Geothermal Resource Evaluation of the Middle Permian Qixia-Maokou Formation in the Central Sichuan Basin, China
-
摘要:
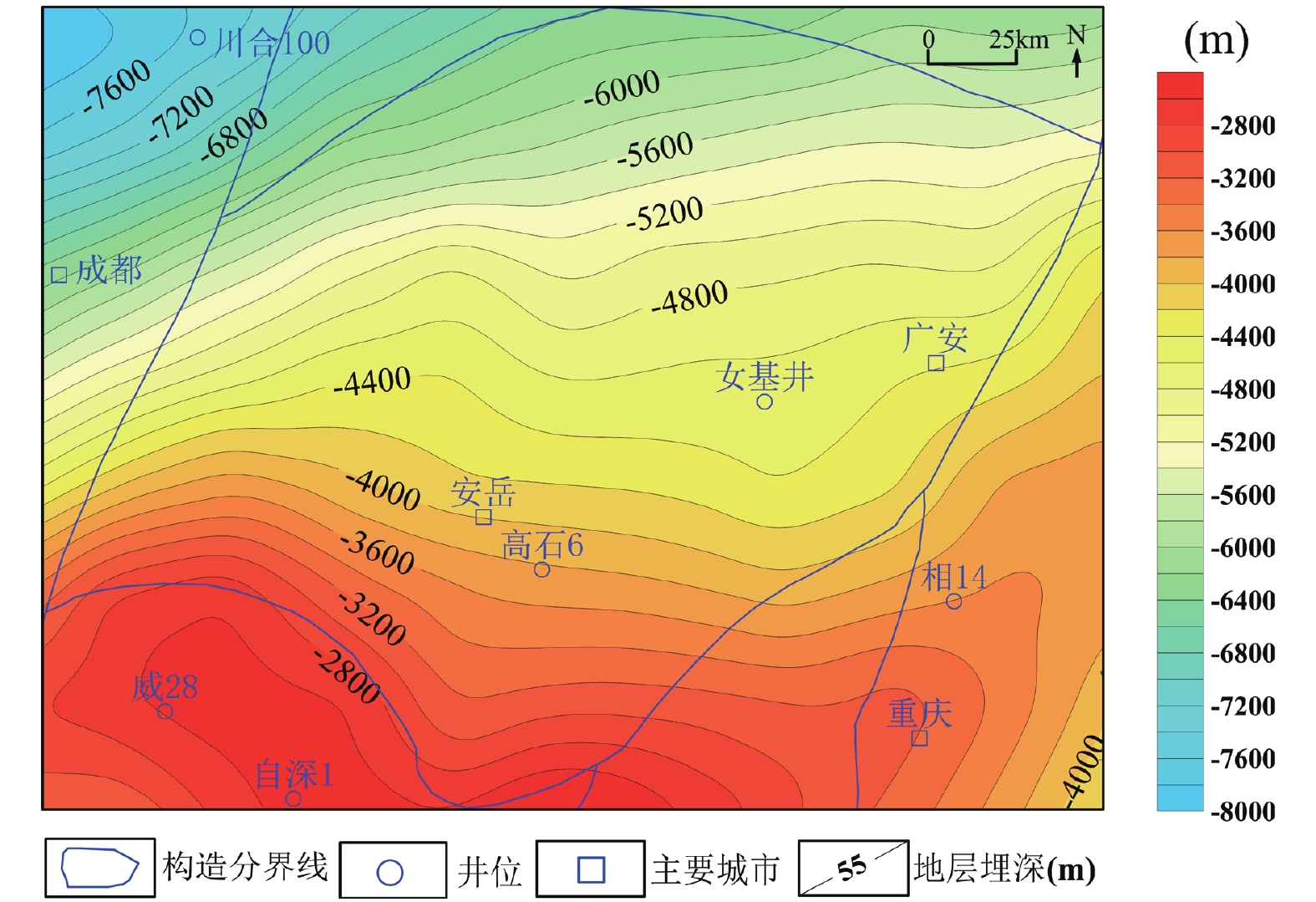
含油气盆地在勘探和开发中,拥有大量的地质、地球物理和地球化学数据,对地质构造和地热储层有着全面的认识,在地热能开发利用中具有得天独厚的优势。四川盆地作为中国重要的含油气盆地,同样富含水热型地热资,该文在收集相关资料、总结以往油气勘探成果的基础上,确定了川中地区地温梯度大部均在24℃/km以上,大地热流大部均在60 mW/m2以上,为四川盆地相对高值异常区。考虑到热储温度及埋深是地热开发是否具有经济效益的重要因素,重点选择埋深相对较浅(
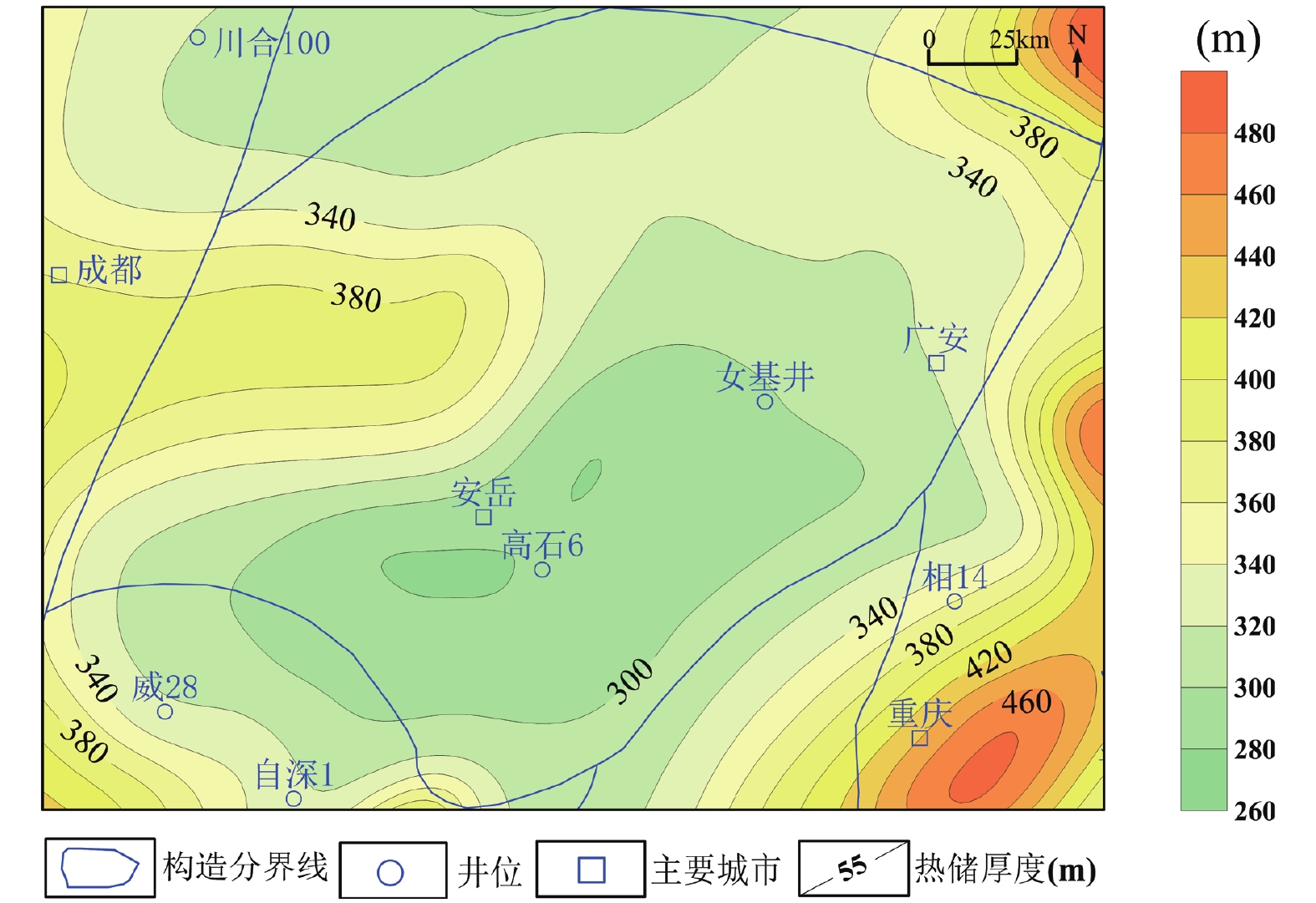
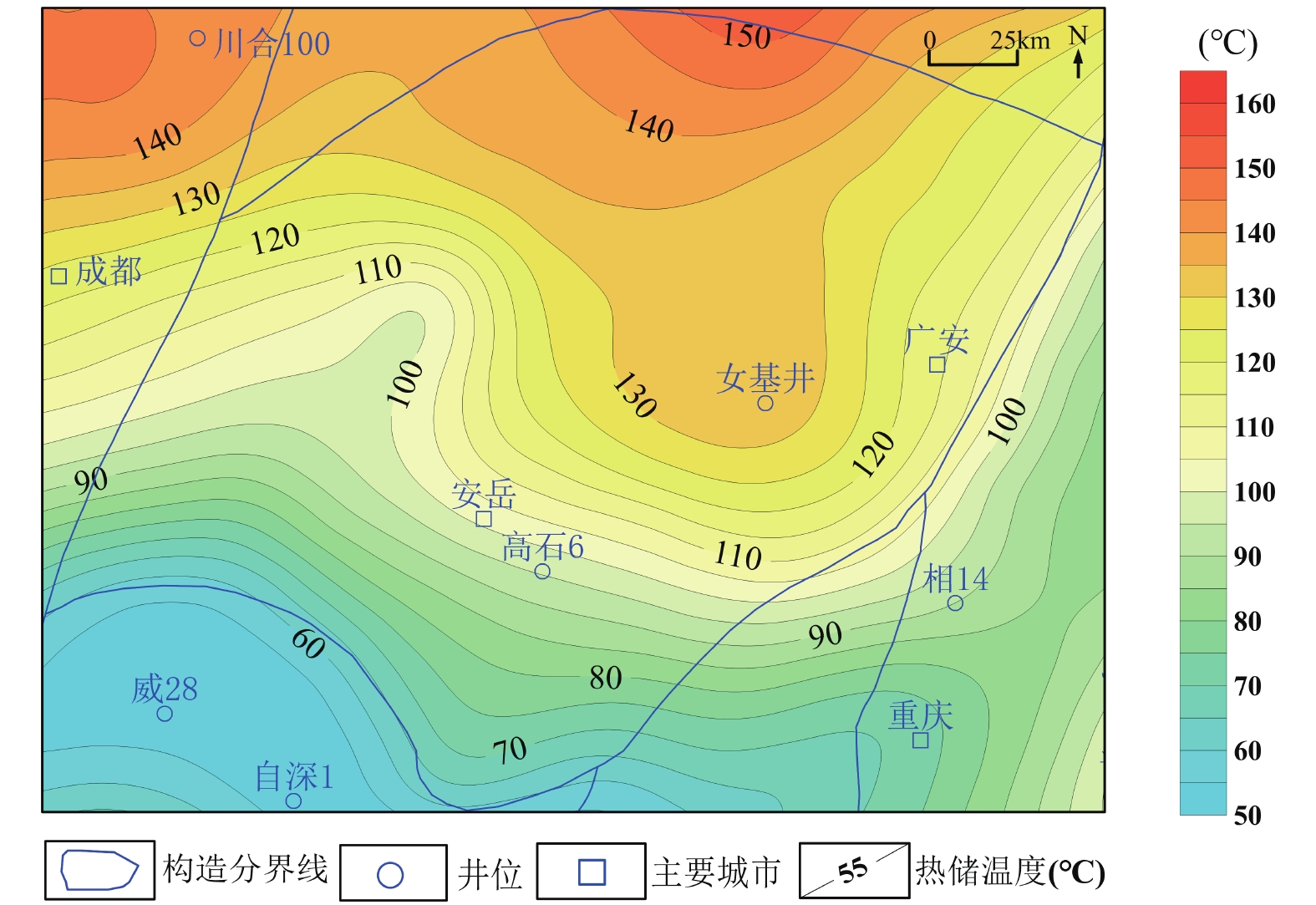
3000 ~6000 m)、热储温度相对较高(65~155℃)和热储相对较厚(280~380 m)的川中地区栖霞-茅口组热储进行地热资源潜力评价。研究中,基于盆地地层参数建立三维地质模型,结合现今地温场、岩石热物性参数,利用一维稳态热传导方程计算得到栖霞-茅口组内部温度分布,最后利用体积法计算得到栖霞-茅口组的地热资源强度和资源量。研究表明,川中地区栖霞-茅口组热储温度为65~155℃,地热资源总量为3.01×1021 J,折合标准煤1030.25 亿吨;可开采地热资源量2.03×1020 J,折合标准煤206.5亿吨。且根据川中地区地热资源特征,提出了优先以研究区中东部为中心开展中低温地热发电、地热干燥、地热农业等综合开发利用和地热梯级利用示范工程的建议,为未来的油气废弃井的二次利用及油田地热开发打下基础。Abstract:In the exploration and development of petroliferous basins, there are a large number of geological, geophysical, and geochemical data. They comprehensively understand the geological structure and geothermal reservoirs and have unique advantages in developing and utilizing geothermal energy. As an important petroliferous basin in China, Sichuan Basin is also rich in hydrothermal geothermal resources. Based on collecting relevant data and summarizing previous oil and gas exploration results, it is determined that most of the geothermal gradients in the Central Sichuan Basin are above 24 °C/km and most of the terrestrial heat flow is above 60 mW/m2, which is a relatively high-value anomaly area in Sichuan Basin. Considering that the geothermal reservoir temperature and buried depth are important factors for the economic benefits of geothermal development, the geothermal reservoir of Qixia-Maokou Formation in central Sichuan Basin with relatively shallow buried depth (
3000 ~6000 m), relatively high geothermal reservoir temperature (65 ~ 155 °C) and relatively thick geothermal reservoir (280 ~ 380 m) is selected to evaluate the potential of geothermal resources. In the study, a three-dimensional geological model is established by using different strata thickness parameters. Combined with the current geothermal field and rock thermal physical parameters, the temperature distribution in the middle of the Qixia-Maokou Formation is calculated by using a one-dimensional steady-state heat conduction equation. Finally, the geothermal resource intensity and resource quantity of the Qixia-Maokou Formation are calculated by using the volume method. The results show that the geothermal reservoir temperature of the Qixia-Maokou Formation in central Sichuan is 65 ~ 155 °C, and the total geothermal resource is 3.01 × 1021 J, equivalent to 103.025 billion tons of standard coal. Exploitable geothermal resources 2.03 × 1020 J, equivalent to 20.65 billion tons of standard coal. According to the characteristics of geothermal resources in the Central Sichuan Basin, it is proposed to give priority to the central and eastern parts of the study area to carry out comprehensive development and utilization of medium and low-temperature geothermal power generation, geothermal drying, geothermal agriculture, and geothermal cascade utilization demonstration projects, laying the foundation for the secondary utilization of abandoned oil and gas wells and geothermal development in oil fields in the future. -

-
图 2 川中地区地层综合柱状图(苏桂萍, 2021)
Figure 2.
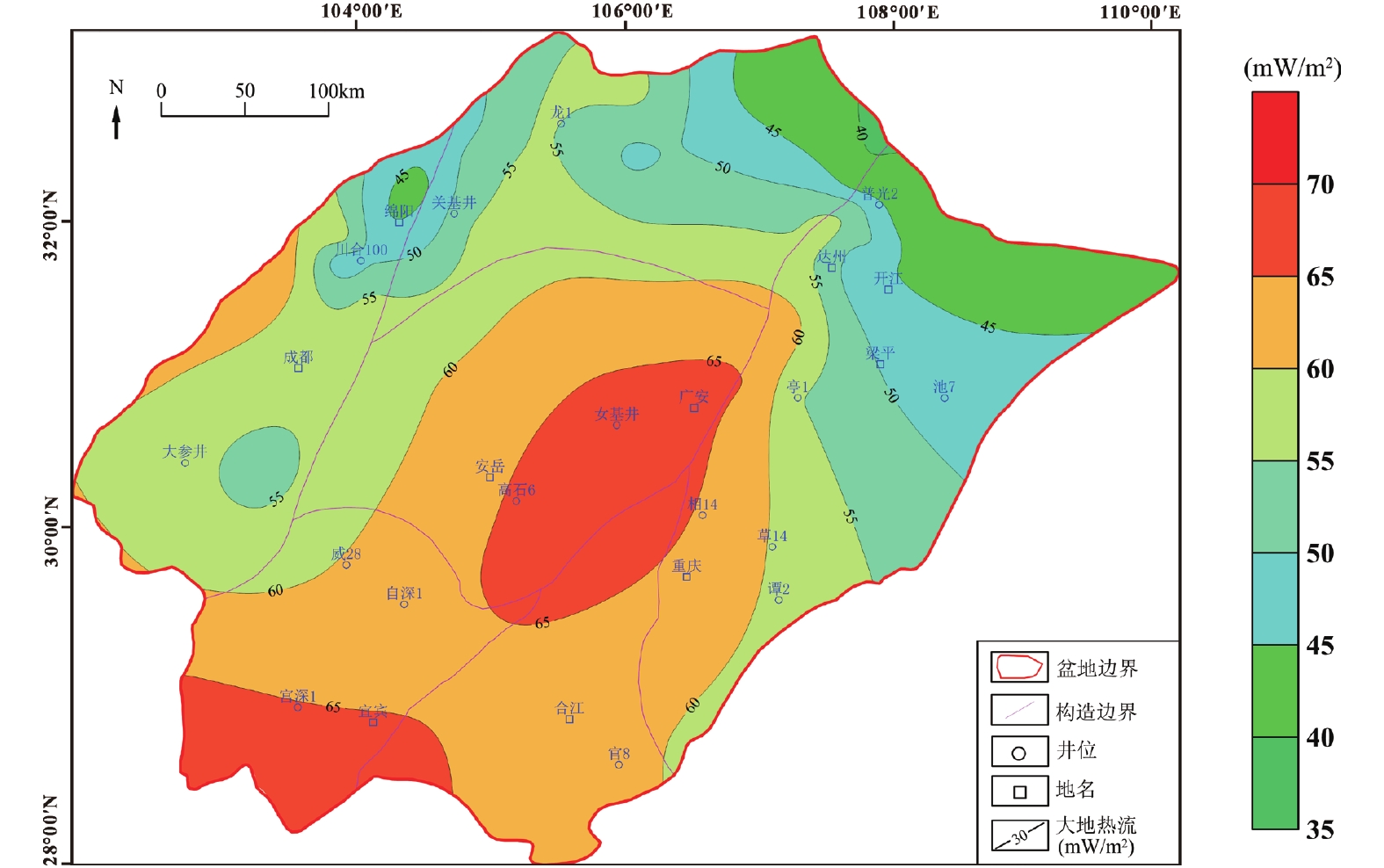
图 3 四川盆地地温梯度等值线图(Xu et al., 2011)
Figure 3.
图 4 四川盆地大地热流等值线图(Xu et al., 2011)
Figure 4.
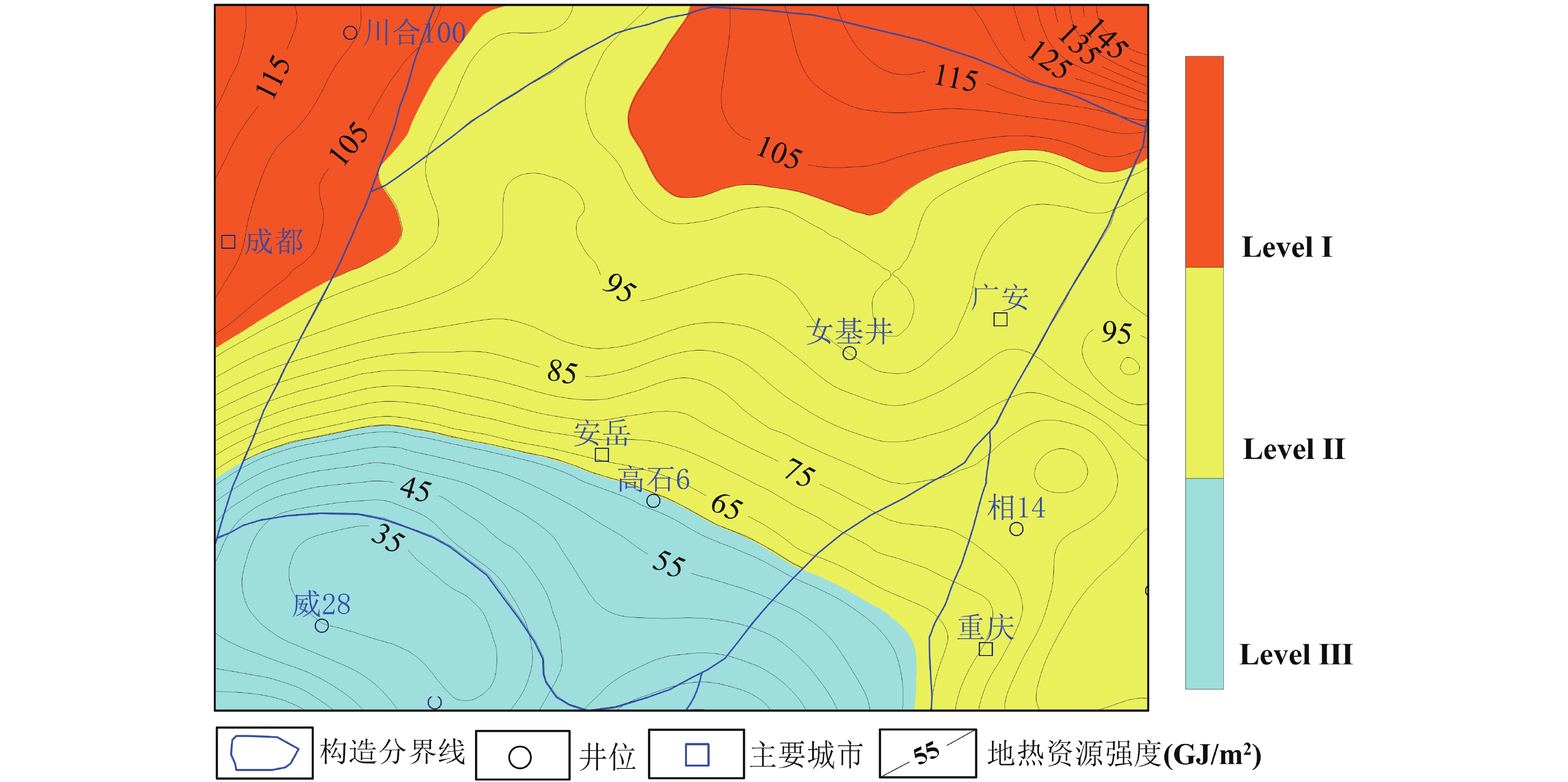
表 1 川中地区地热资源潜力分级表
Table 1. Grading table of geothermal resource potential in the Central Sichuan Basin
分级区域 地热资源强度(GJ/m2) 地温梯度
(℃/km)大地热流(mW/m2) 热储温度(℃) 热储厚度(m) 热储资源量(J) 一级区域 >102 22~23 59~64 135~155 320~380 6.87×1020 二级区域 62~102 22~31 56~67 90~140 280~380 1.98×1021 三级区域 <62 22~25 56~66 75~100 280~360 3.45×1020 -
[1] 陈涛, 李智武, 李金玺, 等, 2022. 川中−川西北加里东期古隆起对比研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质: 1 − 15
Chen T, Li Z W, Li J Xi, et al., 2022. A comparative study of the central Sichuan paleo−uplift and the northwest Sichuan paleo−uplift during the Caledonian period[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology: 1 − 15.
[2] Dai X, Zhang M, Jiang Q, et al. , 2017. Karst reservoirs seismic prediction of lower Permian Maokou formation in central Sichuan basin, SW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(1): 79-88. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30010-1
[3] 冯许魁, 杨雨, 朱亚东, 等, 2023. 四川盆地二叠纪礁滩体发育特征、分布模式及有利勘探区带[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质: 1 − 17
Feng X K, Yang Y, Zhu Y D, et al., 2023. Development Characteristics, Distribution Patterns and Favorable Exploration Zones of Permian Reef Shoals in Sichuan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology: 1 − 17.
[4] Jiang G, Hu S, Shi Y, et al. , 2019. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 753: 36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.01.006
[5] Jiang S, Zuo Y, Yang M, et al. , 2021. Reconstruction of the Cenozoic tectonic-thermal history of the dongpu depression, bohai bay basin, china: constraints from apatite fission track and vitrinite reflectance data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 205: 108809. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108809
[6] Kurek K A, Heijman W, Ophem J, et al. , 2021. The contribution of the geothermal resources to local employment: a case study from Poland [J]. Energy Reports, 7: 1190-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.01.092
[7] Lin W J, Liu Z M, Wang W L, et al. , 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China [J]. Geology in China, 40(1): 312-321.
[8] 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 等, 2013. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 40(01): 312-321 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
Lin W, Liu Z, Wang W, et al. , 2013. Geothermal resources and potential evaluation in China [J]. Geology in China, 40(01): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
[9] Liu X, Falcone G, Alimonti C, 2018. A systematic study of harnessing low-temperature geothermal energy from oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Energy, 142: 346-355. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.10.058
[10] 罗改, 王全伟, 秦宇龙, 等, 2021. 四川省大地构造单元划分及其基本特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(4): 633-647 doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2021.04002
Luo A, Wang Q W, Qin Y L, et al. , 2021. Geotectonic unit division and its basic characteristics in Sichuan Province [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(4): 633-647. doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2021.04002
[11] 宁金野, 徐洪苗, 2011. 合肥地区地热资源潜力评价[J]. 安徽地质, 21(1): 40-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2011.01.009
Ning J Y, Xu H M, 2011. Potential evaluation of geothermal resources in the Hefei area [J]. Geology of Anhui Province, 21(1): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2011.01.009
[12] 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 庞菊梅, 等, 2017. 雄安新区地热资源与开发利用研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 32(11): 1224-1230 doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2017.11.007
Pang Z H, Kong Y L, Pang J M, et al. , 2017. Study on geothermal resources, development, and utilization in Xiongan New Area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese), 32(11): 1224-1230. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2017.11.007
[13] 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 何丽娟, 2019. 沉积盆地地热学[M]. 青岛: 中国石油大学出版社.
Qiu N, Hu S, He L, 2019. Geothermal in Sedimentary Basin [M]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum Press.
[14] 邱楠生, 唐博宁, 朱传庆, 2022. 中国大陆地区温泉分布的深部热背景[J]. 地质学报, 96(1): 195 − 207
Qiu N S, Tang B N, Zhu C Q, 2022. Deep thermal background of hot spring distribution in mainland China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(01): 195 − 207.
[15] 饶诗怡, 伏美燕, 邓虎城, 等, 2022. 基于岩相和地球化学特征的沉积古地貌恢复新方法: 以川中栖霞组为例[J]. 地质科技通报: 1 − 9
Rao S Y, Fu M Y, Deng H C, et al., 2022. A new method for restoring sedimentary palaeogeomorphology based on petrographic and geochemical characteristics: A case study of Qixia Formation in central Sichuan [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 1 − 9.
[16] Singh H K D, Quoc B T, Yong T C, et al., 2016. Mpd closed loop cementing in high−pressure, high−temperature wells in Vietnam [C]//International Petroleum Technology Conference.
[17] 苏桂萍, 2021. 川中古隆起北斜坡区构造特征、演化及其对油气成藏影响研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学.
Su G, 2021. Study on structural characteristics and tectonic evolution in the northern slope of Central Sichuan paleo−uplift and their influences on hydrocarbon accumulation [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology.
[18] Su Y, Su C, Xie Y, et al., 2022. Controlling non−grain production based on cultivated land multifunction assessment[G]//International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
[19] Templeton J D, Ghoreishi-Madiseh S A, Hassani F, et al. , 2014. Abandoned petroleum wells as sustainable sources of geothermal energy[J]. Energy, 70: 366-373. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.006
[20] 拓明明, 2020. 四川盆地东部重庆主城区附近盆地—背斜出露型地下热水特征及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
Tuo M M, 2020. Characteristics and genesis of the thermal groundwater of basin−anticline outcropping type near the main urban area of Chongqing in the Eastern Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing).
[21] 王贵玲, 刘志明, 蔺文静, 等, 2011. 中国地热资源潜力评估[C]//中国科学技术协会,天津市人民政府,中国地质学会.地热能开发利用与低碳经济研讨会——第十三届中国科协年会第十四分会场论文摘要集, 17 − 28.
Wang G L, Liu Z M, Lin W J, et al., 2011. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China [C]// Geothermal Energy Development and Utilization and Low Carbon Economy Seminar -- The 14th session of the 13th Annual Meeting of the China Association for Science and Technology abstract collection, 17 − 28.
[22] 王贵玲, 陆川, 2022. 碳中和目标驱动下地热资源开采利用技术进展[J]. 地质与资源, 31(03): 412-425 doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.03.017
Wang G L, Lu C, 2022. Progress of geothermal resources exploitation and utilization technology driven by carbon neutralization target[J]. Geology and Resources, 31(03): 412-425. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.03.017
[23] 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等, 2017. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 38(4): 449-459 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. , 2017. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(4): 449-459. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02
[24] 汪集旸, 庞中和, 胡圣标, 等, 2015. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
Wang J Y, Pang Z H, Hu S B, et al., 2015. Geothermology and its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press.
[25] 汪集暘, 孔彦龙, 程远志, 2019. 中国地热资源分布与开发利用[C]//国际清洁能源论坛(澳门).国际清洁能源产业发展报告(2019).中国言实出版社, 81 − 88
Wang J Y, Kong Y L, Cheng Y Z, 2019. Distribution, development, and utilization of geothermal resources in China [C]. // International Clean Energy Forum (Macau). International clean energy industry development report (2019). Chinese yanshi press, 81 − 88.
[26] Wang K, Yuan B, Ji G, et al. , 2018. A comprehensive review of geothermal energy extraction and utilization in oilfields[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 168: 465-477. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.05.012
[27] Wang S, Hu J, Yan J, et al. , 2019. Assessment of geothermal resources in petroliferous basins in China [J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 51(3): 271-293. doi: 10.1007/s11004-019-09786-9
[28] Wang S, Yan J, Li F, et al. , 2016. Exploitation and utilization of oilfield geothermal resources in China [J]. Energies, 9(10): 798. doi: 10.3390/en9100798
[29] 王世兴, 2016. 四川盆地下二叠统栖霞组和茅口组测井储层评价研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东).
Wang S X, 2016. Study on Logging Reservoir Evaluation of the Qixia and Maokou Formation of Lower Permian in Sichuan Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China)
[30] Xiao D, Tan X, Xi A, et al. , 2016. An inland facies-controlled exogenetic karst of the carbonate reservoir in the middle Permian Maokou formation, southern Sichuan basin, SW China [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 72: 218-233. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.001
[31] Xu M, Zhu C Q, Tian Y T, et al. , 2011. Borehole temperature logging and characteristics of subsurface temperature in the Sichuan basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(2): 224-233. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.1604
[32] Yang G, Wang H, Shen H, et al. , 2015. Characteristics and exploration prospects of middle Permian reservoirs in the Sichuan basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2(5): 399-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2015.09.015
[33] Yang M, Zuo Y, Zhang J, et al. , 2021. Hydrocarbon kitchen evolution in the early cretaceous bayingebi 2 formations in the chagrin depression, yingen-ejinaqi Basin, north-central China [J]. Acs Omega, 6(18): 12194-12204. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00944
[34] Zhao J, Wang G, Zhang C, et al. , 2021. Genesis of geothermal fluid in typical geothermal fields in western Sichuan, China [J]. Acta geologica Sinica (Beijing), 95(3): 873-882. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14715
[35] 赵铭海, 李晓燕, 宋明水, 等, 2015. 济阳坳陷东营组—馆陶组地热资源评价[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 22(04): 1-5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.04.001
Zhao M H, Li X Y, Song M S, et al. , 2015. Research on geothermal resources assessment of the Guantao-Dongying Formation in Jiyang depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 22(04): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.04.001
[36] 中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2020. 地热资源评价方法及估算规程 DZ/T 0331−2020[S]: 国内−行业标准−行业标准−地质 CN−DZ.
Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC, 2020. Evaluation methods and estimation procedures for geothermal resources DZ/T 0331−2020[S]: Domestic −− Industry Standards−Industry Standards−Geological CN−DZ.
[37] Zhu C, Xu T, Qiu N, et al., 2022. Distribution characteristics of the deep geothermal field in the Sichuan basin and its main controlling factors[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10.
-




 下载:
下载: