Study on the microstructure characteristics of Late Cretaceous aeolian sand in the playa from Chuxiong Basin
-
摘要:
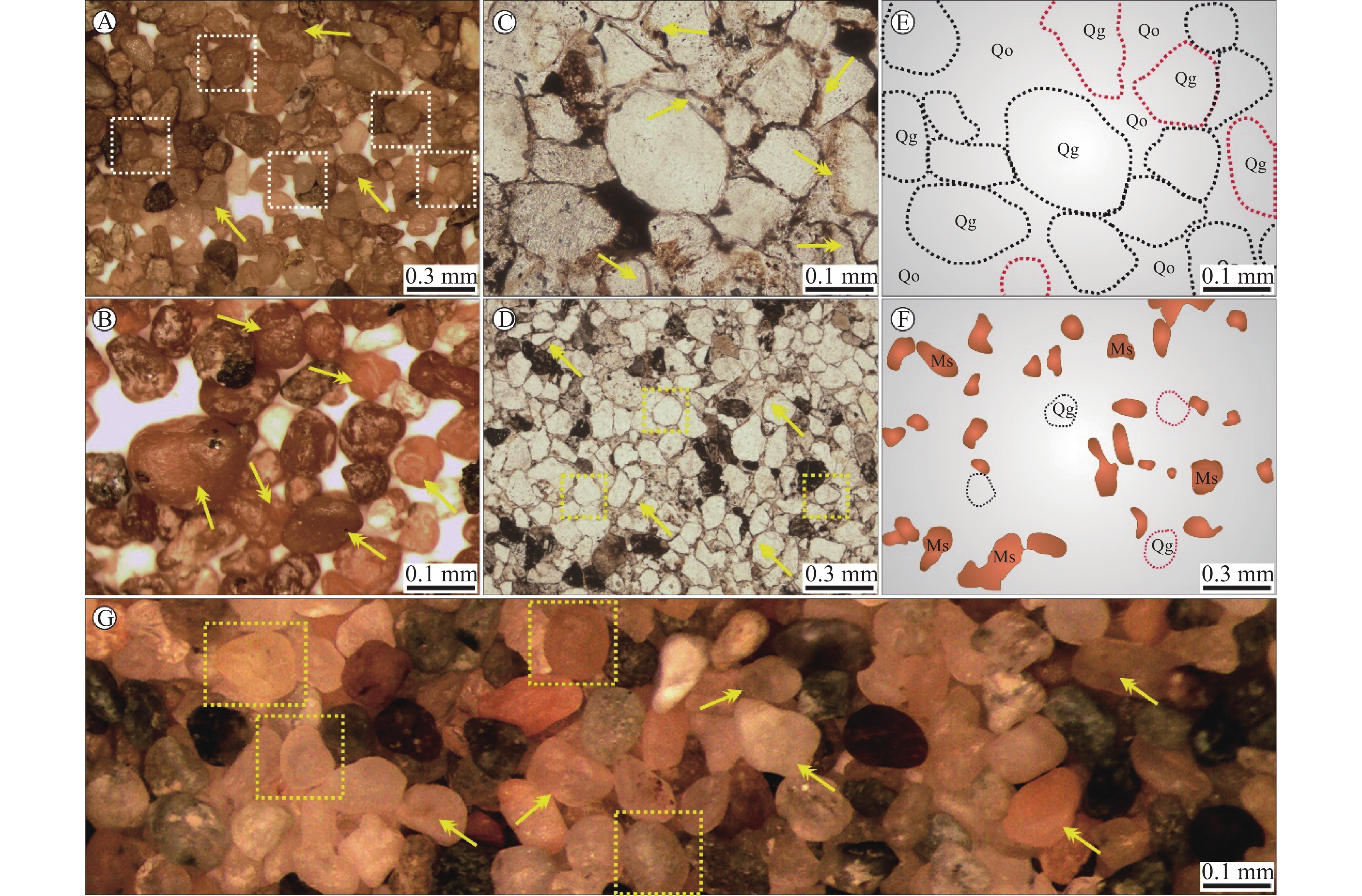
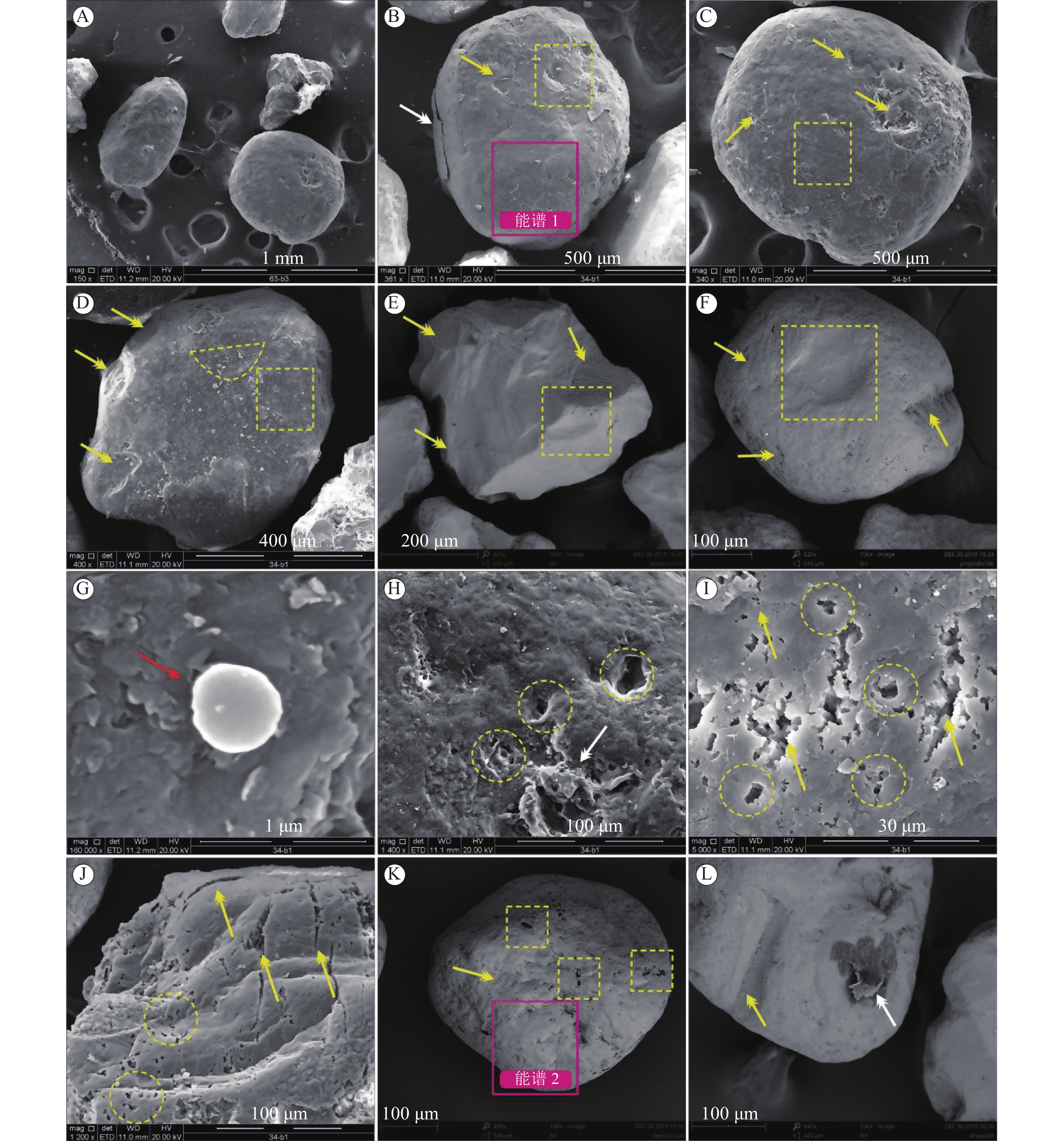
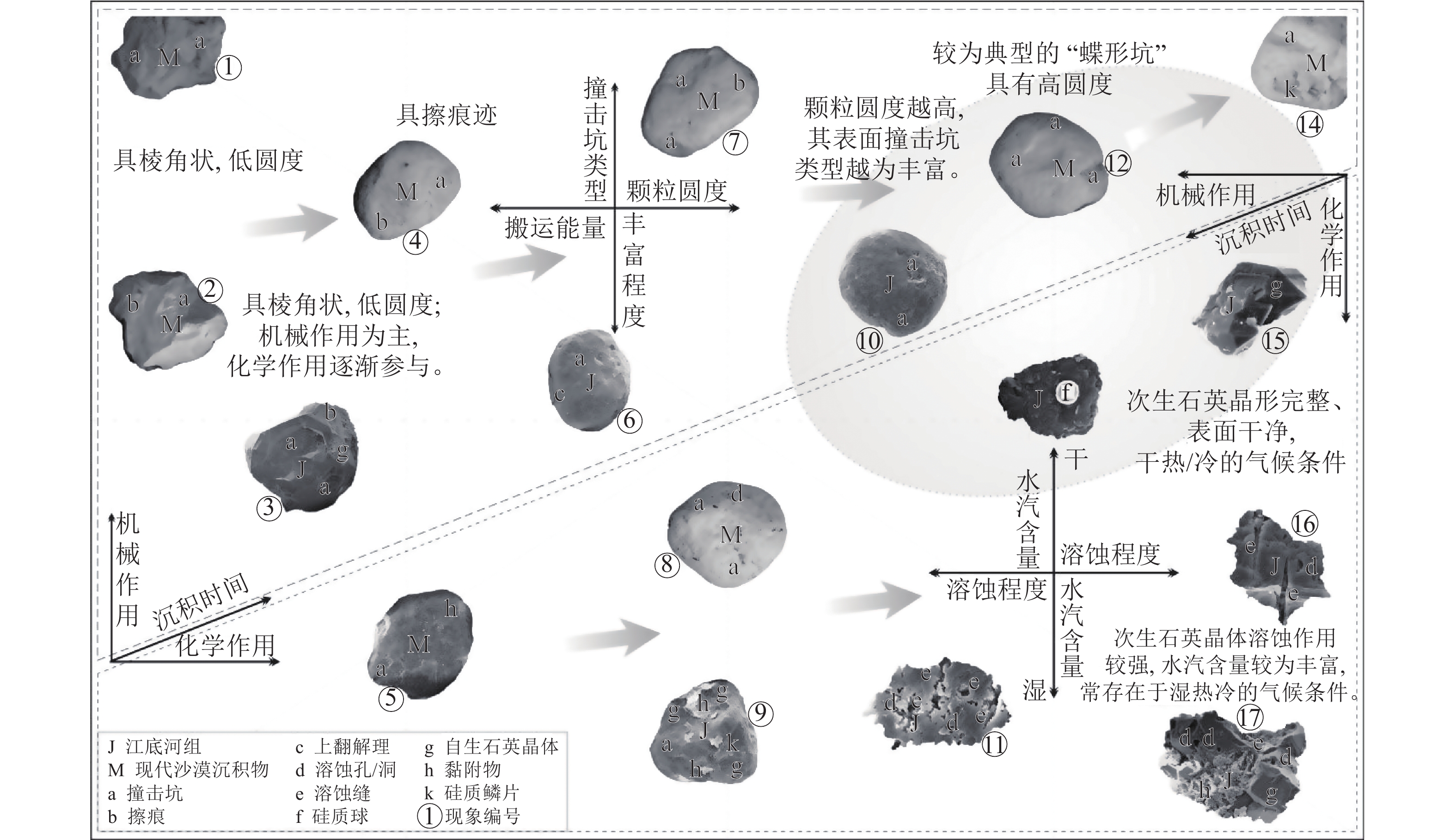
白垩纪是地球历史上一个持续时间较长的典型温室气候期,受区域古地形叠加影响,在东亚地区促成了广泛的干旱气候带,并伴有大面积出露的古沙漠和蒸发岩沉积,而楚雄盆地上白垩统江底河组即为该时期形成的一套干盐湖相红色碎屑岩夹膏盐沉积。通过光学显微镜和扫描电镜(SEM)及能谱(EDS)分析,对江底河组砂岩石英颗粒结构形态及表面微形貌特征进行研究。结果显示,楚雄盆地江底河组砂岩的石英颗粒具有高磨圆度和分选性、碟形撞击坑、“沙漠漆”以及强化学作用溶蚀孔(洞)群等现象,展现出风成砂的典型特征。同时基于石英颗粒表面机械作用、化学(溶蚀、沉淀)作用及其组合特征,系统总结了石英颗粒在不同沉积阶段和环境背景下,其表面微形貌特征的演化规律。这项研究有助于对盐湖环境中风成砂的特征以及风成沉积和水成沉积相互作用机制的认识。
Abstract:Cretaceous greenhouse, a long-lasting typical warminginterval in the history of the earth, and the regional paleotopography effect triggered a wide spread arid-climate belt in East Asia accompanying with extensive paleo-desert outcrops and evaporite deposits. The Upper Cretaceous Jiangdihe Formation in the Chuxiong Basin is characterized by a set of red clastic rocks interbedded with gypsum, being atypical playa environment. Through multiple approaches including optical microscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Spectrum (EDS) analysis, the structural morphology and surface micro-morphology characteristics of quartz grains from the Jiangdihe Fm. sandstones from the Chuxiong basin have been studied. The results show that the quartz grains of the Jiangdihe Fm. sandstone has high roundness and wellsorting, dish-shaped impact scars, "desert varnish", and groups of intense chemical corrosion pores (caves), all of which show the typical characteristics of aeolian sand. In addition, the evolution rule of micro-morphology on the quartz grains under different sedimentary environment has been systematically summarized, based on physical interaction, chemical (dissolution, precipitation) interaction, and their combination characteristics of the quartz grains surface. This study will contribute to the further understanding for the characteristics of aeolian sand deposited in the playa environment and the mechanism of the interacting aeolian-aqueous deposition.
-

-
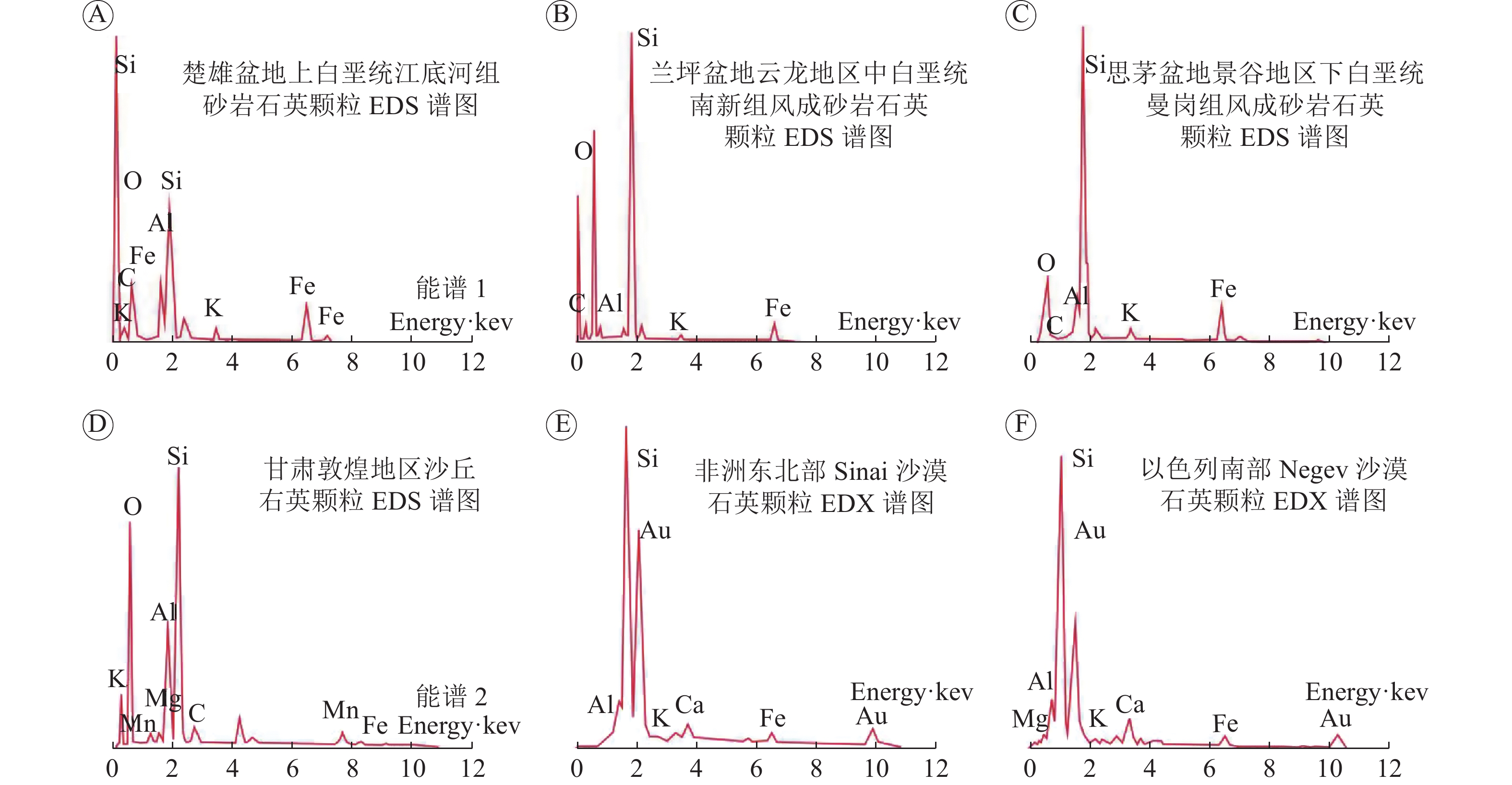
表 1 楚雄盆地上白垩统江底河组砂岩石英颗粒能谱分析(EDS)元素统计
Table 1. Energy spectrum analysis of late Cretaceous Jiangdihe Formation in Chuxiong Basin, Yunnan and modern desert sediments(EDS)
样品编号 元素 ( Wt%: 质量百分比;At%: 原子百分比) 地层 O Si Al Fe K C Mn Wt% At% Wt% At% Wt% At% Wt% At% Wt% At% Wt% At% Wt% At% DC-34b1-1 40.73 55.35 55.00 45.28 0.99 0.80 3.28 1.28 江底
河组DC-34b1-2 52.36 61.01 36.49 24.22 2.25 1.55 8.13 13.62 DC-34b1-3 44.53 60.12 46.56 35.81 1.51 1.21 7.41 2.86 DC-34b1-4 48.10 63.10 44.45 33.22 2.21 1.72 5.24 1.97 DC-34b1-5 37.66 52.46 57.44 45.58 4.90 1.96 DC-34b1-6 32.86 48.36 23.93 20.05 9.63 8.40 25.28 10.66 2.75 1.66 5.55 10.88 DC-34b1-7 47.53 62.65 36.62 27.50 8.32 6.51 6.50 2.45 1.03 0.89 DC-34b1-8 50.05 64.00 45.75 33.33 2.89 2.19 1.31 0.48 DC-34b1-9 45.56 51.19 36.20 23.17 16.32 24.43 DC-34b1-10 45.67 61.10 31.29 23.84 9.93 7.87 13.12 7.18 DC-34b1-11 43.66 55.74 29.54 21.48 8.82 6.68 12.30 6.42 5.69 9.68 平均值 44.43 57.73 40.30 30.32 5.17 4.10 7.70 3.09 7.30 4.04 8.92 14.65 -
[1] Fluteau F, Ramstein G, Besse J, et al. Impacts of palaeogeography and sea level changes on Mid-Cretaceous climate[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 247(3-4):357-381. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.11.016
[2] Chumakov N M, Zharkov M A, Herman A B, et al. Climate belts of the Mid cretaceous time [J]. Stratigraphy and Geological Correlation, 1995, 3: 241–260.
[3] Bowman V C , Francis J E, Riding J B. Late Cretaceous winter sea ice in Antarctica? [J]. Geology, 2013, 41: 1227–1230.
[4] Wang L C, Liu C L, Fei M M , et al. First SHRIMP U-Pb zir con ages of the potash-bearing Mengyejing Formation, Simao Basin, southwestern Yunnan, China [J]. Cretaceous Research, 2015, 52: 238–250.
[5] Hasegawa H, Imsamut S, Charusiri P, et al. Thailand was a desert' during the mid-Cretaceous: equatorward shift of the subtropical high pressure belt indicated by eolian deposits (Phu Thok formation) in the Khorat Basin, northeastern Thailand [J]. Island Arc, 2010, 19: 605–621.
[6] Rodríguez-López J P, Meléndez N , De Boer P L , et al. Aeolian sand sea development along the mid-Cretaceous western Tethyan margin (Spain): erg sedimentology and palaeoclimate implications [J]. Sedimentology, 2008, 55: 1253–1292.
[7] Rodríguez-LópezJ P, Meléndez N , De Boer P L, etal The action of wind and water in a mid-Cretaceous subtropical erg-margin system close to the Variscan Iberian Massif, Spain [J]. Sedimentology, 2010, 57: 1315–1356.
[8] Rodríguez-López J P, Meléndez N, De Boer P L, etal. Controls on marine-erg margin cycle variability: Aeolian-marine interaction in the mid-Cretaceous Iberian Desert System, Spain [J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59: 466–501.
[9] Wu C H, Liu C L, Yi H S , et al. Mid cretaceous desert system in the Simao Basin, southwestern China, and its implications for sea-level change during a greenhouse climate [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017. 468: 529–544.
[10] Wu C H, Rodríguez-López J P, Liu C, et al. Late Cretaceous climbing erg systems in the western Xinjiang Basin: palaeoatmo sphere dynamics and East Asia margin tectonic forcing on desert expansion and preservation [J]. Mar. Petrol. Geol, 2018, 93: 539–552.
[11] Jiang X, Pan Z, Xu J, et al. Late Cretaceous aeolian dunes and reconstruction of palaeo-wind belts of the Xinjiang Basin, Jiangxi province, China. [J]Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol, 2008, 257: 58–66.
[12] Jiao H, Wu C, Rodríguez-López J P, et al. Late Cretaceous plateau deserts in the South China Block, and Quaternary analogues; sedimentology, dune reconstruction and wind-water interactions [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 120. doi: 10. 1016/ j. marpetgeo.
[13] 陈荣林. 江苏及邻区上白垩统赤山组中古沙漠沉积[J]. 江苏地质, 1987(2):20-23.
CHEN R L. Upper Cretaceous Chishan Formation Middle-Pale Desert Deposits in Jiangsu and its adjacent areas[J]. Jiangsu Geology, 1987(2):20-23.
[14] 陈清华, 庞飞. 苏北盆地白垩纪沙漠石英颗粒表面特征及环境意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 2008, 15(5):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2008.05.003
CHEN Q H, PANG F. Surface characteristics and environmental significance of quartz grains in the Cretaceous desert of the Subei Basin[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2008, 15(5):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2008.05.003
[15] 贺其川. 沙漠沉积特征——以江陵凹陷白垩系红花套组为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011 (7): 34-37+5. HE Q C. Sedimentary characteristics of deserts—taking the Cretaceous Honghuatao Formation in Jiangling Sag as an example [J]. Chinese Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2011 (7): 34-37+5.
[16] 江新胜, 潘忠习, 傅清平. 四川盆地白垩纪沙漠风向变化规律及其意义[J]. 岩相古地理, 1999, 19(1):1-11.
JIANG X S, PAN Z X, FU Q P. Variation of wind direction in the Cretaceous desert in the Sichuan Basin and its significance[J]. Lithofacies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(1):1-11.
[17] 刘立安, 姜在兴. 四川盆地古近纪沙漠沉积特征及古风向意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(2):63-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.02.011
LIU L A, JIANG Z X. Sedimentary characteristics of Paleogene desert in Sichuan Basin and significance of paleowind direction[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(2):63-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.02.011
[18] Li G, Wu C, Rodríguez-lópez J P, et al. Mid-Cretaceous aeolian desert systems in the Yunlong area of the Lanping Basin, China: implications for palaeoatmosphere dynamics and paleoclimatic change in East Asia [J]. Sediment Geology, 2018, 364: 121–140.
[19] 袁桃, 吴驰华, 伊海生, 等. 云南思茅盆地景谷地区下白垩统曼岗组风成砂岩沉积学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015(11):2062-2074.
YUAN T, WU C H, YI H S, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and paleoclimatic significance of aeolian sandstones of the Lower Cretaceous Mangang Formation in Jinggu area, Simao Basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Geology, 2015(11):2062-2074.
[20] 龚政, 吴驰华, 伊海生, 等. 滇西思茅盆地景谷地区曼岗组石英颗粒表面特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015(11):2053-2061.
GONG Z, WU C H, YI H S, et al. Surface characteristics of quartz grains in the Mangang Formation in the Jinggu area of the Simao Basin in western Yunnan and their indicative significance[J]. Acta Geology, 2015(11):2053-2061.
[21] 胡煜昭, 吴鹏, 闵朝龙, 等. 楚雄盆地六苴铜矿含矿岩系沉积环境及成矿时代分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(1):427-428.
HU Y Z, WU P, MIN Z L, et al. Analysis of the sedimentary environment and mineralization age of the ore-bearing rock series of the Liuju copper deposit in the Chuxiong Basin[J]. Acta Mineralogy Sinica, 2009, 29(1):427-428.
[22] 陈根文, 夏斌, 王国强, 等. 楚雄盆地砂岩铜矿床构造控矿分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2002(2):167-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2002.02.010
CHEN G W, XIA B, WANG G Q, et al. Analysis of structural ore-controlling of sandstone copper deposits in Chuxiong Basin[J]. Tectonics and Metallogenesis, 2002(2):167-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2002.02.010
[23] 云南省地质矿产局. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990.Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional geology of Yunnan Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990.
[24] 薛传东, 向坤, 胡廷银, 等. 楚雄盆地北部桂花铜矿区晚白垩世含矿岩系沉积环境[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(3):491-501.
XUE C D, XIANG K, HU T Y, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Late Cretaceous ore-bearing rock series in the Guihua copper mining area in the northern Chuxiong Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(3):491-501.
[25] Margolis S. V, Kennett J P. Cenozoic paleoglacial history of Antarctica recorded in Subantarctic deep-sea cores[J]. American Journal of ence, 1971, 271(1):1-36.
[26] Krinsley, David H, Doornkamp. Atlas of quartz sand surface textures [M]. Cambridge University Press, 1973.
[27] 蒲心纯, 尹福光, 朱同兴. 楚雄前陆盆地的充填层序与造山作用[J]. 岩相古地理, 1996, 16(3):47-58.
PU X C, YIN F G, ZHU T X. Filling sequence and orogen in the Chuxiong Foreland Basin[J]. Lithofacies and Palaeogeography, 1996, 16(3):47-58.
[28] 刘和甫, 汪泽成, 熊保贤, 等. 中国中西部中、新生代前陆盆地与挤压造山带耦合分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(3):55-72.
LIU H F, WANG Z C, XIONG B X, et al. Coupling analysis of Mesozoic and Cenozoic foreland basins and compressional orogenic belts in central and western China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2000, 7(3):55-72.
[29] 张志斌, 曹德斌. 滇中楚雄中生代盆地的形成、演化及其与哀牢山造山带的关系——以楚雄西舍路至禄丰碧城镇区域地质综合剖面为例[J]. 地球学报, 2002 (2): 129-134.
ZHANG Z B, CAO D B.The formation and evolution of the Chuxiong Mesozoic basin in central Yunnan and its relationship with the Ailao Mountain Orogenic Belt: taking the regional geological comprehensive section from Xishe Road to Lufeng Bicheng Town in Chuxiong as an example[J]. Acta Geosciences, 2002 (2): 129 -134.
[30] 李儒峰, 马永生, 汤良杰, 等. 云南楚雄盆地波动特征及构造沉积演化[J]. 地球科学, 2002, 29(2):129-134.
LI R F, MA Y S, TANG L J, et al. Formation and evolution of the Chuxiong Mesozoic basin in central Yunnan and its relationship with the Ailao Mountain Orogenic Belt: Taking the regional geological comprehensive section from Xishe Road to Lufeng Bicheng Town in Chuxiong as an example[J]. Acta Geosciences, 2002, 29(2):129-134.
[31] 朱同兴, 黄志英, 尹福光. 盆山转换与沉积地质记录——以楚雄前陆盆地分析为例[J]. 岩相古地理, 1999, 19(3):1-15.
ZHU T X, HUANG Z Y, YIN F G. Basin-Mountain transition and sedimentary geological record: taking Chuxiong Foreland Basin as an example[J]. Lithofacies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(3):1-15.
[32] 江新胜. 中国白垩纪沙漠及其古气候[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2003.
JIANG X S. Cretaceous desert in China and its paleoclimate [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2003.
[33] 孙勇. 云南西北早白垩世环境与气候分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012.
SUN Y. Analysis of early Cretaceous environment and climate in Northwestern Yunnan [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012.
[34] 陈根文, 夏斌, 吴延之, 等. 楚雄盆地砂岩铜矿成矿机理研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30:169-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2000.02.009
CHEN G W, XIA B, WU Y Z, et al. Research on metallogenic mechanism of sandstone copper deposit in Chuxiong Basin[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2000, 30:169-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2000.02.009
[35] 顾知微. 记滇中几个晚白垩世淡水瓣鳃类化石并略回顾云南陆相白垩系的研究[J]. 古生物学报, 1962 (3): 287-311. GU Z W. A record of several Late Cretaceous freshwater palipes fossils in central Yunnan and a brief review of the research on the terrestrial Cretaceous in Yunnan[J]. Acta Paleontology, 1962 (3): 287-311.
[36] Gao L, Yang Z Y, Tong Y B , et al. New paleomagnetic studies of Cretaceous and Miocene rocks from Jinggu, western Yunnan, China: evidence for internal deformation of the Lanping-Simao Terrane. Journal of Geodynamics, 2015, 89: 39–59.
[37] 陈丽华, 缪昕, 魏宝和. 扫描电镜在石油地质上的应用[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1986.
CHEN L H, MIAO X, WEI B H. Application of scanning electron microscope in petroleum geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1986.
[38] Vos K. , Vandenberghe N, Elsen J. Surface textural analysis of quartz grains by scanning electron microscopy (SEM): From sample preparation to environmental interpretation[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 128:93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.10.013
[39] D. H Campbell. Percussion marks on quartz grains[J]. Sediment. Petrol, 1963, 33(4):855-859.
[40] Lancaster, Nicholas. The geomorphology of desert dunes [M]. Routledge; Macmillan Publishers NZ, Limited [Distributor], 1995.
[41] 谢又予. 中国石英砂表面结构特征图谱[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984.
XIE Y Y. Characteristic map of the surface structure of quartz sand in China[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1984.
[42] Higgs R. Quartz-grain surface features of mesozoic-cenozoic sands from the labrador and western greenland continental margins[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1979, 49(2):599-610.
[43] William Mahaney. Atlas of sand grain surface textures and applications [M]. USA, Oxford University Press, 2002.
[44] Reading, Harold G. Sedimentary environments and facies [M]. Cambridge University Press, 1978.
[45] Nagy B. , Nagy L A, Rigali M J, et al. Rock varnish in the sonoran desert: microbiologically mediated accumulation of manganiferous sediments[J]. Sedimentology, 2010, 38(6):1153-1171.
[46] Pye Kenneth. Aeolian sand and sand dunes [M]. Springer, 2009.
[47] L E Frostick, I Reid. Desert sediments: ancient and modern [M]. Geological Society, 1987.
[48] Thiagarajan N. , Lee C T A. Trace-element evidence for the origin of desert varnish by direct aqueous atmospheric deposition[J]. Earth and Planetary ence Letters, 2004, 224(1-2):131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.04.038
[49] Engel C. G, Sharp R P. Chemical data on desert varnish[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1958, 69(5):273-286.
[50] 陈涛. 末次冰消期以来柴达木盆地东部风成沉积记录的气候变化[D]. 西安: 中国科学院研究生院(地球环境研究所), 2015.
CHEN T. Climate change recorded by aeolian deposits in the eastern part of the Qaidam Basin since the last deglacial period [D]. Xi'an, : Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Earth Environment), 2015.
[51] 范庆斌, 叶玮, 陈渠. 江西南昌横岗“砂山”石英颗粒表面形态特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 2014(6):1170-1181.
FAN Q B, YE W, CHEN Q. Surface morphological characteristics of the “sand hills” quartz grains in Henggang, Nanchang, Jiangxi[J]. Arid Zone Geography, 2014(6):1170-1181.
[52] 张光威, 杨子赓. 南黄海第四纪时期古英砂表面结构特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996(3):37-47.
ZHANG G W, YANG Z G. Surface structure characteristics and environmental significance of ancient British sands in the South Yellow Sea during the Quaternary Period[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1996(3):37-47.
[53] David H. , Krinsley Jack Donahue. Environmental interpretation of sand grain surface textures by electron microscopy[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1968, 79(6):743-748. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1968)79[743:EIOSGS]2.0.CO;2
[54] 任明达, 缪昕. 石英砂表面的微结构——一种沉积环境标志[J]. 地质论评, 1984, 30(1):36-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1984.01.005
REN M D, MIU X. Microstructure on the surface of quartz sand——a sign of sedimentary environment[J]. Geological Review, 1984, 30(1):36-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1984.01.005
[55] Pittman E. Diagenesis of quartz in sandstones as revealed by scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1972, 42(3):507-519.
[56] Marzolf, J. Sand-grain frosting and quartz overgrowth examined by scanning electron microscopy: The Navajo sandstone (Jurassic (?)), Utah[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1976, 46(4):906-912.
[57] Wu Chihua, Liu Chenglin, Shen Lijian, et al. A Cretaceous desert-playa sedimentary system controlled the potash formation in Simao Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2017, 91(3):1143-1144. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13334
-




 下载:
下载: