Geochemical Characteristics and Re-Os isotopic dating of Tongde Graphite Deposit, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
攀枝花同德石墨矿床位于扬子板块西缘增生带,本文对矿区矿石和赋矿围岩进行全岩地球化学分析、对矿石进行碳同位素测定、Re-Os同位素测年、对矿石及其赋矿岩石进行了原岩恢复并探讨了成矿环境。研究表明,矿石SiO2为55.65%~61.68%,SiO2/Al2O3比值为4.59~5.42,Ni/Co比值6.23~12.88,富集Ba、Rb、Sr等大离子亲石元素和Nb、Zr、Hf、Th、U等高场强元素。矿石的稀土元素总量ΣREE为149.13×10-6~195.37×10-6,具有弱的Ce负异常和Eu负异常,代表了缺氧的海相沉积环境。矿石中δ13CV-PDB值为-25.0‰~-23.5‰,位于生物成因的有机碳范围内,表明其成矿碳质主要来源于有机物。石墨的Re-Os同位素年龄为983±72 Ma(MSWD=1.7),时代归属为新元古代早期,早于同德周边岩浆岩侵入时代。Re的含量介于27.66×10-9~79.81×10-9,普通Os和187Os的含量分别为0.52×10-9~2.16×10-9、0.28×10-9~0.83×10-9,相对于Re、Os在地壳中的丰度显著富集。187Re/188Os比值为122.9~350.5,Os同位素初始比值187Os/188Os=0.31±0.21。结合野外地质调查对同德地区矿石和赋矿云母石英片岩进行原岩恢复,得出其原岩为沉积岩。
-
关键词:
- 石墨 /
- Re-Os同位素体系 /
- 地球化学特征 /
- 碳同位素 /
- 扬子西缘
Abstract:The Tongde Graphite Deposit in Panzhihua is located in the accretionary zone on the western margin of the Yangtze plate. In this paper, the whole rock geochemical analysis, C isotope determination and Re-Os isotope dating of the ore in Tongde graphite mining area are carried out, the original rock of the ore is restored, and the metallogenic environment is discussed. Research shows that the ore SiO2 is 55.65~61.68%, SiO2/Al2O3 ratio is 4.59~5.42, and Ni/Co ratio is 6.23~12.88. It is rich in Ba, Rb, Sr and other large ion lithophile elements and Nb, Zr, Hf, Th, U and other high field strength elements. Total rare earth elements of ore ΣREE is 149.13×10-6~195.37×10-6, with weak Ce negative anomaly and Eu negative anomaly, representing the anoxic marine sedimentary environment. The Carbon isotope δ13CV-PDB in ore is -25.0‰~-23.5‰, which is within the range of biogenic organic carbon, indicating that the ore-forming carbon mainly comes from organic matter. The Re-Os isotopic age of graphite is 983 ± 72 Ma (MSWD=1.7), belonging to the early Neoproterozoic, earlier than the intrusion age of magmatic rocks around Tongde. The content of re is between 27.66×10-9~79.81×10-9, the contents of ordinary Os and 187Os are 0.52 ×10-9~2.16×10-9, 0.28 × 10-9~0.83×10-9,respectively ,it is significantly enriched relative to the abundance of Re and Os in the crust. The 187re/188os ratio is 122.9~350.5, and the initial Os isotope ratio 187Os/188Os=0.31±0.21. Combined with the field geological survey, the original rock of ore and ore bearing mica quartz schist in Tongde area is restored, and it is concluded that the original rock is sedimentary rock.
-

-
图 1 (a)扬子地块西缘康滇地区地质示意图;(b)中国大陆主要构造单元示意图[8]
Figure 1.
图 2 攀枝花同德区域地质简图[9]
Figure 2.
图 5 (a)同德石墨矿矿石、白云母石英片岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图 (b)稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图[19]
Figure 5.
图 7 同德石墨矿和其他石墨矿石墨碳同位素特征对比[36]
Figure 7.
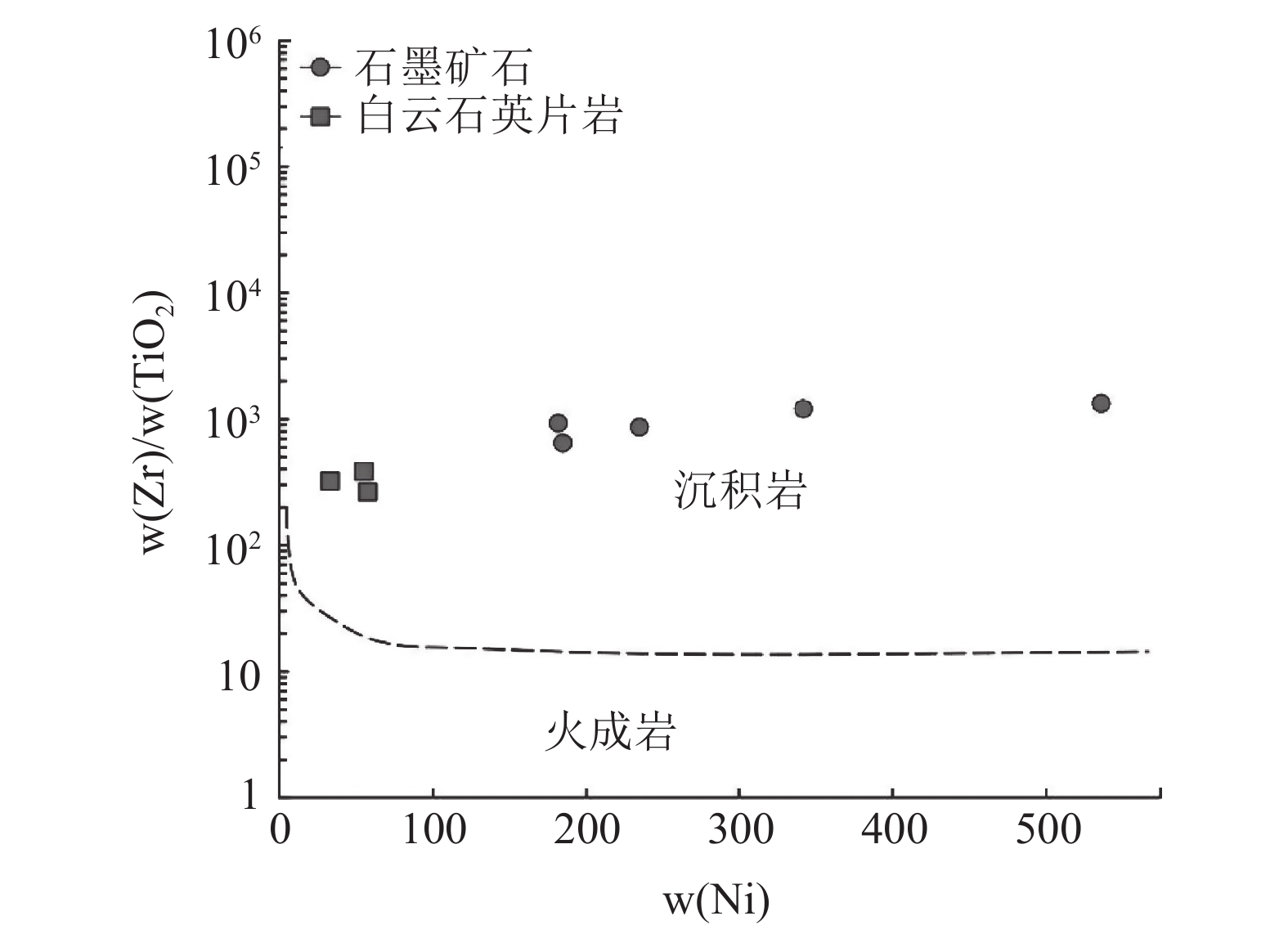
图 8 石墨矿石与白云石英片岩w(Zr)/w(TiO2)-w(Ni)[37]
Figure 8.
表 1 主量(%)、微量和稀土元素(×10-6)分析结果
Table 1. Whole-rock major elements(%),trace elements and REE data(×10-6) from graphite ore in Tongde Graphite Deposit
测试项目 石墨矿 云母石英片岩 TD-7 TD-8 TD-9 TD-10 TD-11 TD-15 TD-16 TD-17 SiO2 61.68 55.65 55.83 57.42 58.13 59.55 63.45 56.10 Al2O3 13.33 11.36 12.16 12.07 10.72 15.40 14.17 15.28 Fe2O3 3.61 2.71 3.58 3.97 3.55 2.09 1.12 1.69 FeO 2.51 2.68 2.05 2.43 1.80 3.94 5.11 5.87 CaO 2.69 6.98 3.57 5.45 4.43 7.83 4.04 4.45 MgO 2.54 2.48 1.19 1.33 0.64 2.98 3.52 4.22 K2O 2.22 1.57 1.78 2.29 1.91 1.32 1.83 1.87 Na2O 1.28 0.51 0.64 0.56 0.45 1.65 2.39 2.16 TiO2 0.37 0.43 0.21 0.30 0.23 0.68 0.63 0.97 P2O5 0.45 0.33 1.24 0.47 1.14 0.25 0.15 0.24 MnO 0.14 0.35 0.11 0.13 0.35 0.19 0.22 0.15 V2O5 0.06 0.05 0.10 0.07 0.23 0.02 0.02 0.03 Mn 0.11 0.27 0.08 0.10 0.27 0.15 0.17 0.12 烧失量 8.48 13.30 13.70 12.26 13.66 2.90 3.00 3.30 合计 99.47 98.67 96.24 98.85 97.51 98.96 99.82 96.46 固定碳 3.73 3.32 8.78 5.61 8.54 0.53 0.17 0.33 A/CNK 1.58 0.78 1.82 0.98 1.28 0.86 1.09 1.16 A/NK 2.96 4.48 4.08 3.55 3.82 3.72 2.40 2.74 SiO2/Al2O3 4.63 4.90 4.59 4.76 5.42 3.87 4.48 3.67 N2O+K2O 3.50 2.08 2.42 2.85 2.36 2.97 4.22 4.03 K2O/N2O 1.73 3.08 2.78 4.09 4.24 0.80 0.77 0.87 CaO/MgO 1.06 2.81 3.00 4.10 6.92 2.63 1.15 1.05 Rb 72.5 60.2 61.4 78.9 66.5 53.4 68.6 71.7 Ba 1200 1000 1700 1300 2400 630 740 670 Th 9.72 11.39 14.99 8.68 9.79 6.45 8.79 6.99 U 3.37 2.78 3.87 4.79 6.64 1.61 1.25 1.72 Nb 7.86 9.79 7.06 6.68 6.50 7.59 8.80 10.8 Ta 0.750 0.820 0.610 0.550 0.510 0.560 0.710 0.780 Sr 240 270 350 150 370 630 370 380 Zr 270 321 279 255 280 221 244 259 Hf 4.47 4.71 4.38 4.26 4.52 4.28 4.24 3.77 Cr 154 136 147 125 187 118 124 130 Co 32.2 29.7 31.2 28.9 41.6 24.3 22 27.2 Ni 235 185 342 182 536 33.3 55.4 57.9 Ni/Co 7.30 6.23 10.96 6.30 12.88 1.37 2.52 2.13 Rb/Sr 0.300 0.220 0.180 0.530 0.180 0.080 0.190 0.190 Sr/Ba 0.200 0.270 0.210 0.120 0.150 1.000 0.500 0.570 U/Th 0.350 0.240 0.260 0.550 0.680 0.250 0.140 0.250 La 31.9 35.0 48.4 34.5 45.0 26.5 23.3 28.1 Ce 52.3 58.1 75.8 55.8 60.9 44.0 35.4 49.9 Pr 7.35 7.77 10.72 7.81 9.57 6.13 5.19 6.64 Nd 30.9 32.7 45 32.4 40.1 25.8 22.1 28.8 Sm 6.24 6.71 9.14 6.54 7.99 5.3 4.64 6.11 Eu 1.34 1.47 2.27 1.46 1.89 1.68 1.26 1.68 Gd 5.62 6.48 8.36 5.93 7.95 4.81 4.42 5.54 Tb 0.88 1.06 1.26 0.96 1.26 0.78 0.74 0.88 Dy 5.10 6.40 7.06 5.62 7.90 4.72 4.55 5.16 Ho 1.05 1.38 1.41 1.18 1.74 0.99 1.01 1.08 Er 2.80 3.80 3.56 3.12 4.80 2.70 2.81 2.91 Tm 0.460 0.620 0.550 0.500 0.770 0.440 0.490 0.480 Yb 2.78 3.96 3.37 3.17 4.78 2.9 3.29 3.01 Lu 0.410 0.590 0.510 0.470 0.720 0.440 0.530 0.470 Y 36.7 49.4 52.9 41.2 73.9 31.9 32.4 33.7 ΣREE 149.13 166.04 217.41 159.46 195.37 127.19 109.73 140.76 LREE 130.0 141.8 191.3 138.5 165.5 109.4 91.9 121.2 HREE 19.1 24.29 26.08 20.95 29.92 17.78 17.84 19.53 LREE/HREE 6.81 5.84 7.34 6.61 5.53 6.15 5.15 6.21 (La/Yb)N 8.23 6.34 10.3 7.81 6.75 6.55 5.08 6.70 δEu 0.690 0.680 0.790 0.720 0.720 1.020 0.850 0.880 δCe 0.840 0.860 0.820 0.830 0.720 0.850 0.790 0.900 表 2 同德石墨矿石墨矿石Re-Os同位素数据
Table 2. Re-Os isotope data of graphite from Tongde graphite deposit
样品编号 样品质量(g) Re/(ng·g-1) 普Os/(ng·g-1) 187Re/(ng·g-1) 187Os(ng·g-1) 187Re/188Os 187Os/188Os 模式年龄/Ma 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ 测定值 1σ TD-1 0.5049 79.81 0.36 1.49 0.16 49.96 0.23 0.834 0.014 252.7 7.6 4.372 0.034 993 17 TD-2 0.5256 51.92 0.68 2.16 0.47 32.50 0.43 0.567 0.070 112.9 3.4 2.103 0.015 1038 128 TD-3 0.4979 27.66 0.21 0.59 0.03 17.31 0.13 0.278 0.008 222.5 6.7 3.913 0.057 958 28 TD-4 0.5038 52.60 0.71 1.49 0.13 32.92 0.44 0.599 0.055 166.4 5.0 3.101 0.032 1081 98 TD-5 0.5167 52.80 0.79 1.65 0.18 33.06 0.49 0.588 0.019 150.2 4.5 2.949 0.025 1058 33 TD-6 0.5079 38.85 0.52 0.52 0.03 24.32 0.32 0.410 0.018 350.5 10.5 6.048 0.047 1003 43 表 3 同德石墨矿与同类型矿床碳同位素对比
Table 3. Carbon isotope correlation between Tongde graphite deposit and the same type deposits
矿区 编号 岩矿名称 δ13CV-PDB/‰ 同德 TDC-3 片岩型石墨 -24.9 TDC-4 -24.8 TDC-5 -25.0 TDC-6 -23.5 中坝[21] ZB-01 含晶质石墨大理岩 -27.64 ZB-05 晶质石墨片岩 -28.22 ZB-06 -28.44 ZB-07 -28.41 ZB-08 -28.01 大河坝[22] 1 石墨片岩 -21.4 2 -19.5 3 -19.9 4 -19.5 5 含石墨大理岩 -19.0 南江坪河[23] 1 石墨矿 -24.5 2 -22.0 3 大理岩 0.60 4 1.50 鸡西柳毛[24] 1 石墨片岩 -21.4 2 -19.9 3 -32.1 4 -20.7 5 -21.3 6 -24.4 7 -16.8 8 -18.9 9 -17.5 山东南墅[25] 1 石墨矿 -21.2 2 -24.0 3 白云质大理岩 0.80 4 1.50 -
[1] 高照国, 刘红召, 杨卉芃, 等. 世界石墨资源分布概况及供求变化趋势[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(3):26-29. GAO Z G, LIU H Z, YANG H P, et al. General distribution and demand-supply tendency for worldwide graphite resources[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(3):26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.03.004
[2] 李超, 王登红, 赵鸿, 等, 中国石墨矿成矿规律概要[J]. 矿床地质, 2015(6): 1223-1236.
LI C, WANG D H, ZHAO H, et al. Minerogenetic regularity of graphite deposits in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(6): 1223-1236.
[3] 黎广, 马源. 自然电位法在四川攀枝花晶质石墨找矿中的应用[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2019(A1):93-95. LI G, MA Y. Application of spontaneous potential method in prospecting for crystalline graphite in Panzhihua, Sichuan[J]. China Non-metallic Minerals Industry, 2019(A1):93-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2019.z1.017
[4] 冯锋, 王光洪, 彭召强, 等. 四川省攀枝花市仁和区新民石墨矿矿床成因及成矿规律探讨[J]. 四川地质学报, 2021, 41(2):226-230. FENG F, WANG G H, PENG Z Q, et al. Genesis and metallogeny of the Xinmin graphite deposit in Renhe District, Panzhihua, Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2021, 41(2):226-230.
[5] 罗改, 王全伟, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川省大地构造单元划分及其基本特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(4):633-647. LUO G, WANG Q W, QIN Y L, et al. Divisions and their basic characteristics of tectonic units in Sichuan Province[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2021, 41(4):633-647. doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2021.04002
[6] 刘益. 扬子地块西缘高家村杂岩体岩石成因与成矿潜力研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018: 1-119.
LIU Y. The petrogenesis and mineralization potential of Gaojiacun complex, in western maigin of the Yangtze Block, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018: 1-119.
[7] Du L L, Guo J H, Allen P N, et al. Implications for Rodinia reconstructions for the initiation of Neoproterozoic subductionat~860 Ma on the western margin of the Yangtze Block: Evidence from the Guandaoshan Pluton[J]. Lithos, 2014, 196-197:67-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.002
[8] Zhou M F, Yan D P, Kennedy A K, et al. SHRIMP U–Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Late Proterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196:51-67. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00595-7
[9] 纪相田等. 同德幅G47E008023-1/5万地质图说明书[DS]. 全国地质资料馆, 1999.
JI X T, et al. Tongde G47E008023-1/50000 geological map description[DS] National Geological Data Center, 1999.
[10] 路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 33(5):459-464. LU Y F. Geokit-ageochemical toolkit for microsoft excel[J]. Geochimica, 2004, 33(5):459-464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004
[11] QI L, ZHOU M F, GAO J F, et al. An improved Carius tube technique for determination of low concentrations of Re and Os in pyrites[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2010, 25(4):585-589. doi: 10.1039/b919016c
[12] Roser B P, Korsch R J. Geochemical characterization, evolution and source of a Mesozoic accretionary wedge: the Torlesse terrane, New Zealand[J]. Geological Magazine, 1999, 136:493-512. doi: 10.1017/S0016756899003003
[13] 史会娟. 辽宁省北镇市石墨矿地质地球化学特征及原岩恢复[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
SHI H J. Geoehemical fcaturcs and protolith Restoration of Beizhen City graphite mine in Liaoning Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing ), 2015.
[14] 蔡文春, 曾忠诚, 宋曙光, 等. 陕西商南湘河晶质石墨矿床地质特征与成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(3):220-232. CAI W C, ZENG Z C, SONG S G, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Xianghe crystalline graphite deposit in Shangnan County of Shaanxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(3):220-232.
[15] 柴广路, 李双应. 北淮阳东段佛子岭群变质岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(4):29-45. CAI G L, LI S Y. Geochemical characteristics and geological implications for the metamorphic rocks of Foziling Group in Eastern of North Huaiyang Tectonic Belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(4):29-45.
[16] 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999(2):63-66. YANG S Y, LI C X. Research Progress in REE Tracer for Sediment source[J]. Advances in earth science, 1999(2):63-66. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010
[17] 刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.
LIU Y J, CAO L M. An introduction to element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987.
[18] 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑东段纳赤台岩群变沉积岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3):489-500. CHEN Y X, PEI X Z, LI R B, et al. Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Meta-sedimentary Rocks from Naij Tal Group, Eastern Section of East Kunlun[J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(3):489-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.03.005
[19] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics in ocean basalt: Implication for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders A D, Norry M J (eDs. ), Magmatism in the Ocean Basins[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[20] Ludwig K. Isoplot /Ex, Version 3.0: A geochronological tool kit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2001:43.
[21] 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 肖克炎, 等. 四川省中坝晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6):1286-1294. XIA J S, SUN L, XIAO K Y, et al. Geochemical features and genesis snalysis of the Zhongba scaly graphite deposit in Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(6):1286-1294. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.06.14
[22] 段威, 唐文春, 黎龙昌, 等. 四川旺苍大河坝浅变质岩型石墨矿床地球化学特征与成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3):599-607. DUAN W, TANG W C, LI L C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of daheba epimetamorphic graphite deposit in Wangchang, Sichuan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(3):599-607.
[23] 马志鑫, 罗茂金, 刘喜停, 等. 四川南江坪河石墨矿炭质来源及成矿机制[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3):134-139. MA Z X, LUO M J, LIU X T, et al. Carbon source and metallogenic mechanism of Pinghe graphite deposit at Nanjiang, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3):134-139. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0318
[24] 李光辉, 黄永卫, 吴润堂, 等. 鸡西柳毛石墨矿碳质来源及铀、钒的富集机制[J]. 世界地质, 2008, 27(1):19-22. LI G H, HUANG Y W, WU R T, et al. Origin of carbon and concentration of uranium and vanadium from Liumao graphite formation in Jixi[J]. Global Geology, 2008, 27(1):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.01.004
[25] 于方, 魏绮英. 中国典型矿床[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1997.
YU F, WEI Q Y. Typical deposits in China[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1997
[26] Hannah J L, SteinHJ, ZimmermanA, et al. Precise 2004±9 Ma Re–Os age for Pechenga black shale: Comparison of sulfides and organic material[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70:A228.
[27] 李欣尉, 李超, 周利敏, 等. 贵州正安县奥陶系—志留系界线碳质泥岩Re-Os同位素精确厘定及其古环境反演[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2):251-261. LI X W, LI C, ZHOU L M, et al. Accurate determination of the age of the carbonaceous mudstone of the ordovician—silurian boundary in Zheng'an County, Guizhou Province by Re-Os isotope dating method and its application in Paleoenvironmental inversion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2):251-261. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310116
[28] Toma J, Creaser R A, Card C, et al. Re-Os systematics and chronology of graphite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022, 323:164-182. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2022.02.012
[29] 耿元生, 杨崇辉, 王新社, 等. 扬子地台西缘结晶基底的时代[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):429-441. GENG Y S, YANG C H, WANG X S, et al. Age of crystalline basement in Western Margin of Yangtze Terrane[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3):429-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.012
[30] 刘文中. 攀西元古代麻粒岩的地质年代学与下地壳折返运动轨迹[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2004.
LIU W Z. Geochronology of Proterozoic granulites and the lower crust exhumation in Panzhihua-Xichang region[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing university, 2004.
[31] 徐士进, 刘文中, 王汝成, 等. 攀西微古陆块的变质演化与地壳抬升史-中基性麻粒岩的Sm-Nd, (40)Ar/~(39)Ar和FT年龄证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2004, 47(8):689-703. XU S J, LIU W Z, WANG R C, et al. The history of crustal uplift and metamorphic evolution of Panzhihua-Xichang micropalaeoland, SW China: Constraints on Sm-Nd, 40Ar/39Ar and FT ages of granulit es[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2004, 47(8):689-703.
[32] Esser B K, Turekian Karl K. The osmium isotopic composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(13):3093-3104. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90296-9
[33] Hannah J L, Bekker A, Stein H J, et al. Primitive Os and 2316 Ma age for marine shale: implications for Paleoproterozoic glacial events and the rise of atmospheric oxygen[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 225(1-2):43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.06.013
[34] Ravizza G, Turekian K K. Application of the 187Re-187Os system to black shale geochronometry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53:3257-3262. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90105-1
[35] 龙涛. 黑龙江省鸡西市柳毛石墨矿床地球化学特征及其成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
LONG T. The geochemical characteristics and deposit genesis analysis of Liu Mao graphite deposit in Ji Xi County of Hei Long jiang Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
[36] 朱建江, 刘福来, 刘福兴, 等. 胶-辽-吉造山带辽河群石墨矿碳同位素特征及成因分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(2):599-618. ZHU J J, LIU F L, LIU F X, et al. Carbon isotope and genesis studies of graphite deposits in the Liaohe Group of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(2):599-618. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.02.17
[37] 王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等. 变质岩原岩图解判别法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986.
WANG R M, HE G P, CHEN Z Z, et al. Graphic discrimination of metamorphic rocks[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986.
[38] 林治家, 陈多福, 刘芊. 海相沉积氧化还原环境的地球化学识别指标[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(1):72-80. LIN Z J, CHEN D F, LIU Q. Geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments[J]. Bulletinof Mineralogy, Petrologyand Geochemistey, 2008, 27(1):72-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.01.012
[39] 王益友, 郭文莹, 张国栋. 几种地球化学标志在金湖凹陷阜宁群沉积环境中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 1979(2):54-63. WANG Y Y, GUO W Y, ZHANG G D. Application of some geochemical indicators in determining of sedimentary environment of the Funing Group(Paleogene), Jin-Hu Depression, Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 1979(2):54-63.
[40] 朱维光. 扬子地块西缘新元古代镁铁质-超镁铁质岩的地球化学特征及其地质背景-以盐边高家村杂岩体和冷水箐101号杂岩体为例[D]. 广州: 中国科学院地球化学研究所, 2004.
ZHU W G. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of Neoproterozoic mafic-ultramafic rocks in western margin of the Yangtze Carton-exampled by the complex and Lengshuiqing No. 101 complex[D]. Guangzhou: Institute of geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004: 1-135.
-




 下载:
下载: