Optimization of Arsenic Leaching From Lead Converter Ash by Response Surface Methodology
-
摘要:
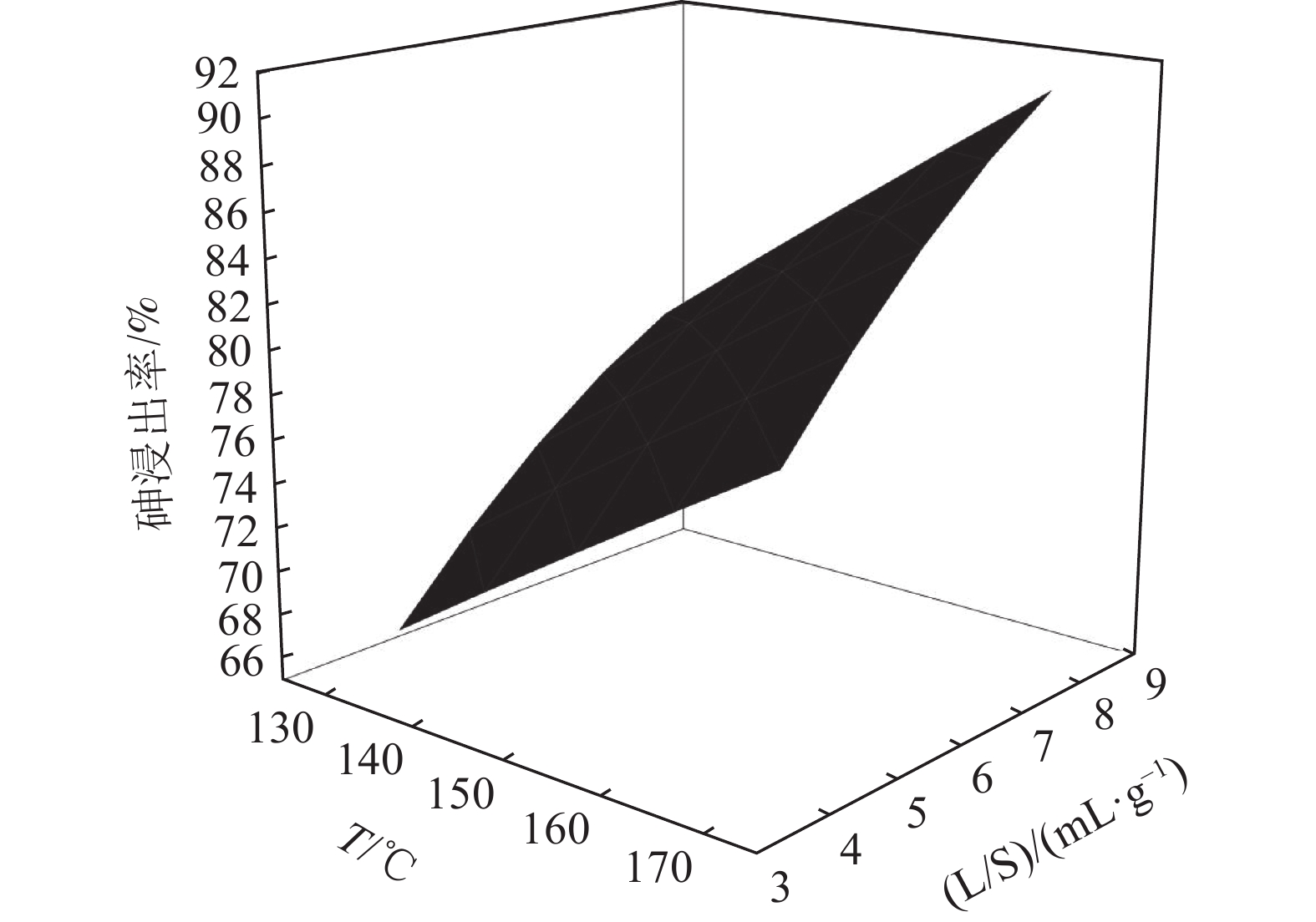
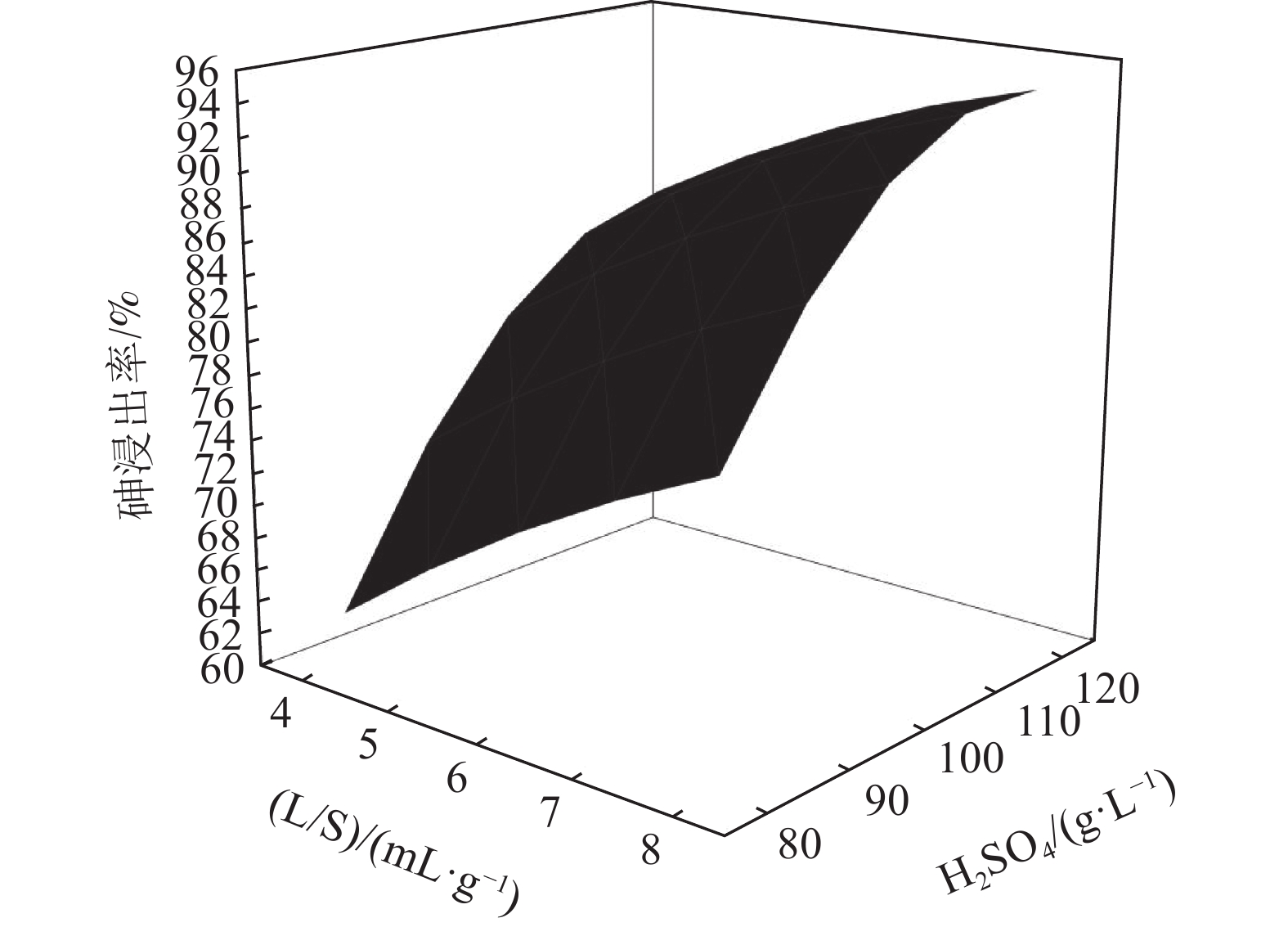
以硫酸为浸出介质,通过响应面方法和Box-Behnken设计(BBD)对浸出条件,包括酸浓度、液固比和温度进行优化。结果表明,酸浓度是最重要的因素,其次是温度和液固比。通过响应面优化,确定在酸浓度为116.77 g/L,液固比为8,温度为170℃的较佳工艺条件下,铜转炉灰中砷的提取率达到94.49%,说明响应面方法可以成功优化铅转炉砷灰的酸提取实验。
-
关键词:
- 响应曲面法 /
- 除砷 /
- 砷烟灰 /
- 酸浸 /
- Box-Behnken
Abstract:Sulfuric acid was used as the leaching medium, and the leaching conditions, including acid concentration, liquid-solid ratio and temperature, were optimized by response surface methodology and Box-Behnken design (BBD). The results showed that the acid concentration was the most important factor, followed by temperature and liquid-solid ratio. Through response surface optimization, the optimal process conditions were determined as follows: acid concentration of 116.77 g/L, liquid-solid ratio of 8, and temperature of 170℃. Under these conditions, the arsenic extraction rate of copper converter reached 94.49%, indicating that the acid extraction experiment of lead converter arsenic ash could be successfully optimized by response surface methodology.
-
Key words:
- Response surface methodology /
- Arsenic removal /
- Arsenic smelter /
- Acid leaching /
- Box-Behnken
-

-
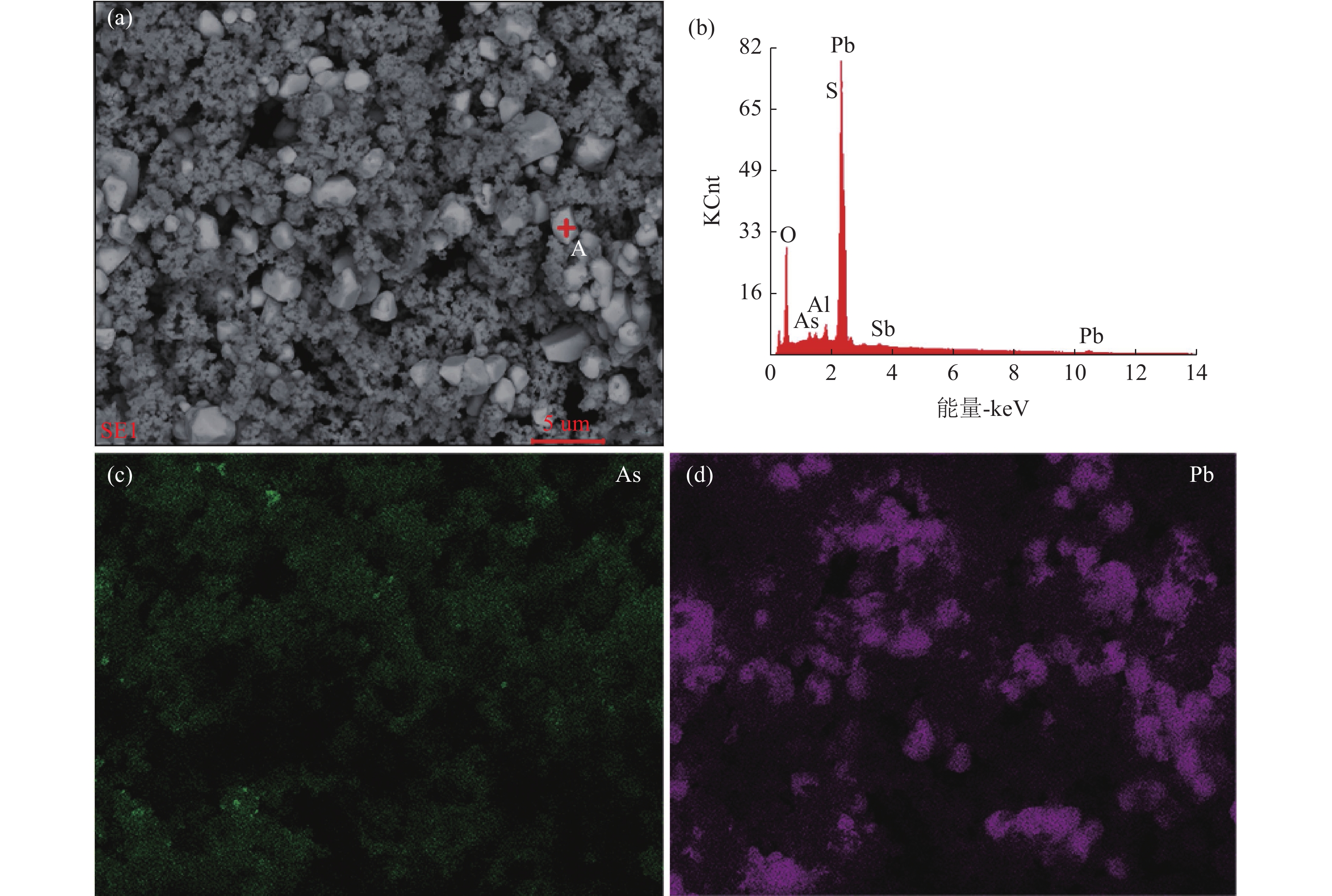
表 1 高砷铅冶炼粉尘的主要化学成分/%
Table 1. Main chemical composition of high arsenic lead smelting dust
As Pb Cd Sb S 34.20 11.10 6.63 7.36 3.28 表 2 酸浸响应曲面分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of acid leaching response surface
编号 因素 砷浸出率/% T/
℃(S/L)/
( g·mL-1)[H2SO4]/
( g·L-1)1 130 4 100 66.17 2 170 4 100 77.35 3 130 8 100 79.07 4 170 8 100 91.61 5 130 6 80 58.06 6 170 6 80 71.35 7 130 6 120 77.65 8 170 6 120 91.42 9 150 4 80 59.06 10 150 8 80 71.25 11 150 4 120 78.63 12 150 8 120 86.07 13 150 6 100 79.49 14 150 6 100 79.96 15 150 6 100 79.58 表 3 酸浸过程中各模型的回归系数
Table 3. Regression coefficients of each model during acid leaching
参数 DF Adj SS Adj MS F -value P -value 模型 9 0.137905 0.015323 63.65 0.000 线性 3 0.128149 0.042716 177.43 0.000 温度 1 0.032230 0.032230 133.87 0.000 液固比 1 0.027378 0.027378 113.72 0.000 酸度 1 0.068541 0.068541 284.70 0.000 平方 3 0.009142 0.003047 12.66 0.009 温度*温度 1 0.000006 0.000006 0.03 0.879 液固比*液固比 1 0.000366 0.000366 1.52 0.272 酸度*酸度 1 0.008969 0.008969 37.25 0.002 两种因素交互 3 0.000614 0.000205 0.85 0.523 温度*液固比 1 0.000046 0.000046 0.19 0.680 温度*酸度 1 0.000006 0.000006 0.02 0.882 液固比*酸度 1 0.000562 0.000562 2.34 0.187 误差 5 0.001204 0.000241 失拟 3 0.001192 0.000397 64.95 0.015 纯差
总计2
140.000012
0.1391090.000006 DF-自由度; adj SS-调整后的方差之和; adj MS-调整后的均方差 表 4 浸出渣主要元素化学成分/.%
Table 4. Chemical composition of main elements of leaching residue
As Pb Cd Sb 4.67 8.18 4.20 6.37 -
[1] H L Steven, J B Isabella, F Hamid, et al. A review of low-dose arsenic risks and human cancers[J]. Toxicology, 2021, 5(456):1-17.
[2] W Yan, Y Jianglong, W Zhihua, et al. A review on arsenic removal from coal combustion: Advances, challenges and opportunities[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 6(414):1-18.
[3] Wenjuan Zhang, Jianyong Che, Liu Xia, et al. Efficient removal and recovery of arsenic from copper smelting flue dust by a roasting method: process optimization, phase transformation and mechanism investigation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 6(412):1-13.
[4] Lei Zhang, Xueyi Guo, Qinghua Tian, et al. Selective removal of arsenic from high arsenic dust in the NaOH-S system and leaching behavior of lead, antimony, zinc and tin[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2021, 6(202):1-10.
[5] Erjun Zhang, Kanggen Zhou, Wei Chen, et al. Separation of As and Bi and enrichment of As, Cu, and Zn from copper dust using an oxidation-leaching approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 4(1):1-7.
[6] Yang Kang, Liu Wei, Zhang Tianfu, et al. Water leaching of arsenic trioxide from metallurgical dust with emphasis on its kinetics[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(9):2328-2339. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4177-5
[7] Liu Wei, Chang Huang, Junwei Han, et al. Removal and reuse of arsenic from arsenic-bearing purified residue by alkaline pressure oxidative leaching and reduction of As (V)[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2021(199):105541.
[8] 信晓飞, 张晋霞, 冯洪均. 响应曲面法优化含锌尘泥选择性浸出工艺[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):146-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.025
XIN X F, ZHANG J X, FENG H J. Optimization of selective leaching technology from zinc-bearing dust using response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):146-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.025
[9] 方楠, 吴健, 何强, 等. 响应面法优化铁尾矿砂对铜(II)的吸附条件[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.029
FANG N, WU J, HE Q, et al. Optimization of adsorption conditions of copper (II) on ferrous mill tailings by response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.029
[10] 周庆立, 白丽梅, 马玉新, 等. 响应曲面法优化振动磨磨矿工艺参数试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):203-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.032
ZHOU Q L, BAI L M, MA Y X, et al. Experimental study on optimization of vibration grinding parameters by response surface method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):203-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.032
[11] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 李松, 等. 响应曲面优化NH3-(NH4)3AC-H2O 体系浸出冶金废渣提锌工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.031
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Study on zinc extraction process of NH3-(NH4)3AC-H2O system by response surface optimization[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.031
[12] V Panwar, D K Sharma, K V Pradeep Kumar, et al. Experimental investigations and optimization of surface roughness in turning of en 36 alloy steel using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm[J]. Materials today: Proceedings, 2021, 4(19).
[13] Wei Liu, Wenhua Li, Junwei Han, et al. Preparation of calcium stannate from lead refining slag by alkaline leaching purification-causticization process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019(212): 119-125.
[14] C P Lawagon, G M Nisola, R A I Cuevas, et al. Li1−xNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Ag for electrochemical lithium recovery from brine and its optimized performance via response surface methodology[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 4(212):416-426.
-



 下载:
下载: