Continuous Leaching Test of Ion-type Rare Earth Ore at Different Depths
-
摘要:
这是一篇冶金工程领域的论文。以赣州地区某离子型稀土矿为研究对象,采用连续搅拌浸出和柱浸的方式,研究不同条件下矿样中稀土及杂质元素的浸出情况,为离子型稀土矿产资源的绿色高效开采提供参考。实验结果表明:连续搅拌浸出过程中稀土浸出率均在80%左右,二次浸出液中TREO/Al明显增大,TREO/Ca明显减小,TREO/Mg略微减小;柱浸实验中随着浸矿深度的增加,浸出液pH值逐步上升,TREO/Al增加至15.52,TREO/Ca降低至0.64。稀土浸出率均达到96%以上,但随着深度的增加轻稀土配分由49.43%上升到了53.28%,重稀土配分从35.91%逐步下降至32.18%。连续搅拌浸出和柱浸实验均表明随着矿样深度的增加,稀土浸出率无明显降低,低品位矿层稀土浸出仍然具有一定的可行性。
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of metallurgical engineering. The ion-type rare earth ore in Ganzhou was treated as the research object. Continuous stirring leaching and column leaching were used to study the leaching of rare earth and impurity elements in ore samples. The test results provide a reference for the green and efficient mining of ion-type rare earth mineral resources. The test results show that the rare earth leaching rate is about 80% in the continuous stirring leaching process. The TREO/Al in the secondary leaching solution increases significantly, while the TREO/Ca decreases significantly and the TREO/Mg decreases slightly. With the increase of ore depth, the pH value of leachate gradually increased, TREO/Al increased to 15.52, and TREO/Ca decreased to 0.64. The leaching rate of rare earths all reached more than 96%, but with the increase of depth, the proportion of light rare earth increased from 49.43% to 53.28%, and the proportion of heavy rare earth gradually decreased from 35.91% to 32.18%. The continuous stirring leaching and column leaching tests both show that with the increase of the depth of the ore sample, the leaching rate of rare earth does not decrease significantly, and the leaching of rare earth in low-grade ore seams is still feasible.
-

-
表 1 矿样主要化学成分/%
Table 1. Main chemical composition of mineral samples
名称 MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 K2O CaO TiO2 MnO Fe2O3 TREO ZK-1(6~10 m) 0.268 16.701 67.680 0.056 4.654 0.037 0.510 0.094 3.296 0.045 ZK-2(11~15 m) 0.243 16.399 67.758 0.063 4.543 0.039 0.545 0.118 3.744 0.025 ZK-3(16~20 m) 0.302 16.604 67.793 0.049 3.800 0.065 0.511 0.069 3.592 0.044 ZK-4(21~23 m) 0.226 17.386 66.903 0.046 4.495 0.032 0.536 0.088 3.479 0.022 表 2 矿样pH值测定结果
Table 2. Determination results of pH value
名称 ZK-1 ZK-2 ZK-3 ZK-4 pH值 5.23 6.18 6.26 6.08 表 3 矿样离子相稀土含量测定结果
Table 3. Analysis results of rare earth content in ionic phase of ore samples
名称 淋洗
液体
积/mLpH值 淋洗液中各
元素含量/(mg/L)矿样TREO
(离子相)
品位/(g/t)TFe Al Ca Mg TREO ZK-1 126 4.45 0.076 26.0 59.6 27.5 89.2 224.8 ZK-2 126 4.90 <0.01 1.95 96.1 24.1 58.1 146.4 ZK-3 130 5.14 <0.01 0.226 98.3 24.1 54.0 140.4 ZK-4 126 5.08 <0.01 0.642 150 41.9 58.7 147.9 表 4 连续搅拌浸出实验结果
Table 4. Continuous stirring leaching test results
名称 体积/
mLpH
值溶液中各元
素含量/(mg/L)TREO
浸出
率/%TREO Al Ca Mg TFe 一次
浸出浸出液 82 4.27 82.2 17.5 67.9 46.1 <0.01 79.50 洗液 57 4.73 38.5 7.53 31.8 22.5 <0.01 二次
浸出浸出液 54 4.57 127 6.91 223 90.3 <0.01 82.34 洗液 30 4.86 57.6 3.89 99.3 46.1 <0.01 表 5 连续搅拌浸出溶液中稀土与杂质质量比
Table 5. Mass ratio of rare earth to impurities in the continuous stirring leaching solution
名称 TREO/Al TREO/Ca TREO/Mg 一次浸出 浸出液 4.70 1.21 1.78 洗液 5.11 1.21 1.71 二次浸出 浸出液 18.38 0.57 1.41 洗液 14.81 0.58 1.25 表 6 柱浸浸出液中稀土与杂质质量比
Table 6. Mass ratio of rare earth to impurities in the column leaching solution
名称 溶液中稀土与杂质元素质量比 TREO/Al TREO/Ca TREO/Mg ZK-5 3.47 1.52 3.19 ZK-6 5.80 0.96 2.88 ZK-7 10.00 0.78 2.66 ZK-8 15.52 0.64 2.22 表 7 不同深度浸出液中稀土配分分析结果/(mg/L)
Table 7. Partition analysis results of rare earth in leaching solution at different depths
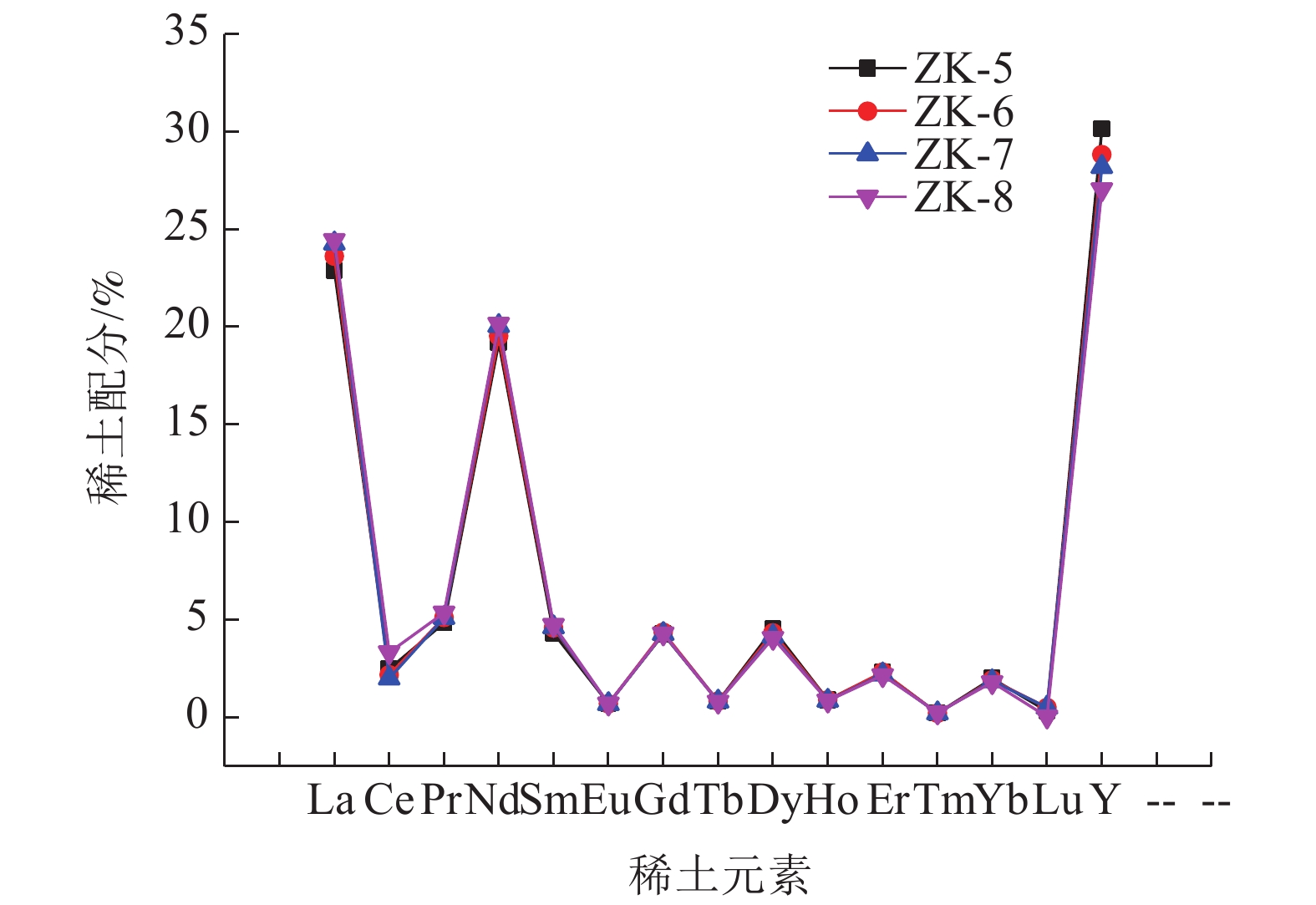
名 称 ZK-5 ZK-6 ZK-7 ZK-8 轻稀土 La 50.367 41.097 36.179 35.926 Ce 5.475 3.802 2.992 4.898 Pr 10.679 8.918 7.619 7.881 Nd 42.226 33.989 29.887 29.616 中稀土 Sm 9.522 7.983 6.904 6.965 Eu 1.559 1.221 1.051 1.040 Gd 9.394 7.604 6.396 6.323 Tb 1.818 1.461 1.235 1.184 Dy 9.951 7.543 6.219 5.991 重稀土 Ho 1.991 1.577 1.301 1.258 Er 5.069 4.037 3.302 3.190 Tm 0.493 0.371 0.332 0.374 Yb 4.393 3.349 2.793 2.661 Lu 0.742 0.895 0.775 0.075 Y 66.323 50.151 42.016 39.748 所有稀土元素均按氧化物含量计算。 -
[1] 程建忠, 车丽萍. 中国稀土资源开采现状及发展趋势[J]. 稀土, 2010, 31(2):65-69. CHENG J Z, CHE L P. Current mining situation and potential development of rare earth in China[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2010, 31(2):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
CHENG J Z, CHE L P. Current mining situation and potential development of rare earth in China[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2010, 31(2): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
[2] 张博, 宁阳坤, 曹飞, 等. 世界稀土资源现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(4):7-12. ZHANG B, NING Y K, CAO F, et al. Current situation of worldwide rare earth resources[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(4):7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.04.002
ZHANG B, NING Y K, CAO F, et al. Current situation of worldwide rare earth resources[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(4): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.04.002
[3] 张臻悦, 何正艳, 徐志高, 等. 中国稀土矿稀土配分特征[J]. 稀土, 2016, 37(1):121-127. ZHANG Z Y, HE Z Y, XU Z G, et al. Rare earth partitioning characteristics of China rare earth ore[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(1):121-127.
ZHANG Z Y, HE Z Y, XU Z G, et al. Rare earth partitioning characteristics of China rare earth ore[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(1): 121-127.
[4] 周贺鹏, 胡洁. 离子型稀土矿化学溶浸影响因素及其调控[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(3):146-151. ZHOU H P, HU J. Influencing factors and control of chemical leaching of ion-type rare earth ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(3):146-151.
ZHOU H P, HU J. Influencing factors and control of chemical leaching of ion-type rare earth ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(3): 146-151.
[5] 池汝安, 李隆峰, 王淀佐. 吸附稀土的粘土矿离子交换平衡研究[J]. 中南矿冶学院学报, 1991(2):142-148. CHI R A, LI L F, WANG D Z. Studies of ion exchange equilibrium in clay minerals of adsorbed rare earth[J]. Journal of Central-South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1991(2):142-148.
CHI R A, LI L F, WANG D Z. Studies of ion exchange equilibrium in clay minerals of adsorbed rare earth[J]. Journal of Central-South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1991, (2): 142-148.
[6] 何耀, 程柳, 李毅, 等. 离子吸附型稀土矿的成矿机理及找矿标志[J]. 稀土, 2015, 36(4):98-103. HE Y, CHENG L, LI Y, et al. The mineralization mechanism of the ion adsorption type rare earths ore and prospecting marks[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2015, 36(4):98-103. doi: 10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.201504017
HE Y, CHENG L, LI Y, et al. The mineralization mechanism of the ion adsorption type rare earths ore and prospecting marks[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2015, 36(4): 98-103. doi: 10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.201504017
[7] 池汝安, 田君. 风化壳淋积型稀土矿化工冶金[M]. 科学出版社, 2006.
CHI R A, TIAN J. Weathered crust rare earth ore chemical metallurgy [M]. Science Press, 2006.
[8] 舒荣波, 程蓉, 李超, 等. 一种离子型稀土的渗流控制原位开采方法[P]. CN110055414A, 2019.
SHU R B, CHENG R, LI C, et al. A seepage-controlled in-situ mining method for ionic rare earth[P]. CN110055414A, 2019.
[9] 陈启仁, 丁嘉瑜. "江西稀土"的崛起——为"江西稀土"的发现, 命名和工艺的发明十七周年而作[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 1988(3):3-4. CHEN Q R, DING J Y. The rise of "Jiangxi rare earths": for the seventeenth anniversary of the discovery, naming and invention of "Jiangxi rare earths"[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 1988(3):3-4.
CHEN Q R, DING J Y. The rise of "Jiangxi rare earths": for the seventeenth anniversary of the discovery, naming and invention of "Jiangxi rare earths"[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 1988(3): 3-4.
[10] 丁嘉榆. 离子型稀土矿开发的历史回顾——纪念赣州有色冶金研究所建所60周年[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(4):6. DING J Y. Historical review of ionic rare earth ore development——commemorating the 60th anniversary of Ganzhou nonferrous metallurgy research institute[J]. Nonferrous Metal Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4):6.
DING J Y. Historical review of ionic rare earth ore development——commemorating the 60th anniversary of Ganzhou nonferrous metallurgy research institute[J]. Nonferrous Metal Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4): 6.
[11] 池汝安 王淀佐. 稀土矿物加工[M]. 科学出版社, 2014.
CHI R A, WANG D Z. Rare earth mineral processing [M]. Science Press, 2014.
-




 下载:
下载: