-
摘要:
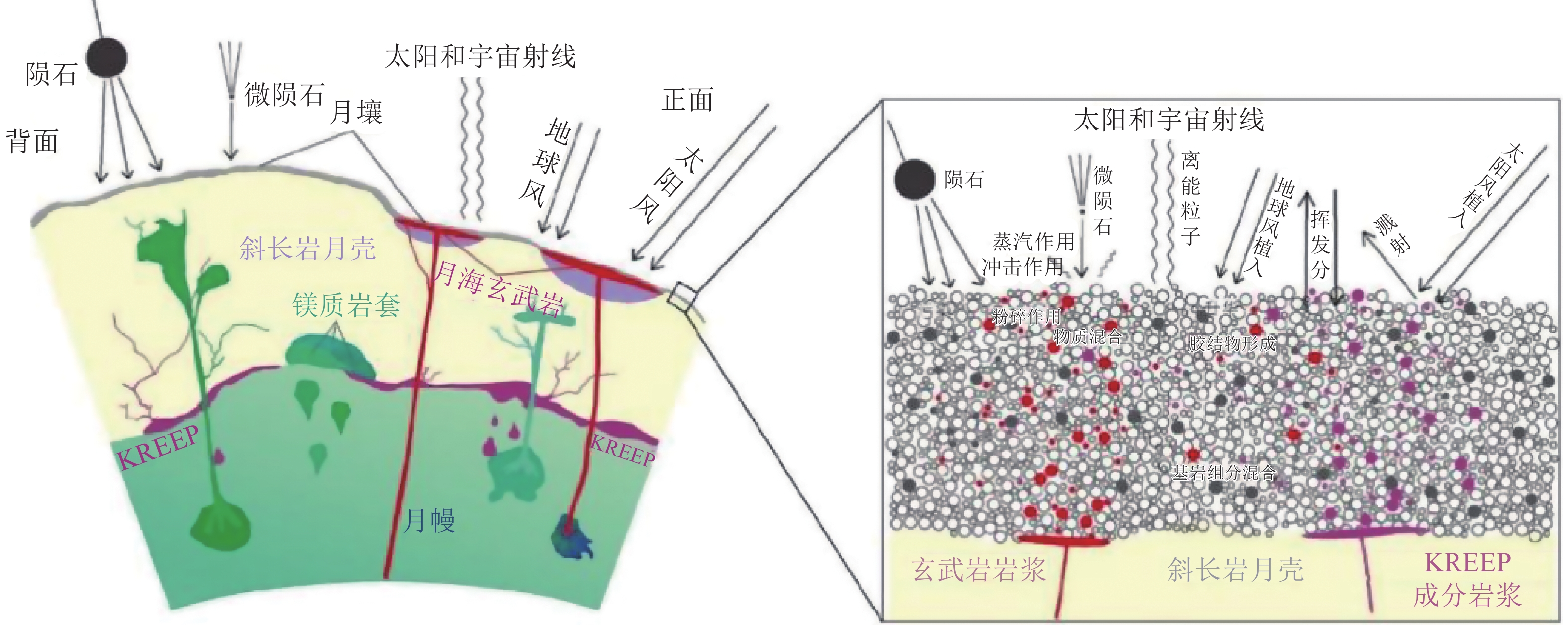
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。几十年来,太空探索一直是炙手可热的话题,随着嫦娥五号的发射,正式开启了我国首次地外天体采样返回之旅,象征着我国月球基地建设方案正式提上日程。月球探索是人类进行深空探索的第一步,月球原位资源利用对于月球探索具有重大意义。增材制造是进行月球原位资源利用建设月球基地的有效手段。本文阐述了月壤的基本特性以及模拟月壤的特点及组成,重点总结了目前国内外模拟月壤增材制造的研究进展。提出了面向月球风化层(即月壤)的增材制造关键技术的重要挑战。围绕我国月球基地建设工程,讨论了增材制造技术的发展前景与可能的实施途径。
-
关键词:
- 陶瓷及复合材料 /
- 增材制造 /
- 模拟月壤 /
- 原位资源利用(ISRU) /
- 成形精度
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of ceramics and composites. For decades, space exploration has been a hot topic. With the launch of Chang'e 5, China officially opened the first extraterrestrial celestial body sampling return journey. The lunar base construction program in China is officially on the agenda. Lunar exploration is the first step for human to conduct deep space exploration, and the utilization of lunar in-situ resources is of great significance for lunar exploration. Additive manufacturing is an effective means to carry out in-situ lunar resource utilization to build a lunar base. This paper describes the basic properties of lunar soil and the characteristics and composition of simulated lunar soil, and focuses on summarizing the current research progress of simulated lunar soil additive manufacturing in China and abroad. Important challenges are presented for the key technology of additive manufacturing for the lunar weathering layer (i.e., lunar soil). The development prospect of additive manufacturing technology and possible ways of implementation are discussed around China's lunar base construction project.
-

-
表 1 月壤的颗粒形态
Table 1. Particle morphology of lunar soil
参数 平均比值 描述 延性 1.35 稍长条状 长度直径比 0.55 稍长条状至中等长条状 圆度轮廓 0.21 次棱角状 平行光 0.22 棱角状 体积系数 0.3 长条状 比表面积/(m2/g) 0.5 不规则、凹角状 成分 Apollo11 Apollo14 JSC-1 MLS-1 CAS-1 NEU-1 南京月壤 CUG-/A LRS CLRS-2 SiO2 42.2 48.1 47.71 43.86 49.24 44.92 48.05 47.54 41.89 TiO2 7.8 1.7 1.59 6.32 1.91 2.87 1.18 1.74 7.62 Al2O3 13.6 17.4 15.02 13.68 15.8 17.23 17.08 14.01 13.41 FeO 15.3 10.4 7.35 13.4 11.47 13.09 13.84 10.28 15.90 Fe2O3 — — 3.44 2.6 — — — — — MgO 7.8 9.4 9.01 6.68 8.72 4.37 0.14 9.77 7.06 CaO 11.9 10.7 10.42 10.13 7.25 9.44 5.58 7.14 9.70 Cr2O3 0.3 0.23 0.04 — — 0.04 — — — Na2O 0.47 0.7 2.7 2.12 3.08 3.79 8.45 4.57 2.34 K2O 0.16 0.55 0.82 0.28 1.03 3.01 2.56 3.38 0.78 MnO 0.2 0.14 0.18 0.2 0.14 0.34 1.2 0.13 0.20 P2O5 0.05 0.51 0.66 0.2 0.3 0.54 0.61 0.74 0.25 SO3 n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. n.a. 0.71 合计 99.78 99.83 98.94 99.47 98.94 99.64 98.89 99.81 99.86 -
[1] 李雯, 徐可宁, 黄勇, 等. 基于SLM的模拟月壤原位成形技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(10):1931-1937. LI W, XU K N, HUANG Y, et al. SLM-based in situ forming technique for simulated lunar soil[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(10):1931-1937. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0690
LI W, XU K N, HUANG Y, et al. SLM-based in situ forming technique for simulated lunar soil [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(10): 1931-1937. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0690
[2] 王功, 赵伟, 刘亦飞, 等. 太空制造技术发展现状与展望[J]. 中国科学:物理学力学天文学, 2020, 50(4):95-105. WANG G, ZHAO W, LIU Y F, et al. Current status and prospects of space manufacturing technology development[J]. Chinese Science:Physics, Mechanics, Astronomy, 2020, 50(4):95-105.
WANG G, ZHAO W, LIU Y F, et al. Current status and prospects of space manufacturing technology development [J]. Chinese Science: Physics, Mechanics, Astronomy, 2020, 50(4): 95-105.
[3] 孙一萌, 陈盛贵, 花开慧, 等. 模拟月壤原位增材制造技术研究进展[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2021, 15(2):178-185. SUN Y M, CHEN S G, HUA K H, et al. Research progress on in situ additive manufacturing technology for simulated lunar soil[J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2021, 15(2):178-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.02.014
SUN Y M, CHEN S G, HUA K H, et al. Research progress on in situ additive manufacturing technology for simulated lunar soil [J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2021, 15(2): 178-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.02.014
[4] Devezas T, Melo F C L D, Gregori M L, et al. The struggle for space: Past and future of the space race [J]. Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 2012, 79(5).
[5] Niu X, Singh S, Garg A, et al. Review of materials used in laser-aided additive manufacturing processes to produce metallic products [J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 14(3).
[6] A. T S, M. M. Laser additive manufacturing of titanium-based functionally graded materials: areview [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(8).
[7] Ding Y, Dwivedi R, Kovacevic R. Process planning for 8-axis robotized laser-based direct metal deposition system: A case on building revolved part [J]. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2017, 44.
[8] Buchbinder D, Schleifenbaum H, Heidrich S, et al. High power selective laser melting (HP SLM) of aluminum parts [J]. Physics Procedia, 2011, 12.
[9] Lee P-H, Chang E, Yu S, et al. Modification and characteristics of biodegradable polymer suitable for selective laser sintering [J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2013, 14(6).
[10] Vehse M, Seitz H. A new micro-stereolithography-system based on diode laser curing (DLC) [J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2014, 15(10).
[11] Elisabeth P, Jeremias H, Florian B, et al. Wear resistance of 3D-printed materials: A systematic review [J]. Dentistry Review, 2022, 2(2).
[12] Hua Z, Lu M, Shaoying L, et al. Development of lunar regolith composite and structure via laser-assisted sintering[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 17(1):6-18. doi: 10.1007/s11465-021-0662-2
[13] Füri E, L. Z, A. E. S. Apollo 15 green glass He-Ne-Ar signatures – In search for indigenous lunar noble gases [J]. Geochemical Perspectives Letters, 2018, (1-5).
[14] Füri E, Zimmermann L, Deloule E, et al. Cosmic ray effects on the isotope composition of hydrogen and noble gases in lunar samples: Insights from Apollo 12018 [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 550(116550).
[15] O’brien P B S. Physical and chemical evolution of lunar mare regolith[J]. J Geophys Res Planets, 2021, 126:1-47.
[16] Xu X, Hui H, Chen W, et al. Formation of lunar highlands anorthosites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 536(116138):1-11.
[17] 石忠宁, 刘爱民, 管晋钊, 等. 月壤资源原位提取金属和制备氧气的方法与技术[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2022, 21(2):79-94. SHI Z N, LIU A M, GUAN J Z, et al. Methods and techniques for in situ extraction of metals and preparation of oxygen from lunar soil resources[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2022, 21(2):79-94. doi: 10.14186/j.cnki.1671-6620.2022.02.001
SHI Z N, LIU A M, GUAN J Z, et al. Methods and techniques for in situ extraction of metals and preparation of oxygen from lunar soil resources [J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2022, 21(2): 79-94. doi: 10.14186/j.cnki.1671-6620.2022.02.001
[18] Liu M, Tang W, Duan W, et al. Digital light processing of lunar regolith structures with high mechanical properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 45(5):5829-5836.
[19] Qian Y, Xiao L, Yin S, et al. The regolith properties of the Chang'e-5 landing region and the ground drilling experiments using lunar regolith simulants[J]. Icarus, 2020, 337(113508):1-13.
[20] Zhou S, Lu C, Zhu X, et al. Preparation and characterization of high-strength geopolymer based on bh-1 lunar soil simulant with low alkali content[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(11):1631-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2020.10.016
[21] Tracie P, Niki W, Frank L, et al. 3D printing in zero g technology demonstration mission: complete experimental results and summary of related material modeling efforts [J]. The International journal, advanced manufacturing technology, 2019, 101(1-4).
[22] 王敏, 于涛, 张骁, 等. 美国在轨制造技术发展现状及启示[J]. 航天器工程, 2019, 28(3):86-91. WANG M, YU T, ZHANG X, et al. Current status and insights of the development of in-orbit manufacturing technology in the United States[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2019, 28(3):86-91.
WANG M, YU T, ZHANG X, et al. Current status and insights of the development of in-orbit manufacturing technology in the United States [J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2019, 28(3): 86-91.
[23] 田小永, 李涤尘, 卢秉恒. 空间3D打印技术现状与前景[J]. 载人航天, 2016, 22(4):471-476. TIAN X Y, LI D C, LU B H. Current status and prospects of space 3D printing technology[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2016, 22(4):471-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2016.04.011
TIAN X Y, LI D C, LU B H. Current status and prospects of space 3D printing technology [J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2016, 22(4): 471-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2016.04.011
[24] Balla, Krishna V, Roberson, et al. First demonstration on direct laser fabrication of lunar regolith parts[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2012, 18(6):451-457. doi: 10.1108/13552541211271992
[25] 王超, 张光, 吕晓辰, 等. 模拟月壤激光熔融成型工艺参数实验初探[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2021, 38(5):575-580. WANG C, ZHANG G, LYU X C, et al. A preliminary investigation of simulated lunar soil laser melting and forming process parameters[J]. Spacecraft Environmental Engineering, 2021, 38(5):575-580. doi: 10.12126/see.2021.05.013
WANG C, ZHANG G, LYU X C, et al. A preliminary investigation of simulated lunar soil laser melting and forming process parameters [J]. Spacecraft Environmental Engineering, 2021, 38(5): 575-580. doi: 10.12126/see.2021.05.013
[26] Hintze P E, Quintana S. Building a lunar or martian launch pad with in situ materials: recent laboratory and field studies[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2013, 26(1):134-142. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000205
[27] Yuan P F, Xinjie Z, Hao W, et al. Robotic 3D printed lunar bionic architecture based on lunar regolith selective laser sintering technology[J]. Architectural Intelligence, 2022, 1(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s44223-022-00002-z
[28] RinaldiM, Ferrara, et al. Additive manufacturing of polyether ether ketone-based composites for space application: a mini-review [J]. CEAS Space Journal, 2021, 1(1-11).
[29] Toutanji H A, Evans S, Grugel R N. Performance of lunar sulfur concrete in lunar environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 29:444-448. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.10.041
[30] Taylor, A. P, Kahanpää, et al. On pressure measurement and seasonal pressure variations during the Phoenix mission[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Planets, 2010, 115:1-11.
[31] Wan L, Wendner R, Cusatis G. A novel material for in situ construction on Mars: experiments and numerical simulations[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 120:222-231. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.05.046
[32] Montes C, Broussard K, Gongre M, et al. Evaluation of lunar regolith geopolymer binder as a radioactive shielding material for space exploration applications[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56(6):1212-1221. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2015.05.044
[33] Hertel T, Pontikes Y. Geopolymers, inorganic polymers, alkali-activated materials and hybrid binders from bauxite residue (red mud) – Putting things in perspective[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258:120610. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120610
[34] Taylor S L, Jakus A E, Koube K D, et al. Sintering of micro-trusses created by extrusion-3D-printing of lunar regolith inks[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 143:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.11.005
[35] Jakus A E, D K K, R G N, et al. Robust and elastic lunar and martian structures from 3d-printed regolith inks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 71(7):1-8.
[36] Zhao H, Lu M, Shaoying L, et al. Development of lunar regolith composite and structure via laser-assisted sintering [J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 17(1).
[37] Cesaretti G, Dini E, De Kestelier X, et al. Building components for an outpost on the Lunar soil by means of a novel 3D printing technology[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 93:430-450. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2013.07.034
[38] 刘洋, 周建平, 张晓天. 增材制造技术在载人航天工程中的应用与展望 [J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022: 1-11.
LIU Y, ZHOU J P, ZHANG X T. Application and prospect of additive manufacturing technology in human space engineering [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022: 1-11.
[39] Liu M, Tang W, Duan W, et al. Digital light processing of lunar regolith structures with high mechanical properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5):5829-5836. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.049
[40] Dou R, Tang W Z, Wang L, et al. Sintering of lunar regolith structures fabricated via digital light processing[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(14):17210-17215. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.276
[41] Schlüter L, Cowley A, Pennec Y, et al. Gas purification for oxygen extraction from lunar regolith[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 179:371-381. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.11.014
[42] Chen H, Guanglin N, Yehua L, et al. Improving relative density and mechanical strength of lunar regolith structures via DLP-stereolithography integrated with powder surface modification process[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(18):26874-26883. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.390
[43] Sun J, Binner J, Bai J. Effect of surface treatment on the dispersion of nano zirconia particles in non-aqueous suspensions for stereolithography[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4):1660-1667. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.10.024
[44] Liu Y, Cheng L, Li H, et al. Formation mechanism of stereolithography of Si3N4 slurry using silane coupling agent as modifier and dispersant[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):14583-14590. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.258
[45] Wang C, Gong H, Wei W, et al. Vat photopolymerization of low-titanium lunar regolith simulant for optimal mechanical performance[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(20):29752-29762. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.06.235
[46] Reitz B, Lotz C, Gerdes N, et al. Additive manufacturing under lunar gravity and microgravity[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2021, 33(25):1-12.
[47] Fateri M, Sottong R, Kolbe M, et al. Thermal properties of processed lunar regolith simulant[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2019, 16(6):2419-2428. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13267
[48] Goulas A, Friel R J. 3D printing with moondust[J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2016, 22(6):864-870. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-02-2015-0022
[49] Goulas A, Binner J G P, Harris R A, et al. Assessing extraterrestrial regolith material simulants for in situ resource utilisation based 3d printing[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2017, 6:54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2016.11.004
[50] Levent K, David K, Aleksander G, et al. Cold sintering as a promising ISRU technique: A case study of Mars regolith simulant[J]. Icarus, 2023, 389(115270):1-8.
-

| 引用本文: | 吴灵芝, 尹海清, 张聪, 张瑞杰, 王永伟, 姜雪, 曲选辉. 增材制造月壤原位成形技术的研究现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2023, 44(6): 99-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.06.015 |
| Citation: | Wu Lingzhi, Yin Haiqing, Zhang Cong, Zhang Ruijie, Wang Yongwei, Jiang Xue, Qu Xuanhui. Research Status of Additive Manufacturing Lunar in-situ Forming Technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023, 44(6): 99-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.06.015 |


 下载:
下载: