Spatio-temporal variations in grain size of surficial sediment on tidal flat of Langqi Island in Minjiang River estuary
-
摘要:
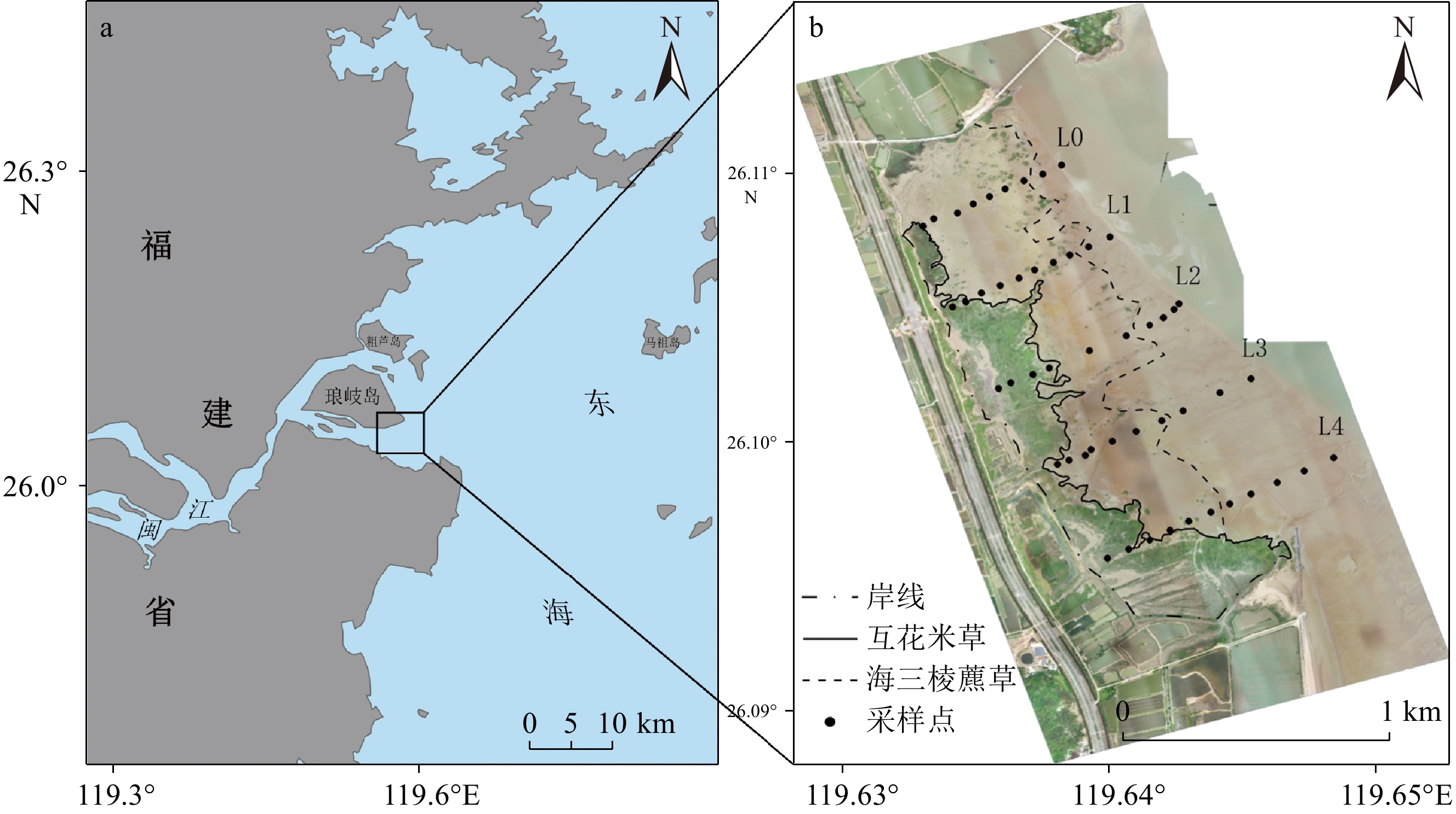
潮滩位于陆地与海洋相互作用的敏感地带,其沉积环境变化与海岸带生态系统演化、海岸带开发利用等密切相关。为了清晰认识河口潮滩时空变化特征,选取闽江口琅岐岛东侧潮滩作为研究区域,通过采集和分析不同季节表层沉积物粒度组成,探讨琅岐岛潮滩沉积物粒度的时空变化特征,为深刻理解河口潮滩沉积过程对环境变化响应提供科学依据。研究结果表明,琅岐岛潮滩沉积物组成总体以粉砂为主,砂和黏土含量呈现较大的时空差异;时间上,琅岐岛潮滩表层沉积物平均粒径为2.2~7.4 Φ,呈现出显著的季节性差异,夏季节沉积物平均粒径Φ值大,冬季节沉积物平均粒径Φ值小,春季和秋季位于过渡期间。空间上,由西向东,随着离岸距离的增加,沉积物平均粒径Φ值总体呈现出先减小后增大的趋势;由北向南,表层沉积物粗颗粒组分的分布范围逐渐增大。闽江口琅岐岛潮滩沉积物分布格局与国内外其他河口、海湾及开放型潮滩沉积物分布格局一致,是物源、水动力和地貌综合作用的结果,但研究区水动力强度、植被覆盖和沉积物供应季节差异显著,引起潮滩沉积物组成的季节变化十分显著,沉积物粒度组成对环境变化响应非常敏感。
Abstract:Tidal flats are located in sensitive areas of interaction between land and ocean, and their sedimentary environment changes are closely related to the evolution of coastal ecosystems and coastal development and utilization. In order to clearly understand the spatio-temporal variations of estuarine tidal flats, we selected the tidal flat of Langqi Island in the Minjiang River estuary as the study area, studied surficial sediment composition in different seasons, and discussed the spatio-temporal variations in sediment grain size distribution, providing a scientific basis for a deep understanding of the sedimentary process of the estuarine tidal flats in response to environmental changes. Results indicate that the surficial sediment composition of inter-tidal flat on Langqi Island is dominated by silt, with significant differences of sand and clay contents. The mean grain-size ranges from 2.2 Φ to 7.4 Φ, and shows a significant seasonal variations, with the average mean grain-size in summer being smaller than in winter. From west to east, the mean grain-size increases first and then decreases seaward, and the distribution area of coarse grain component in gradually increases from north to south. The distribution pattern of sediment on the inter-tidal flat of Langqi Island at the Minjiang River estuary is consistent with that of other estuaries, bays, and open tidal flats in the world, reflecting the result of the among sediment sources, hydrodynamics, and local geomorphology. However, due to significant differences in hydrodynamics, vegetation coverage and sediment supply in the study area, which cause significant seasonal changes in the sediment composition, the sediment grain-size compsition of the tidal flat in the Minjiang River estuary are very sensitive to environmental changes.
-
Key words:
- grain-size parameter /
- seasonal variation /
- tidal flat /
- Langqi Island /
- Minjiang River estuary
-

-
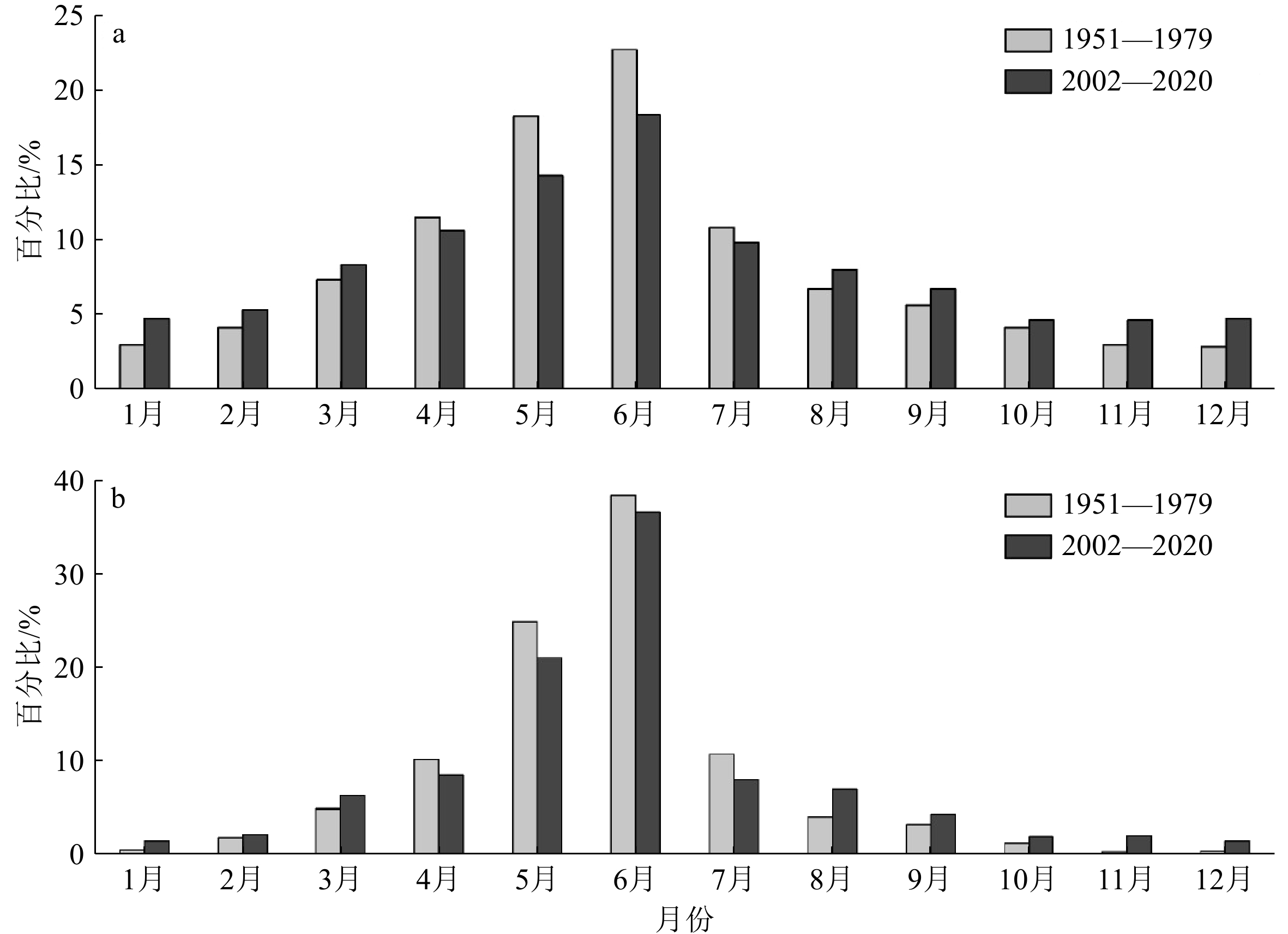
图 5 不同时段闽江入海径流量(a)和泥沙通量(b)多年月平均百分比[33]
Figure 5.
表 1 琅岐岛潮滩不同季节表层沉积物粒度特征统计值
Table 1. Statistical value of surficial sediment composition and grain-size parameters on tidal flat of Langqi Island in different seasons
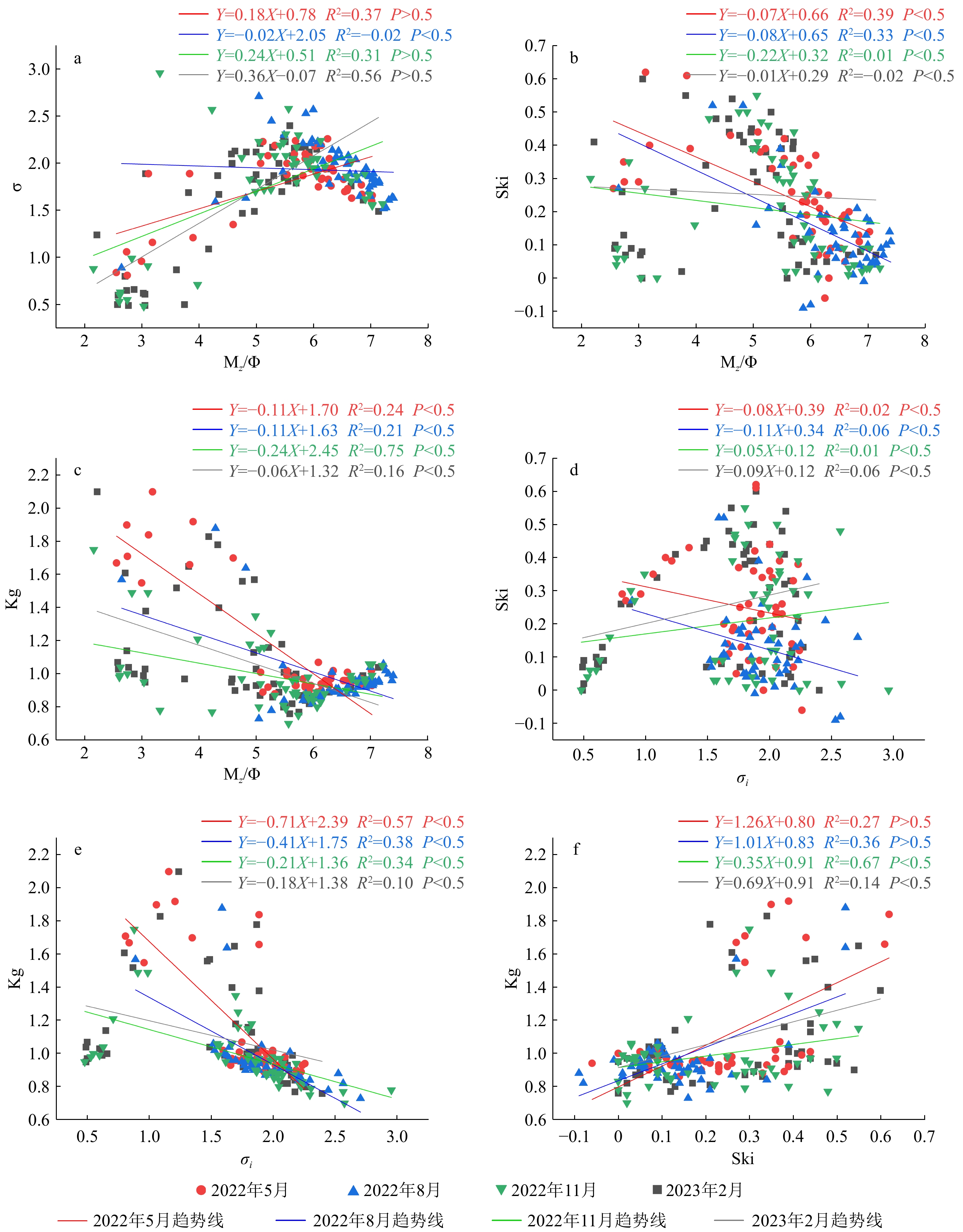
时间 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% Mz/Φ σ Ski Kg 2022年5月 44.58 45.04 10.38 4.73 1.62 0.25 1.09 2022年8月 25.77 58.10 16.13 5.56 1.80 0.25 1.11 2022年12月 13.02 62.65 24.33 6.40 1.92 0.13 0.97 2023年2月 33.64 51.46 14.89 5.27 1.76 0.20 0.99 表 2 琅岐岛潮滩不同区域的粒度组成及粒度参数
Table 2. Surficial sediment composition and grain-size parameters in different zones of tidal flat of Langqi Island
沉积区域 时间 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% Mz/Φ σ Ski Kg 植被生长状况 互花米草区 2022年5月 35.44 51.92 12.63 4.71 4.98 1.54 0.31 茂密 2022年8月 13.86 66.28 19.86 5.89 6.11 1.81 0.22 2022年12月 7.97 66.90 25.13 6.47 6.63 1.81 0.16 2023年2月 25.26 56.69 18.05 5.45 5.64 1.83 0.19 海三棱藨草区 2022年5月 58.61 35.50 5.88 3.83 4.10 1.30 0.29 发芽 2022年8月 35.41 51.34 13.25 4.86 5.10 1.67 0.29 茂密 2022年12月 17.62 60.27 22.11 6.02 6.14 1.93 0.15 无植被 2023年2月 44.44 44.11 11.44 4.57 4.80 1.52 0.23 无植被 光滩 2022年5月 29.25 55.03 15.72 5.33 5.52 2.16 0.17 无植被覆盖 2022年8月 17.14 64.27 18.59 5.73 5.97 2.04 0.19 2022年12月 9.29 63.55 27.16 6.59 6.66 1.99 0.08 2023年2月 22.69 59.21 18.10 5.56 5.74 2.09 0.17 -
[1] 任美锷. 中国淤泥质潮滩沉积研究的若干问题[J]. 热带海洋, 1985(2):6-14,99
REN Meie. A Study on sedimentation of tidal mud flats of China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1985(2):6-14,99.
[2] 时钟, 陈吉余, 虞志英. 中国淤泥质潮滩沉积研究的进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1996, 11(6):555-562 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.06.005
SHI Zhong, CHEN Jiyu, YU Zhiying. Sedimentation on the intertidal mudflat in China: an overview[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1996, 11(6):555-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.06.005
[3] Murray N J, Clemens R S, Phinn S R, et al. Tracking the rapid loss of tidal wetlands in the Yellow Sea[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2014, 12(5):267-272. doi: 10.1890/130260
[4] Murray N J, Phinn S R, Clemens R S, et al. Continental scale mapping of tidal flats across East Asia using the Landsat archive[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(11):3417-3426. doi: 10.3390/rs4113417
[5] 任美锷. 中国滩涂开发利用的现状与对策[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 1996(6):440-443
REN Meie. Current situation and countermeasures of beach development and utilization in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1996(6):440-443.
[6] 许炯心, 李炳元, 杨小平, 等. 中国地貌与第四纪研究的近今进展与未来展望[J]. 地理学报, 2009, 64(11):1375-1393 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.11.009
XU Jiongxin, Li Bingyuan, Yang Xiaoping, et al. Recent progress in geomorphology and quaternary geology in China and some perspectives[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2009, 64(11):1375-1393. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.11.009
[7] 王颖, 朱大奎. 中国的潮滩[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, 10(4):291-300
WANG Ying, ZHU Dakui. Tidal flats of China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1990, 10(4):291-300.
[8] 杨世伦. 中国淤泥质海岸的发育特点[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 1990(4):85-91
YANG Shilun. The developmental characteristics of muddy coasts in China[J]. Journal of East China Normal University:Natural Science, 1990(4):85-91.
[9] 梁喜幸, 王日明, 戴志军, 等. 茅尾海钦江河口光滩时空变化过程研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(3):107-118
LIANG Xixing, WANG Riming, DAI Zhijun, et al. Spatial-temporal variations of bare flats in the Qinjiang River estuary, Maowei Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(3):107-118.
[10] 李东义, 徐勇航, 王爱军, 等. 福建安海湾表层沉积物粒度特征及其现代沉积过程分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(4):724-734
LI Dongyi, XU Yonghang, WANG Aijun, et al. Analysis of surface sediment grain size characteristics and modern sedimentary process in Fujian Anhai gulf[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(4):724-734.
[11] 徐晓晖, 陈坚, 赖志坤. GIS支持下近百年来闽江口海底地形地貌演变[J]. 台湾海峡, 2009, 28(4):577-585
XU Xiaohui, CHEN Jian, LAI Zhikun. Seabed morphological evolution in Minjiang estuary in recent one hundred years based on GIS tools[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2009, 28(4):577-585.
[12] Eisma D. Intertidal Deposits: River Mouths, Tidal Flats, and Coastal Lagoons[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1998.
[13] Murray N J, Phinn S R, Dewitt M, et al. The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7738):222-225. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0805-8
[14] 汪亚平, 贾建军, 杨阳, 等. 长江三角洲蓝图重绘的基础科学问题: 进展与未来研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(10):2-12
WANG Yaping, JIA Jianjun, YANG Yang, et al. Fundamental scientific issues for the Changjiang River delta associated with the new blueprint of future development: overview and prospect[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(10):2-12.
[15] Yang S L, Luo X X, Temmerman S, et al. Role of delta-front erosion in sustaining salt marshes under sea-level rise and fluvial sediment decline[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2020, 65(9):1990-2009. doi: 10.1002/lno.11432
[16] Dai Z J. Changjiang Riverine and Estuarine Hydro-morphodynamic Processes: In the Context of Anthropocene Era[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2021.
[17] Xie W M, Sun J W, Guo L C, et al. Distinctive sedimentary processes on two contrasting tidal flats of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 10:1259081. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1259081
[18] 谢津剑, 王爱军, 叶翔, 等. 闽江河口水下三角洲及周边海域现代沉积环境演化及其对人类活动的响应[J/OL]. 沉积学报, 2022: 1-23
XIE Jinjian, WANG Aijun, Ye Xiang, et al. Contemporary sedimentary environment evolution and its response to human activities in the Minjiang subaqueous delta and surrounding waters[J/OL]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022: 1-23.
[19] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志: 第十四分册[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1998
State Oceanic Administration. China embayment (No. 14: Important river estuaries)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1998: 626-691.
[20] 李东义, 陈坚, 王爱军, 等. 闽江河口沉积动力学研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2008, 27(2):111-116 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.02.017
LI Dongyi, CHEN Jian, WANG Aijun, et al. Recent progress in sediment transport research in Minjiang Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2008, 27(2):111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2008.02.017
[21] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1):3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[22] 卢连战, 史正涛. 沉积物粒度参数内涵及计算方法的解析[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2010, 35(6):54-60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
LU Lianzhan, SHI Zhengtao. Analysis for sediment grain size parameters of connotations and calculation method[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2010, 35(6):54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
[23] 王颖. 渤海湾西部贝壳堤与古海岸线问题[J]. 南京大学学报:自然科学版, 1964(3):424-440,462-464
WANG Ying. The shell coast ridges and the old coastlines of the west coast of the Pohai bay[J]. Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Sciences, 1964(3):424-440,462-464.
[24] Evans G. Intertidal flat sediments and their environments of deposition in the Wash[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society, 1965, 121(1-4):209-240. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.121.1.0209
[25] Reineck H E. German North Sea tidal flats[M]//Ginsburg R N. Tidal Deposits. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1975: 5-12.
[26] 任美锷, 张忍顺, 杨巨海. 江苏王港地区淤泥质潮滩的沉积作用[J]. 海洋通报, 1984(1):40-54
REN Meie, ZHANG Renshun, YANG Junhai. Sedimentation on tidal mud flat in Wanggang area, Jiangsu province, China[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1984(1):40-54.
[27] Uncles R J, Stephens J A, Harris C. Seasonal variability of subtidal and intertidal sediment distributions in a muddy, macrotidal estuary: the Humber-Ouse, UK[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1998, 139(1):211-219. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.139.01.17
[28] Gao S. Geomorphology and sedimentology of tidal flats[M]//Coastal Wetlands. 2nd ed. Singapore: Elsevier, 2019: 359-381.
[29] Gao S, Collins M B. Holocene sedimentary systems on continental shelves[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352:268-294. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.03.021
[30] Le Hir P, Roberts W, Cazaillet O, et al. Characterization of intertidal flat hydrodynamics[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(12-13):1433-1459. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00031-5
[31] Fan D D, Wang Y, Liu M. Classifications, sedimentary features and facies associations of tidal flats[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 2(1):66-80.
[32] 王爱军, 叶翔, 赖志坤, 等. 闽江口及周边海域沉积物输运及资源效应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(5):1013-1024 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200100024
WANG Aijun, YE Xiang, LAI Zhikun, et al. Sediment transport in Minjiang River Estuary and adjacent shelf area and associated resource effect[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(5):1013-1024. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200100024
[33] 王爱军, 叶翔, 徐晓晖, 等. 亚热带中小型山溪性河流—宽陆架系统“源—汇”过程——以闽江—东海陆架系统为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(6):1615-1634
WANG Aijun, YE Xiang, XU Xiaohui, et al. "Source-to-sink" Processes of a subtropical mid-small mountainous river-wide continental shelf system: a case study from the Minjiang river-east China sea system[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(6):1615-1634.
[34] 王爱军, 李海琪, 叶翔. 河口潮滩季节性冲淤变化格局及其控制机制——以闽江口琅岐岛潮滩为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质
WANG Aijun, LI Haiqi, YE Xiang. Seasonal variations of erosion-accretion pattern of estuaries tidal flat and associated mechanims: A case study of tidal flat in Minding estuary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology.
[35] Yang S L, Milliman J D, Li P, et al. 50, 000 dams later: Erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2011, 75(1-2):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.09.006
[36] 杨世伦, 朱骏, 李鹏. 长江口前沿潮滩对来沙锐减和海面上升的响应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2005, 23(2):152-158 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.005
YANG Shilun, ZHU Jun, LI Peng. Response of tidal bank on the Changjiang river mouth foreland to drastic decline in riverine sediment supply and sea level rise[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2005, 23(2):152-158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.02.005
[37] 时连强, 夏小明. 我国淤泥质海岸侵蚀研究现状与展望[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(4):72-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.011
SHI Lianqiang, XIA Xiaoming. Erosion on muddy coasts in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(4):72-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.011
[38] 张雨晨, 余建奎, 任宗海, 等. 入海泥沙减少对黄河三角洲潮滩粒度特征的影响: 物理模型实验[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(6):34-46
ZHANG Yuchen, YU Jiankui, REN Zonghai, et al. Influence of reduced sediment supply on the particle size distribution on tidal flats of the Yellow River Delta: a physical experimental study[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(6):34-46.
[39] 伊锋. 黄河入海泥沙减少对潮滩地貌冲淤影响的物理模型研究[D]. 鲁东大学硕士学位论文, 2020
YI Feng. Study on physical model of tidal flat development response to the reduction of the Yellow River sediment into sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Ludong University, 2020.
[40] Yang S L, Zhao Q Y, Belkin I M. Temporal variation in the sediment load of the Yangtze river and the influences of human activities[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 263(1-4):56-71. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00028-8
[41] 张云峰. 现代人类活动影响下长江口启东嘴潮滩沉积特征与物质来源变化[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2015
ZHANG Yunfeng. Sedimentary characteristics and sediment source of tidal flat under the influence of human activities at Qidong Foreland, the Yangtze Estuary[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2015.
[42] Dai Z J, Mei X F, Darby S E, et al. Fluvial sediment transfer in the Changjiang (Yangtze) river-estuary depositional system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 566:719-734. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.019
[43] 朱博渊, 刘凌峰, 李江夏, 等. 径流变化下长江口多分汊系统冲淤分布差异及动力机制[J]. 水科学进展, 2023, 34(4):585-598
ZHU Boyuan, LIU Lingfeng, LI Jiangxia, et al. Erosion-deposition change pattern and hydrodynamic mechanism for the multilevel bifurcating system of Yangtze River Estuary under runoff variation[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2023, 34(4):585-598.
[44] Luan H L, Ding P X, Yang S L, et al. Accretion-erosion conversion in the subaqueous Yangtze Delta in response to fluvial sediment decline[J]. Geomorphology, 2021, 382:107680. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107680
[45] Wang A J, Ye X, Lin Z K, et al. Response of sedimentation processes in the Minjiang River subaqueous delta to anthropogenic activities in the river basin[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 232:106484. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106484
[46] 陈坚, 余兴光, 李东义, 等. 闽江口近百年来海底地貌演变与成因[J]. 海洋工程, 2010, 28(2):82-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2010.02.013
CHEN Jian, YU Xingguang, LI Dongyi, et al. Characteristics of underwater morphology evolution of the Minjiang Estuary in recent 100 years and its reasons[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2010, 28(2):82-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2010.02.013
[47] 陈祥锋, 马淑燕, 刘苍字. 闽江口动力沉积特征的探讨[J]. 海洋通报, 1998(6):40-47
CHEN Xiangfeng, MA Shuyan, LIU Cangzi. Dynamic deposition characteristics of the Minjiang estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1998(6):40-47.
[48] Shi B W, Cooper J R, Pratolongo P D, et al. Erosion and accretion on a mudflat: The importance of very shallow-water effects[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2017, 122(12):9476-9499. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012316
[49] Shi B W, Yang S L, Wang Y P, et al. Role of wind in erosion-accretion cycles on an estuarine mudflat[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2017, 122(1):193-206. doi: 10.1002/2016JC011902
[50] 王爱军, 叶翔, 陈坚. 台风作用下的港湾型潮滩沉积过程: 以2008年“凤凰”台风对福建省罗源湾的影响为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(6):77-86
WANG Aijun, YE Xiang, CHEN Jian. Effects of typhoon on sedimentary processes of embayment tidal flat: A case study from the "Fenghuang" typhoon in 2008[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(6):77-86.
[51] 王爱军, 叶翔. 福建省东北部沿海罗源湾互花米草盐沼环境下粘性沉积物的侵蚀-沉降过程[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(3):582-593 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.03.19
WANG Aijun, YE Xiang. Erosion and deposition processes of cohesive sediment in Spartina alterniflora marsh, Luoyuan bay in the north of Fujian coast, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(3):582-593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.03.19
[52] De Vet P L M, Van Prooijen B C, Colosimo I, et al. Variations in storm-induced bed level dynamics across intertidal flats[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1):12877. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69444-7
[53] Liu X Y, Xing F, Shi B W, et al. Erosion and accretion patterns on intertidal mudflats of the Yangtze River Estuary in response to storm conditions[J]. Anthropocene Coasts, 2023, 6(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s44218-023-00020-y
[54] 杨世伦, 陈吉余. 试论植物在潮滩发育演变中的作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(6):631-635 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.06.010
YANG Shilun, CHEN Jiyu. The role of vegetation in mud coast processes[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(6):631-635. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.06.010
[55] 王爱军, 高抒, 贾建军. 互花米草对江苏潮滩沉积和地貌演化的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(1):92-99
WANG Aijun, GAO Shu, JIA Jianjun. Impact of Spartina alterniflora on sedimentary and morphological evolution of tidal salt marshes of Jiangsu, China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2006, 28(1):92-99.
[56] Wang A J. Hydrodynamics and associated sediment transport over coastal wetlands in Quanzhou Bay, China[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2011, 25(1):59-72. doi: 10.1007/s13344-011-0005-x
[57] 周曾, 陈雷, 林伟波, 等. 盐沼潮滩生物动力地貌演变研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2021, 32(3):470-484
ZHOU Zeng, CHEN Lei, LIN Weibo, et al. Advances in biogeomorphology of tidal flat-saltmarsh systems[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2021, 32(3):470-484.
[58] 龚政, 陈欣迪, 周曾, 等. 生物作用对海岸带泥沙运动的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(1):53-62 doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0291
GONG Zheng, CHEN Xindi, ZHOU Zeng, et al. The roles of biological factors in coastal sediment transport: A review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(1):53-62. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0291
[59] Zhang H Y, Zhou Y, Sun T, et al. Advances in biophysical feedbacks and the resulting stable states in tidal flat systems[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(5):457-468. doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0475
[60] Li H, Yang S L. Trapping effect of tidal marsh vegetation on suspended sediment, Yangtze Delta[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2009, 25(4):915-924,930.
[61] 沈永明, 张忍顺, 王艳红. 互花米草盐沼潮沟地貌特征[J]. 地理研究, 2003, 22(4):520-527 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.04.014
SHEN Yongming, ZHANG Renshun, WANG Yanhong. The tidal creek character in salt marsh of Spartina alterniflora Loisel on strong tide coast[J]. Geographical Research, 2003, 22(4):520-527. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2003.04.014
[62] Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J, et al. Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 291-294:147-161. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.01.004
-



 下载:
下载: