Numerical simulation and environmental impact prediction of karst groundwater in Sangu Spring Basin, China
-
Abstract:
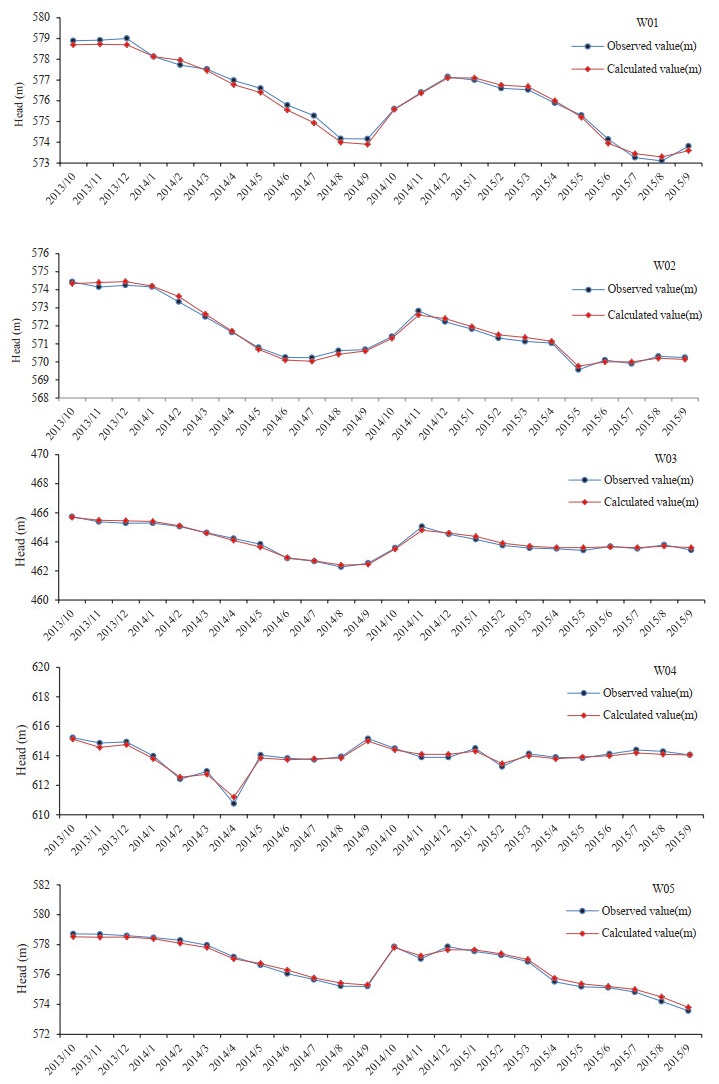
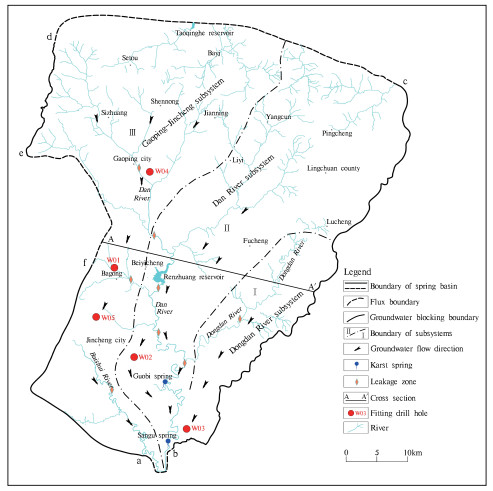
The changes of development and utilization of karst groundwater in Sangu Spring Basin have made the original groundwater resource evaluation unable to meet the needs of future economic development. Based on analysis of existing data, combined with the characteristics of supplement, runoff and draining of regional karst groundwater, the Visual Modelflow software was used to build a numerical simulation model of Sangu spring Basin. The amount of karst groundwater resource and groundwater environment of the Basin were evaluated under different exploitation schemes, and the changes of karst groundwater environment in the future ten years were also predicted. The fitting error which is less than 0.5 m between the calculated value and measured value of the water level in the fitted borehole accounts for 93%. For the lithologically and structurally complex Sangu Spring Basin, the fitting effect of numerical simulation model was ideal. On the basis of the current mining amount of 111.80 million m3/a, the total redistributed exploited amount in the spring region was 61.79 million m3/a. Under the condition that the quantity of recoverable resources reached 173.59 million m3/a and under different precipitation schemes, all constraint conditions were satisfied, such as regional water level drawdown, maximum allowable water level drawdown in every simulated water source area and the flow rate of Guobi Spring. The results will provide a scientific basis for the rational development and utilization of karst groundwater in Sangu Spring Basin.
-
Key words:
- Sangu Spring Basin /
- Karst groundwater /
- Numerical simulation /
- Constraints
-

-
Table 1. Mean rainfall and rainfall in different guaranteed rates
Series Mean 50% 75% 95% Jin-cheng Ling-chuan Gao-ping Jin-cheng Ling-chuan Gao-ping Jin-cheng Ling-chuan Gao-ping Jin-cheng Ling-chuan Gao-ping Multi-year mean 605.16 604.28 595.32 613.3 588.9 584.2 497.1 512.0 502.4 388.4 428.7 382.9 Recent year mean 563.94 569.84 537.47 558.6 560.3 487.6 525.5 543.0 435.6 414.0 471.90 378.6 Table 2. Renzhuang reservoir leakage in different water level
Elevation of reservoir's water level (m) 758~760 760~761 761~762 762~763 763~764 764~765 765~766 766~767 767~768 Leakage amount (m3/s) 0.027 6 0.087 1 0.322 0.404 0.479 0.912 0.988 1.245 2.282 Table 3. Hydrogeological parameters identification of model
Partition No. Txx(m2/d) Tyy(m2/d) Ss Partition No. Txx(m2/d) Tyy(m2/d) Ss 1 50 50 0.054 14 2 100 6 500 0.030 2 40 40 0.052 15 2 000 2 500 0.030 3 70 55 0.005 16 900 1 350 0.005 4 110 25 0.020 17 4 210 6 000 0.010 5 90 65 0.015 18 35 35 0.002 6 120 150 0.003 19 550 1 700 0.008 7 30 50 0.040 20 170 750 0.018 8 2 520 1 800 0.008 21 400 740 0.064 9 5 050 5 210 0.017 22 800 4 500 0.006 10 20 40 0.013 23 2 450 25 000 0.008 11 580 580 0.005 24 750 1500 0.019 12 40 130 0.026 25 70 810 0.074 13 420 80 0.045 Table 4. Groundwater balance in simulation period
Supplement items (×104 m3/a) Drainage items (×104 m3/a) Rainfall infiltration supplement 16 784.79 Karst spring drainage 14 921.87 Upper layer leakage supplement 9 125.87 Drainage of karst groundwater to watercourses 5 009.28 Watercourse seepage supplement 3 469.66 Undercurrent amount of karst groundwater 1 221.16 Reservoir seepage supplement 162.66 Exploitation amount of karst groundwater 11 180 Total 29 542.98 Total 32 332.31 Balance difference -2 789.33 Table 5. Redistribution of water resources exploitation in simulated water sources
Water sources Exploitation schemes Recoverable amount (m3/s) Recoverable amount
(ten thousand m3/a)Gaoping 0.10 304.68 Bagong 0.16 499.68 Beishidian 0.19 584.99 Urban area 0.39 1 243.11 Mianshang 0.41 1 304.05 Guobinan 0.71 2 242.48 Total 1.96 6 179.00 Table 6. The depth of water level in funnel center of water source under different precipitation schemes
Forecast time Multiyear average precipitation plan Forecast precipitation plan Gaoping Urban area Beishidian Bagong Guobi Gaoping Urban area Beishidian Bagong Guobi April 2020 -8.20 -7.73 -7.20 -7.93 -1.30 -8.33 -7.40 -6.87 -8.13 -1.40 April 2024 -12.13 -11.87 -10.87 -11.60 -2.13 -12.47 -11.53 -11.27 -11.80 -2.21 Table 7. Forecast results of Karst spring flow
Forecast time Spring flow rate (m3/s) Multiyear average precipitation schemes Forecast precipitation schemes Guobi Spring Sangu Spring Guobi Spring Sangu Spring April 2014 0.40 3.50 0.40 3.50 April 2020 0.18 3.09 0.173 3.04 April 2024 0.133 2.978 0.126 2.945 -
Abdulrahman Th-mohammad, Qassemh-jalut, Nadia L-abbas. 2020. Predicting groundwater level of wells in the Diyala River Basin in eastern Iraq using artiicial neural network. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engi-neering, 8(1): 87-96. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_journal-groundwater-science-engineering_thesis/0201277582482.html
FANG Xiang-qing, FU Yao-jun. 2011. Impact of coal mining on karst water system in North China. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 3: 293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2011.09.097
HOU Xin-wei, WANG Zhen-xing, LI Xiang-quan, et al. 2016. Hydrogeological environment geological survey report of Jindong energy base. Geological library of Shanxi Province: 45-189.
LI Hui-qing. 2018. Analysis on the groundwater ecological status in the Sanguquan Spring-feeding area of Jincheng City and restoration countermeasures. Shanxi Hydrotechnics, 2: 61-64, 67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sxslkj201802020
LI Xue-liang. 2003. Study on karstic groundwater boundary dividing in Sangu Spring area. Groundwater, 4: 224-225. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dixs200304005
LIU Xiao-hong, ZHANG Yong-bo. 2009. Groundwater resources evaluation on Sangu Spring region of Jincheng in Shanxi Province. Journal of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 30(3): 261-263. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TYZX200903018.htm
LU Yao-ru, ZHAO Cheng-liang, LIU Fu-can. 1966. Primary discussion on karstification and its types. Selected Papers of the First National Conference of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology. Beijing: China Industrial Press: 1-28.
SHEN Nan, PANG Ai-ping, LI Chun-hui, et al. 2010. Study on ecological compensation mechanism of Xin'an Spring water source protection zone in Shanxi Province, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2: 1063-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.118
SHU Long-cang, WANG Mao-mei, LIU Rui-guo, et al. 2007. Sensitivity analysis of parameters in numerical simulation of groundwater. Journal of Hohai University (Nature Sciences), 5: 493-494. http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=HHDX200705002&dbcode=CJFD&year=2007&dflag=pdfdown
SUN Cong-jun, HAN Zhen-bo, ZHAO Zhen, et al. 2013. Advances in research and application of groundwater numerical simulation. Environment Engineering, 5: 9-13. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201305003.htm
WANG Gui-ling, CHEN De-hua, LIN Wen-jing, et al. 2007. Reasonable exploitation and utilization of groundwater resource in North China. Journal of Desert Research, 27(4): 684-689. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm200704027
WANG Wen-ke, YANG Ze-yuan, CHENG Dong-hui, et al. 2011. Methods of ecology-oriented groundwater resource assessment in arid and semi-arid area. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 1: 159-167. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201101019
WANG Yan-xin, MA Teng, LUO Zhao-hui. 2001. Geostatistical and geochemical analysis of surface water leakage into groundwater on a regional scale: A case study in the Liulin karst system, Northwestern China. Journal of Hydrology: 223-234, 246.
WANG Yan-xin, GUO Qing-hai, SU Chun-li, et al. 2006. Strontium isotope characterization and major ion geochemistry of karst water flow, Shentou, northern China. Journal of Hydrology: 328, 592-603. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2afbbbc33c152531b783ad1e2dafb729
WANG Zhen-xing, HOU Xin-wei, LI Xiang-quan, et al. 2019. Study on the influence of coal mining to the groundwater in north karst area. Yellow River, 41(2):76-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rmhh201902017
WANG Zhen-xing, LI Xiang-quan, HOU Xin-wei, et al. 2019. Karst aquifer protection evaluation to the Sangu Spring Basin under the condition of coal mining. Carsologica Sinica, 38(1): 28-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyr201901004
WU Qiang, XING Li-ting, ZHOU Wan-fang. 2010. Chapter 10.10: Case Study: Utilization and protection of large karst springs in China. Groundwater Hydrology of Springs: 543-565.
XIE Zhong-an. 2007. Test study on engineering characteristics of gypsum breccia in Taihang Mountain tunnel. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 6: 632-636. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdqwlxb200706024
XU Zhi-feng, ZHANG Zhi-xiang, LIU Xiao-xia. 2012. Water environmental quality assessment and strategy for water pollution control in Sangu Spring Basin. Groundwater, 4: 87-90. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201204036.htm
YANG Sheng-qi, CHEN Miao, JING Hong-wen, et al. 2017. A case study on large deformation failure mechanism of deep soft rock roadway in Xin'An coal mine, China. Engineering Geology: 217, 89-101. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795216308614
ZHAI Yuan-zheng, WANG Jin-sheng, SU Xiao-si, et al. 2010. Sensitivity analysis of parameters in numerical simulation of groundwater. Yellow River, 32(12): 99-101. http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=HHDX200705002&dbcode=CJFD&year=2007&dflag=pdfdown
ZHANG Chun-chao, LI Xiang-quan, GAO Ming, et al. 2017. Exploitation of groundwater resources and protection of wetland in the Yuqia Basin. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 5(3): 222-234. http://gwse.iheg.org.cn/EN/abstract/abstract276.shtml
-



 下载:
下载: