Effect of Asphalt Cemented Phosphogypsum on its Performance and Microscopic Analysis
-
摘要:
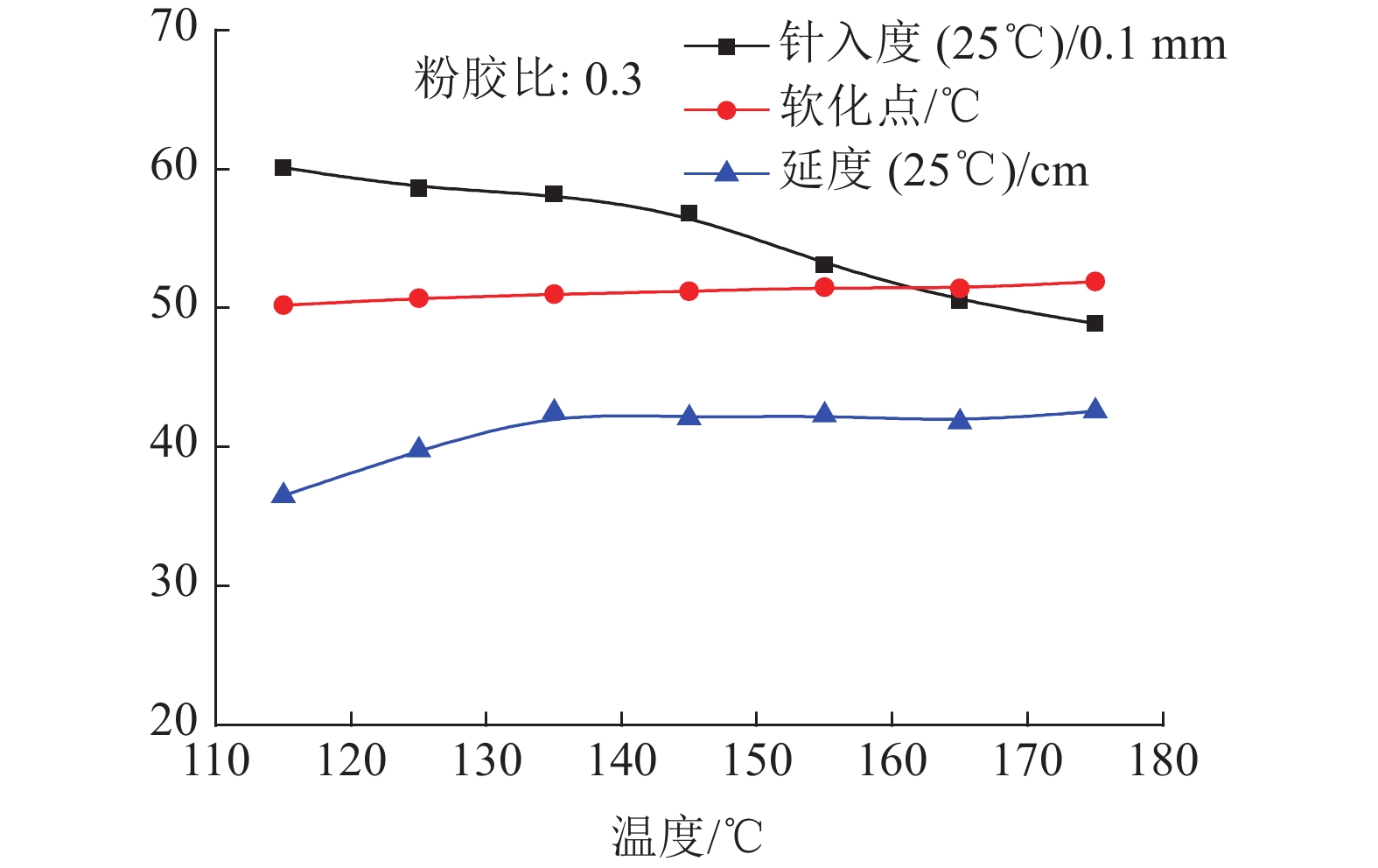
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。为探索磷石膏在道路材料应用新途径,采用磷石膏粉与沥青胶浆搅拌混合,制备磷石膏改性沥青混料。研究搅拌温度、粉胶比及多聚磷酸掺入量对磷石膏改性沥青三大指标的影响。研究结果表明:搅拌温度的增加,软化点也随之提升,延度先升高随后不再提升,考虑能效及老化温度,沥青的加工温度应在135~145 ℃之间;增大粉胶比可以提升改性沥青的软化点,同时会使沥青的延度下降,故以磷石膏为改性剂改性沥青时粉胶比不应大于0.9;多聚磷酸掺入改性沥青对软化点有较大的提升,但会使其延度和针入度下降,多聚磷酸较佳掺入量应为1.5%;红外光谱(FTIR)和热重分析(TG-DSC)表明,磷石膏与沥青仅为物理胶结,多聚磷酸掺入沥青时会与沥青发生化学反应。研究结果可为磷石膏在道路材料的工程应用和理论研究提供参考。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of ceramics and composites. In order to explore a new way for the application of phosphogypsum in road materials, phosphogypsum powder and asphalt mortar were mixed to prepare phosphogypsum modified asphalt. The effects of mixing temperature, powder-binder ratio and polyphosphoric acid content on the three major indicators of phosphogypsum modified asphalt were studied. The research results show that the softening point increases as the mixing temperature increases, and the ductility increased first and then kept constant. Considering energy efficiency and aging temperature, the processing temperature of asphalt should be in the range 135 °C and 145 °C. increasing the powder gum ratio can increase the softening point of the modified asphalt and decrease the ductility of the asphalt. Therefore, the ratio of filler bitumen should not be greater than 0.9 using phosphogypsum as the modifier. The addition of polyphosphoric acid greatly increases the softening point of modified asphalt, but reduces its ductility and penetration. The optimal amount of polyphosphoric acid should be around 1.5%. Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TG-DSC) showed that phosphogypsum physically functioned with Asphalt. When polyphosphoric acid was mixed into asphalt, it would react chemically with asphalt. The research results could provide references for the engineering application and theoretical research of phosphogypsum in road materials.
-

-
表 1 磷石膏样品XRF分析结果/%Table 1 XRF analysis results of phosphogypsum samples
Al2O3 P2O5 SiO2 Na2O K2O CaO TiO2 SO2 SrO F 其他 1.10 4.63 2.31 1.62 0.24 34.33 0.12 49.04 0.67 2.86 3.08 表 2 SHELL-70#基质沥青三大指标性能实验结果
Table 2. SHELL-70#matrix asphalt three index performance results
项目 实测值 技术要求 针入度(25 ℃)/0.1 mm 74.5 60~80 软化点/℃ 48.5 >45 延度(25 ℃)/cm 114.4 >100 表 3 沥青及改性沥青的DSC分析
Table 3. DSC analysis of asphalt and modified asphalt
样品 焓/(J/g) 峰值温度/℃ 峰宽度/℃ 基质沥青 2.85 460.0 242.3~498.9 磷石膏改性沥青 1.27 462.3 238.9~498.5 多聚磷酸复合改性沥青 1.04 461.3 235.6~490.5 -
[1] 刘虹利, 张均, 王永卿, 等. 磷矿固体废弃物资源化利用问题及建议[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(1):6-11.LIU H L, ZHANG J, WANG Y Q, et al. Resource utilization problems and suggestions of phosphate rock solid waste[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(1):6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.01.002
LIU H L, ZHANG J, WANG Y Q, et al. Resource utilization problems and suggestions of phosphate rock solid waste[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(1):6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.01.002
[2] 叶学东. 2018年我国磷石膏利用现状、问题及建议[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2019, 034(7):1-4.YE X D. Utilization status, problems and suggestions of phosphogypsum in China, 2018[J]. Phosphate Fertilizers and Compound Fertilizers, 2019, 034(7):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2019.07.002
YE X D. Utilization status, problems and suggestions of phosphogypsum in China, 2018[J]. Phosphate Fertilizers and Compound Fertilizers, 2019, 034(7):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2019.07.002
[3] 王圳, 张均, 陈芳, 等. 贵州省磷矿固体废弃物治理现状与建议[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019, 000(1):11-15.WANG Z, ZHANG J, CHEN F, et al. Status and suggestions on the treatment of phosphate rock solid waste in Guizhou Province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 000(1):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.003
WANG Z, ZHANG J, CHEN F, et al. Status and suggestions on the treatment of phosphate rock solid waste in Guizhou Province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 000(1):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.003
[4] 胡敏, 彭丽, 郭娜, 等. 磷石膏- 炭化污泥胶凝材料力学性能试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):196-201.HU M, PENG L, GUO N, et al. Study on mechanical properties of phosphogypsum-carbonized sludge composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
HU M, PENG L, GUO N, et al. Study on mechanical properties of phosphogypsum-carbonized sludge composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
[5] 刘香香, 贾晓东. 多重因素作用下沥青老化性能研究[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 048(10):2399-2402.LIU X X, JIA X D. Research on asphalt aging performance under multiple factors[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 048(10):2399-2402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.10.030
LIU X X, JIA X D. Research on asphalt aging performance under multiple factors[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 048(10):2399-2402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.10.030
[6] 张洪波, 孙祝华. 沥青拌合站运行中的安全事故隐患及预防措施探讨[J]. 城市建设理论研究: 电子版, 2013(15):1-9.ZHANG H B, SUN Z H. Discussion on hidden dangers and preventive measures of safety accidents in the operation of asphalt mixing plant[J]. Urban Construction Theory Research: Electronic Edition, 2013(15):1-9.
ZHANG H B, SUN Z H. Discussion on hidden dangers and preventive measures of safety accidents in the operation of asphalt mixing plant[J]. Urban Construction Theory Research: Electronic Edition, 2013(15):1-9.
[7] 董刚. 多聚磷酸及多聚磷酸/聚合物复合改性沥青的性能和机理分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018.DONG G. Performance and mechanism analysis of polyphosphoric acid and polyphosphoric acid/polymer composite modified asphalt [D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2018.
DONG G. Performance and mechanism analysis of polyphosphoric acid and polyphosphoric acid/polymer composite modified asphalt [D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2018.
[8] 王岚, 任敏达, 李超. 多聚磷酸改性沥青改性机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(10):2330-2336.WANG L, REN M D, LI C. Modification mechanism of polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2017, 34(10):2330-2336.
WANG L, REN M D, LI C. Modification mechanism of polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2017, 34(10):2330-2336.
[9] 王晓鹏. 酸雨对沥青及沥青混合料的侵蚀破坏机理研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学.WANG X P. Study on the erosion and destruction mechanism of asphalt and asphalt mixture by acid rain[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science and Technology.
WANG X P. Study on the erosion and destruction mechanism of asphalt and asphalt mixture by acid rain[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science and Technology.
[10] 徐鸥明, 韩森, 李洪军. 紫外线对沥青特征官能团和玻璃化温度的影响[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 27(2):16-20.XU O M, HAN S, LI H J. The effect of ultraviolet on characteristic functional groups and glass transition temperature of asphalt[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 27(2):16-20.
XU O M, HAN S, LI H J. The effect of ultraviolet on characteristic functional groups and glass transition temperature of asphalt[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 27(2):16-20.
[11] 徐惠生. 改性沥青红外光谱分析[J]. 安徽化工, 2007, 33(1):62-64.XU H S. Infrared spectroscopy analysis of modified asphalt[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 2007, 33(1):62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-553X.2007.01.022
XU H S. Infrared spectroscopy analysis of modified asphalt[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 2007, 33(1):62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-553X.2007.01.022
[12] 刘少文, 张茜, 吴元欣, 等. 热分析在磷石膏制酸反应研究中的应用[J]. 化工进展, 2008(5):761-764.LIU S W, ZHANG Q, WU Y X, et al. Application of thermal analysis in the study of phosphogypsum acid production[J]. Progress in Chemical Industry, 2008(5):761-764. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6613.2008.05.026
LIU S W, ZHANG Q, WU Y X, et al. Application of thermal analysis in the study of phosphogypsum acid production[J]. Progress in Chemical Industry, 2008(5):761-764. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6613.2008.05.026
[13] 刁梦娜. 磷石膏晶须对沥青性能的改性研究[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学, 2015.DIAO M N. Study on modification of asphalt performance by phosphogypsum whiskers[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University, 2015.
DIAO M N. Study on modification of asphalt performance by phosphogypsum whiskers[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University, 2015.
[14] 张铭铭. 多聚磷酸改性沥青微观结构及技术性能研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.ZHANG M M. Research on the microstructure and technical performance of polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2012.
ZHANG M M. Research on the microstructure and technical performance of polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt[D]. Xi’an: Chang'an University, 2012.
[15] 姚青梅. 改性沥青的发展现状及应用前景[J]. 科技传播, 2010(18): 156+159.YAO Q M. The development status and application prospects of modified asphalt[J]. Science and Technology Communication, 2010(18): 156+159.
YAO Q M. The development status and application prospects of modified asphalt[J]. Science and Technology Communication, 2010(18): 156+159.
-




 下载:
下载: