Study on Low Rank Coal Flotation Enhancement by Carboxylic Acid Collector Prepared from Gutter Oil
-
摘要:
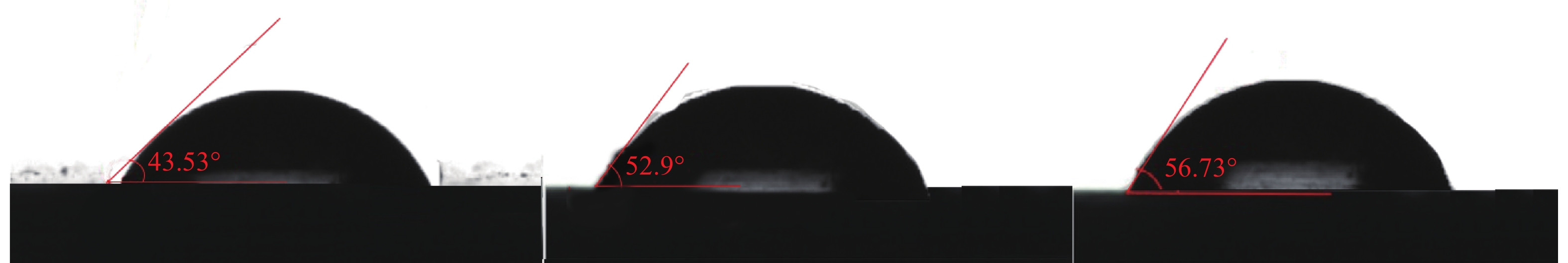
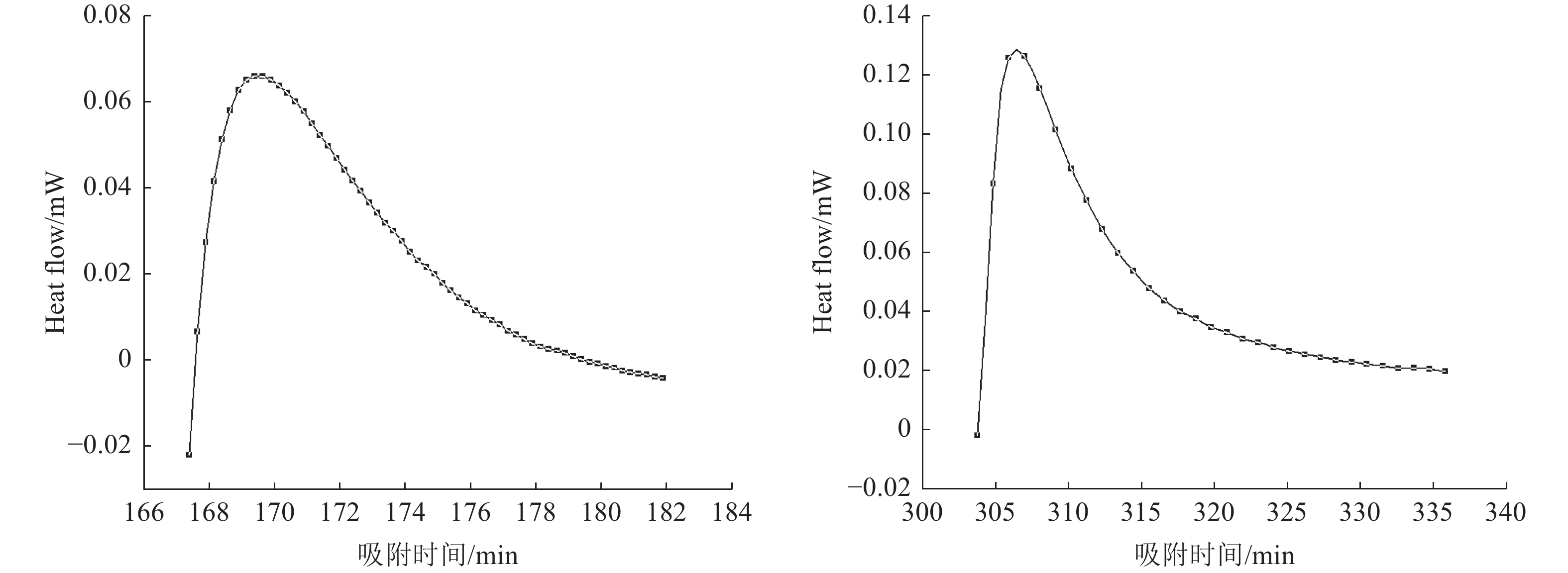
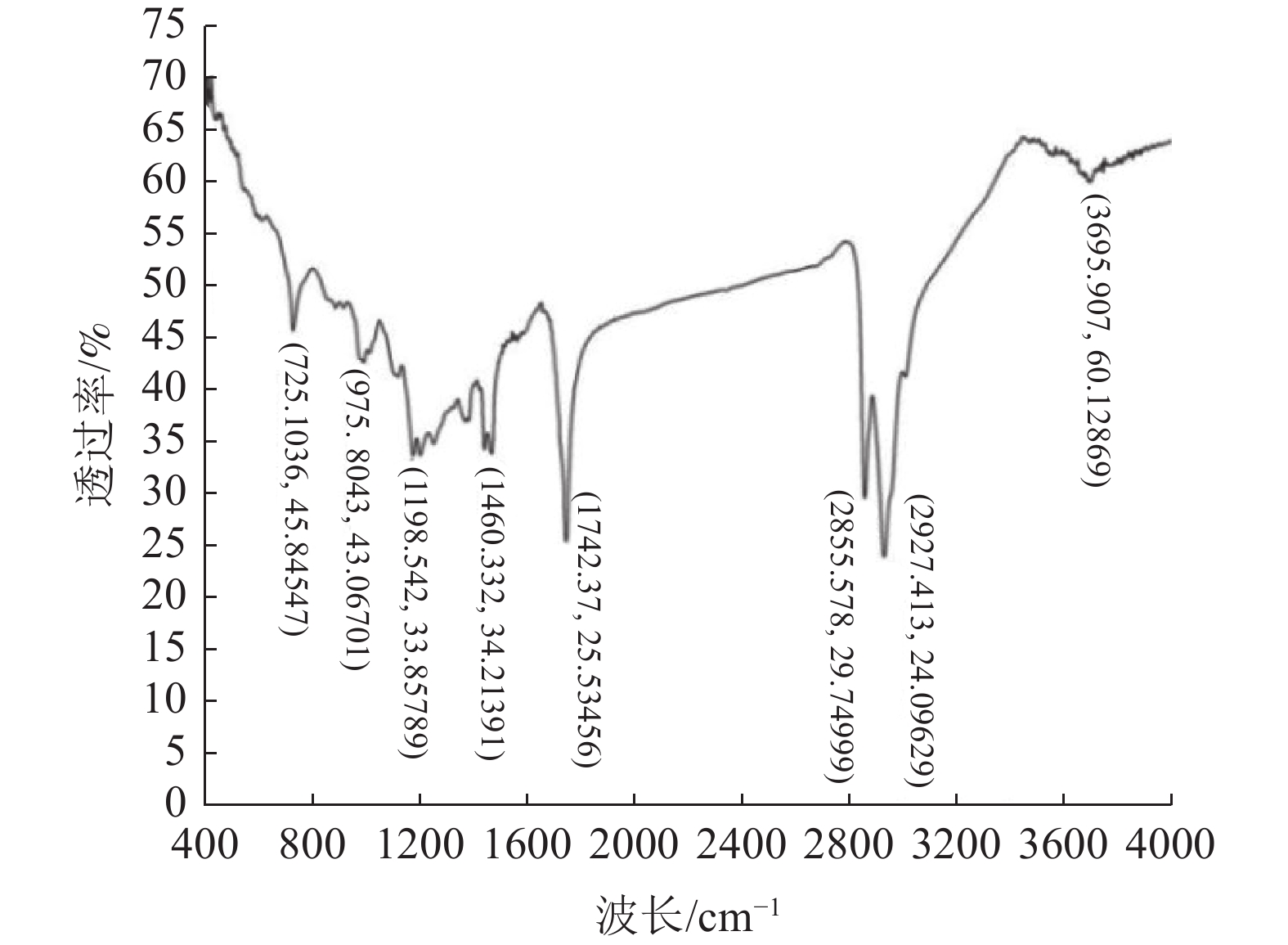
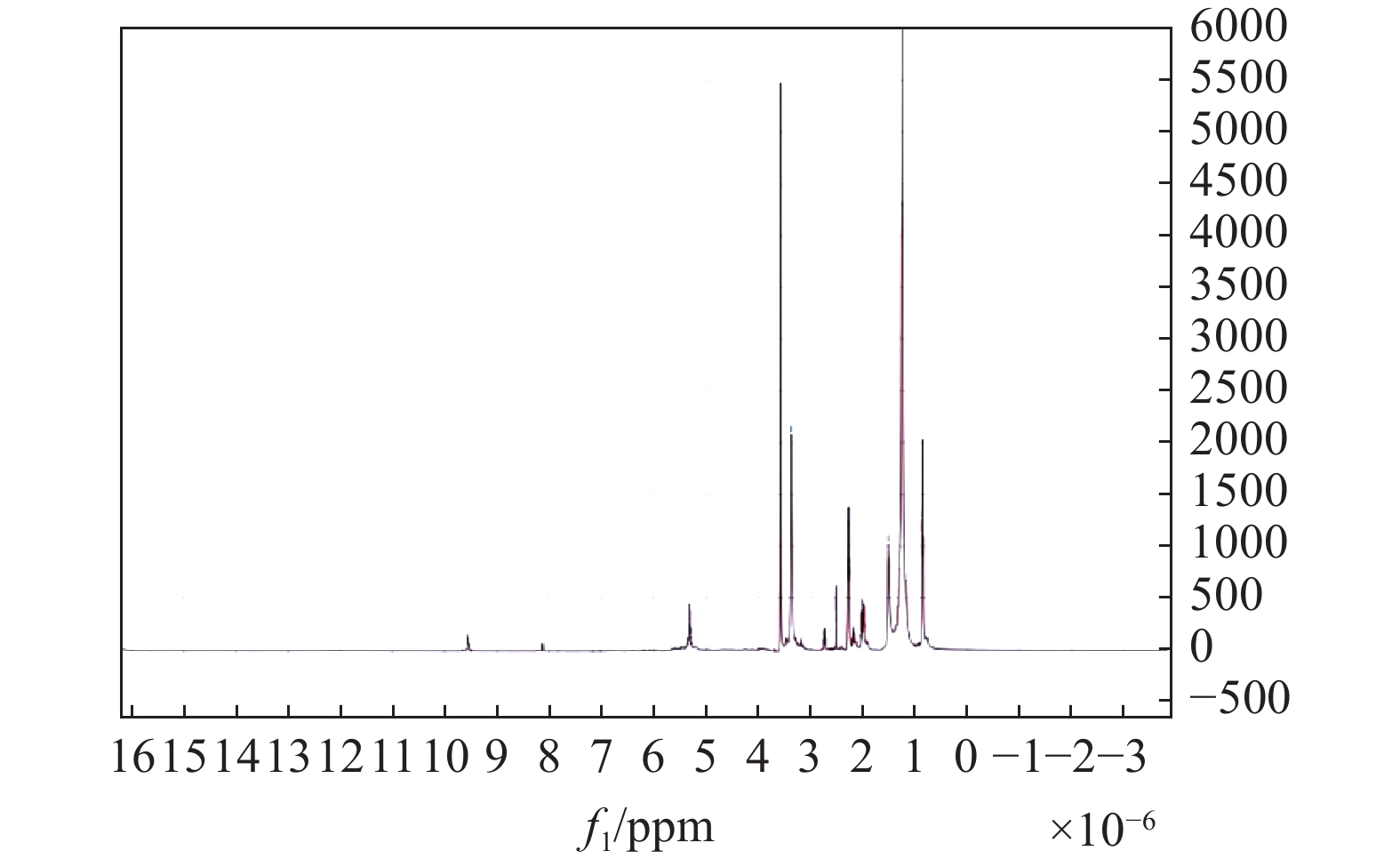
由于低阶煤表面含氧官能团的存在,用传统的非极性油捕收剂无法实现低阶煤泥的有效回收。与使用传统柴油捕收剂对比,本文在地沟油醇解为生物柴油的基础上进一步合成含有羧酸官能团的捕收剂来强化低阶煤浮选。通过红外光谱分析、核磁氢谱分析、X射线光电子能谱分析和接触角测定进一步分析了捕收剂促进浮选的机理。分别使用羧酸捕收剂、0#柴油与生物柴油对某低阶极难浮选煤样进行浮选实验,结果表明,羧酸捕收剂获得的浮选精煤效果最好,比柴油捕收剂,精煤产率提升了14.63%,灰分下降了12.06%。
Abstract:Traditional non-polar oil collectors cannot achieve high recovery of low-rank coal because of the presence ofoxygen-containing groups at coal surface. Compared with the traditional diesel collector, the collector containing carboxylic acid functional groups was further synthesized to enhance the flotation of low rank coal based on the alcoholysis of waste oil into biodiesel. The mechanism of collector promoting flotation was further analyzed by infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic hydrogen spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and contact angle measurement. Carboxylic acid collector, 0# diesel oil and biodiesel were used to carry out flotation tests on a low-level extremely difficult coal sample. The results showed that the carboxylic acid collector had the best flotation effect on clean coal. Compared with diesel collector, the yield of clean coal increased by 14.63%, and the ash content decreased by 12.06%.
-

-
表 1 煤样筛析结果
Table 1. Sieve analysis results of coal sample
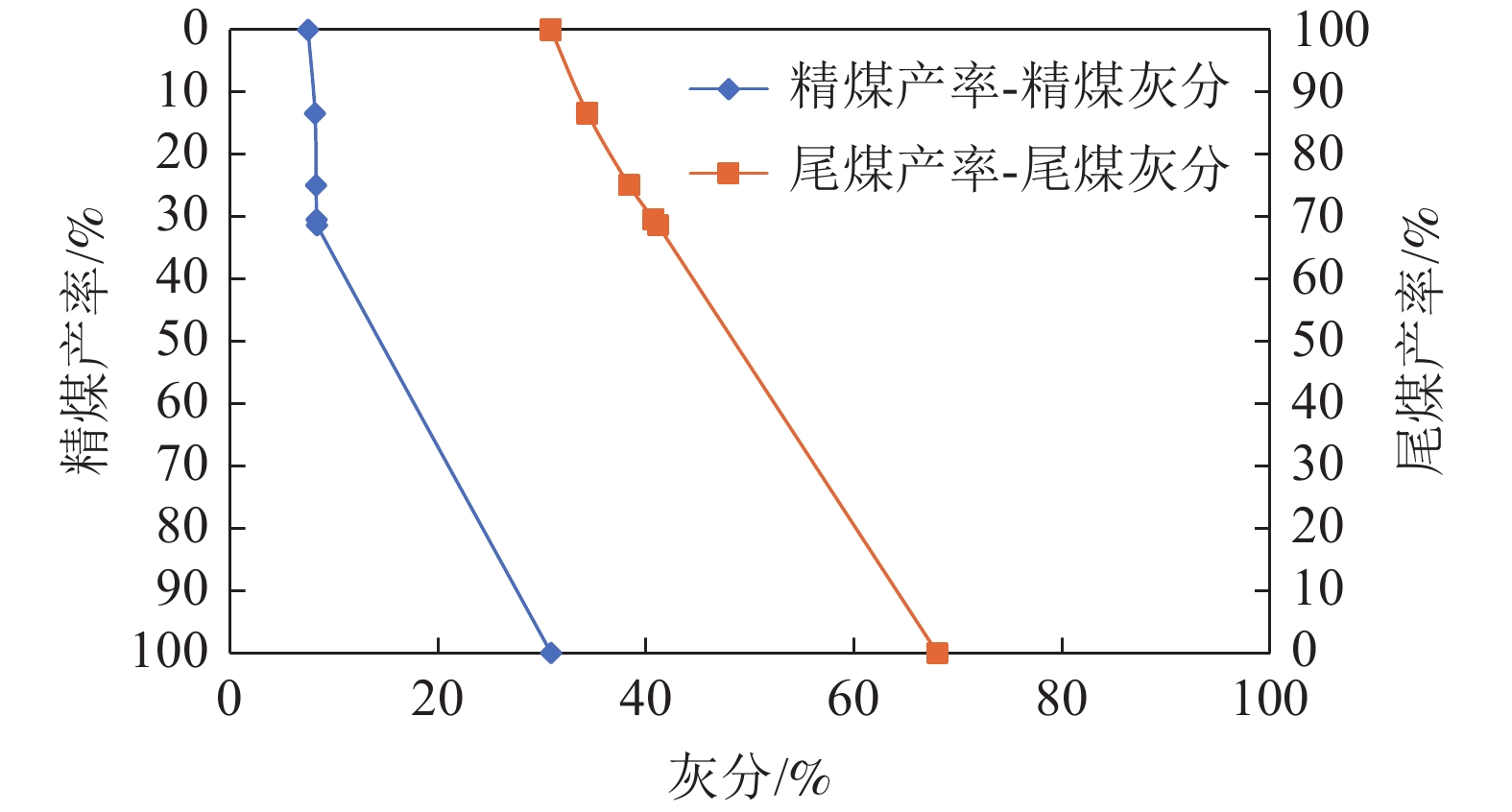
粒级/mm 产率/% 灰分/% 累计产率/% 累计灰分/% +0.250 25.19 15.75 25.19 15.75 -0.250+0.178 14.39 31.93 39.59 21.63 -0.178+0.124 17.06 43.42 56.65 28.19 -0.124+0.089 11.80 40.55 68.44 30.32 -0.089+0.074 6.48 37.35 74.93 30.93 -0.074 25.07 29.76 100.00 30.64 合计 100.00 30.64 —— —— 表 2 低阶煤煤样浮选速度实验结果
Table 2. Flotation velocity test results of low rank coal samples
产物 产率
/%灰分
/%精煤累计 尾煤累计 产率/% 灰分/% 产率/% 灰分/% 精煤1 14.00 8.17 14.00 8.17 100.00 31.42 精煤2 11.18 8.39 25.18 8.27 86.00 35.20 精煤3 3.60 8.55 28.78 8.30 74.82 39.21 精煤4 0.87 9.26 29.65 8.33 71.22 40.75 尾煤 70.35 41.14 100.00 31.42 70.35 41.14 合计 100.00 31.42 表 3 不同捕收剂浮选实验结果
Table 3. Flotation test results of different collectors
实验编号 捕收剂种类 起泡剂 捕收剂用量/ (kg·t-1) 药剂比 精煤 尾煤 产率/% 灰分/% 产率/% 灰分/% NO.1 0#柴油 仲辛醇 0.12 10︰1 8.27 23.67 91.73 30.08 NO.2 生物柴油 仲辛醇 0.12 10︰1 6.91 18.13 93.09 30.13 NO.3 羧酸捕收剂 仲辛醇 0.12 10︰1 22.90 11.61 77.10 34.23 -
[1] 商林萍, 石磊, 王艳. 青海某银矿浮选试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):62-64. SHANG L P, SHI L, WANG Y. Experimental study on flotation of a silver ore in Qinghai[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.013
[2] 黄秀兰, 普婧, 康娟雪, 等. 微波干燥软锰矿机理研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):194-198. HAUNG X L, PU J, KANG J X, et al. Mechanism of microwave drying pyrolusite[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):194-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.039
[3] Ahmed, Hussin AM, Drzymala, et al. Upgrading difficult-to-float coal using microemulsion[J]. Minerals & Metallurgical Processing, 2012, 29(2):88-96.
[4] 朱一民. 2019年浮选药剂的进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):1-17. ZHU Y M. Development of flotation reagent in 2019[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):1-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.001
[5] Gui Xiahui, Xing Yaowen, Wang Tingxia, et al. Intensification mechanism of oxidized coal flotation by using oxygen-containing collector α-furanacrylic acid[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 305:109-116. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.09.058
[6] 康永锋, 史华进, 赵子琦, 等. 超声波辅助潲水油直接酯交换法制备生物柴油[J]. 化工新型材料, 2014, 42(7):71-73. KANG Y F, SHI H J, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Preparation of biodiesel by ultrasonic-assisted direct transesterification of trapped oil[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2014, 42(7):71-73.
[7] 艾亚妮, 王介妮, 赵维娜, 等. 利用乙醇制备地沟油生物柴油的应用前景[J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(13):46-51. AI Y N, WANG J N, ZHAO W N, et al. Application prospect of preparation of waste oil biodiesel using ethanol[J]. Materials Review, 2014, 28(13):46-51. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2014.7A.009
[8] 李玉芹, 曾虹燕. 酯交换法制备生物柴油研究[J]. 湖南理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2005, 14(3):51-54. LI Y Q, ZENG H Y. Study on preparation of biodiesel by transesterification[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2005, 14(3):51-54.
[9] 康倩楠. 两渡氧化煤的表面性质及浮选机理研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2018.
KANG Q N. Surface properties and flotation mechanism of Liangdu oxidized coal[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018.
[10] 王海京, 杜泽学, 高国强. 近/超临界醇解制备生物柴油的研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2017(6):35-38. WANG H J, DU Z X, GAO G Q. Research on preparation of biodiesel by near/supercritical alcoholysis[J]. Petroleum Refining and Chemical Industry, 2017(6):35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2017.06.009
[11] 崔广文, 王京发, 王乐明, 等. 新型煤泥浮选自乳化捕收剂SEC的应用研究[J]. 选煤技术, 2014(3):6-8. CUI G W, WANG J F, WANG L M, et al. Application of a new type of slime float selected from emulsification collector SEC[J]. Coal Preparation Technology, 2014(3):6-8. doi: 10.16447/j.cnki.cpt.2014.03.005
[12] 孙乾予, 印万忠, 朱张磊, 等. 丁基钠黄药浮选斑铜矿的吸附热力学和动力学研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(4):121-126. SUN Q Y, YIN W Z, ZHU Z L, et al. Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of bornite by sodium butyl xanthate flotation[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 40(4):121-126. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2019.04.023
[13] Oepen B. Von, K Rdel W., Klein W. Sorption of nonpolar and polar compounds to soils: Processes, measurements and experience with the applicability of the modified OECD-Guideline 106[J]. Chemosphere, 1991, 22(3-4):285-304. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(91)90318-8
[14] 田全志. 含氧捕收剂在低阶煤浮选中的应用研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.
TIAN Q Z. Application of oxygen-containing collectors in low-rank coal flotation[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017.
[15] 郑云婷. 低阶煤表面性质研究与浮选药剂的筛选[D], 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.
ZHENG Y T. Research on surface properties of low-rank coal and screening of flotation reagents [D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017.
-



 下载:
下载: