system. Otherwise, it could be a ‘gradience impedance matching’ system. The Ω classification of beaches obtained by dimensionless settling velocity was a typical example for these two ‘impedance matching’ systems. Based on the new concept, we reviewed geomorphological studies on mangrove ecosystems, and revealed the ‘impedance matching’ and the energy dissipation across the interfaces of tidal creek–tidal flat–mangrove systems. In addition, we discussed how the energy dissipation could affect the growth of mangroves through hydrodynamics and thermal dynamics, and pointed out that the three-dimensional structure of tidal creek–tidal flat is very important to maintain the stability of mangrove ecosystems and therefore should be considered in the future mangrove restoration projects.
-
Key words:
- energy dissipation /
- sedimentary geomorphology /
- mangrove /
- tidal creek /
- tidal flat
-

-
图 1 海滩Ω分类概念模式图[7]
Figure 1.
图 2 河口湾成因-地貌分类概念模式图[8]
Figure 2.
-
[1] 郭振仁. 能量耗散率极值原理评述[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 1983(2):95-100
GUO Zhenren. Comments on the law of extreme rate on energy dissipation[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 1983(2):95-100.
[2] Yang C T, Song C C S. Theory of minimum rate of energy dissipation[J]. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, 1979, 105(7):769-784. doi: 10.1061/JYCEAJ.0005235
[3] 黄万里. 连续介体动力学最大能量消散率定律[J]. 清华大学学报, 1981, 21(1):87-96
HUANG Wanli. The law of maximum rate of energy dissipation on continuum dynamics[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University, 1981, 21(1):87-96.
[4] 黄才安, 赵晓冬, 周济人. 明渠水力设计中的能耗极值假说[J]. 水道港口, 2010, 31(5):330-334
HUANG Caian, ZHAO Xiaodong, ZHOU Jiren. Extremal hypotheses of energy dissipation used in open channel design[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2010, 31(5):330-334.
[5] 李炎, 陈一宁, 吴祥柏. 论陆-海界面的复参数化[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(3):3-8
LI Yan, CHEN Yining, WU Xiangbai. Complex parameterization for land-ocean interface: a perspective[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(3):3-8.
[6] 席兵. 关于传输线阻抗匹配问题的分析[J]. 重庆邮电学院学报, 1999, 11(2):42-44,87
XI Bing. Analysis on impedance matching problems about transmission line[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 1999, 11(2):42-44,87.
[7] Wright L D, Short A D. Morphodynamic variability of surf zones and beaches: a synthesis[J]. Marine Geology, 1984, 56(1-4):93-118. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(84)90008-2
[8] Perillo G M E. Chapter 2 Definitions and geomorphologic classifications of estuaries[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1995, 53:17-47.
[9] Lewis III R R. Ecological engineering for successful management and restoration of mangrove forests[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 24(4):403-418. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.10.003
[10] Goldberg L, Lagomasino D, Thomas N, et al. Global declines in human-driven mangrove loss[J]. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(10):5844-5855. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15275
[11] Schwarz C, van Rees F, Xie D H, et al. Salt marshes create more extensive channel networks than mangroves[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1):207. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29654-1
[12] Chen Y N, Li Y, Cai T L, et al. A comparison of biohydrodynamic interaction within mangrove and saltmarsh boundaries[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2016, 41(13):1967-1979. doi: 10.1002/esp.3964
[13] Chen Y N, Li Y, Thompson C, et al. Differential sediment trapping abilities of mangrove and saltmarsh vegetation in a subtropical estuary[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 318:270-282. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.018
[14] 陈一宁, 陈鹭真, 蔡廷禄, 等. 滨海湿地生物地貌学进展及在生态修复中的应用展望[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(5):1055-1065
CHEN Yining, CHEN Luzhen, CAI Tinglu, et al. Advances in biogeomorphology in coastal wetlands and its application in ecological restoration[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(5):1055-1065.
[15] Nepf H M. Flow and transport in regions with aquatic vegetation[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2012, 44:123-142. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-120710-101048
[16] Chang Y, Chen Y N, Li Y. Flow modification associated with mangrove trees in a macro-tidal flat, southern China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 38(2):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1163-y
[17] Chen L Z, Feng H Y, Gu X X, et al. Linkages of flow regime and micro-topography: prediction for non-native mangrove invasion under sea-level rise[J]. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 2020, 6(1):1780159. doi: 10.1080/20964129.2020.1780159
[18] Kirwan M L, Megonigal J P. Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise[J]. Nature, 2013, 504(7478):53-60. doi: 10.1038/nature12856
[19] Ahmed M R. Assessing changes in Sundarbans mangrove wetlands: identifying influencing factors and developing effective management strategies[D]. Coastal and Ocean Management Institute, 2023.
[20] 王文卿, 石建斌, 陈鹭真, 等. 中国红树林湿地保护与恢复战略研究[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2021
WANG Wenqing, SHI Jianbin, CHEN Luzhen, et al. Research of Conservation and Restoration Strategy of Mangrove Wetlands in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group, 2021.
[21] Xiao M, Cai T L, Wang X K, et al. Response of native and exotic saltmarsh species to sediment deposition addition[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 888:164271. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164271
[22] 李屹, 陈一宁, 李炎. 红树林与互花米草盐沼交界区空间格局变化规律的遥感分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(3):348-360 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.014
LI Yi, CHEN Yining, LI Yan. Remote sensing analysis of the changes in the ecotone of mangrove forests and Spartina alterniflora saltmarshes[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(3):348-360. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.03.014
[23] Furukawa K, Wolanski E, Mueller H. Currents and sediment transport in mangrove forests[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1997, 44(3):301-310. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1996.0120
[24] Massel S R, Furukawa K, Brinkman R M. Surface wave propagation in mangrove forests[J]. Fluid Dynamics Research, 1999, 24(4):219-249. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5983(98)00024-0
[25] Mazda Y, Kobashi D, Okada S. Tidal-scale hydrodynamics within mangrove swamps[J]. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 2005, 13(6):647-655. doi: 10.1007/s11273-005-0613-4
[26] Horstman E M, Dohmen-Janssen C M, Bouma T J, et al. Tidal-scale flow routing and sedimentation in mangrove forests: combining field data and numerical modelling[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 228:244-262. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.08.011
[27] Vo-Luong P, Massel S. Energy dissipation in non-uniform mangrove forests of arbitrary depth[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2008, 74(1-2):603-622. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.05.004
[28] Tanino Y, Nepf H. Laboratory investigation of mean drag in a random array of Rigid, Emergent Cylinders[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2008, 134(1):34-41. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:1(34)
[29] Horstman E M, Dohmen-Janssen C M, Narra P M F, et al. Wave Attenuation in Mangroves: A Quantitative Approach to Field Observations. Coastal Engineering, 2014, 94: 47-62.
[30] Hu Z, Van Belzen J, Van Der Wal D, et al. Windows of opportunity for salt marsh vegetation establishment on bare tidal flats: the importance of temporal and spatial variability in hydrodynamic forcing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences, 2015, 120(7):1450-1469. doi: 10.1002/2014JG002870
[31] Kamil E A, Takaijudin H, Hashim A M. Mangroves as coastal bio-shield: a review of mangroves performance in wave attenuation[J]. Civil Engineering Journal, 2021, 7(11):1964-1981. doi: 10.28991/cej-2021-03091772
[32] Adytia D, Husrin S. Numerical simulations of nonbreaking solitary wave attenuation by a parameterized mangrove forest model[J]. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2019, 8(1.9):10-16.
[33] Braatz S, Fortuna S, Broadhead J et al. Coastal protection in the aftermath of the Indian Ocean Tsunami: what role for forests and trees?[C]//Proceedings of the Regional Technical Workshop. Khao Lak, Thailand, 2007: 161-184.
[34] Zhang K Q, Liu H Q, Li Y P, et al. The role of mangroves in attenuating storm surges[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 102-103:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.02.021
[35] Allen J R L. Morphodynamics of Holocene salt marshes: a review sketch from the Atlantic and southern North Sea coasts of Europe[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(12):1155-1231. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00034-7
[36] 汪亚平, 张忍顺. 江苏弶港盐沼风车河潮沟地貌与动力演化[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 1999(41):40-50
WANG Yaping, ZHANG Renshun. Evolution of geomorphology and hydrodynamics in Fengche creek at Jianggang Saltmarsh, Jiangsu, China[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 1999(41):40-50.
[37] 汪亚平, 张忍顺, 高抒. 论盐沼-潮沟系统的地貌动力响应[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(21): 2315-2320
WANG Yaping, ZHANG Renshun, GAO Shu. Geomorphic and hydrodynamic responses in salt marsh-tidal creek systems, Jiangsu, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(6): 544-549.
[38] 汪亚平, 高抒, 贾建军. 浪流联合作用下潮滩沉积动力过程的高分辨率数据采集与分析[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(3): 339-348
WANG Yaping, GAO Shu, JIA Jianjun. High-resolution data collection for analysis of sediment dynamic processes associated with combined current-wave action over intertidal flats[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(7): 866-877.
[39] Coco G, Zhou Z, Van Maanen B, et al. Morphodynamics of tidal networks: advances and challenges[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 346:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.08.005
[40] Liu B, Cai T L, Chen Y N, et al. Sediment dynamic changes induced by the presence of a dyke in a Scirpus mariqueter saltmarsh[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2022, 174:104119. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2022.104119
[41] Kim D, Cairns D M, Bartholdy J. Tidal creek morphology and sediment type influence spatial trends in salt marsh vegetation[J]. The Professional Geographer, 2013, 65(4):544-560. doi: 10.1080/00330124.2013.820617
[42] 龚政, 白雪冰, 靳闯, 等. 基于植被和潮动力作用的潮滩剖面演变数值模拟[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(6):877-886
GONG Zheng, BAI Xuebing, JIN Chuang, et al. A numerical model for the cross-shore profile evolution of tidal flats based on vegetation growth and tidal processes[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(6):877-886.
[43] Chen Y, Thompson C E L, Collins M B. Saltmarsh creek bank stability: biostabilisation and consolidation with depth[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 35:64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.12.009
[44] Van Zee R. The role of creeks for tidal exchange in the mangrove forest of Lac Bay, Bonaire[D]. Master Dissertation of University of Twente, 2022: 84.
[45] 张忍顺, 王雪瑜. 江苏省淤泥质海岸潮沟系统[J]. 地理学报, 1991, 46(2):195-206 doi: 10.11821/xb199102008
ZHANG Renshun, WANG Xueyu. Tidal creek system on tidal mud flat of Jiangsu province[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1991, 46(2):195-206. doi: 10.11821/xb199102008
[46] Hosseini S T, Chegini V, Sadrinasab M, et al. Temperature, salinity and water-age variations in a tidal creek network, Bushehr Port, Iran[J]. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 2018, 22(6):1093-1106. doi: 10.1007/s11852-018-0616-y
[47] Chen Y N, Chen L Z, Zhang Z Y, et al. Tidal creeks mediate micro-climate within artificial mangroves at their northmost boundary in China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2023, 192:106970. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2023.106970
[48] Borges J S, De Grande F R, Costa T M. Do Lower air or water temperatures limit the southern distribution of the white mangrove Laguncularia racemosa in South America?[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 230:106449. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106449
[49] 卢昌义, 金亮, 叶勇, 等. 秋茄红树林湿地土壤呼吸昼夜变化及其温度敏感性[J]. 厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 51(4):793-797
LU Changyi, JIN Liang, YE Yong, et al. Diurnal variation of soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity in Kandelia candel mangrove wetland[J]. Journal of Xiamen University:Natural Science, 2012, 51(4):793-797.
[50] Chen E J, Blaze J A, Smith R S, et al. Freeze tolerance of poleward-spreading mangrove species weakened by soil properties of resident salt marsh competitor[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2020, 108(4):1725-1737. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.13350
[51] 陈鹭真, 杜晓娜, 陆銮眉, 等. 模拟冬季低温和夜间退潮对无瓣海桑幼苗的协同作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(4):953-958
CHEN Luzhen, DU Xiaona, LU Luanmei, et al. Synergistic effects of low temperature in winter and ebb tide at night on Sonneratia apetala seedlings growth and key eco-physiological traits[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(4):953-958.
-

| 引用本文: | 李炎, 陈一宁. 基于能量耗散视角的红树林海岸沉积地貌学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(6): 25-33. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2023091301 |
| Citation: | LI Yan, CHEN Yining. Sedimentary geomorphology of mangrove coasts in perspective of energy dissipation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(6): 25-33. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2023091301 |



 下载:
下载: