Experimental Research on Influence Factors of Fine-grained Hematite Flotation Concentrate Based on Orthogonal Test
-
摘要:
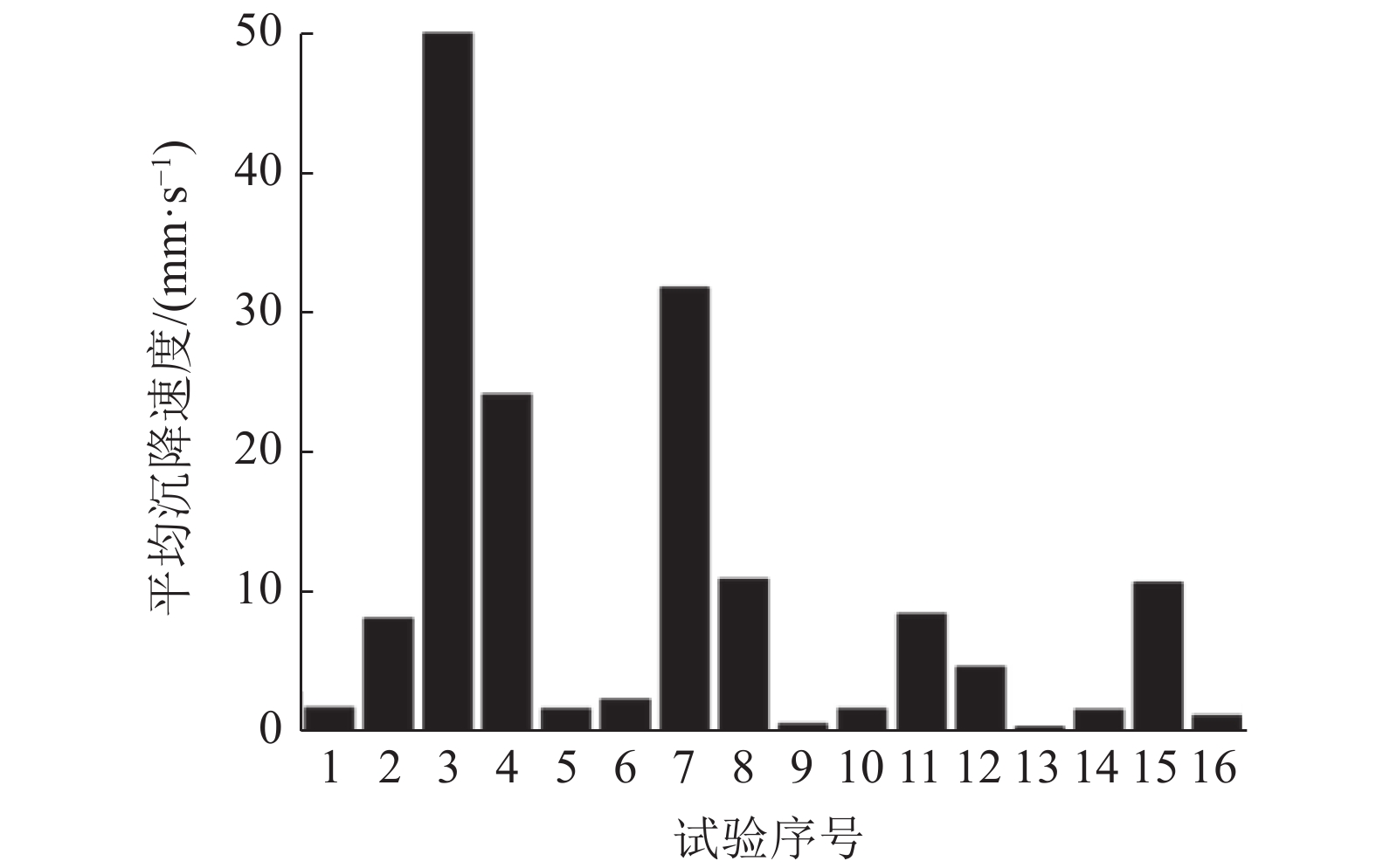
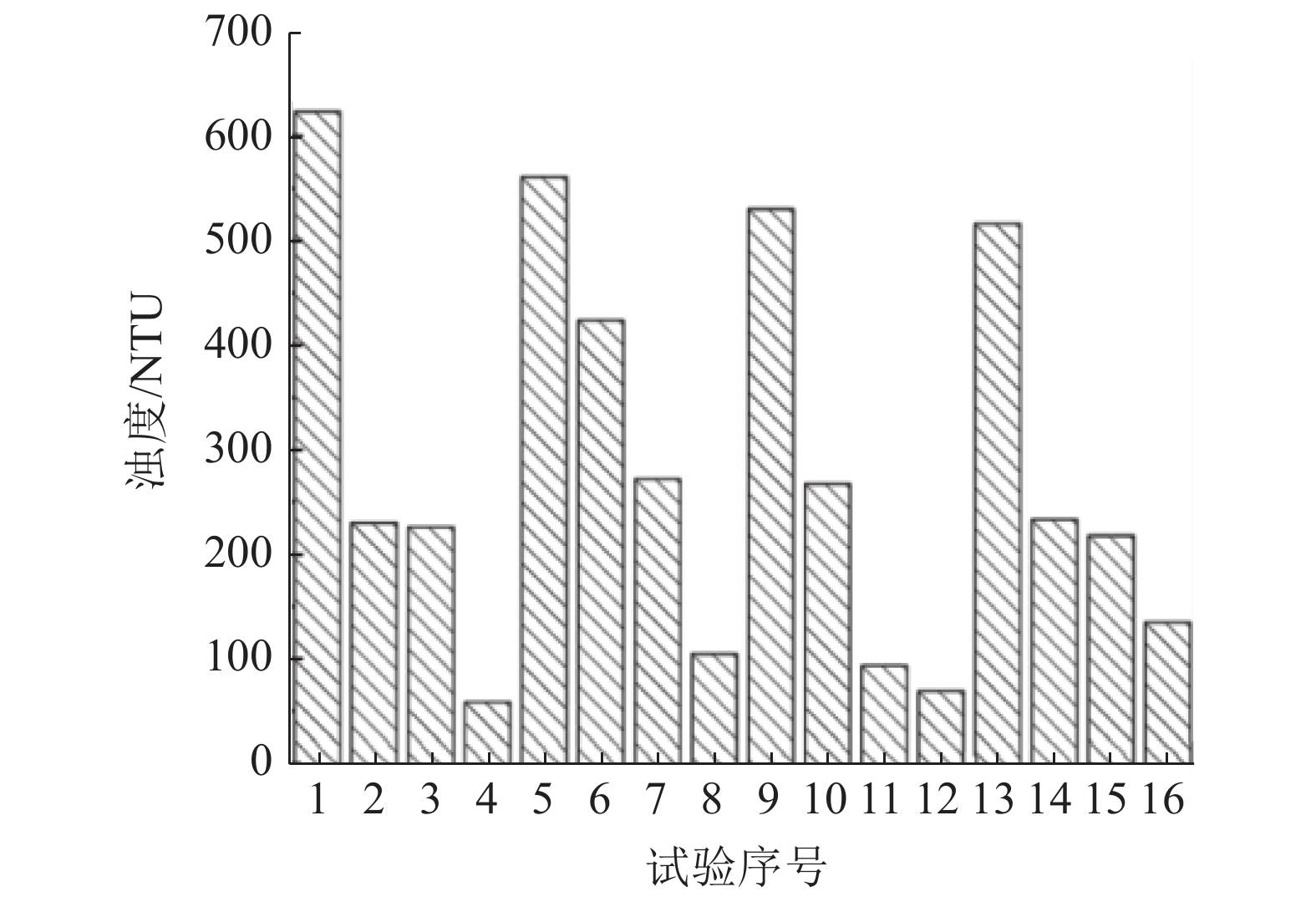
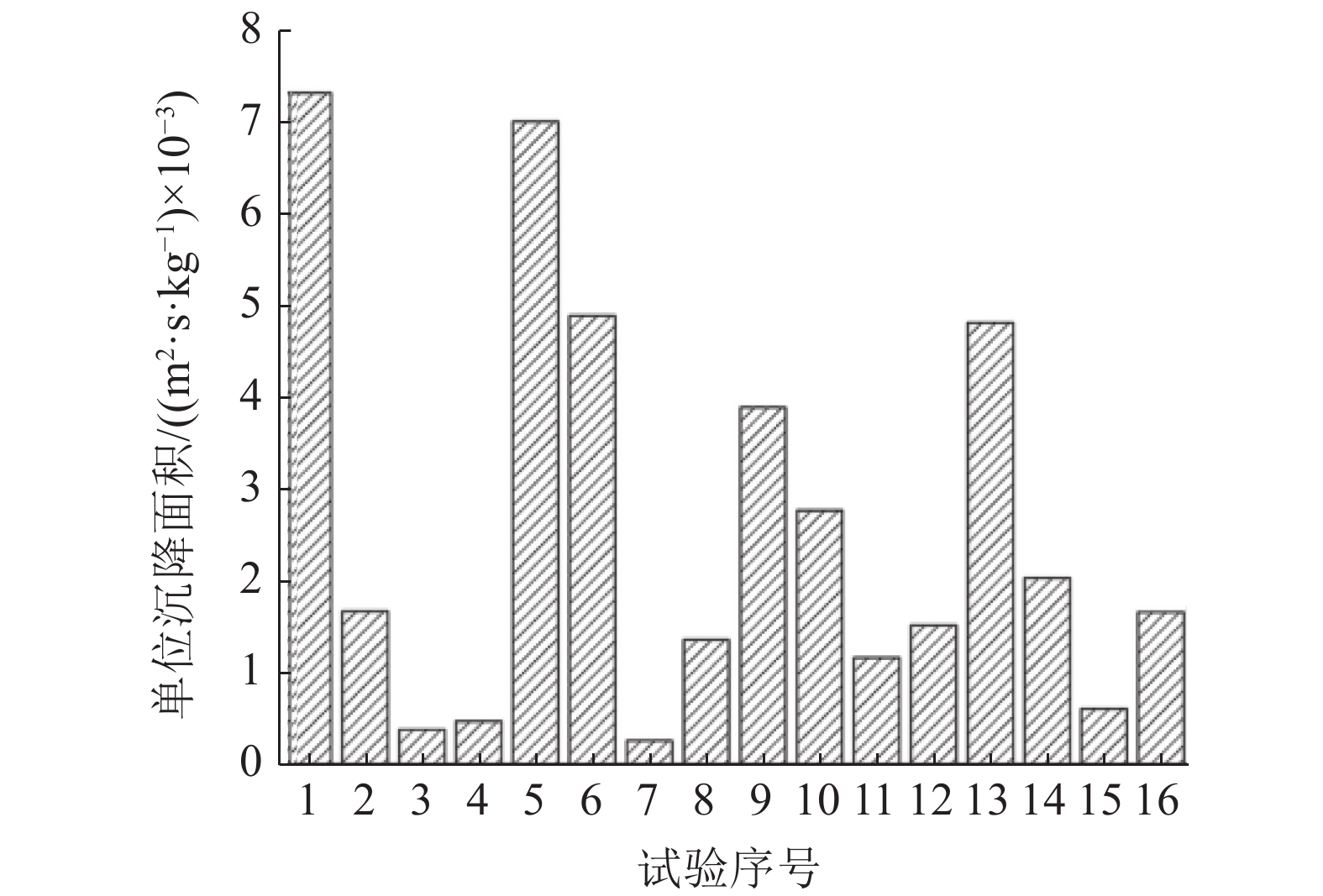
本文以细粒赤铁矿精矿作为研究对象,为探究铁精矿在实际生产浓密脱水阶段产生的浓密池溢流损失严重等问题,通过澄清层分界面平均沉降速度、上清液浊度和单位沉降面积等研究指标,考查细粒赤铁矿精矿的入料浓度、絮凝剂分子量、絮凝剂单耗、絮凝剂溶液浓度等因素对细粒赤铁矿精矿絮凝沉降的影响。设计正交实验探究细粒赤铁矿精矿絮凝沉降影响因素的实验研究。借助SPSS26统计软件对实验结果展开分析。研究结果表明:影响因素对平均沉降速度影响程度大小顺序为:絮凝剂单耗>絮凝剂溶液浓度>入料浓度>絮凝剂分子量;对上清液浊度影响程度大小顺序为:絮凝剂单耗>絮凝剂溶液浓度>入料浓度>絮凝剂分子量;对单位沉降面积影响程度大小顺序为:絮凝剂溶液浓度>入料浓度>絮凝剂单耗>絮凝剂分子量。综合考虑,在本实验中细粒赤铁矿精矿絮凝沉降效果较优条件为:絮凝剂分子量为1500万、入料浓度为10%、絮凝剂单耗为60 g/t、絮凝剂溶液浓度为0.10%。
Abstract:This paper takes the fine-grained hematite concentrate as the research object. In order to explore the serious overflow loss of the thickening tank in the actual production of thickening and dehydration, the average sedimentation velocity of the clarification layer interface, supernatant turbidity and the unit sedimentation area and other research indicators were used to investigate the effects of fine-grained hematite concentrate feed concentration, flocculant molecular weight, flocculant unit consumption, and flocculant solution concentration on the flocculation and sedimentation of fine-grained hematite concentrate. An experimental study on the influencing factors of flocculation and sedimentation of fine-grained hematite concentrate was designed by designing an orthogonal test. The test results were analyzed with the help of SPSS26 statistical software. The research results show that the order of the influence factors on the average settling velocity is: flocculant unit consumption > flocculant solution concentration > feed concentration > flocculant molecular weight; the order of influence on supernatant turbidity is: flocculant unit consumption > flocculant solution concentration > feed concentration > flocculant molecular weight; the order of the degree of influence on the unit settling area is: flocculant solution concentration > feed concentration > flocculant unit consumption > flocculant molecular weight. Considering comprehensively, the optimal conditions for the flocculation and sedimentation effect of fine-grained hematite concentrate in this experiment are: the molecular weight of the flocculant is 15 million, the feed concentration is 10%, the unit consumption of the flocculant is 60 g/t, and the concentration of the flocculant solution is 0.10%.
-
Key words:
- Hematite /
- Flocculant /
- Flocculation and sedimentation /
- Orthogonal test /
- Variance analysis
-

-
表 1 试样化学多元素分析/%
Table 1. Sample chemical multi-element analysis
TFe SiO2 Al2O3 S P Mn Zn CaO 64.80 4.80 1.572 0.018 0.043 0.151 0.003 0.013 表 2 试样粒度分析
Table 2. Sample particle size analysis
粒径/μm +74 -74~+38 -38~+15 -15~+10 -10~+5 -5 产率/% 3.76 18.44 21.78 10.45 17.33 28.24 表 3 正交实验因素与水平
Table 3. Orthogonal test factors and levels
水平 因素 入料
浓度/%絮凝剂
分子量/万絮凝剂
单耗/(g·t-1)絮凝剂
溶液浓度/%1 10 900 40 0.05 2 15 1300 50 0.10 3 20 1500 60 0.15 4 25 1800 70 0.20 表 4 正交实验方案(L16(45))
Table 4. Orthogonal text scheme (L16(45))
实验序号 入料
浓度/%絮凝剂
分子量/万絮凝剂
单耗/(g·t-1)絮凝剂
溶液浓度/%1 10 900 40 0.05 2 10 1300 50 0.10 3 10 1500 60 0.15 4 10 1800 70 0.20 5 15 900 50 0.15 6 15 1300 40 0.20 7 15 1500 70 0.05 8 15 1800 60 0.10 9 20 900 60 0.20 10 20 1300 70 0.15 11 20 1500 40 0.10 12 20 1800 50 0.05 13 25 900 70 0.10 14 25 1300 60 0.05 15 25 1500 50 0.20 16 25 1800 40 0.15 表 5 方差分析主体间效应检验
Table 5. ANOVA test for between-subject effects
源 因变量 Ⅲ类平方和 自由度 均方 F 显著性 修正模型 平均沉降速度 2807.378a 12 233.948 5.081 0.103 浊度 513718.030b 12 42809.860 9.727 0.043 单位沉降面积 76.210c 12 6.351 5.966 0.084 截距 平均沉降速度 1622.132 1 1622.132 35.232 0.010 浊度 1299999.030 1 1299999.03 295.378 0.000 单位沉降面积 109.512 1 109.512 102.868 0.002 入料浓度 平均沉降速度 830.377 3 276.792 6.012 0.087 浊度 20810.092 3 6936.697 1.576 0.359 单位沉降面积 3.208 3 1.069 1.004 0.499 絮凝剂分子量 平均沉降速度 1437.730 3 479.243 10.409 0.043 浊度 473620.192 3 157873.397 35.871 0.008 单位沉降面积 63.421 3 21.140 19.858 0.018 絮凝剂单耗 平均沉降速度 448.076 3 149.359 3.244 1.180 浊度 6215.792 3 2071.931 0.471 0.724 单位沉降面积 8.391 3 2.797 2.627 0.224 絮凝剂溶液浓度 平均沉降速度 91.195 3 30.398 0.660 0.629 浊度 13072.242 3 4357.414 0.990 0.503 单位沉降面积 1.190 3 0.397 0.373 0.781 误差 平均沉降速度 138.126 3 46.024 浊度 13203.422 3 4401.141 单位沉降面积 3.194 3 1.065 总计 平均沉降速度 4567.636 16 浊度 1826920.77 16 单位沉降面积 188.915 16 修正后总计 平均沉降速度 2945.504 15 浊度 526921.739 15 单位沉降面积 79.404 15 注:a.R2=0.953(调整后R2=0.766);b.R2=0.975(调整后R2=0.875);c.R2=0.960(调整后R2=0.799)。 表 6 单因素分析(入料浓度)
Table 6. Univariate analysis (Feed concentration)
考查指标 入料浓度/% 平均值 标准偏差 95%置信区间 下限 上限 平均沉降
速度10 21.156 21.640 -13.278 55.591 15 11.765 14.152 -10.754 34.285 20 3.871 3.554 -1.784 9.527 25 3.483 4.879 -4.282 11.248 浊度 10 284.400 239.448 -96.615 665.415 15 340.450 196.502 27.771 653.129 20 239.875 212.538 -98.321 578.071 25 275.450 166.082 11.177 539.723 单位沉降
面积10 2.463 3.294 -2.780 7.705 15 3.383 3.126 -1.590 8.357 20 2.339 1.246 0.357 4.320 25 2.280 1.795 -0.576 5.137 表 7 单因素分析(絮凝剂分子量)
Table 7. Univariate analysis (Flocculant molecular weight)
考查指标 分子量/万 平均值 标准偏差 95%置信区间 下限 上限 平均沉降
速度900 1.092 0.718 -0.049 2.234 1200 3.466 3.185 -1.603 8.535 1500 25.405 19.700 -5.942 56.752 1800 10.312 10.190 -5.902 26.527 浊度 900 557.500 47.543 481.849 633.151 1200 288.500 91.879 142.301 434.699 1500 202.300 76.527 80.529 324.071 1800 91.875 34.768 36.551 147.199 单位沉降
面积900 5.763 1.672 3.102 8.423 1200 2.843 1.444 0.545 5.141 1500 0.604 0.402 -0.036 1.243 1800 1.255 0.534 0.404 2.106 表 8 单因素分析(絮凝剂单耗)
Table 8. Single factor analysis (Unit consumption of flocculant)
考查指标 单耗/(g·t-1) 平均值 标准偏差 95%置信区间 下限 上限 平均沉降
速度40 3.459 3.410 -1.967 8.885 50 6.333 3.986 -0.009 12.676 60 15.897 23.430 -21.385 53.178 70 14.587 16.000 -10.873 40.046 浊度 40 318.750 250.570 -79.963 717.463 50 269.575 207.577 -60.727 599.877 60 273.450 180.876 -14.364 561.264 70 278.400 187.027 -19.201 576.001 单位沉降
面积40 3.763 2.894 -0.842 8.368 50 2.703 2.912 -1.930 7.337 60 1.917 1.484 -0.443 4.278 70 2.081 2.149 -1.390 5.450 表 9 单因素分析(絮凝剂溶液浓度)
Table 9. Univariate analysis (Flocculant solution concentration)
考查指标 溶液浓度/% 平均值 标准偏差 95%置信区间 下限 上限 平均沉降
速度0.05 10.022 14.726 -13.411 33.455 0.10 7.031 4.527 -0.331 14.394 0.15 13.710 24.413 -25.137 52.557 0.20 9.513 10.823 -7.710 26.735 浊度 0.05 299.325 232.968 -71.380 670.030 0.10 236.000 196.673 -76.951 548.951 0.15 297.200 184.342 3.871 590.529 0.20 307.650 210.586 -27.440 642.740 单位沉降
面积0.05 2.785 3.117 -2.175 7.745 0.10 2.254 1.721 -0.485 4.993 0.15 2.957 2.876 -1.619 7.533 0.20 2.469 2.263 -1.132 6.071 -
[1] 高太, 郭小飞, 袁致涛, 等. 我国赤铁矿选矿技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 金属矿山, 2010(8):97-101. GAO T, GUO X F, YUAN Z T, et al. Application and development tendency of beneficiation on technology of hematite in China[J]. Metal Mine, 2010(8):97-101.
[2] 唐雪峰. 难处理赤铁矿选矿技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 现代矿业, 2014, 30(3):14-19. TANG X F. Research status and development trend of beneficiation technology on hematite[J]. Modern Mining, 2014, 30(3):14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2014.03.005
[3] 梁爽, 熊伟, 路亮, 等. 絮凝剂在选矿废水中的应用进展[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(S2):295-297. LIANG S, XIONG W, LU L, et al. Application progress of flocculant in beneficiation wastewater[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(S2):295-297.
[4] 赵继领, 王晨, 王仕兴等. 基于正交试验法优化废汽车尾气催化剂中贵金属的浸出[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(6):101-104. ZHAO J L, WANG C, WANG S X, et al. Optimization of leaching of noble metals from waste automobile exhaust catalyst by orthogonal method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6):101-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.022
[5] 周贺鹏, 胡洁. 离子型稀土矿化学溶浸影响因素及其调控[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(3):146-151. ZHOU H P, HU J. Influencing factors and control of chemical leaching of ion-type rare earth ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(3):146-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.03.032
[6] 田明明, 徐文彬, 王成龙, 等. 玲珑金矿全尾砂絮凝沉降特性试验[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(1):120-124. TIAN M M, XU W B, WANG C L, et al. Test on flocculation sedimentation characteristic of unclassified tailing from ling long gold mine[J]. Metal Mine, 2019(1):120-124. doi: 10.19614/j.cnki.jsks.201901023
[7] 诸利一, 杨鹏, 吕文生. 全尾砂絮凝沉降与浓密影响因素试验研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2021, 41(8):59-64. ZHU L Y, YANG P, LV W S. Experimental study on influencing factors of flocculation sedimentation and thickening of unclassified tailings[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2021, 41(8):59-64. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2021.08.011
[8] 王勇, 吴爱祥, 王洪江, 等. 絮凝剂用量对尾矿浓密的影响机理[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(11):1419-1423. WANG Y, WU A X, WANG H J, et al. Influence mechanism of flocculant dosage on tailings thickening[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2013, 35(11):1419-1423. doi: 10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2013.11.005
[9] 陈婉琦. 细粒赤铁矿助沉团聚行为的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2016.
CHEN W Q. Study on the sedimentation improvement and flocculation of ultra-hematite[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[10] 王宇斌, 文堪, 雷大士, 等. 基于正交试验的某浸渣氧化铜粗选条件优化[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(5):58-62. WANG Y B, WEN K, LEI D S, et al. Optimization of copper oxide roughing conditions in a leaching residue based on orthogonal experiment[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(5):58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.05.012
[11] 王丛飞, 张芹, 王永龙, 等. 运用稳态浓缩模型硫精矿沉降絮凝剂的优选[J]. 现代矿业, 2014, 30(2):20-24. WANG C F, ZHANG Q, WANG Y L, et al. Optimization of the sulfur concentrate pulp flocculants by using steady settlement model[J]. Modern Mining, 2014, 30(2):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2014.02.007
-




 下载:
下载: