Discussion on Metallogenic Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Shuanghe Barite-Fluorite Deposit in Wuchuan, Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
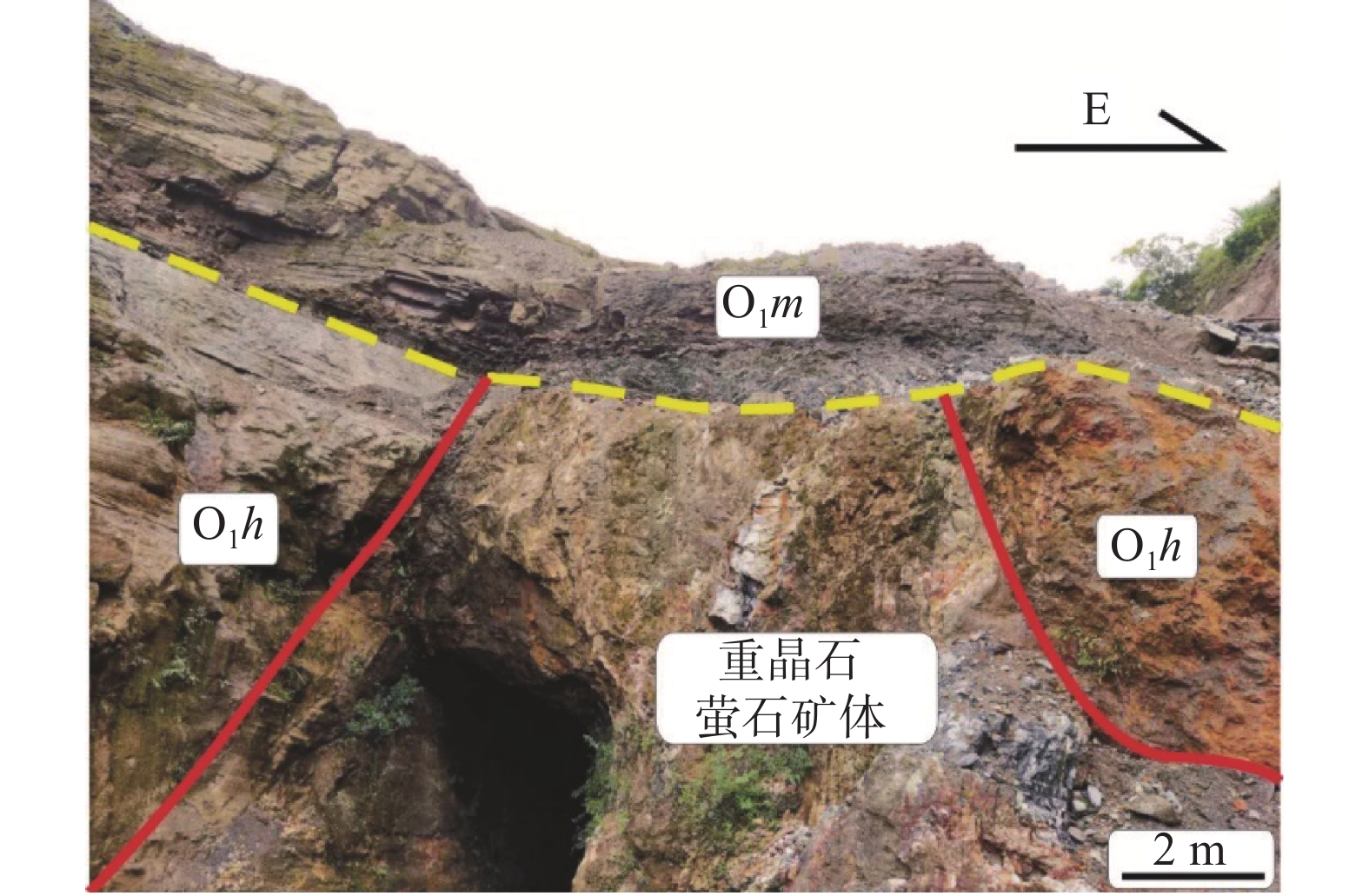
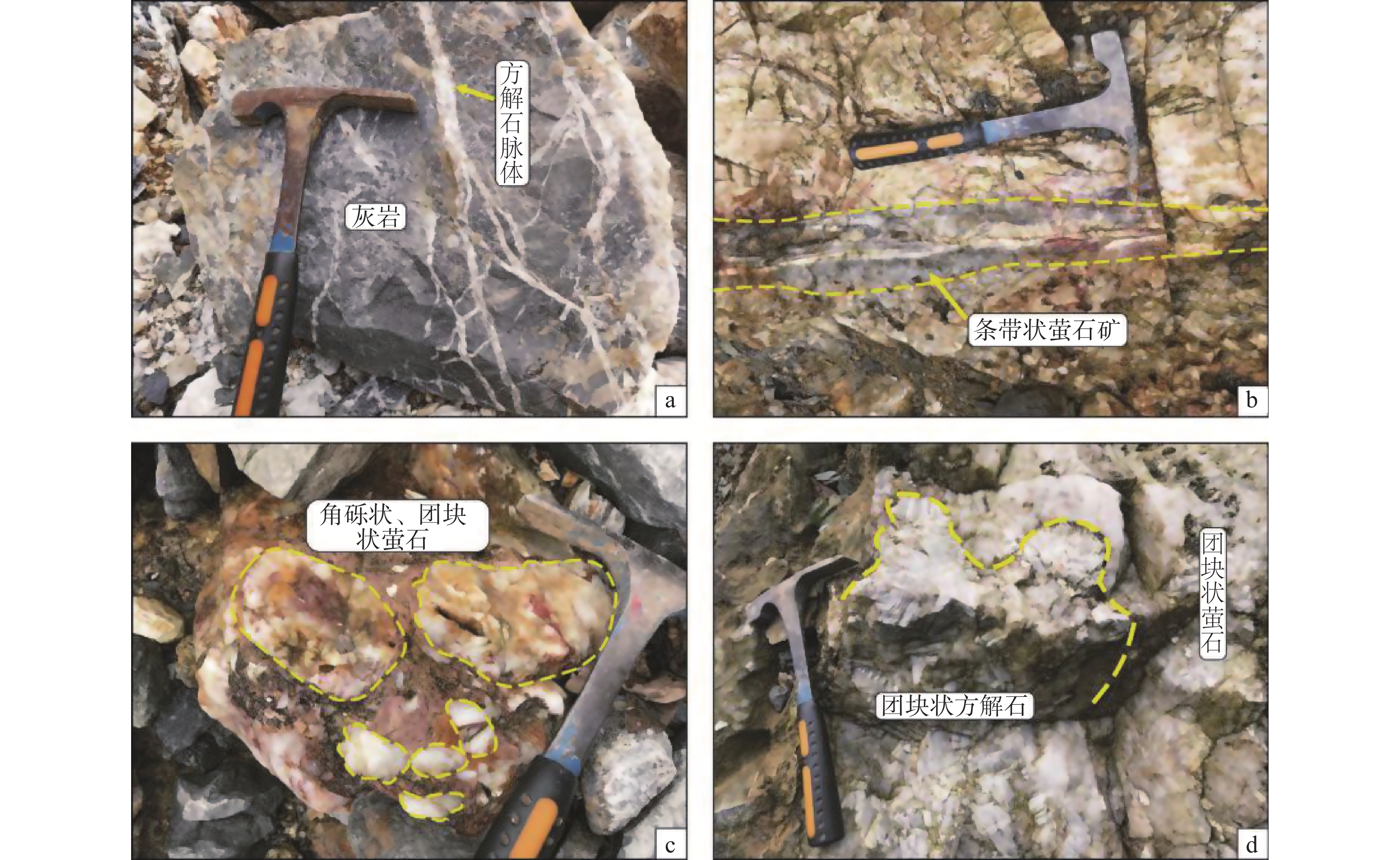
萤石主要应用于钢铁和化工行业,市场对萤石的需求一直在持续增长,萤石已经成为中国战略性矿产。随着低品位重晶石萤石共生矿综合利用关键技术取得重要突破,在武陵山地区(渝黔湘交汇区)重晶石萤石共生矿床逐渐被重视及利用。通过野外地质工作,以务川双河重晶石-萤石矿矿床地质特征为研究对象,认为务川双河重晶石-萤石矿床受地层、构造2个因素共同控制成矿,主要赋矿层位为奥陶系下统红花园组,提出重晶石-萤石矿体受奥陶系下统红花园组及北西向构造控制的找矿方向,该认识有助于贵州武陵山地区开展进一步找矿工作,并积极助力该区矿业开发、服务脱贫攻坚工作。
Abstract:Fluorite is mainly used in the steel and chemical industries. The market demand for fluorite has been growing, and fluorite has become a strategic mineral in China. With the exhaustion of fluorite resources in the main producing areas (Zhejiang, Hunan, etc.), the barite fluorite deposit has been paid more attention and utilized in Wuling Mountain area (the adjacent place of Chongqing, Guizhou and Hunan). Through field geological work, the geological characteristics of shuanghe Barite-fluorite deposit in Wuchuan were studied, it is considered that the Shuanghe Barite-fluorite deposit in Wuchuan is controlled by the lower Ordovician Honghuayuan formation and the NW trending development of tensile fractures, the ore-bearing horizon is the Lower Ordovician Honghuayuan group, It is proposed that the ore-prospecting direction of the barite-fluorite ore body is controlled by the Lower Ordovician Honghuayuan Formation and the NW direction structure, It is helpful for further prospecting work in Wuling Mountain area of Guizhou province, it will actively support the development of mining industry in the region and provide services for poverty alleviation.
-

-
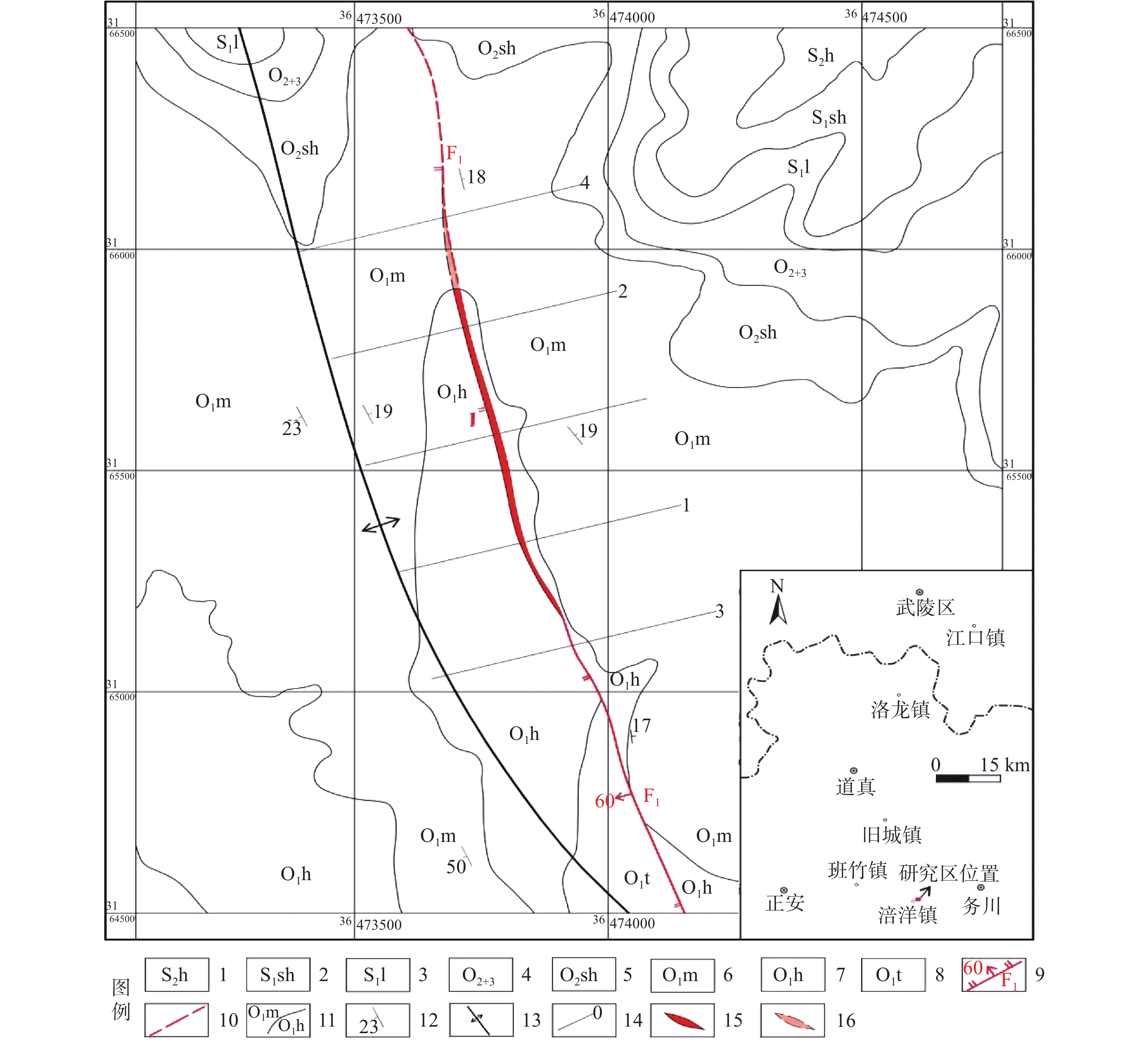
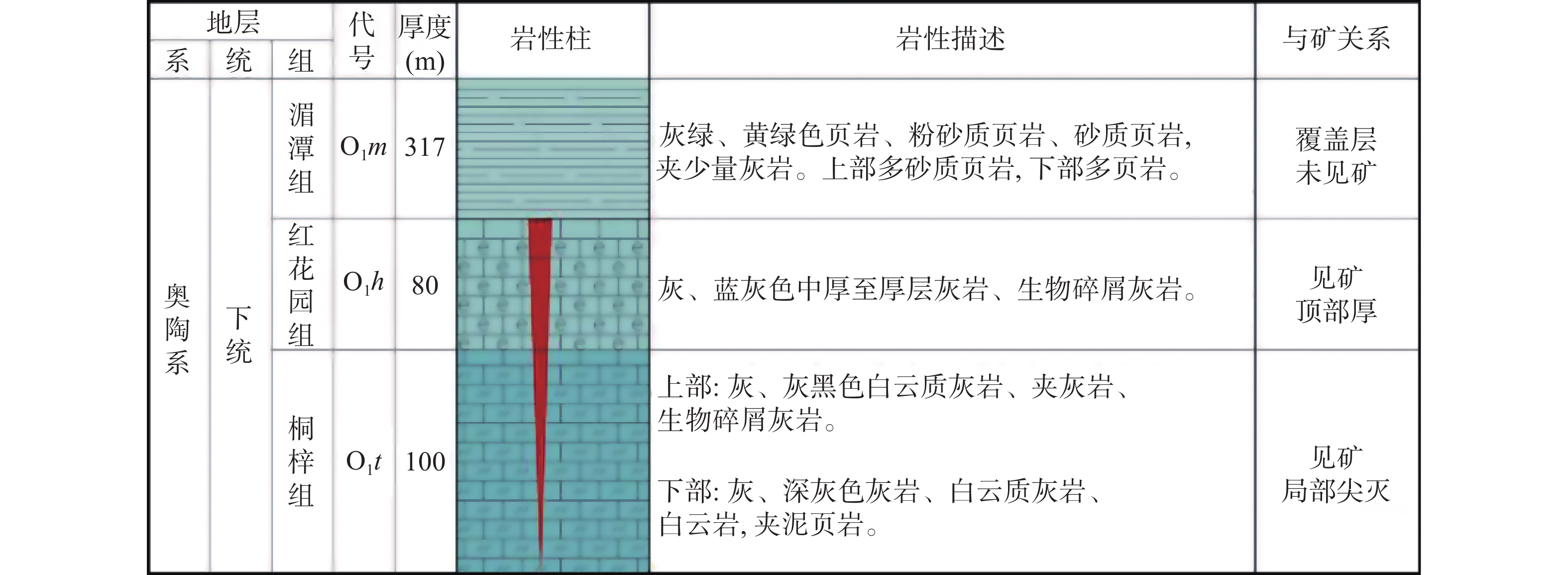
图 3 矿区含矿地层柱状图[10]
Figure 3.
表 1 川东南及邻区下寒武统地层Ba含量[11]
Table 1. Ba content in lower Cambrian strata in Southeast Sichuan and adjacent areas
地层名称 地层代号 岩性 Ba/×10-6 震旦系上统陡山沱组 Z2d 深灰、黑色粉砂质页 1135 寒武系下统牛蹄塘组 Є 1n 深灰、黑色粉砂质页岩 13220 寒武系下统清虚洞组 Є 1q 灰色、深灰色白云质灰岩 含Ba层 寒武系中统高台组 Є 2g 黑色页岩 4260 寒武系上统毛田组 Є 3m 深色灰岩 200~1547 奥陶系下统桐梓组 O1t 深灰色灰岩 728~1761 奥陶系下统红花园组 O1h 灰色、深灰色灰岩 赋矿层 奥陶系上统五峰组 O3w 黑色页岩 1715 表 2 川东南邻区震旦-寒武系地层不同岩性F含量 [11]
Table 2. F content in different lithology of Sinian-Cambrian strata in Southeast Sichuan and adjacent areas
地层名称 地层 岩性 F /% 寒武系下统明心寺组 Є 1mx 页岩 0.60-0.76 寒武系下统牛蹄塘组 Є 1n 灰色页岩 1.42-1.46 震旦系上统陡山沱组 Z2d 白云岩 0.57-0.76 -
[1] 王吉平, 商朋强, 牛桂芝. 中国萤石矿主要矿集区及其资源潜力探讨[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2010, 32(2):87-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2010.02.003
WANG J P, SHANG P Q, NIU G Z. Discussion on the main ore concentration areas and resource potential of fluorite mines in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2010, 32(2):87-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5296.2010.02.003
[2] 殷科华, 吕天权, 翁申富. 德江县大元萤石矿床地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 贵州地质, 2008, 96(3):196-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2008.03.009
YIN K H, LV T Q, WENG S F. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of Dayuan fluorite deposit in Dejiang County[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2008, 96(3):196-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2008.03.009
[3] 候兵德. 沿河丰水岭萤石矿地质特征及成因浅析[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2011(5):149-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2011.05.051
HOU B D. Analysis on the geological characteristics and genesis of the fluorite mine in Fengshuiling along the river[J]. Western Exploration Engineering, 2011(5):149-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2011.05.051
[4] 邹灏, 徐旃章, 张寿庭, 等. 重庆彭水火石垭重晶石-萤石矿床控矿因素与成因[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(1):89-96.
ZOU H, XU Z Z, ZHANG S T, et al. Ore-controlling factors and genesis of the Huoshiya barite-fluorite deposit in Pengshui, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 40(1):89-96.
[5] 陈云明, 刘志臣. 贵州务川地区重晶石—萤石矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2014, 26(11):141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2014.11.046
CHEN Y M, LIU Z C. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of barite-fluorite deposits in Wuchuan area of Guizhou[J]. West China Prospecting Engineering, 2014, 26(11):141-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2014.11.046
[6] 贵州省地质调查院. 贵州省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
Guizhou Provincial Geological Survey Institute. Regional geology of Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017.
[7] 冯学仕, 王尚彦. 贵州省区域矿床成矿系列与成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.
FENG X S, WANG S Y. The mineralization series and laws of regional mineral deposits in Guizhou Province[M]. Geological Publishing House, 2004.
[8] 贵州地矿局108地质大队. 1: 20万正安幅区调报告[R]. 1972.
108 Geological Brigade, Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. 1: 200, 000 Zheng'an Area survey report [R]. 1972.
[9] 贵州地矿局108地质大队. 1: 20万南川幅区调报告[R]. 1976.
108 Geological Brigade, Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. 1: 200, 000 Nanchuan Area survey report [R]. 1976.
[10] 贵州地层古生物工作队. 贵州各时代地层分区图及对比简表[R]. 1975.
Guizhou Stratigraphy and Paleontology Task Force. Stratigraphic zoning map and comparison table of various eras in Guizhou [R]. 1975.
[11] 中国地质大学, 成都理工大学. 川东南(武陵山)地区重晶石-萤石矿成矿控制条件及其时、空演变特征与资源评价[R]. 2012.12.
China University of Geosciences, Chengdu University of Technology. Barite-fluorite mineralization control conditions and its temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and resource evaluation in the southeastern Sichuan (Wulingshan) area [R]. 2012.12.
[12] 王淑丽, 郑绵平, 焦健. 上扬子区寒武系蒸发沉积相及成钾潜力分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(5): 85-96.
WANG S L, ZHEN M P, JIAO J. Analysis of the cambrian evaporative sedimentary facies and potassium formation potential in the upper Yangtze Region[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2012, 48(5): 85-96.
[13] 潘忠华, 范德廉. 川东南脉状萤石一重晶石矿床同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 1996, 12(1): 127-136.
PAN Z H, FAN D L. Isotope geochemistry of vein-like fluorite-barite deposits in Southeastern Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1996, 12(1): 127-136.
-




 下载:
下载: