Investigation and evaluation of shallow geothermal energy resources in key areas of Chengdu
-
摘要:
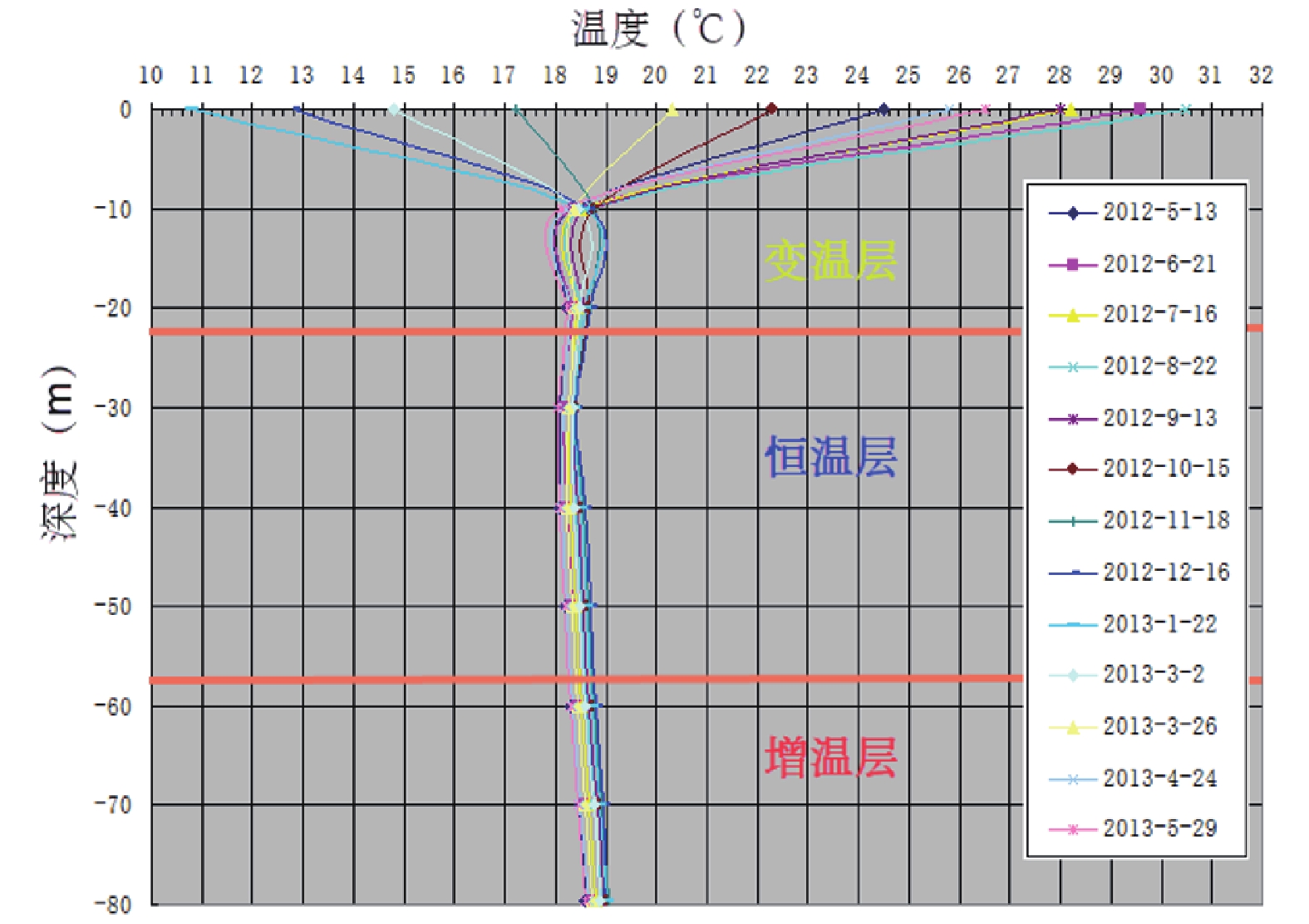
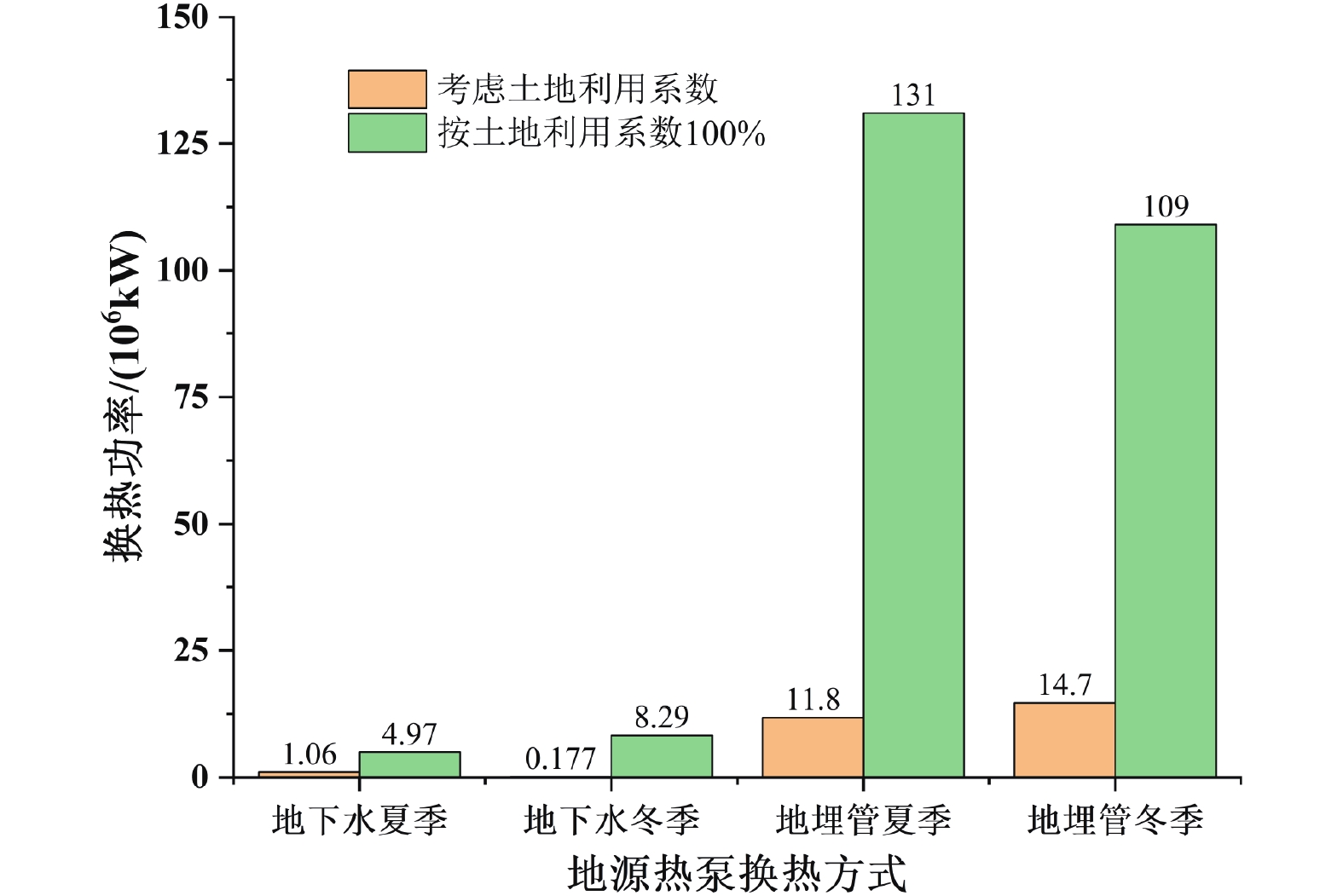
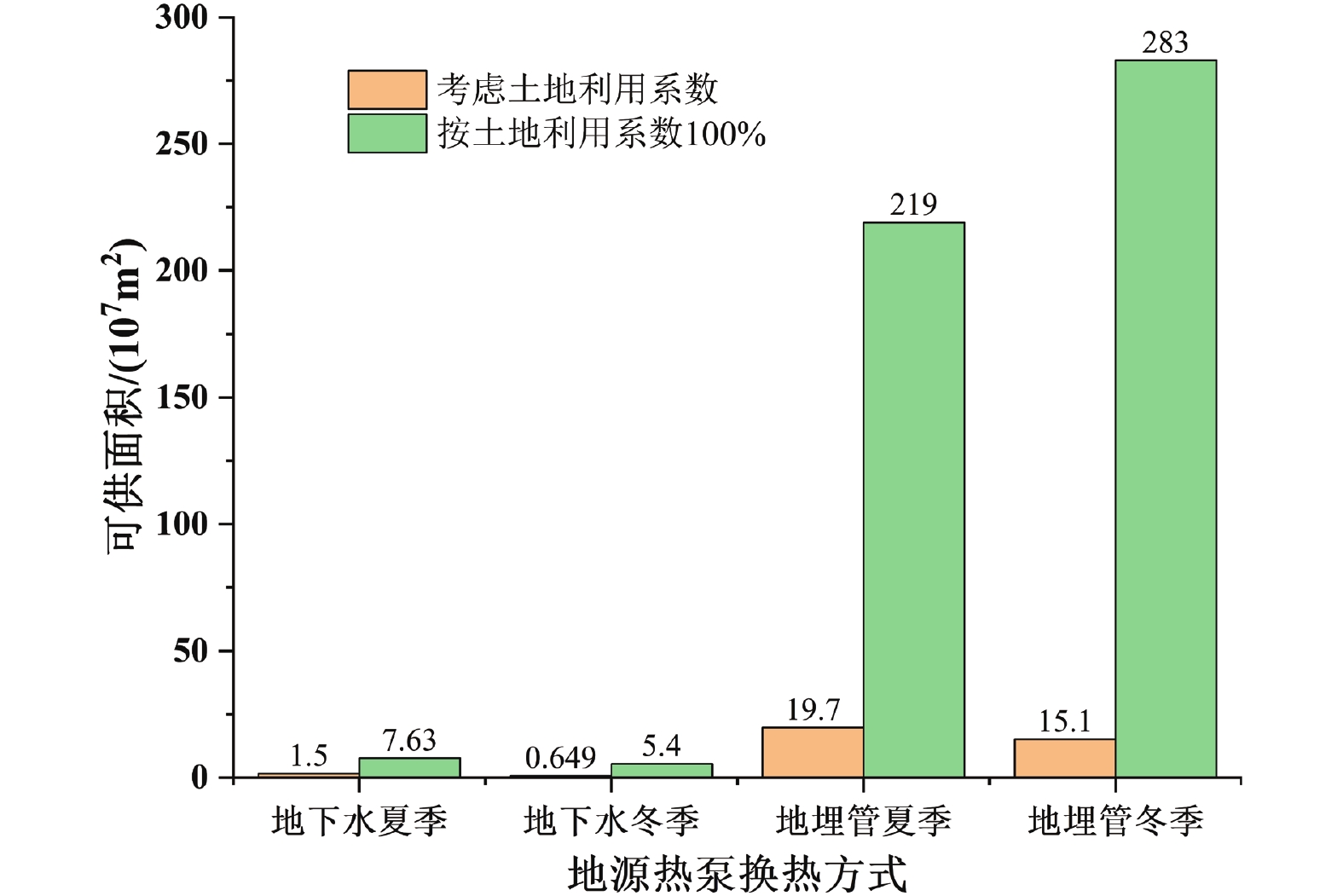
在“双碳”目标背景下,浅层地热能作为节能环保能源,其勘探开发及利用力度亟须加强。基于现场热响应测试、抽水及回灌试验以及岩土体热物性测试,获取水文地质和热物性参数,采用层次分析法开展成都市浅层地热能适宜性评价,估算浅层地热能热容量、换热功率、资源潜力及环境效益。实测成都市研究区200 m以浅平均地层温度在18.59~19.76℃,地层平均导热率介于1.89~3.12 W/m·℃。成都市浅层地热能适宜采用地下水和地埋管地源热泵方式开发,地下水地源热泵方式适宜区面积占16.36%,较适宜区面积占19.72%,不适宜面积占63.92%;除原芒硝矿采空区域外,研究区均适宜及较适宜地埋管地源热泵方式开发。浅层地热能夏季制冷换热功率总量为1.19×107 kW,可制冷面积达1.98×108 m2;冬季供暖换热功率总量为1.48×107 kW,可供暖面积达1.57×108 m2。据估算,成都市开发浅层地热能每年可节省标准煤169万吨,减排各类废气污染约425万吨,节能减排效果显著。
Abstract:In order to achieve carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, shallow geothermal energy as an energy-saving and environmental-friendly energy, its exploration and utilization should be strengthened urgently. Based on the field thermal response test and the pumping and recharging tests, hydrogeological and thermal physical parameters were obtained, and the suitability evaluation of shallow geothermal energy in Chengdu was carried out by using the analytic hierarchy process. The estimated evaluation of shallow geothermal energy heat capacity, heat exchange power and resource potential were obtained. The measured average formation temperature above 200 m in the study area of Chengdu is 18.59-19.76℃, and the average thermal conductivity of the formation is between 1.89-3.12 W/m·℃. The shallow geothermal energy in Chengdu is suitable for the development of groundwater and ground source heat pump system. The area of suitable area accounts for 16.36%, the relatively suitable area accounts for 19.72%, and the unsuitable area accounts for 63.92. Except for the abandoned Mangniu Mine area, all areas are suitable and relatively suitable for the development of ground source heat pump system. The total cooling power of shallow geothermal energy in summer is 1.19×107 kW, and the cooling area is 1.98×108 m2. The total heating power in winter is 1.48×107 kW, and the heating area is 1.57×108 m2. It is estimated that the development of shallow geothermal energy in Chengdu can save 1.69 million tons of standard coal per year, and reduce the emission of various types of waste gas pollution by about 4.25 million tons. The effect of energy saving and emission reduction is remarkable.
-
Key words:
- Shallow geothermal energy /
- field test /
- fuitability zoning /
- fesource evaluation /
- Chengdu
-

-
表 1 研究区第四系地层平面分布情况表
Table 1. The plane distribution of Quaternary strata in the study area
地层时代及代号 面积(km2) 研究区比例(%) 分布位置 第四系全新统冲积层(Q4al) 121.35 10.2 江安河以及府河沿河两侧 全新统冲洪积层(Q4al-pl) 42.16 3.6 鹿溪河、西江河及其支流沿河两侧 上更新统冰水-流水堆积层(Q3fgl-al) 522.18 44.0 平原区河间地块 上更新统成都粘土(Q3eol) 317.33 26.8 成都东部台地之上 中、下更新统冰水-流水堆积层(Q1+2fgl-al) 38.32 3.2 南部台地及东部台地丘顶 基岩残坡积层 144.67 12.2 苏码头背斜附近大面铺、新兴镇一带 表 2 现场热响应试验岩土热物性参数表
Table 2. Geothermal physical parameters of field thermal response test
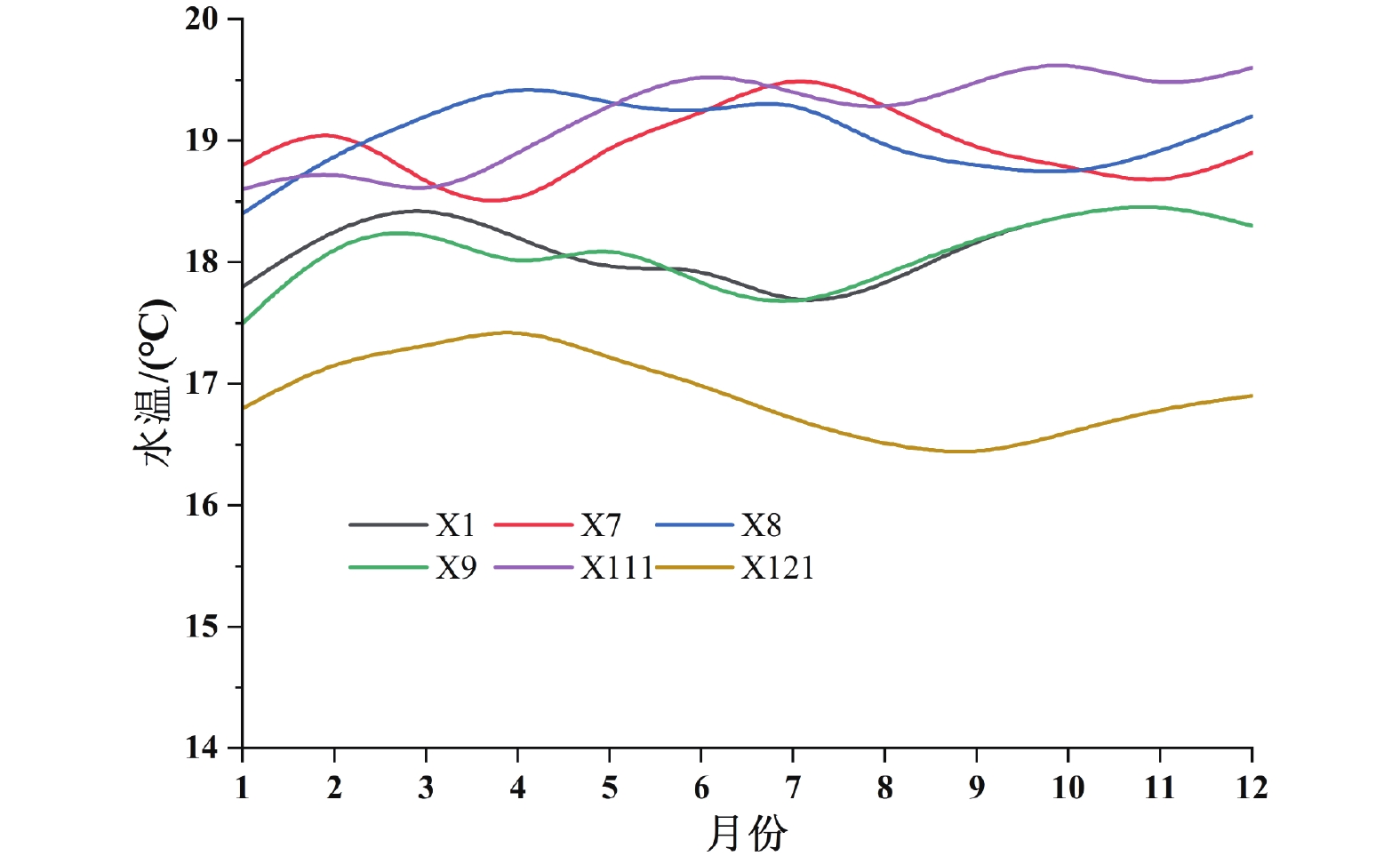
序号 试验编号 地质特征 平均原始地温(℃) 导热系数(W/m·℃) 1 ZK16 西部成都平原第四系砂卵石地层 18.95 1.89 2 ZK18 19.62 2.27 3 ZK19 18.59 2.01 4 ZK20 19.5 2.7 5 ZK21 20.2 2.15 6 ZK22 19.9 2.95 7 X8 18.86 2.14 8 X9 18.94 3.41 9 X111 18.9 2.13 10 ZK01 东部台地区,上部10~20 m粘土地区,
下部为红层砂泥岩地层19.26 2.27 11 ZK02 18.65 2.53 12 ZK03 19.58 2.34 13 ZK15 19.18 2.04 14 ZK17 19.15 2.75 15 ZK23 18.7 2.72 16 ZK24 19.22 2.72 17 ZK25 19.15 2.76 18 ZK26 19.35 3.06 19 X1 18.47 2.45 20 X7 18.82 3.52 21 X112 18.79 2.62 22 ZK10 简州新城丘陵区以砂泥岩互层为主地层 19.73 2.23 23 ZK11 20.12 1.49 24 ZK12 19.76 1.88 25 ZK13 19.68 1.3 26 ZK14 19.45 1.56 27 ZK04 淮州新城丘陵区以厚层砂岩为主地层 18.8 3.35 28 ZK05 18.71 2.71 29 ZK06 18.82 2.37 30 ZK07 19.25 3.14 31 ZK08 19.69 2.44 32 ZK09 19.71 3.3 表 3 抽水及回灌试验统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of pumping and recharge test
回灌试验编号 含水层厚度(m) 平均影响半径(m) 单位涌水量(L/s·m) 回灌量(L/s·m) 灌采比 H41 12.5 89.00 2.388 1.978 0.829 H42 12.5 99.68 2.360 2.000 0.847 H33 28 84.18 3.883 3.544 0.913 H34 28 87.68 4.067 3.752 0.923 H46 8.5 78.09 1.609 1.217 0.757 H37 14.1 109.49 2.643 2.093 0.792 H38 15.2 139.04 2.577 2.545 0.988 H05 19.97 149.45 2.158 1.004 0.465 H32 24.5 88.74 3.814 2.705 0.709 H31 24.5 83.82 3.444 2.537 0.737 H30 25.1 132.90 3.187 2.833 0.889 H09 28.06 235.83 5.720 5.362 0.937 H03 17.7 175.40 2.494 2.375 0.952 H08 28.06 237.24 6.525 6.244 0.957 H27 24.5 131.80 3.274 3.162 0.966 H28 24 134.90 3.169 3.105 0.980 H29 25.1 136.30 3.230 3.184 0.986 H02 18 122.60 2.530 2.509 0.992 H44 11.8 91.16 2.268 0.745 0.328 H43 11.4 99.93 1.976 0.696 0.352 H47 15 70.43 2.197 0.839 0.382 H48 15 76.10 2.217 0.848 0.383 H45 9.8 97.88 1.843 0.776 0.421 表 4 岩土体热物性参数平均值表
Table 4. Average value of physical properties and thermophysical parameters of rock mass
地层时代 岩性 热物性参数 热导率(W/m·℃) 热扩散系数(m2/s) 比热容(J/kg·℃) 第四系 粘土 0.98 0.30×10−6 1724.40 粉质粘土 1.07 0.85×10−6 410.20 粉土 1.19 0.83×10−6 724.37 细砂 0.69 0.66×10−6 448.52 砂砾卵石 1.23 0.79×10−6 231.59 基岩 泥岩 1.79 0.71×10−6 1068.71 粉砂质泥岩 1.35 0.64×10−6 878.88 含钙芒硝粉砂质泥岩 1.53 0.67×10−6 839.57 砂质泥岩 1.13 0.50×10−6 827.26 砂岩 1.56 0.67×10−6 802.85 细砂岩 1.60 0.92×10−6 758.99 泥质砂岩 1.33 0.54×10−6 939.38 泥质粉砂岩 1.25 0.57×10−6 823.88 表 5 各因素综合权重表
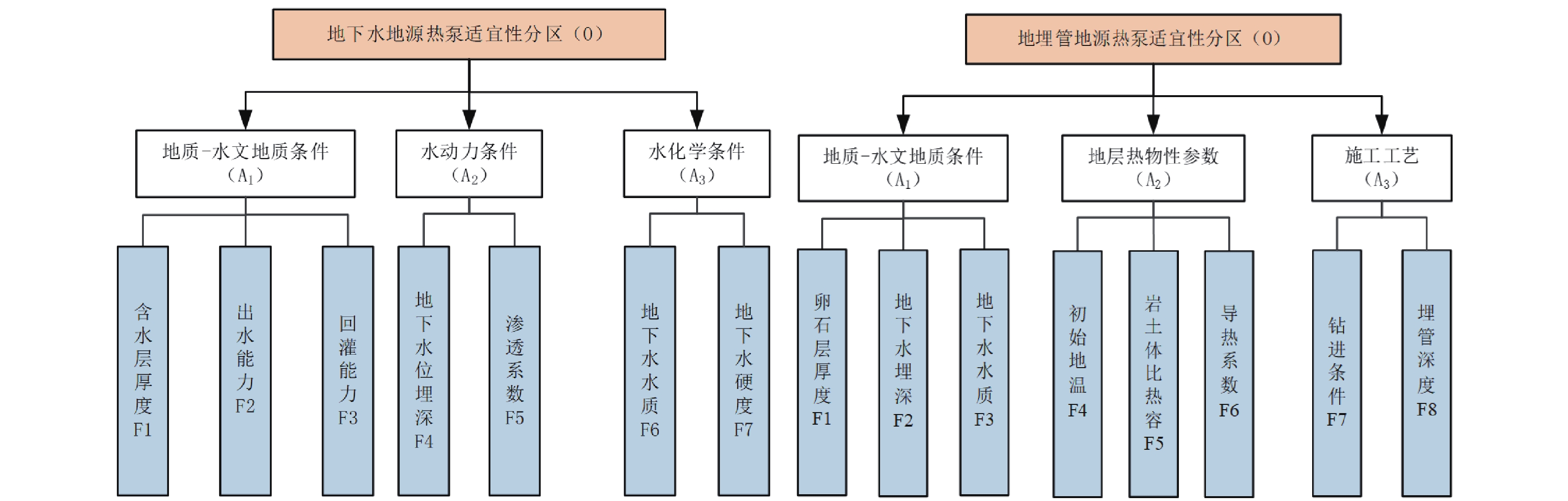
Table 5. Comprehensive weight table of each factor
地下水地源热泵系统 地埋管地源热泵系统 因素 综合权重 因素 综合权重 含水层厚度 0.0599 卵石层厚度 0.1735 含水层出水能力 0.2764 地下水位埋深 0.0546 含水层回灌能力 0.2887 地下水水质 0.0688 地下水位埋深 0.0795 导热系数 0.2158 含水层渗透系数 0.1590 岩土体比热容 0.2158 地下水水质 0.0683 初始地温 0.1079 地下水硬度 0.0682 埋管深度 0.0545 钻进条件 0.1089 表 6 成都市浅层地热能热容量计算结果汇总表
Table 6. Summary of calculation results of shallow geothermal energy heat capacity in Chengdu
评价区域 包气带热容量(kJ/℃) 饱水带热容量(kJ/℃) 总热量(kJ/℃) 地下水地源热泵适宜区和较适宜区 1.06×1013 6.54×1014 6.65×1014 地埋管地源热泵适宜区和较适宜区 1.04×1013 6.33×1014 6.43×1014 表 7 成都市浅层地温能资源利用节能减排量分析表
Table 7. Analysis of energy conservation and emission reduction of shallow geothermal energy resource utilization in Chengdu
项目 CO2 SO2 NOx 粉尘 灰渣 系数 2.386 1.7% 0.6% 0.8% 0.1% 总量/(kg/a) 1.69×109 4.03×109 2.87×107 1.01×107 1.35×107 -
[1] Carlino S, Somma R, Troiano A, et al. , 2014. The geothermal system of Ischia Island (southern Italy): Critical review and sustainability analysis of geothermal resource for electricity generation [J]. Renewable Energy, 62: 177-196. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2013.06.052
[2] Galgaro A, Di Sipio E, Teza G, et al. , 2015. Empirical modeling of maps of geo-exchange potential for shallow geothermal energy at regional scale [J]. Geothermics, 57: 173-184. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2015.06.017
[3] Haehnlein S, Bayer P, Blum P, 2010. International legal status of the use of shallow geothermal energy [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 14(9): 2611-2625. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2010.07.069
[4] Song C, Li Y, Rajeh T, et al. , 2021. Application and development of ground source heat pump technology in China [J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 6(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/s41601-021-00195-x
[5] Shrestha G, Yoshioka M, Fujii H, et al. , 2020. Evaluation of suitable areas to introduce a closed-loop ground source heat pump system in the case of a standard Japanese detached residence [J]. Energies, 13(17): 1-15.
[6] 郭镜, 夏时斌, 2022. 川东褶皱带地热系统的空间载体——相互连通的断裂系统: 以四川广安牟家镇地热井为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(4): 642-652
Guo J, Xia S B, 2022. Spatial carrier of geothermal system in eastern Sichuan fold zone——interconnected fault system: A case study of geothermal well in Moujia Town, Guang’an, Sichuan [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(4): 642-652.
[7] 韩再生, 冉伟彦, 佟红兵, 等, 2007. 浅层地热能勘查评价[J]. 中国地质, 34(6): 1115-1121
Han Z S, Ran W Y, Tong H B, et al. , 2007. Shallow geothermal energy exploration and evaluation [J]. China Geology, 34(6): 1115-1121.
[8] 韩丽莎, 2006. 成都温江金马地区环境地球化学异常成因机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.
Han L S, 2006. Study on the genetic mechanism of environmental geochemical anomalies in Jinma area, Wenjiang, Chengdu [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology(in Chinese).
[9] 何雪冰, 丁勇, 刘宪英, 2004. 地源热泵埋管换热器传热模型及其应用[J]. 重庆建筑大学学报, (2): 76-80
He X B, Ding Y, Liu X Y, 2004. Heat transfer model of ground source heat pump buried tube heat exchanger and its application [J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, (2): 76-80.
[10] 黄露玉, 梁金龙, 刘斌, 等, 2022. 基于组合赋权法的广安市地源热泵适宜性分区[J]. 科学技术与工程, (013): 022. .
Huang L Y, Liang J L, Liu B, et al., 2022. Suitability zoning of ground source heat pump in Guang’an City based on combination weighting method [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 22(13): 5116 − 5124(in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 金婧, 席文娟, 陈宇飞, 等, 2012. 基于AHP的浅层地热能适宜性分区评价[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 23(3): 91-93
Jin J, Xi W J, Chen Y F, et al. , 2012. Evaluation of shallow geothermal energy suitability zoning based on AHP [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering, 23(3): 91-93.
[12] 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 等, 2013. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 040(001): 312-321
Lin W J, Liu Z M, Wang W L, et al. , 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China [J]. China Geology, 040(001): 312-321.
[13] 刘宪英, 王勇, 胡鸣明, 等, 1999. 地源热泵地下垂直埋管换热器的试验研究[J]. 重庆建筑大学学报, (5): 21-26
Liu X Y, Wang Y, Hu M M, et al. , 1999. Experimental study on underground vertical ground heat exchanger of ground source heat pump [J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, (5): 21-26.
[14] 刘宪英, 张素云, 胡鸣明, 等, 2000. 地热源热泵冬夏暖冷联供试验研究[J]. 水利电力施工机械, (1): 14-22
Liu X Y, Zhang S Y, Hu M M, et al. , 2000. Geothermal source heat pump combined winter and summer heating and cooling [J]. Water conservancy and power construction machinery, (1): 14-22.
[15] 龙西亭, 袁瑞强, 皮建高, 等, 2016. 长沙浅层地热能资源调查与评价[J]. 自然资源学报, (1): 14
Long X T, Yuan R Q, Pi J G et al. , 2016. Survey and Evaluation of Shallow Geothermal Energy in Changsha [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, (1): 14.
[16] 卢玮, 尚永升, 申云飞, 2022. 浅层地热能地下换热系统适宜性评价与优化设计——以郑州市浅层地热能示范工程为例[J]. 探矿工程-岩土钻掘工程, 49(3): 146 − 153
Lu W, Shang Y S, Shen Y F, 2022. Suitability evaluation and optimization design of the shallow geothermal energy underground heat exchange system——Taking Zhengzhou shallow geothermal energy demonstration project as an example [J]. Drilling Engineering, 49(3): 146 − 153(in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] 罗改, 王全伟, 陈宇龙, 等, 2021. 四川省大地构造单元划分及其基本特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(4): 633-647
Luo G, Wang Q W, Chen Y L, et al. , 2021. Division and basic characteristics of tectonic units in Sichuan Province [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(4): 633-647.
[18] 宋帅良, 2018. 菏泽市浅层地温能开发利用适宜性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
Song S L, 2018. Study on the suitability of shallow geothermal energy development and utilization in Heze City [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese).
[19] 宋小庆, 2018. 贵州主要城市浅层地热能利用潜力评价[J]. 中国岩溶, 037(001): 9-16
Song X Q, 2018. Evaluation on utilization potential of shallow geothermal energy in major cities of Guizhou [J]. Karst in China, 037(001): 9-16.
[20] 唐永香, 2014. 滨海新区浅层地热能赋存规律及其开发利用对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学.
Tang Y X, 2014. Study on the occurrence law and development and utilization countermeasures of shallow geothermal energy in Binhai New Area [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(in Chinese).
[21] 王贵玲, 刘彦广, 朱喜, 等, 2020. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 27(1): 1 − 9.
Wang G L, Liu Y G, Zhu X, et al. , 2020. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(1): 1 − 9
[22] 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等, 2017. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 38(4): 12
Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. , 2017. Evaluation of Geothermal Resources Potential in China [J]. Earth Journal, 38(4): 12.
[23] 王楠, 曹剑峰, 赵继昌, 等, 2012. 长春市区浅层地温能开发利用方式适宜性分区评价[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 42(4): 6
Wang N, Cao J F, Zhao J C, et al. , 2012. Suitability zoning evaluation of shallow geothermal energy development and utilization in Changchun City [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 42(4): 6.
[24] 魏林森, 丁宏伟, 王婷, 等, 2016. 基于层次分析法的浅层地温能适宜性评价分析——以兰州市中心城区为例[J]. 地球科学前沿, 6(5): 412-421
Wei L S, Ding H W, Wang T, et al. , 2016. Analysis of suitability evaluation of shallow geothermal energy based on analytic hierarchy process-a case study of the central urban area of Lanzhou [J]. Front of Earth Science, 6 (5): 412-421.
[25] 许苗娟, 姜媛, 谢振华, 等, 2009. 基于层次分析法的北京市平原区水源热泵适宜性分区研究[J]. 城市地质, 4(1): 18-22
Xu M J, Jiang Y, Xie Z H, et al. , 2009. Study on suitability zoning of water source heat pump in Beijing plain area based on analytic hierarchy process [J]. Urban geology, 4(1): 18-22.
[26] 张承斌, 2022. 基于层次分析法-模糊综合评价模型的浅层地热能适宜性评价——以山东省昌乐县为例[J]. 中国地质调查, 9(2): 91-99 doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2022.02.09
Zhang C B, 2022. Suitability evaluation of shallow geothermal energy based on analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation: A case study of Changle County in Shandong Province [J]. Geological Survey of China, 9(2): 91-99. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2022.02.09
[27] 张甫仁, 朱方圆, 彭清元, 等, 2013. 重庆主城区浅层地温能适宜性分区评价[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 32(4): 647-651
Zhang F R, Zhu F Y, Peng Q Y, et al. , 2013. Evaluation of suitability zoning of shallow geothermal energy in the main urban area of Chongqing [J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition), 32(4): 647-651.
[28] 张甫仁, 彭清元, 朱方圆, 等, 2013. 重庆主城区浅层地温能资源量评价研究[J]. 中国地质, 40(3): 974-980 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.03.027
Zhang F R, Peng Q Y, Zhu F Y, et al. , 2013. Evaluation of shallow geothermal energy resources in the main urban area of Chongqing [J]. China Geology, 40(3): 974-980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.03.027
[29] 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2009. 浅层地热能勘察评价规范DZ/T0225—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People 's Republic of China, 2009. DZ / T0225−2009 [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press.
[30] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2010. 地热资源地质勘查规范GB/T11615—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People 's Republic of China, 2010. Geothermal Resources Geological Exploration Specification GB / T11615−2010 [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press.
-




 下载:
下载: