Distribution of strategic key metals in deep-sea polymetallic nodules and their controlling factors
-
摘要:
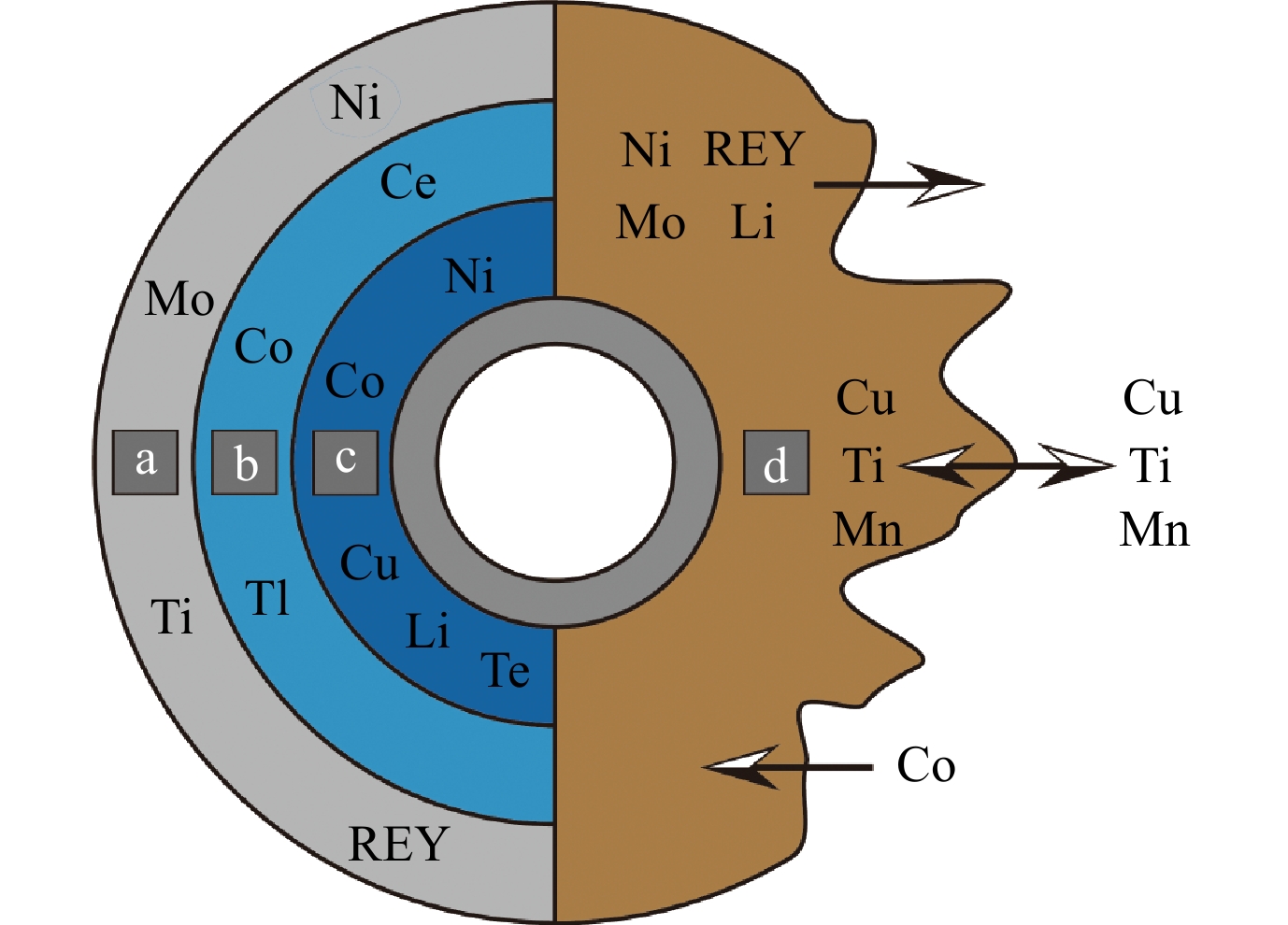
深海多金属结核富集经济发展和人民生活亟需的战略性关键金属,资源潜力巨大。通过对前人研究工作的系统性归纳总结,揭示不同类型、不同环境多金属结核内主要分布于锰氧化物中的Co、Cu、Li、Mn、Mo、Ni、Tl,以及主要分布在铁羟基氧化物内的REY、Te、Ti的含量,赋存状态,迁移演化过程及富集机制。表面吸附作用首先驱动这些战略性关键金属富集进入多金属结核,其中Mo、Ni、REY和Ti仅通过吸附作用就能实现高度富集。随后Ce、Co和Tl发生的氧化反应,以及Co、Cu、Li、Ni和Te通过晶格进入的方式继续增强这些金属在结核内的富集程度。当结核被沉积物埋藏且周边环境由氧化向次氧化转变后,发生的大规模矿物相变会导致结核富集Co而强烈亏损Ni、REY、Mo和Li。结核最终处于还原环境时,其矿物晶体格架会彻底崩塌和溃散,推测仅有部分铁氧化物组分会残留下来。未来亚微米尺度和原位高精度的实验研究工作,将提升对于这些金属,尤其是诸如Te、Tl等低含量金属在结核内分布、富集过程和控制因素的深刻理解,助力深海金属矿产资源勘查和选冶利用。
Abstract:Deep-sea polymetallic nodules are widely recognized as potential resources in future for strongly enriching in many strategic key metals for high-technology applications and economic prosperity. By summarizing previous studies, the contents, occurrence, enrichment mechanism, migration, and evolution of Co, Cu, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, and Tl distributed mainly in manganese oxides, and REY, Te, Ti distributed mainly in iron oxyhydroxides in different types and settings of polymetallic nodules were analyzed. The surface sorption drove these metals to enrich into polymetallic nodules first, in which Mo, Ni, REY, and Ti could achieve high enrichment in this stage alone. Subsequently, the oxidation of Ce, Co, and Tl, and the structural incorporation of Co, Cu, Li, Ni, and Te continued to be enriched in these strategic metals in polymetallic nodules. When the polymetallic nodules were buried by abyssal sediments, and the surrounding environment changed from oxic conditions to suboxic conditions, the large-scale mineralogical transformation could lead to the enrichment of Co, but strongly depleted in Ni, REY, Mo, and Li compared to surface nodules. When buried polymetallic nodules were finally in reduced conditions, the mineral crystal lattice of these nodules would dissolve and collapse completely, perhaps only some iron oxyhydroxides component of the former nodule could remain. Future sub-micron and in-situ high-precision experimental research work will improve our deep understanding of the distribution, enrichment history, and controlling factors of these strategic key metals in nodules, especially low-content metals of Te and Tl, and help the exploration and utilization of deep-sea polymetallic nodules.
-
Key words:
- polymetallic nodules /
- strategic key metals /
- distribution /
- constraint
-

-
[1] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. 13.11 - deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2014, 13:273-291.
[2] Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer, 2017: 23-63.
[3] Bruland K W, Middag R, Lohan M C. 8.2 - controls of trace metals in seawater[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 2014, 8:19-51.
[4] Rudnick R L, Gao S. 4.1 - composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 2014, 4:1-51.
[5] 《矿产资源工业要求参考手册》编委会. 矿产资源工业要求参考手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021
Reference Manual for Industrial Requirements of Mineral Resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.]
[6] Mizell K, Hein J R, Au M, et al. Estimates of metals contained in abyssal manganese nodules and ferromanganese crusts in the global ocean based on regional variations and genetic types of nodules[M]//Sharma R. Perspectives on Deep-Sea Mining: Sustainability, Technology, Environmental Policy and Management. Cham: Springer, 2022: 53-80.
[7] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Kuhn T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(3):158-169.
[8] 国土资源部信息中心. 世界矿产资源年评-2016[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016
Information Center of Ministry of Land and Resources, China. World Mineral Resources Annual Review 2016[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.]
[9] 国土资源部, 国家发展和改革委员会, 工业和信息化部, 等. 全国矿产资源规划(2016—2020年)[R]. 北京, 2016
Ministry of Land and Resources, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, et al. National mineral resources planning (2016-2020)[R]. Beijing, 2016.]
[10] 陈其慎, 张艳飞, 邢佳韵, 等. 国内外战略性矿产厘定理论与方法[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(2):137-144
CHEN Qishen, ZHANG Yanfei, XING Jiayun, et al. Methods of strategic mineral resources determination in China and abroad[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(2):137-144.]
[11] 陈甲斌, 霍文敏, 冯丹丹, 等. 中国与美欧战略性(关键)矿产资源形势分析[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2020, 33(8):9-17
CHEN Jiabin, HUO Wenmin, FENG Dandan, et al. Analysis of strategic (critical) mineral resources situation in China and the U. S. and the EU[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2020, 33(8):9-17.]
[12] 王登红, 孙艳, 代鸿章, 等. 我国“三稀矿产”的资源特征及开发利用研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2019, 21(1):119-127 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2019.01.017
WANG Denghong, SUN Yan, DAI Hongzhang, et al. Characteristics and exploitation of rare earth, rare metal and rare-scattered element minerals in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2019, 21(1):119-127.] doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2019.01.017
[13] Belkin I M, Andersson P S, Langhof J. On the discovery of ferromanganese nodules in the World Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2021, 175:103589. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2021.103589
[14] 张海文. 《联合国海洋法公约》开放签署四十周年: 回顾与展望[J]. 武大国际法评论, 2022, 6(6):1-14
ZHANG Haiwen. The 40th anniversary of the opening for signature of the united nations convention on the law of the sea: retrospect and prospect[J]. Wuhan University International Law Review, 2022, 6(6):1-14.]
[15] 许东禹, 金庆焕, 梁德华. 太平洋中部多金属结核及其形成环境[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994
XU Dongyu, JIN Qinghuan, LIANG Dehua. Polymetallic Nodules and Their Formation Environment in the Central Pacific Ocean[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1994.]
[16] 许东禹. 多金属结核的特征及成因[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993
XU Dongyu. Characteristics and Genesis of Polymetallic Nodules[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993.]
[17] 许东禹. 大洋矿产地质学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2013
XU Dongyu. Ocean Mineral Geology[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2013.]
[18] ISA. (International Seabed Authority)[EB/OL]. 2023. https://www.isa.org.jm/exploration-contracts/.
[19] 中华人民共和国常驻国际海底管理局代表处. 国际海底管理局第28届第二期会议闭幕[EB/OL]. (2023-08-01). http://isa.china-mission.gov.cn/xwdt/202308/t20230801_11120483.htm
Permanent Mission of PRC to International Seabed Authority. Closure of the second part of the 28th session of the International Seabed Authority[EB/OL]. (2023-08-01). http://isa.china-mission.gov.cn/xwdt/202308/t20230801_11120483.htm.]
[20] Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87:3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003
[21] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[22] 王嫱, 苏轶娜, 闻少博, 等. 主要矿产品供需形势分析报告(2020年)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020
WANG Qiang, SU Yina, WEN Shaobo, et al. Analysis on Supply and Demand Situation of Mineral Resources (2020)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.]
[23] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[24] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Halbach P, et al. Iron and manganese oxide mineralization in the Pacific[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1997, 119:123-138. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1997.119.01.09
[25] Post J E, Heaney P J, Hanson J. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of the structure and dehydration behavior of todorokite[J]. American Mineralogist, 2003, 88(1):142-150. doi: 10.2138/am-2003-0117
[26] Bodeï S, Manceau A, Geoffroy N, et al. Formation of todorokite from vernadite in Ni-rich hemipelagic sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(23):5698-5716. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.020
[27] Post J E, McKeown D A, Heaney P J. Raman spectroscopy study of manganese oxides: Tunnel structures[J]. American Mineralogist, 2020, 105(8):1175-1190. doi: 10.2138/am-2020-7390
[28] Kuhn T, Bostick B C, Koschinsky A, et al. Enrichment of Mo in hydrothermal Mn precipitates: possible Mo sources, formation process and phase associations[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 199(1-2):29-43. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00054-8
[29] Azami K, Koyama K, Machida S, et al. Formation of hydrothermal ferromanganese oxides from the Daigo-Kume Knoll in the middle Okinawa Trough, Japan[J]. Marine Geology, 2023, 463:107117. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2023.107117
[30] Gueguen B, Rouxel O, Fouquet Y. Nickel isotopes and rare earth elements systematics in marine hydrogenetic and hydrothermal ferromanganese deposits[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 560:119999. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119999
[31] Shaw T J, Gieskes J M, Jahnke R A. Early diagenesis in differing depositional environments: The response of transition metals in pore water[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(5):1233-1246. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90149-F
[32] Von Stackelberg U. Growth history of manganese nodules and crusts of the Peru Basin[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1997, 119:153-176. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1997.119.01.11
[33] Volz J B, Mogollón J M, Geibert W, et al. Natural spatial variability of depositional conditions, biogeochemical processes and element fluxes in sediments of the eastern Clarion-Clipperton Zone, Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018, 140:159-172. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.08.006
[34] Mewes K, Mogollón J M, Picard A, et al. Impact of depositional and biogeochemical processes on small scale variations in nodule abundance in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2014, 91:125-141. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.06.001
[35] Mewes K, Mogollón J M, Picard A, et al. Diffusive transfer of oxygen from seamount basaltic crust into overlying sediments: An example from the Clarion–Clipperton Fracture Zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 433:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.10.028
[36] Wegorzewski A V, Kuhn T. The influence of suboxic diagenesis on the formation of manganese nodules in the Clarion Clipperton nodule belt of the Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357:123-138. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.004
[37] Koschinsky A, Winkler A, Fritsche U. Importance of different types of marine particles for the scavenging of heavy metals in the deep-sea bottom water[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(5):693-710. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00161-0
[38] Foster A L, Klofas J M, Hein J R, et al. Speciation of energy critical elements in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules by principal component analysis and least-squares fits to XAFS spectra[C]//American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2011. 2011.
[39] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Halliday A N. Global occurrence of tellurium-rich ferromanganese crusts and a model for the enrichment of tellurium[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(6):1117-1127. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01279-6
[40] Wang X Y, Sherman D M. Molecular speciation of Mo (VI) on goethite and its implications for molybdenum and its isotopic cycle in ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 313:116-132. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.08.040
[41] Kashiwabara T, Takahashi Y, Tanimizu M, et al. Molecular-scale mechanisms of distribution and isotopic fractionation of molybdenum between seawater and ferromanganese oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(19):5762-5784. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.07.022
[42] Hodkinson R A, Stoffers P, Scholten J, et al. Geochemistry of hydrothermal manganese deposits from the Pitcairn Island hotspot, southeastern Pacific[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(22):5011-5029. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90228-3
[43] Manceau A, Simionovici A, Findling N, et al. Crystal chemistry of thallium in marine ferromanganese deposits[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2022, 6(5):1269-1285. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00447
[44] Rehkämper M, Frank M, Hein J R, et al. Thallium isotope variations in seawater and hydrogenetic, diagenetic, and hydrothermal ferromanganese deposits[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 197(1-2):65-81. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00462-4
[45] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3-4):331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00122-1
[46] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24):5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[47] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine co-rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer, 2017: 65-141.
[48] Astakhova N V. Occurrence forms and distribution of precious and base metals in ferromanganese crusts from the Sea of Japan[J]. Oceanology, 2013, 53(6):686-701. doi: 10.1134/S0001437013050019
[49] Marcus M A, Toner B M, Takahashi Y. Forms and distribution of Ce in a ferromanganese nodule[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2018, 202:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.03.005
[50] Peacock C L. Physiochemical controls on the crystal-chemistry of Ni in birnessite: Genetic implications for ferromanganese precipitates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(12):3568-3578. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.020
[51] Peacock C L, Sherman D M. Crystal-chemistry of Ni in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules[J]. American Mineralogist, 2007, 92(7):1087-1092. doi: 10.2138/am.2007.2378
[52] Kashiwabara T, Takahashi Y, Tanimizu M. A XAFS study on the mechanism of isotopic fractionation of molybdenum during its adsorption on ferromanganese oxides[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(6):e31-e36. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0060
[53] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493:224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045
[54] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10):1709-1725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00063-4
[55] 姜学钧, 林学辉, 姚德, 等. 稀土元素在水成型海洋铁锰结壳中的富集特征及机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(2): 197-204
JIANG Xuejun, LIN Xuehui, YAO De, et al. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 197-203.]
[56] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1):37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[57] Bidoglio G, Gibson P N, O'Gorman M, et al. X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation of surface redox transformations of thallium and chromium on colloidal mineral oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(10):2389-2394. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90576-I
[58] Bau M. Scavenging of dissolved yttrium and rare earths by precipitating iron oxyhydroxide: experimental evidence for Ce oxidation, Y-Ho fractionation, and lanthanide tetrad effect[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(1):67-77. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00014-9
[59] Yang P, Post J E, Wang Q, et al. Metal adsorption controls stability of layered manganese oxides[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(13):7453-7462.
[60] Peacock C L, Moon E M. Oxidative scavenging of thallium by birnessite: Explanation for thallium enrichment and stable isotope fractionation in marine ferromanganese precipitates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 84:297-313. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.01.036
[61] Lide D R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics[M]. Florida: CRC Press, 2010.
[62] Manceau A, Lanson M, Takahashi Y. Mineralogy and crystal chemistry of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu in a deep-sea Pacific polymetallic nodule[J]. American Mineralogist, 2014, 99(10):2068-2083. doi: 10.2138/am-2014-4742
[63] Sherman D M, Peacock C L. Surface complexation of Cu on birnessite (δ-MnO2): Controls on Cu in the deep ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(23):6721-6730. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.08.042
[64] Manceau A, Marcus M A, Grangeon S. Determination of Mn valence states in mixed-valent manganates by XANES spectroscopy[J]. American Mineralogist, 2012, 97(5-6):816-827. doi: 10.2138/am.2012.3903
[65] Halbach P, Scherhag C, Hebisch U, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical control of different genetic types of deep-sea nodules from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1981, 16(1):59-84.
[66] Jiang X J, Lin X H, Yao D, et al. Geochemistry of lithium in marine ferromanganese oxide deposits[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2007, 54(1):85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2006.10.004
[67] Kashiwabara T, Oishi Y, Sakaguchi A, et al. Chemical processes for the extreme enrichment of tellurium into marine ferromanganese oxides[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 131:150-163. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.01.020
[68] Hens T, Brugger J, Etschmann B, et al. Nickel exchange between aqueous Ni(II) and deep-sea ferromanganese nodules and crusts[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 528:119276. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119276
[69] Heller C, Kuhn T, Versteegh G J M, et al. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018, 142:16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2018.09.008
[70] Wegorzewski A V, Grangeon S, Webb S M, et al. Mineralogical transformations in polymetallic nodules and the change of Ni, Cu and Co crystal-chemistry upon burial in sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 282:19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.04.012
[71] Marcus M A, Edwards K J, Gueguen B, et al. Iron mineral structure, reactivity, and isotopic composition in a South Pacific Gyre ferromanganese nodule over 4 Ma[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 171:61-79. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.08.021
[72] Huang F, Fu Y, Li D F, et al. Early diagenetic REE migration from Fe-Mn nodules to fish teeth in deep sea sediments[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023, 160:105581. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105581
[73] Atkins A L, Shaw S, Peacock C L. Nucleation and growth of todorokite from birnessite: Implications for trace-metal cycling in marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 144:109-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.08.014
[74] Missen O P, Etschmann B, Mills S J, et al. Tellurium biogeochemical transformation and cycling in a metalliferous semi-arid environment[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022, 321:265-292. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.12.024
[75] Morishita Y, Usui A, Takahata N, et al. Secondary ion mass spectrometry microanalysis of platinum in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[M]//Sharma R. Perspectives on Deep-Sea Mining: Sustainability, Technology, Environmental Policy and Management. Cham: Springer, 2022: 115-133.
[76] de Matos C S, Benites M, Jovane L, et al. Chemical-mineralogical characterization of critical elements into ferromanganese crusts[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 25:5633-5649. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.07.021
[77] Sutherland K M, Wankel S D, Hein J R, et al. Spectroscopic insights into ferromanganese crust formation and diagenesis[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2020, 21(11):e2020GC009074. doi: 10.1029/2020GC009074
-




 下载:
下载: