Geochemical characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, Xiong'an New Area
-
摘要:
研究目的 白洋淀为雄安新区核心生态功能区,为支撑白洋淀湿地生态修复与保护,系统开展了全淀区表层沉积物环境质量调查。
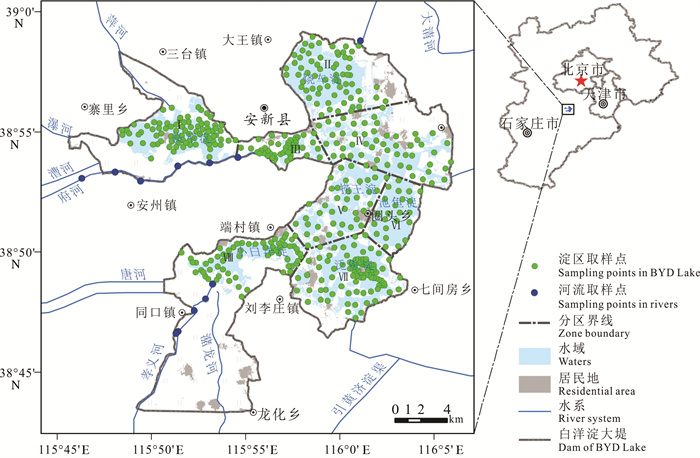
研究方法 在白洋淀湿地采集表层沉积物样品484组,查明了白洋淀表层沉积物重金属地球化学特征,并采用地累积指数法、潜在生态风险指数法等多种方法开展了重金属生态风险评价。
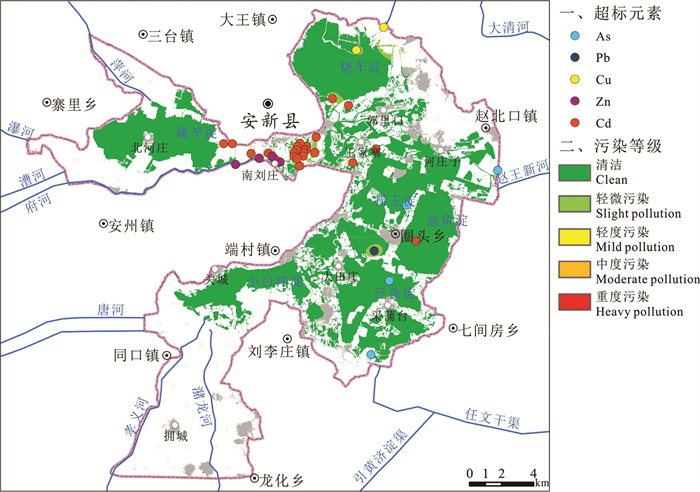
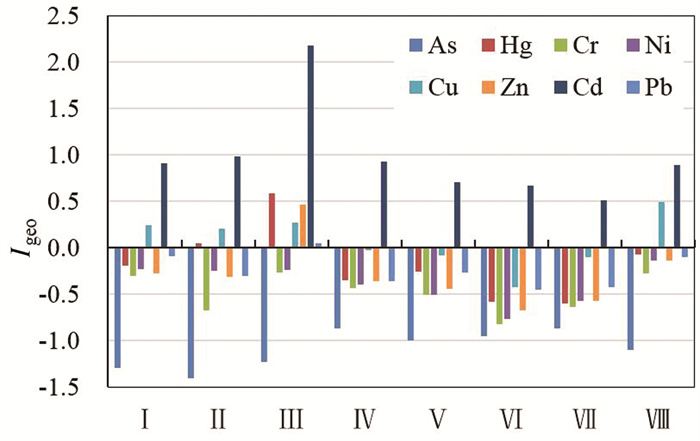
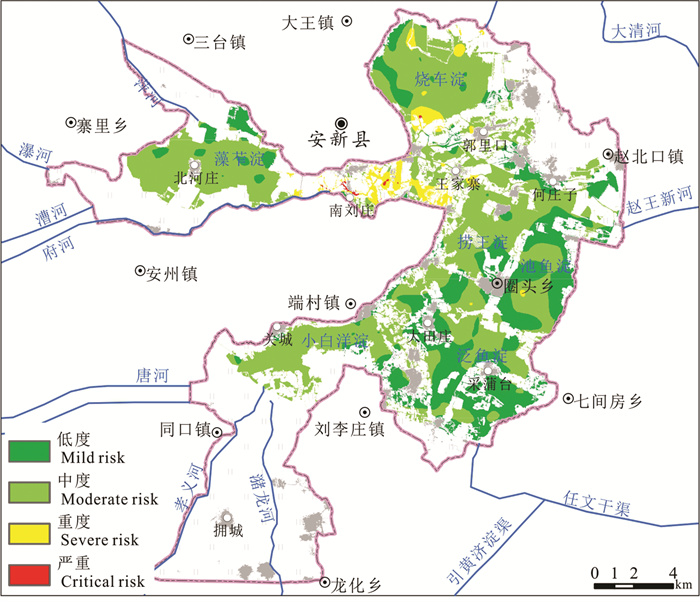
研究结果 白洋淀表层沉积物重金属含量普遍偏高于河北省表层土壤重金属含量背景值,府河入淀口及白沟引河入淀口为重金属元素主要富集区,入淀河流输入为白洋淀重金属主要来源;环境地球化学综合评价结果为清洁无污染等级分布面积144.54 km2,占表层沉积物分布总面积的96.68%;各重金属污染程度由重到轻排序为Cd>Cu>Hg>Pb>Zn>Ni>Cr>As,Cd元素污染程度等级以中度和偏中度为主,Cu元素以轻度和清洁为主,其他元素以清洁无污染为主;重金属潜在生态风险以轻度和中度为主,河流入淀口所在淀区重金属潜在生态风险高于其他淀区,潜在生态风险由高到低排序为南刘庄>烧车淀>小白洋淀>王家寨>藻苲淀>捞王淀>池鱼淀>泛鱼淀。
结论 白洋淀表层沉积物环境质量总体较好,南刘庄等局部淀区存在重金属污染潜在生态风险,以Cd元素污染最为突出。
Abstract:This peper is the result of environmental geological survry engineering.
Objective Baiyangdian Lake(BYD Lake)is the main ecological function area of Xiong'an New Area. In order to provide support for ecological restoration and protection of BYD Lake, we conducted a comprehensive survey on the environmental quality of the surface sediments in BYD Lake.
Methods We collected 484 sets of surface sediment samples from Baiyangdian wetland, identified the geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baiyangdian lake, and used multiple methods such as geo- accumulation index method and potential ecological risk index method to evaluate the ecological risk of heavy metals.
Results The results indicate that the average content of most heavy metal elements in the surface sediments of BYD Lake is significantly higher than the soil background value in Hebei Province. The entrance of Fuhe river and Baigou river are the main rich areas of heavy metal elements, rivers are the main sources of heavy metals in the surface sediments of BYD Lake. The distribution area of clean and pollution-free grade is 144.54 km2, accounting for 96.68% of the total surface sediment distribution area. The pollution degree of each heavy metal can be ranked as Cd > Cu > Hg > Pb > Zn > Ni > Cr > As. The pollution degree of Cd is mainly moderate, the pollution degree of Cu is mainly light and clean, and the pollution degrees of other elements are mainly clean and pollution-free. The potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of BYD Lake is mainly mild and moderate, and the potential ecological risk level of heavy metals near the river entrance is higher than that of other areas. The potential ecological risk levels can be ranked as Nanliuzhuang > Shaochedian > Xiaobaiyangdian > Wangjiazhai > Zaozhadian > Laowangdian > Chiyudian > Fanyudian.
Conclusions The environmental quality of the surface sediments in BYD Lake is generally good, with heavy metals exceeding the standard in some areas. The environmental quality of surface sediments in Baiyangdian is generally good. There are potential ecological risks of heavy metal pollution in Nanliuzhuang and other areas, and Cd is the main pollution element.
-

-
表 1 农用地土壤污染风险筛选值与管制值
Table 1. Risk screening values and risk intervention values for soil contamination of agricultural land
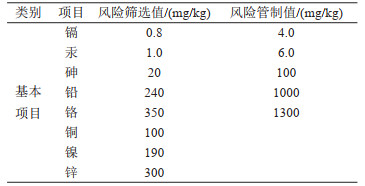
表 2 环境地球化学等级
Table 2. Geochemical grade of soil environment
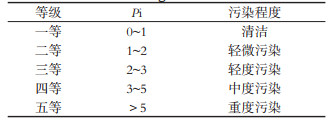
表 3 重金属污染程度等级
Table 3. Classification of heavy metal pollution grade
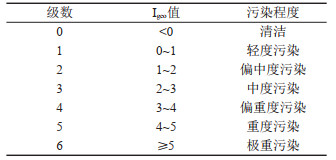
表 4 重金属潜在生态风险等级
Table 4. Potential ecological risk grade of heavy metals
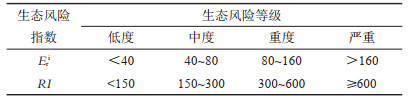
表 5 白洋淀表层沉积物重金属含量特征统计
Table 5. Characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments of BYD Lake

表 6 中国中东部主要湖泊表层沉积物重金属含量统计
Table 6. Statistics of heavy metals in surface sediments of main lakes in eastern China
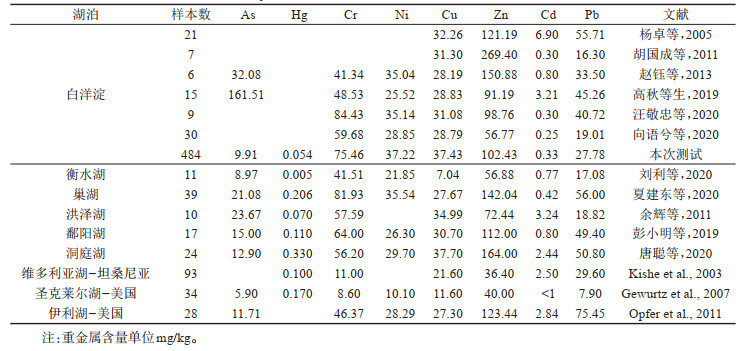
表 7 白洋淀表层沉积物各重金属元素污染指数及各等级样本数统计
Table 7. Statistics of pollution index and sample numbers of each grade of heavy metal elements in surface sediments of BYD Lake
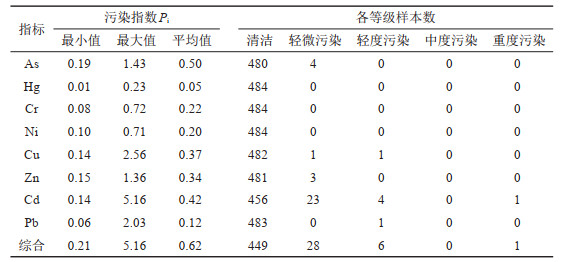
表 8 白洋淀表层沉积物地累积指数分级统计
Table 8. Classification statistics of geoaccumulation index of surface sediment in BYD Lake
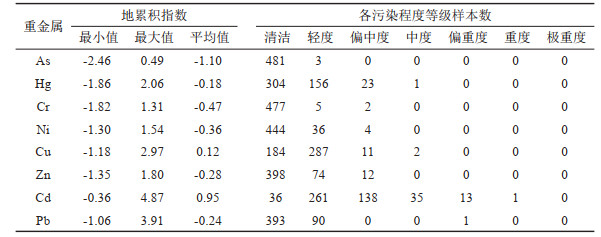
表 9 白洋淀表层沉积物重金属元素潜在生态风险指数分级统计
Table 9. Statistics of potential ecological risk index of heavy metal elements in surface sediments of BYD Lake
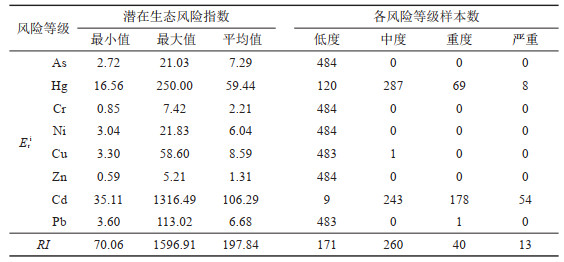
表 10 白洋淀表层沉积物重金属含量相关性
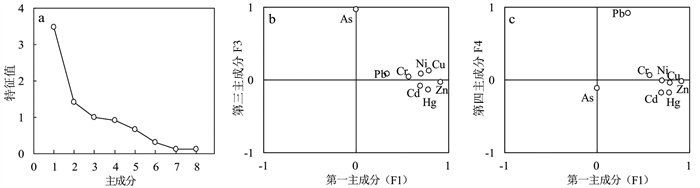
Table 10. Correlation of heavy metal content in surface sediments of BYD Lake

-
Bao Liran, Deng Hai, Jia Zhongmin, Li Yu, Dong Jinxiu, Yan Mingshu, Zhang Fenglei. 2020. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1625-1636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Jingshen, Wang Zhong, Liu Yuji. 1989. Potential hazards of metal pollution in surface water: Evaluation by sedimentological methods[J]. Environmental Science and Technology (Liaoning), 9(1): 16-25(in Chinese).
Dai G, Liu X, Liang G. 2011. Distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in surface water and sediments from Baiyangdian Lake in North China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(10): 1640-1649. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60633-X
Dai Jierui, Zhu Decheng, Pang Xugui, Yang Lizhi, Peng Guanfeng, Ning Zhenguo. 2015. Geochemical characteristics and environmental quality of soil elements in Jinan City[J]. Geology in China, 42(1): 308-316(in Chinese with English abstract).
Forstner U. 1989. Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences (Contaminated Sediments)[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 107-109.
Gao Qiusheng, Tian Ziqiang, Jiao Lixin, Ding Lin, Yang Suwen, Hao Zifeng, Cui Zhidan, Jia Haibin. 2019. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 9(1): 66-75(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gewurtz S B, Helm P A., Waltho J, Stern G A., Reiner E J, Painter S, Marvin C H., 2007. Spatial distributions and temporal trends in sediment contamination in Lake St. Clair[J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 33: 668-685. doi: 10.3394/0380-1330(2007)33[668:SDATTI]2.0.CO;2
Gong Xiaofeng, Chen Chunli, Zhou Wenbing, Jian Minfei, Zhang Zhenhui. 2006. Assessment on H eavy M Tetal Pollution in the Sediment of Poyang Lake[J]. Environmental Science, (4): 732-736(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Guocheng, Xu Muqi, Xu Zhencheng. 2011. Pollution characteristic and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment from Fuhe River and Baiyangdian Lake, North China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(1): 146-153.
Hakanson L. 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hu G, Luo X, Li F. 2010. Organochlorine compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediment from Baiyangdian Lake, North China: concentrations, sources profiles and potential risk. [J]. J. Environ., 22(2): 176-183.
Hu Guocheng, Guo Jianyang, Luo Xiaojun, Chen Shejun, Xu Muqi, Dai Jiayin, Mai Bixian, Li Fengchao. 2009. Content, distribution, source and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(3): 321-326 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Guocheng, Li Fengchao, Dai Jiayin, Luo Xiaojun, Mai Bixian, Chen Shejun, Cao Hong, XU Muqi. 2009. Characteristics of distribution and rrisk assessment of DDTs in surface sediments from Fuhe and Baiyangdian[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(8): 891-896 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Guocheng, Xu Muqi, Xu Zhencheng, Dai Jiayin, Cao Hong, Peng Xiaowu, Qi Jianying. 2011. Characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in sediments from Fuhe-Baiyangdian[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(1): 146-153(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ji Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y. 2019. Distribution, ecological risk and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake, Northern China[J]. Chemosphere, 237: 124425-. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124425
Kishe M A, Machiwa J F. 2003. Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Mwanza Gulf of Lake Victoria, Tanzania[J]. Environment International, 28: 619-625. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00099-5
Li Bicai, He Liansheng, Yang Min, Meng Rui, Yuan Donghai, Xi Beidou, Shu Jianmin. 2012. Speciation and vertical distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 33(7): 2376-2383 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jianguo, Li Guibao, Cui Huimin, Wang Dianwu. 2004. Degradation of reed wetland and protection study in Baiyangdian[J]. South-to-North Water Tronsfers and Water Science & Technology, (3): 35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jie, Song Peng, Li Hui, Chen Yunxuan, Jiao Lixin, Li Guodong. 2020. Heavy metal regional characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of lakes and reservoirs in North China[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(11): 4927-4935(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Jingwei, Yang Luhua, Xia Hui, Gao Huiyan, Kang Guofang. 2007. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake by geoaccumulation index method[J]. Yellow River, (12): 59-60, 88 (in Chinese).
Li Yu, Yu Zhiming, Song Xiuxian. 2006. Application of principal component analysis (PCA)for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments[J]. Environmental Science, (1): 137-141(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang Shuxuan, Zhang Zhenran, Qin Zhe, Wang Yu, Liu Lusan. 2016. On the physico-chemical characteristic features and the nutrient distribution in the sediments of Lake Baiyangdian[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 16(1): 294-298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Li, Zhang Jiawen, Chen Fenfei, Sheng Sheng, Tian Ziqiang, Wang Jian. 2020. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Hengshui Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 10(2): 205-211(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Ruiping, Xu Youning, Zhang Jianghua, Wang Wenke, Rafaey M Elwardany. 2020. Effects of heavy metal pollution on farmland soils and crops: A case study of the Xiaoqinling Gold Belt, China[J]. China Geology, 3(3): 402-410.
Ma Zhen, Xia Yubo, Li Haitao, Han Bo, Yu Xuezhong, Zhou Yalong, Wang Yushan, Guo Xu, Li Hongqiang, Pei Yandong. 2021. Analysis of naturalresources and environment eco- geological conditions in the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Geology in China, 48(3): 677- 696 (in Chinese with Englishabstract).
Mao Xin, Liu Linjing, Song Lei, Jiang Gaolei, Li Junfeng, Li Chang 'an. 2020. A 70-year sedimentary record of eco-environment changes in Baiyangdian Lake and its influencing factors[J]. Earth Sciences, 1-18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. 2008. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land GB 15618-2008[S](in Chinese).
Ministry of Land and Resources, PRC. 2016. DZ/T 0295-2016 Land Quality Geochemical Evaluation Criteria[S](in Chinese).
Opfer S E, Farver J R, Miner J G, Krieger K. 2011. Heavy metals in sediments and uptake by burrowing mayflies in western Lake Erie basin[J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 37: 1-8.
State Environmental Protection Bureau, China Environmental Monitoring Station. 1990. Background Values of Soil Elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 326-359(in Chinese).
Tang Cong, Qian Bao, Li Weiqin, Pan Chang, Yang Yu, Xiao Xiao. 2020. Pollution characteristics and risk evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dongting Lake[J]. Yangtze River, 51(6): 49-56, 62(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jingzhong, Liu Zhuo, Wei Hao, Wu Yuhui, Zhan Shuie, Zhu Chi, Zhang Yimiao. 2020. Spatial characteristics, risk assessment, and source analysis of elements in surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 224-231(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yushan, Yin Dechao, Wang Xuqing, Qi Xiaofan, Xia Yubo, Ma Zhitong, Zhang Liang, Xu Rongzhen. 2021. Groundwater-surface water inter actions in the Baiyangdian wetland, Xiong'an New Area and its impact on reed land[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1368-1381. (in Chinese with Englishabstract).
Xia Jiandong, Long Jinyun, Gao Yaping, Chen Yue, Meng Jing, Zhou Yunqiao, Chen Shuqin. 2020. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollutions in sediments of the Chaohu Lake[J]. Earth and Environment, 48(2): 220-227(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiang Yuxi, Wang Xiao, Shan Baoqing, Zhao Yu, Tang Wenzhong, Shu Limin, Jiang Shixin, Cao Yang. 2020. Spatial distribution, fractionation and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments from Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(6): 2237-2246(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu Zhengqi, Ni Shijun, Tuo Xianguo, Zhang Chengjiang. 2008. Calculation of toxic coefficient of heavy metals in evaluation of potential ecological hazard index method[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, (2): 112-115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Hongze, Zhou Guohua, Sun Binbin, He Ling, Liu Yinfei, Hou Shujun. 2018. Geochemical characteristics of the bayberry producing area in Longhai, Fujian[J]. Geology in China, 45(6): 1155-1166(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Zhuo, Li Guibao, Wang Dianwu, Cui Huimin, Shang Tongzhao. 2005. Pollution and the potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, (5): 115-121(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yi Yujun, Lin Chuqiao, Tang Caihong. 2020. Hydrology, environment and ecological evolution of Lake Baiyangdian since 1960s[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 32(5): 1333-1347, 1226(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2020.0500
Zhang Mengman, Wu Xiuqin. 2018. Changes in hydrological connectivity and spatial morphology of Baiyangdian wetland over the last 20 years[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(12): 4205-4213 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Min, Gong Zhaoning, Zhao Wenji, Duo A. 2016. Landscape pattern change and the driving forces in Baiyangdian wetland from 1984 to 2014[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(15): 4780-4791(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Yalong, Yang Zhibin, Wang Qiaolin, Wang Chengwen, Liu Fei, Song Yuntao, Guo Zhijuan. 2020. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil-crop System in Xiong'an New District[J]. Environmental Science, 42(4): 2003-2015(in Chinese with English abstract).
鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 李瑜, 董金秀, 严明书, 张风雷. 2020. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1625-1636. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200602&flag=1
陈静生, 王忠, 刘玉机. 1989. 水体金属污染潜在危害: 应用沉积学方法评价[J]. 环境科技(辽宁), 9(1): 16-25.
代杰瑞, 祝德成, 庞绪贵, 杨丽芝, 彭观峰, 宁振国. 2015. 济南市土壤元素地球化学特征及环境质量[J]. 中国地质, 42(1): 308-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.025 http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150124&flag=1
高秋生, 田自强, 焦立新, 丁琳, 杨苏文, 郝子峰, 崔志丹, 贾海斌. 2019. 白洋淀重金属污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 9(1): 66-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKWZ201901010.htm
弓晓峰, 陈春丽, 周文斌, 简敏菲, 张振辉. 2006. 鄱阳湖底泥中重金属污染现状评价[J]. 环境科学, (4): 732-736. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.04.025
国家环境保护局, 中国环境检测总站. 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 326-359.
胡国成, 郭建阳, 罗孝俊, 陈社军, 许木启, 戴家银, 麦碧娴, 李凤超. 2009. 白洋淀表层沉积物中多环芳烃的含量、分布、来源及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 22(3): 321-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200903011.htm
胡国成, 李凤超, 戴家银, 罗孝俊, 麦碧娴, 陈社军, 曹宏, 许木启. 2009. 府河和白洋淀沉积物中DDTs的分布特征和风险评估[J]. 环境科学研究, 22(8): 891-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200908003.htm
胡国成, 许木启, 许振成, 戴家银, 曹宏, 彭晓武, 齐建英. 2011. 府河-白洋淀沉积物中重金属污染特征及潜在风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(1): 146-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201101025.htm
李必才, 何连生, 杨敏, 孟睿, 袁冬海, 席北斗, 舒俭民. 2012. 白洋淀底泥重金属形态及竖向分布[J]. 环境科学, 33(7): 2376-2383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201207034.htm
李建国, 李贵宝, 崔慧敏, 王殿武. 2004. 白洋淀芦苇湿地退化及其保护研究[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, (3): 35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1683.2004.03.012
李捷, 宋鹏, 李慧, 程云轩, 焦立新, 李国栋. 2020. 北方湖库沉积物重金属区域特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(11): 4927-4935. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.034
李经伟, 杨路华, 夏辉, 高惠嫣, 康国芳. 2007. 白洋淀底泥重金属污染地积累指数法评价[J]. 人民黄河, (12): 59-60, 88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2007.12.029
李玉, 俞志明, 宋秀贤. 2006. 运用主成分分析(PCA)评价海洋沉积物中重金属污染来源[J]. 环境科学, (1): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200601026.htm
梁淑轩, 张振冉, 秦哲, 王瑜, 刘录三. 2016. 白洋淀沉积物理化特性及营养盐分布特征[J]. 安全与环境学报, 16(1): 294-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201601064.htm
刘利, 张嘉雯, 陈奋飞, 盛晟, 田自强, 王俭. 2020. 衡水湖底泥重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 10(2): 205-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKWZ202002012.htm
马震, 夏雨波, 李海涛, 韩博, 余学中, 周亚龙, 王雨山, 郭旭, 李洪强, 裴艳东. 2021. 雄安新区自然资源与环境-生态地质条件分析[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 677-696. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210301&flag=1
毛欣, 刘林敬, 宋磊, 姜高磊, 李峻峰, 李长安. 2020. 白洋淀近70年生态环境演化过程及影响因素[J]. 地球科学: 1-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202107026.htm
唐聪, 钱宝, 李炜钦, 潘畅, 杨宇, 肖潇. 2020. 洞庭湖区表层沉积物重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 人民长江, 51(6): 49-56, 62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE202006010.htm
汪敬忠, 刘卓, 魏浩, 吴玉会, 占水娥, 朱迟, 张益淼. 2020. 白洋淀表层沉积物元素的空间特征、风险评价及来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 224-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202001026.htm
王雨山, 尹德超, 王旭清, 祁晓凡, 夏雨波, 马稚桐, 张亮, 徐蓉桢. 2021. 雄安新区白洋淀湿地地表水和地下水转化关系及其对芦苇分布的影响[J]. 中国地质, 48(5): 1368-1381. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210504&flag=1
夏建东, 龙锦云, 高亚萍, 陈悦, 孟晶, 周云桥, 陈书琴. 2020. 巢湖沉积物重金属污染生态风险评价及来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 48(2): 220-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202002008.htm
向语兮, 王晓, 单保庆, 赵钰, 唐文忠, 束礼敏, 姜时欣, 曹阳. 2020. 白洋淀表层沉积物重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(6): 2237-2246. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202006034.htm
徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 张成江. 2008. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, (2): 112-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS200802029.htm
严洪泽, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 刘银飞, 候树军. 2018. 福建龙海杨梅产地元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 45(6): 1155-1166. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180606&flag=1
杨卓, 李贵宝, 王殿武, 崔惠敏, 商同钊. 2005. 白洋淀底泥重金属的污染及其潜在生态危害评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, (5): 115-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200505022.htm
易雨君, 林楚翘, 唐彩红. 2020. 1960s以来白洋淀水文、环境、生态演变趋势[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(5): 1333-1347, 1226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202005008.htm
张梦嫚, 吴秀芹. 2018. 近20年白洋淀湿地水文连通性及空间形态演变[J]. 生态学报, 38(12): 4205-4213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201812011.htm
张敏, 宫兆宁, 赵文吉, 阿多. 2016. 近30年来白洋淀湿地景观格局变化及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 36(15): 4780-4791. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201615023.htm
中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2016. DZ/T 0295-2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S].
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2018. GB15618-2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准[S].
周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 王成文, 刘飞, 宋云涛, 郭志娟. 2021. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析[J]. 环境科学, 42(4): 2003-2015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104047.htm
-



 下载:
下载: