Effcet of Adding Methods on Neutralization Process for Copper Raffinate
-
摘要:
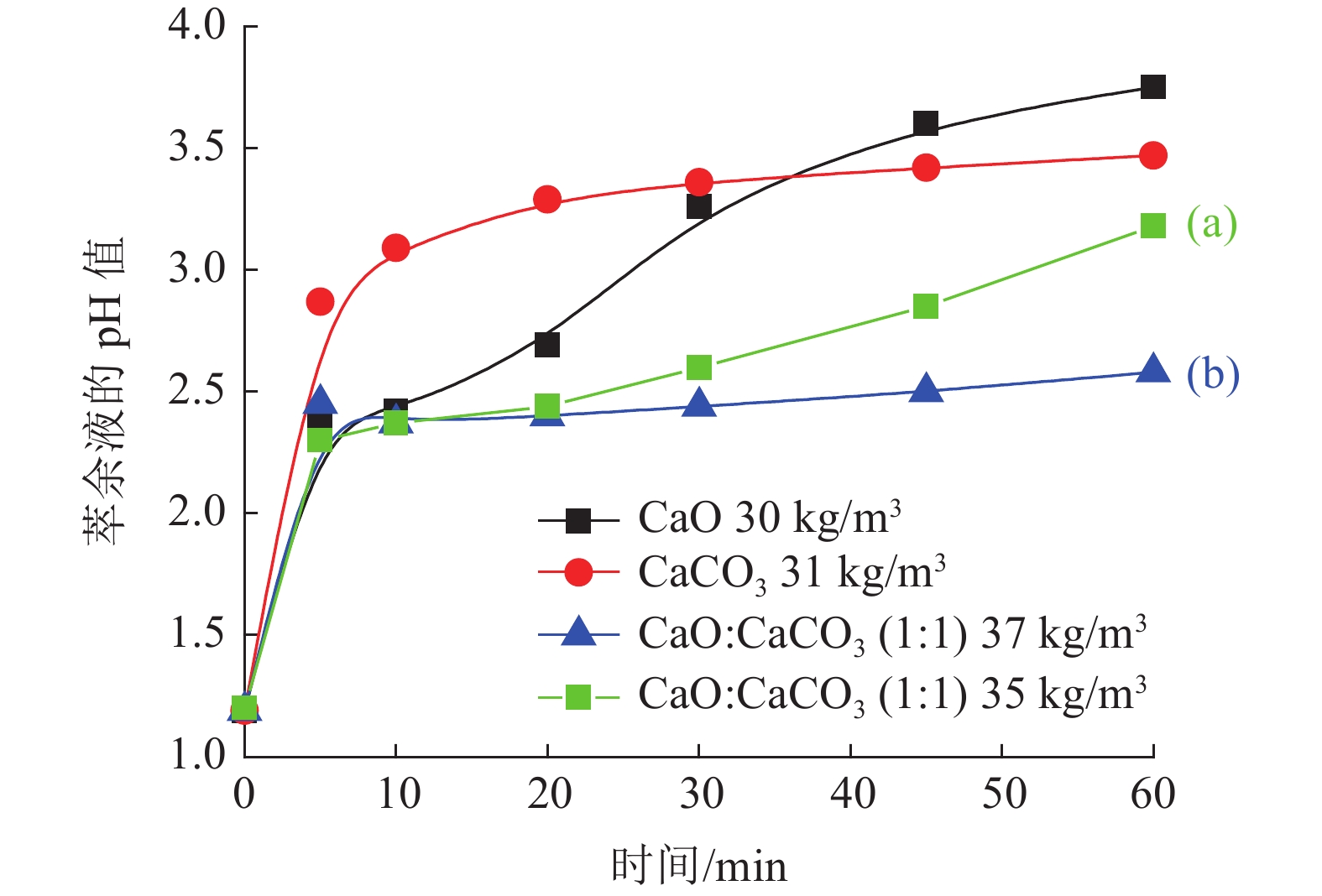
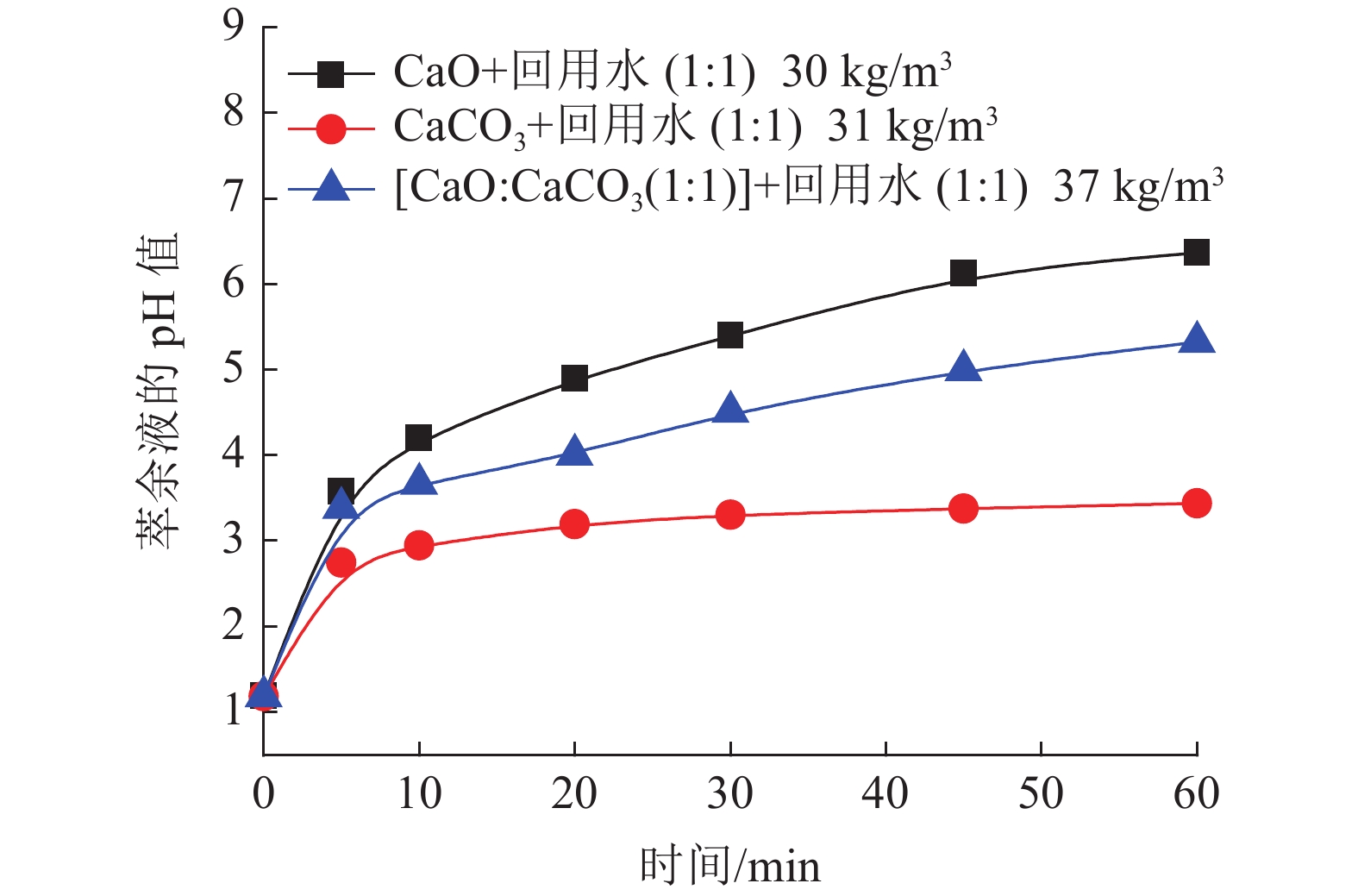
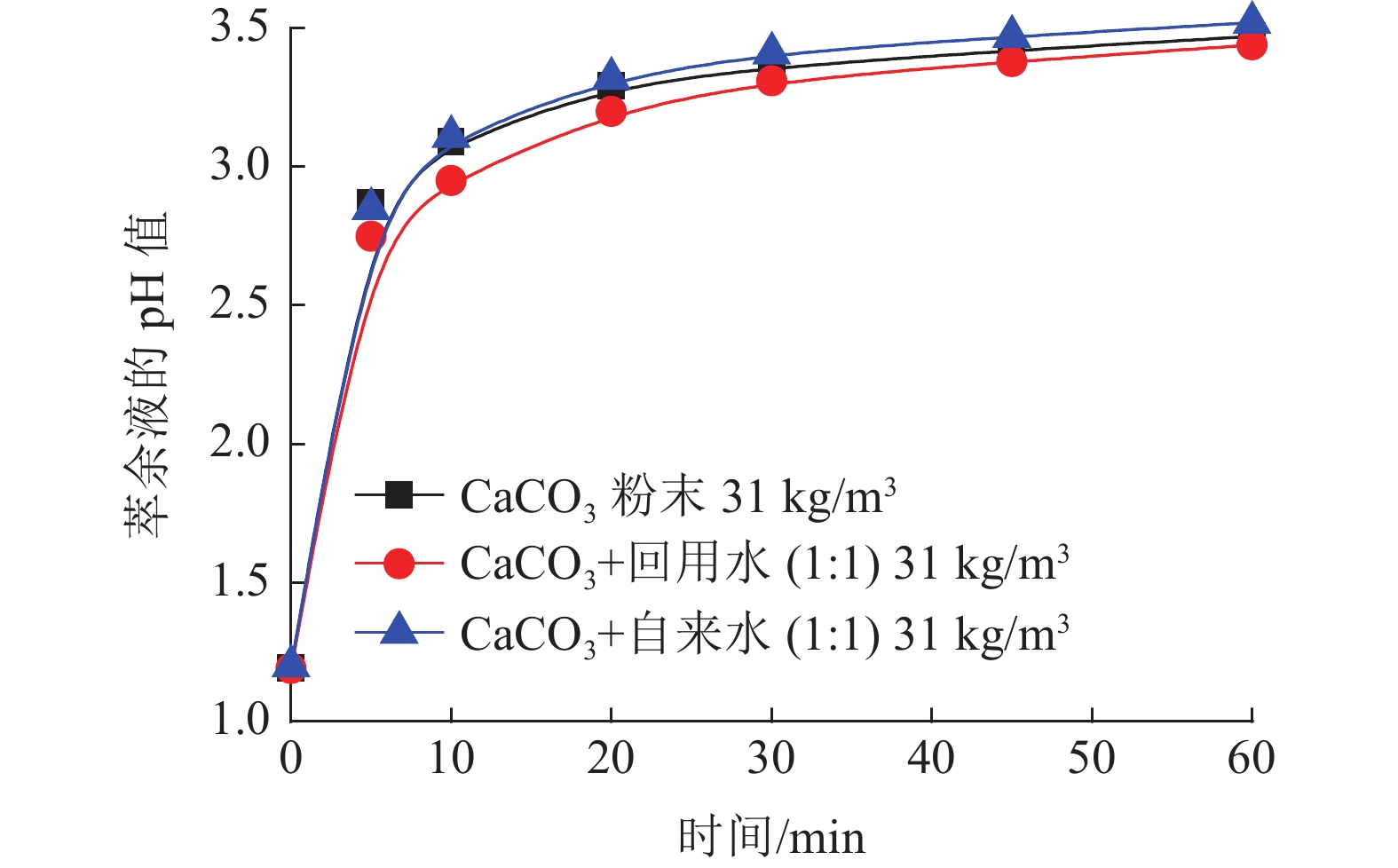
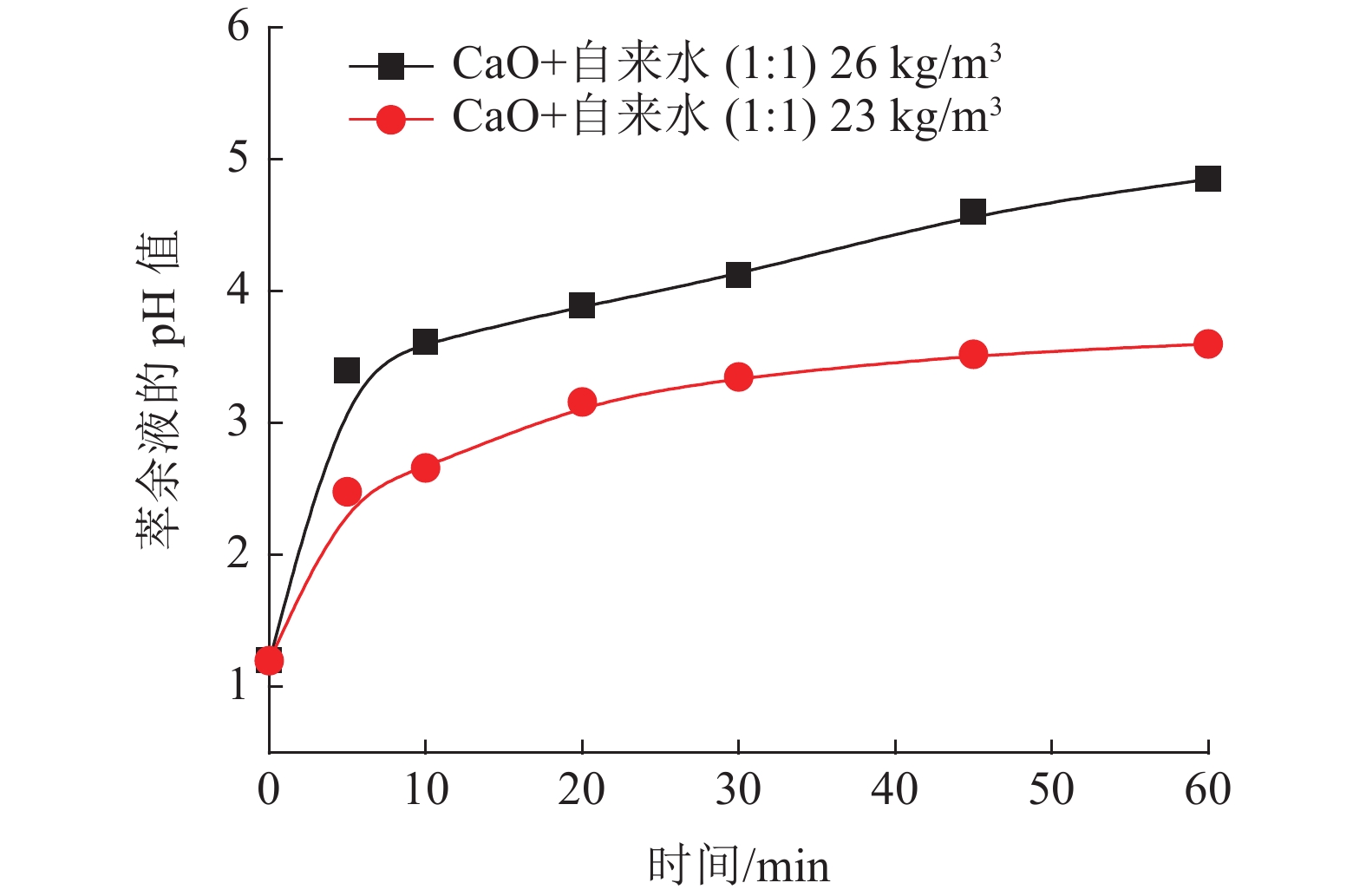
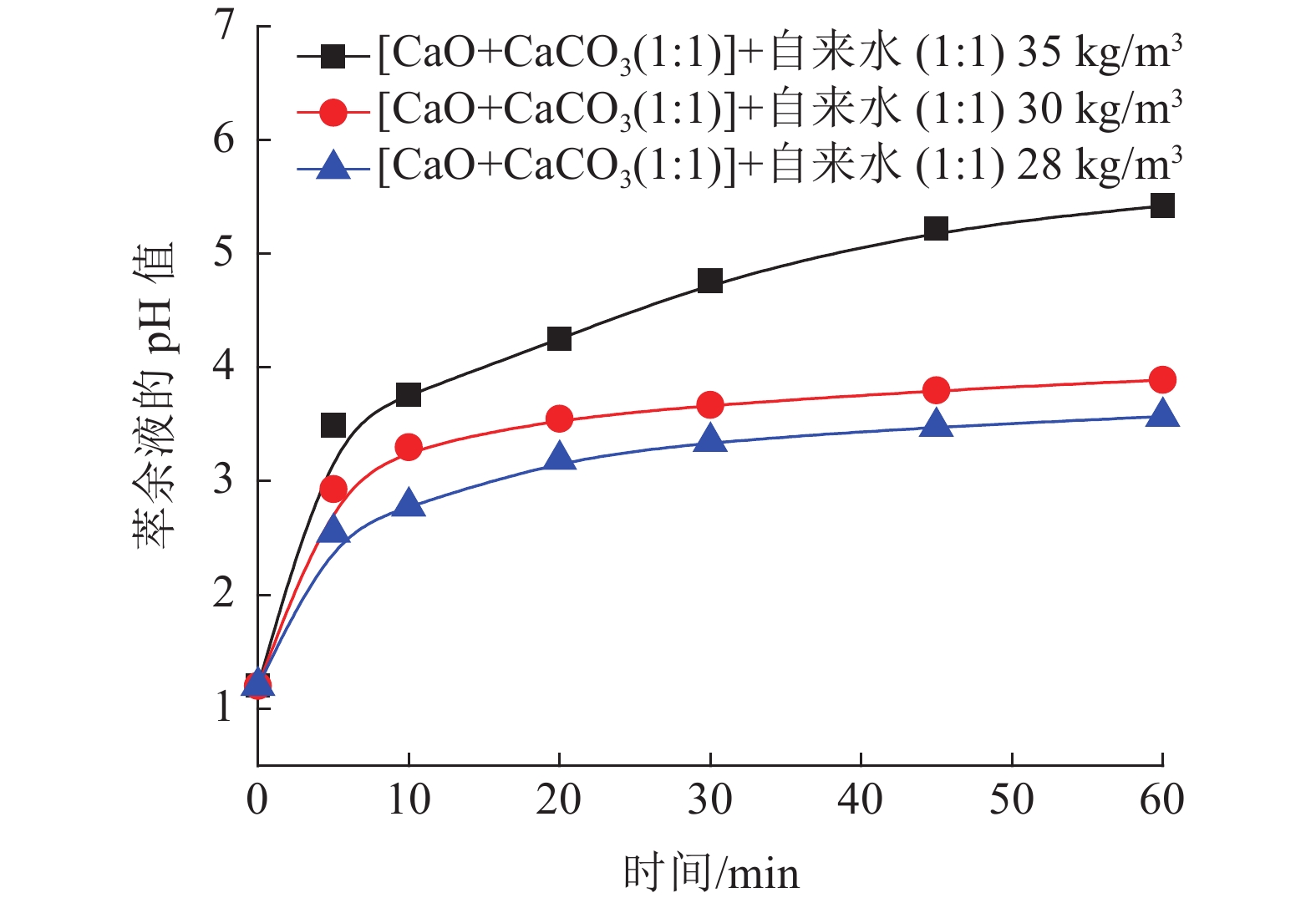
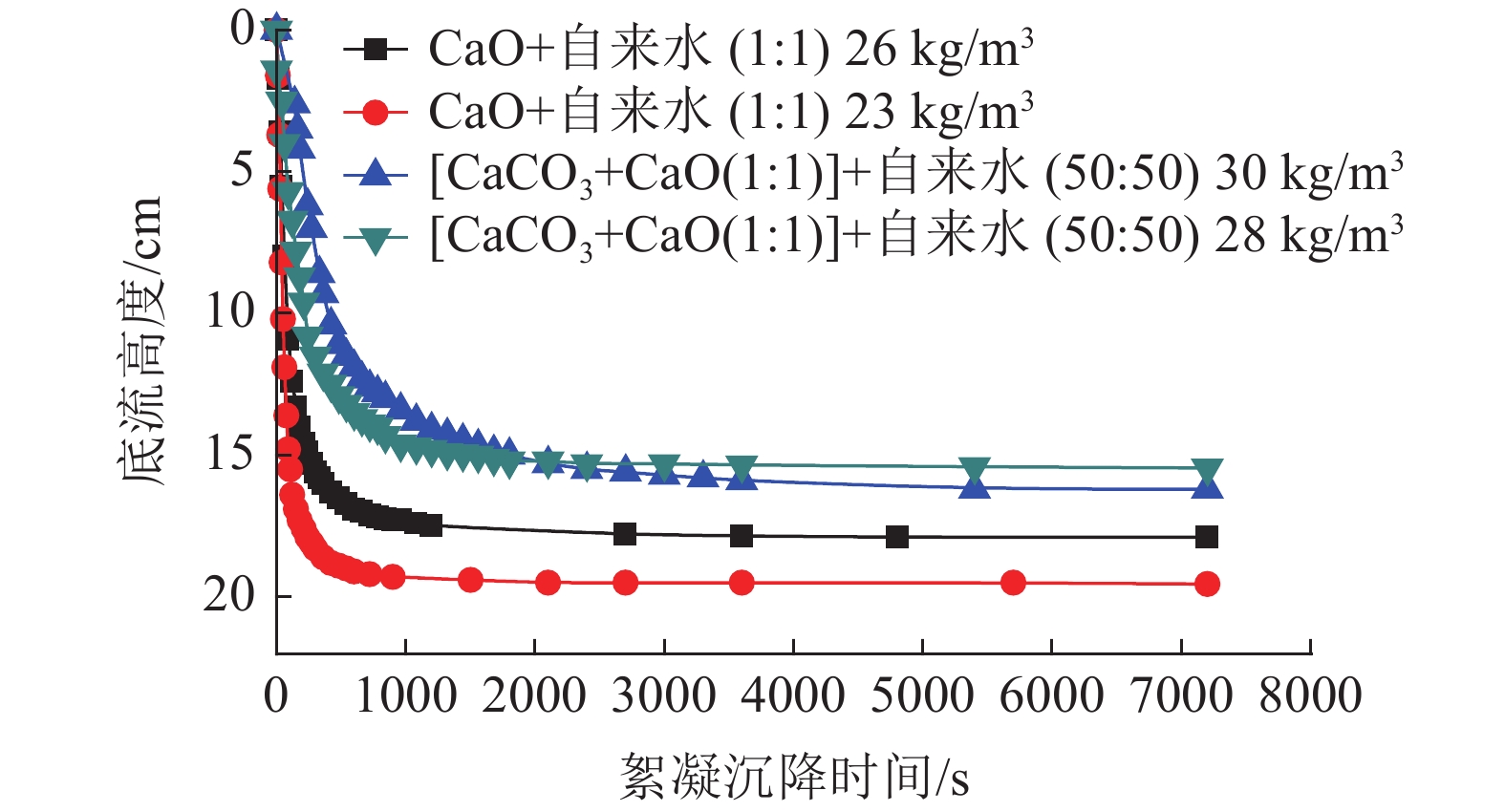
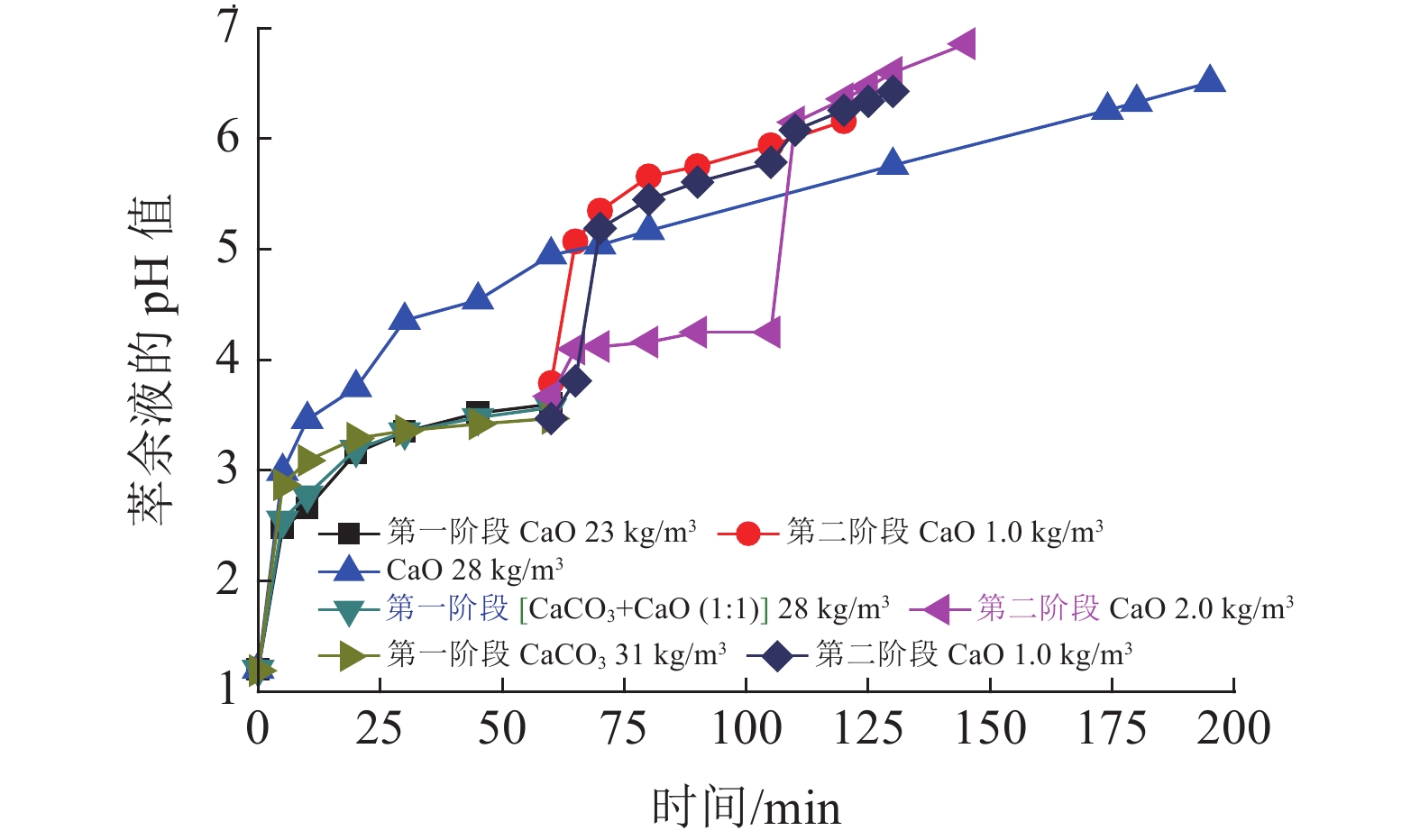
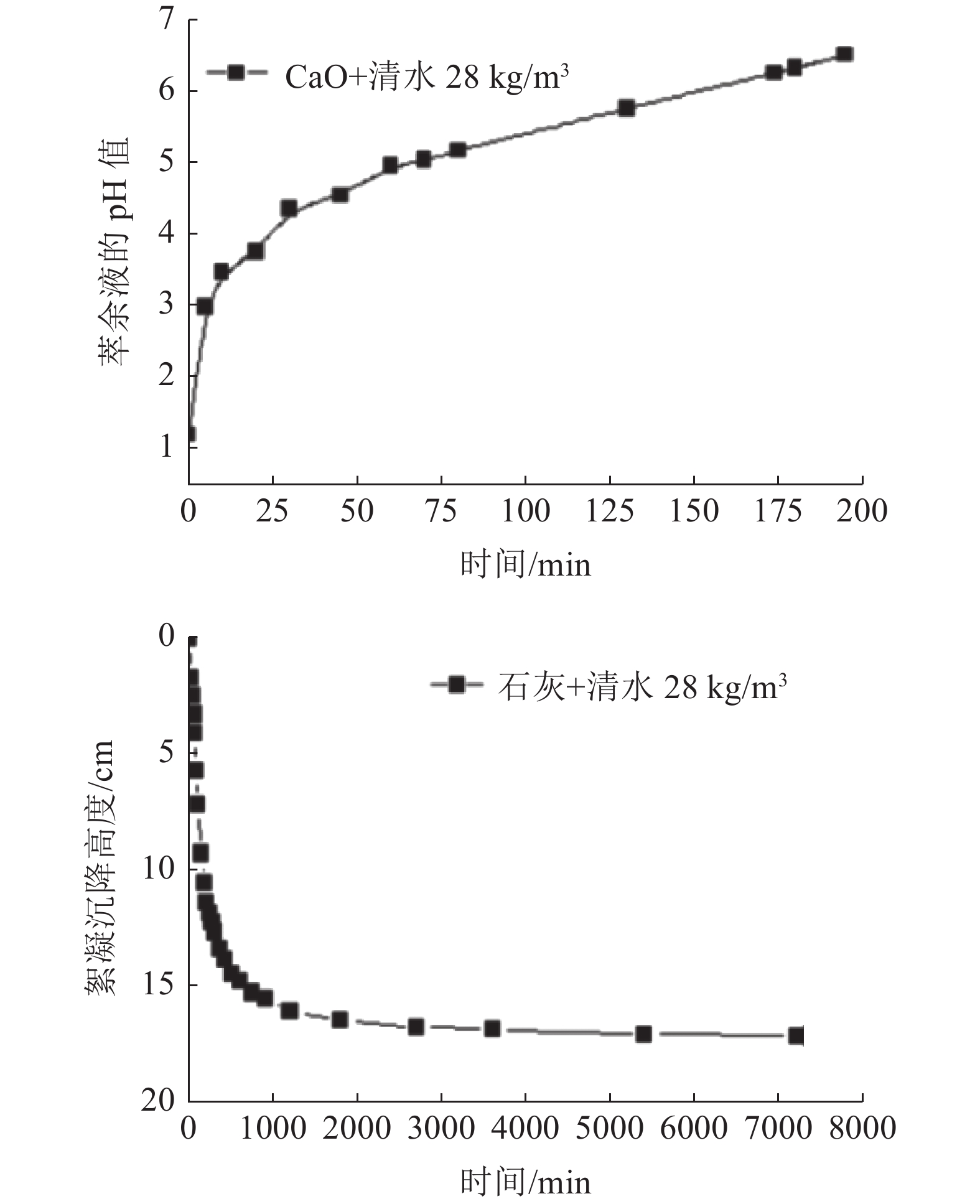
本文验证一段石灰中和工艺,通过调整加药方式、药剂混配、用水类型、加药次数等方式对铜萃余液的pH值的影响,初步对各种中和工艺下的中和渣产量及药剂成本进行分析。结果表明,湿法加药方式比干法的加药方法对铜萃余液的中和效果更好。与现有中和工艺比较,采用石灰乳分两段中和工艺具有药剂成本低和时间短特点,而石灰石-石灰两段中和工艺属于石灰石药剂耗量易控制,理论渣量较小,综合药剂成本较低。
Abstract:In this paper, one-step neutralization process using lime slurry stimulated in the on-site process was conducted as a reference. The adding method of reagent, mixing of reagents, the type of water, and times of adding reagent on the pH value of copper raffinate were investigated. Moreover, the production of neutral slag and cost evaluation of reagents under the condition of various neutralization processes were initially predicted. The test results showed that the wet addition method has better effect than that of the dry one in the neutral performance on the copper raffinate. Compared with one-step neutralization process, the two-step neutralization process using lime slurry has lower cost and shorter reaction time. While neutralization using limestone is used as the first step and the second step using lime slurry, the agent consumption of limestone is easy to control, the amount of slag is the least and the cost of the total reagents is the lowest one.
-

-
表 1 萃余液中主要元素含量/(mg·L-1)
Table 1. Content of main elements in raffinate
Fe3+* Zn2+ Cu2+ Al3+ Ca2+ Mn2+ SO42-* 7.42 170 95.5 955 29.4 26.08 35.74 *单位为g/t。 表 2 四种药剂对萃余液中和沉淀渣量的理论值
Table 2. Theoretical value of four agents for the amount of raffinate and sedimentation residue
列项 两段中和工艺 一段中和工艺 CaO-CaO CaCO3-CaO CaO+CaCO3-CaO CaO 第一段药剂用量/(kg·m-3) 23 31 28 28 第二段药剂用量/(kg·m-3) 1 1 2 0 最小理论干渣量/(kg·m-3) 67.204 63.374 63.343 76.541 最大理论干渣量/(kg·m-3) 74.086 67.490 73.162 84.315 干渣量中间值/(kg·m-3) 70.645 65.432 68.252 80.428 干渣重差值/(kg·m-3) 9.783 14.996 12.176 - 干渣量减少率/% 12.164 18.645 15.139 - 含水率按50%计 最小理论湿渣量/(kg·m-3) 134.408 126.748 126.686 153.082 最大理论湿渣量/(kg·m-3) 148.172 134.980 146.324 168.630 湿渣量中间值/(kg·m-3) 141.290 130.864 136.504 160.856 中间值的湿渣重差值/(kg·m-3) 19.566 29.992 24.352 - 湿渣量减少率/% 12.164 18.645 15.139 - 表 3 不同处理工艺的直接药剂费用对比
Table 3. Comparison of direct chemical costs of different treatment processes
项目 流程1 流程2 流程3 流程4 pH值 第一阶段用量/(kg·m-3) CaO CaCO3 CaO+CaCO3(1∶1,wt:wt) CaO pH1=~3.5 23 31 28 28 小结成本/ (元·m-3) 8.6112 4.31613 7.19082 10.4832 第二阶段用量/(kg·m-3) CaO CaO CaO - pH2=8~9 1.0 1.0 2.0 - 小结成本 / (元·m-3) 0.3744 0.3744 0.7488 - 总用量/(kg·m-3) 24 32 29 10.4832 药剂成本/ (元·m-3) 8.9856 4.6905 7.9396 10.4832 节约费用 /(元·吨-1) 1.4976 5.7927 2.5436 - 成本降低率/% 14.286 55.257 24.2636 - -
[1] 林斌. 某湿法提铜萃余液回收铜锌工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):172-176.
LIN B. Study on recovery of copper and zinc from the raffinate of copper hydrometallurgy[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):172-176.
[2] 马涌, 路殿坤, 金哲男, 等. P204萃取含铜酸性废水中铁的研究[J]. 有色金属, 2010(2):24-27.
MA Y, LU D K, JIN Z N, et al. Study on the extraction of iron from copper-containing acid wastewater with P204[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2010(2):24-27.
[3] 庄明龙. 硫化沉淀—石灰中和工艺处理矿山酸性废水[J]. 化工环保, 2011, 31(1):53-55.
ZHUANG M L. Sulfide precipitation-lime neutralization process for treatment of mine acid wastewater[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2011, 31(1):53-55.
[4] 张玉明, 张福元, 王社古, 等. 湿法炼铜萃余液有价金属综合回收试验研究[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2014(6):71-74.
ZHANG Y M, ZHANG F Y, WANG S G, et al. Experimental study on comprehensive recovery of valuable metals from copper hydrometallurgy raffinate[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2014(6):71-74.
[5] 薛光, 俎小凤. 萃余液预处理方法的试验研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2014, 22(1):92-91.
XUE G, ZU X F. Experimental study on the pretreatment method of raffinate[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 22(1):92-91.
[6] 郭金溢, 陈启斌, 季常青. 紫金山含铜酸性废水处理及综合回收有价金属试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2013(5):63-66+71.
GUO J Y, CHEN Q B, JI C Q. Experimental study on treatment of copper-bearing acid wastewater and comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in Zijin Mountain[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013(5):63-66+71.
[7] 沈青峰, 林国钦, 庄荣传, 等. 中和渣浆絮凝剂选型优化[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(3):108-112.
SHEN Q F, LIN G Q, ZHUANG R Z, et al. Optimization of flocculant selection for neutralization slurry[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(3):108-112.
[8] 杨群, 宁平, 陈芳媛, 等. 矿山酸性废水治理技术现状及进展[J]. 金属矿山, 2009, 391(1):131-134.
YANG Q, NING P, CHEN F Y, et al. Status and progress of mine acid wastewater treatment technology[J]. Metal Mine, 2009, 391(1):131-134.
-



 下载:
下载: