Advancements in the study of shallow gas in the coastal waters of China
-
摘要:
随着海洋开发利用不断深入和全球气候变化持续加剧,近海沉积物中的浅层气(主要成分是甲烷)导致的灾害问题和可能产生的气候影响受到了进一步的关注,但目前为止对浅层气仍然缺乏系统的认识。在此对浅层气相关的主要认识进行了全面梳理,包括形成机理、存在形式、调查技术方法、分布特征、控制因素、主要危害等,以期为后续相关调查、理论研究和减灾防灾技术研发提供支撑。沿海三角洲平原第四纪下切河谷中充填的砂体和近海全新世细颗粒沉积物中普遍存在浅层气,以气包、分散气泡或溶解气的形式存在,近海大部分地区的浅层气主要来源于生物成因。含气沉积物的声学特性(声速、声衰减等)、孔隙水化学组成(如SO42−、溶解气含量)会发生明显改变,这是支撑地球物理和地球化学探测技术应用的理论基础。浅层气的存在会改变土体力学特性,对工程建设造成较大危害;同时沉积物中的甲烷也会逸出到大气中,加剧全球变暖。基于对现有成果的总结,建议进一步加强海底浅层气形成机理、运移特性及其与气候变化的互馈机制方面的理论研究。
Abstract:With the continuous deepening of ocean development and utilization and the ongoing exacerbation of global climate change, the disaster issues caused by shallow gas (mainly methane) in nearshore sediments and the potential climate impacts have received additional attention. However, systematic understanding of shallow gas remains lacking. A comprehensive review of the main knowledge related to shallow gas is conducted, including formation mechanisms, occurrence forms, investigation techniques, distribution characteristics, controlling factors, major hazards, etc., to provide a support for subsequent related investigations, theoretical studies, and development in the technology disaster reduction and prevention. Shallow gas is commonly found in the sand bodies filled in the Quaternary incised valleys of coastal delta plains and in the fine-grained sediments of the nearshore Holocene, in the form of gas pockets, dispersed gas bubbles, or dissolved gas. In most nearshore areas, shallow gas is mainly of biogenic origin. The acoustic properties of gas-bearing sediments (such as sound velocity, sound attenuation, etc.) and the chemical composition of pore water (e.g., SO42−, dissolved gas content) undergo significant changes, providing a theoretical basis for the application of geophysical and geochemical exploration technologies. The presence of shallow gas can alter the mechanical properties of sediments, causing significant hazards to engineering construction; meanwhile, methane in sediments can also escape into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming. Based on the summary of existing achievements, it is recommended to further strengthen the theoretical research on the formation mechanisms, migration characteristics, and feedback mechanisms with climate change of submarine shallow gas.
-
Key words:
- methane /
- formation mechanism /
- distribution characteristics /
- investigation method /
- hazard /
- China Offshore
-

-
图 1 近海沉积物中不同深度产甲烷相关生物地球化学过程示意图[16]
Figure 1.
图 2 近海松散细颗粒沉积物中的浅层气主要存在形式[16]
Figure 2.
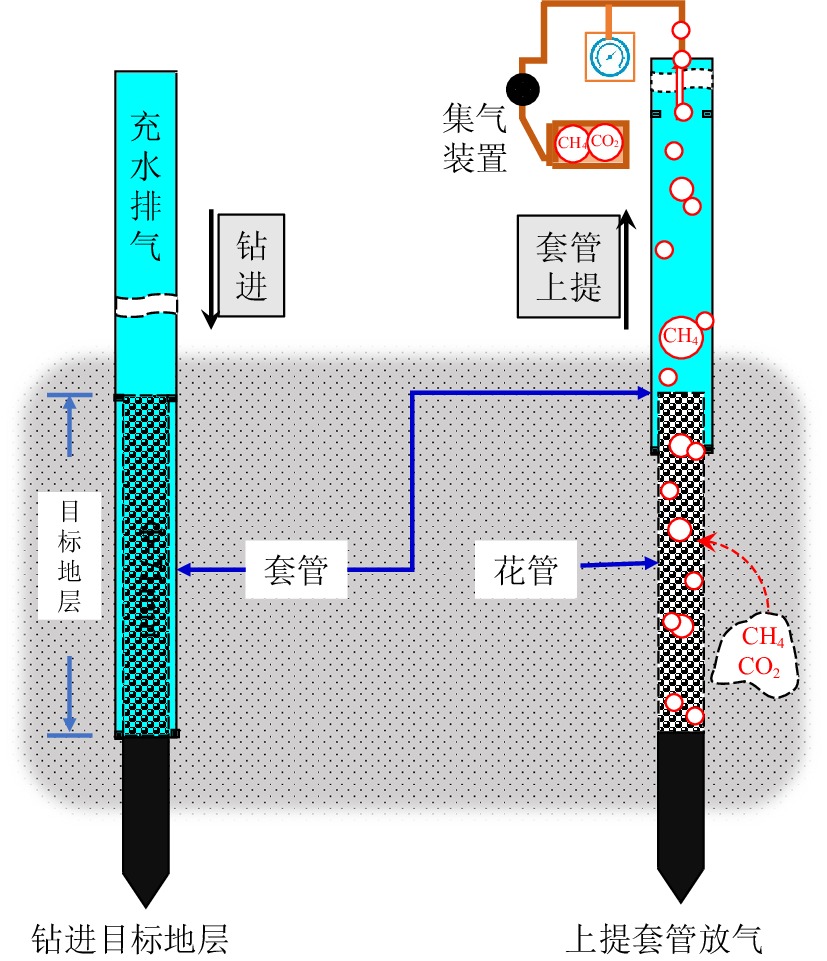
图 8 杭州湾工程地质勘察过程中浅层气灾害事故[77]
Figure 8.
图 9 浅层气存在可能导致的危害[16]
Figure 9.
-
[1] 段晓勇. 近海沉积物中的甲烷[J]. 地球, 2023(5):28-31
DUAN Xiaoyong. Methane in coastal sediment[J]. Earth, 2023(5):28-31.]
[2] Lee T R, Phrampus B J, Skarke A, et al. Global estimates of biogenic methane production in marine sediments using machine learning and deterministic modeling[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2022, 36(7):e2021GB007248. doi: 10.1029/2021GB007248
[3] International Energy Agency. Methane Tracker Database, IEA, Paris. License: Creative Commons Attribution CC BY-SA 4.0. 2022.
[4] Xu Y S, Wu H N, Shen J S, et al. Risk and impacts on the environment of free-phase biogas in Quaternary deposits along the Coastal Region of Shanghai[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 137:129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.03.051
[5] 朱瑶宏, 黄燕庆, 曾洪贤, 等. 杭州湾大桥南岸工程地质特征与浅层气分布[J]. 岩土力学, 2002, 23(S1):215-219
ZHU Yaohong, HUANG Yanqing, ZENG Hongxian, et al. Engineering geological features and shallow gas distribution in south bank of Hangzhou bay bridge[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2002, 23(S1):215-219.]
[6] Teatini P, Tosi L, Strozzi T. Quantitative evidence that compaction of Holocene sediments drives the present land subsidence of the Po Delta, Italy[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B8):B08407.
[7] Emeis K C, Brüchert V, Currie B, et al. Shallow gas in shelf sediments of the Namibian coastal upwelling ecosystem[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2004, 24(6):627-642. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.01.007
[8] Kortekaas S, Sens E, Sarata B. Shallow gas hazard linked to worldwide delta environments[M]//Gourvenec S, White D. Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II. London: CRC Press, 2010: 221-225.
[9] Borges A V, Champenois W, Gypens N, et al. Massive marine methane emissions from near-shore shallow coastal areas[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:27908. doi: 10.1038/srep27908
[10] Egger M, Riedinger N, Mogollón J M, et al. Global diffusive fluxes of methane in marine sediments[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(6):421-425. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0122-8
[11] Glombitza C, Egger M, Røy H, et al. Controls on volatile fatty acid concentrations in marine sediments (Baltic Sea)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 258:226-241. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.05.038
[12] Whiticar M J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial Formation and oxidation of methane[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1-3):291-314. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00092-3
[13] Zhuang G C, Elling F J, Nigro L M, et al. Multiple evidence for methylotrophic methanogenesis as the dominant methanogenic pathway in hypersaline sediments from the Orca Basin, Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 187:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.005
[14] Zhuang G C, Lin Y S, Bowles M W, et al. Distribution and isotopic composition of trimethylamine, dimethylsulfide and dimethylsulfoniopropionate in marine sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2017, 196:35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2017.07.007
[15] Zhuang G C, Heuer V B, Lazar C S, et al. Relative importance of methylotrophic methanogenesis in sediments of the western Mediterranean Sea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 224:171-186. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.12.024
[16] Duan X Y, Yin P, Tsona N, et al. Biogenic methane in coastal unconsolidated sediment systems: a review[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 227:115803. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115803
[17] Beulig F, Røy H, Glombitza C, et al. Control on rate and pathway of anaerobic organic carbon degradation in the seabed[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(2):367-372.
[18] 贺行良, 王江涛, 刘昌岭, 等. 天然气水合物客体分子与同位素组成特征及其地球化学应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):163-174
HE Xingliang, WANG Jiangtao, LIU Changling, et al. Guest molecular and isotopic compositions of natural gas hydrates and its geochemical applications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3):163-174.]
[19] Vanwonterghem I, Evans P N, Parks D H, et al. Methylotrophic methanogenesis discovered in the archaeal phylum Verstraetearchaeota[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2016, 1:16170. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.170
[20] Mayumi D, Mochimaru H, Tamaki H, et al. Methane production from coal by a single methanogen[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6309):222-225. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf8821
[21] Zhou Z, Zhang C J, Liu P F, et al. Non-syntrophic methanogenic hydrocarbon degradation by an archaeal species[J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7892):257-262. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04235-2
[22] Liu L Y, Xie G J, Ding J, et al. Microbial methane emissions from the non-methanogenesis processes: a critical review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806:151362. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151362
[23] Weschenfelder J, Klein A H F, Green A N, et al. The control of palaeo-topography in the preservation of shallow gas accumulation: examples from Brazil, Argentina and South Africa[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 172:93-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.02.005
[24] Karnaukh V N, Astakhov A S, Vereshchagina O F, et al. Formation of subsurface shallow gas accumulations in Amurskiy Bay (Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan) as a result of postglacial sea-level change, paleoceanographic conditions and hydrological activity[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 372:31-52. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.12.004
[25] Lin C M, Li Y L, Zhuo H C, et al. Features and sealing mechanism of shallow biogenic gas in incised valley fills (the Qiantang River, eastern China): a case study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(4):909-922. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.11.006
[26] 林春明, 张霞, 徐振宇, 等. 长江三角洲晚第四纪地层沉积特征与生物气成藏条件分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(5):589-601
LIN Chunming, ZHANG Xia, XU Zhenyu, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and accumulation conditions of shallow-biogenic gas for the Late Quaternary sediments in the Changjiang River Delta area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(5):589-601.]
[27] Brekke T, Lønne Ø, Ohm S E. Light hydrocarbon gases in shallow sediments in the northern North Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 137(1-2):81-108. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(96)00081-3
[28] Rahman M, Mainul Kabir S M, Imam B, et al. Occurrence, distribution, and origin of shallow biogenic gas in Late Quaternary unconsolidated sand deposit of shahbazpur structure, southern Bangladesh[J]. Petroleum and Coal, 2018, 60(6):1216-1227.
[29] García-García A, Orange D, Lorenson T, et al. Shallow gas off the Rhône prodelta, Gulf of Lions[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 234(1-4):215-231. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.09.005
[30] García-García A, Tesi T, Orange D, et al. Understanding shallow gas occurrences in the Gulf of Lions[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2007, 27(2):143-154.
[31] García-García A, Orange D L, Miserocchi S, et al. What controls the distribution of shallow gas in the western Adriatic Sea?[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(3-4):359-374. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.11.003
[32] Orange D L, García-García A, Mcconnell D, et al. High-resolution surveys for Geohazards and shallow gas: NW Adriatic (Italy) and Iskenderun bay (turkey)[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2005, 26(2):247-266.
[33] Orange D L, García-García A, Lorenson T, et al. Shallow gas and flood deposition on the Po Delta[J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 222-223:159-177. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.06.040
[34] Missiaen T, Murphy S, Loncke L, et al. Very high-resolution seismic mapping of shallow gas in the Belgian coastal zone[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(16):2291-2301. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00056-0
[35] Iglesias J, García-Gil S. High-resolution mapping of shallow gas accumulations and gas seeps in San Simón Bay (Ría de Vigo, NW Spain). Some quantitative data[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2007, 27(2):103-114.
[36] Vardar D, Alpar B. High-resolution seismic characterization of shallow gas accumulations in the southern shelf of Marmara Sea, Turkey[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2016, 64(3):589-609. doi: 10.1515/acgeo-2015-0059
[37] 李凤, 段晓勇, 贺行良, 等. 杭州湾沉积物中甲烷的垂向分布及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(6):112-121
LI Feng, DUAN Xiaoyong, HE Xingliang, et al. Vertical distribution and controlling factors of methane in sediments of Hangzhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(6):112-121.]
[38] Kim D C, Lee G S, Lee G H, et al. Sediment echo types and acoustic characteristics of gas-related acoustic anomalies in Jinhae Bay, southern Korea[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2008, 12(1):47-61. doi: 10.1007/s12303-008-0007-8
[39] . 陈雨沣. 长江水下三角洲浅层气发育特征与环境效应[D]. 华东师范大学博士学位论文, 2023
CHEN Yufeng. Development and environmental effects of shallow gas in the Yangtze subaqueous delta[D]. Doctor Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2023.]
[40] Chiu J K, Tseng W H, Liu C S. Distribution of gassy sediments and Mud volcanoes offshore southwestern Taiwan[J]. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 2006, 17(4):703-722. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2006.17.4.703(GH)
[41] Meckel T A, Mulcahy F J. Use of novel high-resolution 3D marine seismic technology to evaluate Quaternary fluvial valley development and geologic controls on shallow gas distribution, inner shelf, Gulf of Mexico[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(1):SC35-SC49. doi: 10.1190/INT-2015-0092.1
[42] Andreassen K, Nilssen E G, Ødegaard C M. Analysis of shallow gas and fluid migration within the Plio-Pleistocene sedimentary succession of the SW Barents Sea continental margin using 3D seismic data[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2007, 27(2):155-171.
[43] Lee S H, Chough S K. Distribution and origin of shallow gas in deep-sea sediments of the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Sea of Japan)[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2002, 22(4):204-209. doi: 10.1007/s00367-002-0114-x
[44] Sun Q L, Wu S G, Cartwright J, et al. Shallow gas and focused fluid flow systems in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 315-318:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.05.003
[45] García-García A, Levey M D, Watson E B. High resolution seismic study of the Holocene infill of the Elkhorn Slough, central California[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 55:108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.01.012
[46] Tóth Z, Spiess V, Mogollón J M, et al. Estimating the free gas content in Baltic Sea sediments using compressional wave velocity from marine seismic data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2014, 119(12):8577-8593. doi: 10.1002/2014JB010989
[47] Tóth Z, Spieß V, Jensen J. Seismo-acoustic signatures of shallow free gas in the Bornholm Basin, Baltic Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 88:228-239. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.08.007
[48] Flury S, Røy H, Dale A W, et al. Controls on subsurface methane fluxes and shallow gas Formation in Baltic Sea sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 188:297-309. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.037
[49] Wever T F, Abegg F, Fiedler H M, et al. Shallow gas in the muddy sediments of Eckernförde Bay, Germany[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1998, 18(14-15):1715-1739. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(98)00055-7
[50] 吴秀山, 童仁园, 李青. 近海浅层气甲烷浓度原位在线监测方法与仪器研究[J]. 传感技术学报, 2023, 36(1):153-158
WU Xiushan, TONG Renyuan, LI Qing. In-situ online monitoring method and instrument study for methane concentration in offshore shallow gas[J]. Chinese Journal of sensors and actuators, 2023, 36(1):153-158.]
[51] 段晓勇, 印萍, 曹珂, 等. 中国地质调查局舟山海洋地质灾害野外科学观测研究站进展与成果[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(6):88-92
DUAN Xiaoyong, YIN Ping, CAO Ke, et al. Introduction of Zhoushan marine geologic hazards field scientific observation and research station, China geological survey[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(6):88-92.]
[52] 贺行良, 谭丽菊, 段晓勇, 等. 杭州湾沉积物中硫酸盐—甲烷转换带内的碳循环[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):51-60
HE Xingliang, TAN Liju, DUAN Xiaoyong, et al. Carbon cycle within the sulfate-methane transition zone in the marine sediments of Hangzhou Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3):51-60.]
[53] Liao C C. Discussion of “Formation mechanism of large pockmarks in the subaqueous Yellow River Delta”[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2019, 37(9):1149-1150.
[54] Tian Z C, Guo X J, Qiao L Z, et al. Formation mechanism of large pockmarks in the subaqueous Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2019, 37(6):651-659.
[55] Schneider von Deimling J, Hoffmann J, Geersen J, et al. Millions of seafloor pits, not pockmarks, induced by vertebrates in the North Sea[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2023, 4(1):478.
[56] 李萍, 杜军, 刘乐军, 等. 我国近海海底浅层气分布特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1):69-74
LI Ping, DU Jun, LIU Lejun, et al. Distribution characteristics of the shallow gas in Chinese offshore seabed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1):69-74.]
[57] 仇建东, 刘健, 孔祥淮, 等. 山东半岛南部滨浅海区的海洋灾害地质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):27-33
QIU Jiandong, LIU Jian, KONG Xianghuai, et al. Marine geo-hazards in the coastal and offshore area of southern Shandong peninsula[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1):27-33.]
[58] 孔祥淮, 刘健, 杜远生, 等. 南黄海西部滨浅海区灾害地质因素特征及分布规律[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(2):43-52
KONG Xianghuai, LIU Jian, DU Yuansheng, et al. Characteristics and distribution of geo-hazard factors in the western South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(2):43-52.]
[59] 张志忠, 顾兆峰, 刘锡清, 等. 南黄海灾害地质及地质环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5):15-22
ZHANG Zhizhong, GU Zhaofeng, LIU Xiqing, et al. Hazardous geology and marine geologic environmental evolution in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(5):15-22.]
[60] 武彬, 林丰增, 张艺武, 等. 福建宁德近岸海域海底浅层气分布特征及成因分析[J]. 华东地质, 2022, 43(1):87-93
WU Bin, LIN Fengzeng, ZHANG Yiwu, et al. Distribution characteristics and genesis analysis of submarine shallow gas in Ningde coastal area, Fujian province[J]. East China Geology, 2022, 43(1):87-93.]
[61] 邢磊, 焦静娟, 刘雪芹, 等. 渤海海域浅层气分布及地震特征分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(11):70-78
XING Lei, JIAO Jingjuan, LIU Xueqin, et al. Distribution and seismic reflection characteristics of shallow gas in Bohai Sea[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(11):70-78.]
[62] 赵卫, 熊元凯, 宫少军, 等. 天津近海海底地质灾害类型及声学特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(2):119-126
ZHAO Wei, XIONG Yuankai, GONG Shaojun, et al. Acoustic characteristics and types of submarine geological hazards in Tianjin offshore areas[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(2):119-126.]
[63] Visnovitz F, Bodnár T, Tóth Z, et al. Seismic expressions of shallow gas in the lacustrine deposits of Lake Balaton, Hungary[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2015, 13(5):433-447. doi: 10.3997/1873-0604.2015026
[64] Laier T, Jensen J B. Shallow gas depth-contour map of the Skagerrak-western Baltic Sea region[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2007, 27(2):127-141.
[65] Lee G H, Kim D C, Kim H J, et al. Shallow gas in the central part of the Korea Strait shelf mud off the southeastern coast of Korea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2005, 25(16):2036-2052. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.08.008
[66] Hagen R A, Vogt P R. Seasonal variability of shallow biogenic gas in Chesapeake Bay[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 158(1-4):75-88. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00185-6
[67] Albert D B, Martens C S, Alperin M J. Biogeochemical processes controlling methane in gassy coastal sediments: part 2: groundwater flow control of acoustic turbidity in Eckernförde Bay Sediments[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1998, 18(14-15):1771-1793. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(98)00057-0
[68] Valentine D L. Biogeochemistry and microbial ecology of methane oxidation in anoxic environments: a review[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2002, 81(1-4):271-282.
[69] Wu Z J, Zhou H Y, Ren D Z, et al. Processes controlling the seasonal and spatial variations in sulfate profiles in the pore water of the sediments surrounding Qi’ao Island, Pearl River Estuary, southern China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 98:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.02.001
[70] Frederick J M, Buffett B A. Submarine groundwater discharge as a possible Formation mechanism for permafrost-associated gas hydrate on the circum-Arctic continental shelf[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2016, 121(3):1383-1404. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012627
[71] Sun H Y, Chen Z X, Lai X H, et al. Influence of shallow gas on the geotechnical properties of pockmark soil: a case study in the East China Sea[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 93:101966. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2019.101966
[72] Lin C M, Gu L X, Li G Y, et al. Geology and Formation mechanism of Late Quaternary shallow biogenic gas reservoirs in the Hangzhou Bay area, eastern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(5):613-625. doi: 10.1306/01070403038
[73] Dalla Valle G, Gamberi F. Pockmarks and seafloor instability in the Olbia continental slope (northeastern Sardinian margin, Tyrrhenian Sea)[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2011, 32(1-2):193-205. doi: 10.1007/s11001-011-9133-1
[74] Papatheodorou G, Ferentinos G. Submarine and coastal sediment failure triggered by the 1995, MS = 6.1 R Aegion earthquake, Gulf of Corinth, Greece[J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 137(3-4):287-304. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(96)00089-8
[75] Riboulot V, Cattaneo A, Sultan N, et al. Sea-level change and free gas occurrence influencing a submarine landslide and pockmark Formation and distribution in deepwater Nigeria[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 375:78-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.05.013
[76] Terrinha P, Duarte H, Brito P, et al. The Tagus River delta landslide, off Lisbon, Portugal. Implications for Marine geo-hazards[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 416:105983. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105983
[77] . 林春明, 张霞. 江浙沿海平原晚第四纪地层沉积与天然气地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018
LIN Chunming, ZHANG Xia. Late Quaternary Stratigraphy, Sedimentology and Natural Gas Geology in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang Coastal Plain[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018.]
[78] Weber T, Wiseman N A, Kock A. Global ocean methane emissions dominated by shallow coastal waters[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1):4584. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12541-7
[79] Palma-Silva C, Marinho C C, Albertoni E F, et al. Methane emissions in two small shallow neotropical lakes: the role of temperature and trophic level[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 81:373-379. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.09.029
[80] Saunois M, Stavert A R, Poulter B, et al. The global methane budget 2000-2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12(3):1561-1623. doi: 10.5194/essd-12-1561-2020
[81] Hu Y, Li H D, Xu J. Shallow gas accumulation in a small estuary and its implications: a case history from in and around Xiamen Bay[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(24):L24605.
[82] Kudo K, Yamada K, Toyoda S, et al. Spatial distribution of dissolved methane and its source in the western Arctic Ocean[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2018, 74(3):305-317. doi: 10.1007/s10872-017-0460-y
[83] Hilligsøe K M, Jensen J B, Ferdelman T G, et al. Methane fluxes in marine sediments quantified through core analyses and seismo-acoustic mapping (Bornholm Basin, Baltic Sea)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 239:255-274. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.07.040
[84] Schmale O, Schneider Von Deimling J, Gülzow W, et al. Distribution of methane in the water column of the Baltic Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(12):L12604.
[85] Shakhova N, Semiletov I, Panteleev G. The distribution of methane on the Siberian Arctic shelves: implications for the marine methane cycle[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(9):L09601.
[86] Matveeva T, Savvichev A S, Semenova A, et al. Source, origin, and spatial distribution of shallow sediment methane in the Chukchi Sea[J]. Oceanography, 2015, 28(3):202-217. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2015.66
[87] Berchet A, Pison I, Crill P M, et al. Using ship-borne observations of methane isotopic ratio in the Arctic Ocean to understand methane sources in the Arctic[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 20(6):3987-3998. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-3987-2020
[88] Scandella B P, Delwiche K, Hemond H F, et al. Persistence of bubble outlets in soft, methane-generating sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences, 2017, 122(6):1298-1320. doi: 10.1002/2016JG003717
[89] Coffin R B, Smith J P, Plummer R E, et al. Spatial variation in shallow sediment methane sources and cycling on the Alaskan Beaufort Sea Shelf/Slope[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 45:186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.05.002
[90] Solomon E A, Kastner M, Macdonald I R, et al. Considerable methane fluxes to the atmosphere from hydrocarbon seeps in the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(8):561-565. doi: 10.1038/ngeo574
[91] Petrenko V V, Smith A M, Brook E J, et al. 14CH4 measurements in Greenland Ice: investigating last glacial termination CH4 sources[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5926):506-508. doi: 10.1126/science.1168909
[92] Jayakumar D A, Naqvi S W A, Narvekar P V, et al. Methane in coastal and offshore waters of the Arabian Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2001, 74(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(00)00089-X
[93] Akam S A, Coffin R B, Abdulla H A N, et al. Dissolved inorganic carbon pump in methane-charged shallow marine sediments: state of the art and new model perspectives[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2020, 7:206. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00206
[94] George R, Gullström M, Mtolera M S P, et al. Methane emission and sulfide levels increase in tropical seagrass sediments during temperature stress: a mesocosm experiment[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 10(4):1917-1928. doi: 10.1002/ece3.6009
[95] Mestdagh T, Poort J, De Batist M. The sensitivity of gas hydrate reservoirs to climate change: perspectives from a new combined model for permafrost-related and marine settings[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 169:104-131. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.04.013
[96] Kretschmer K, Biastoch A, Rüpke L, et al. Modeling the fate of methane hydrates under global warming[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2015, 29(5):610-625. doi: 10.1002/2014GB005011
[97] Dean J F. Old methane and modern climate change[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6480):846-848. doi: 10.1126/science.aba8518
[98] Keil R. Anthropogenic forcing of carbonate and organic carbon preservation in marine sediments[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2017, 9:151-172. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060724
[99] Schout G, Hartog N, Hassanizadeh S M, et al. Impact of an historic underground gas well blowout on the current methane chemistry in a shallow groundwater system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(2):296-301.
[100] Bravo M E, Aliotta S, Fiori S, et al. Distribution, vertical position and ecological implications of shallow gas in Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 202:222-231. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.01.007
[101] de Carlos A, Martínez-Carreño N, Barros-García D, et al. Geochemical and microbial context of the gassy sediments in the Ría de Vigo (NW of Spain)[J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 385:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.12.004
[102] Champilou J B, Baltzer A, Murat A, et al. New evidence of perfect overlapping of Haploops and pockmarks field: is it a coincidence?[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 415:105961. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.105961
[103] Delavy F P, de Figueiredo Jr A G, Martins M V A, et al. High-resolution acoustic mapping of gas charged sediments and living benthic foraminifera assemblages from the NE Region of the Guanabara Bay (Rj, Brazil)[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Environments, 2016, 1(3):367-392.
-




 下载:
下载: