Preparation and Modification of Magnetic LSX Type Molecular Sieve by Directing Agent Method
-
摘要:
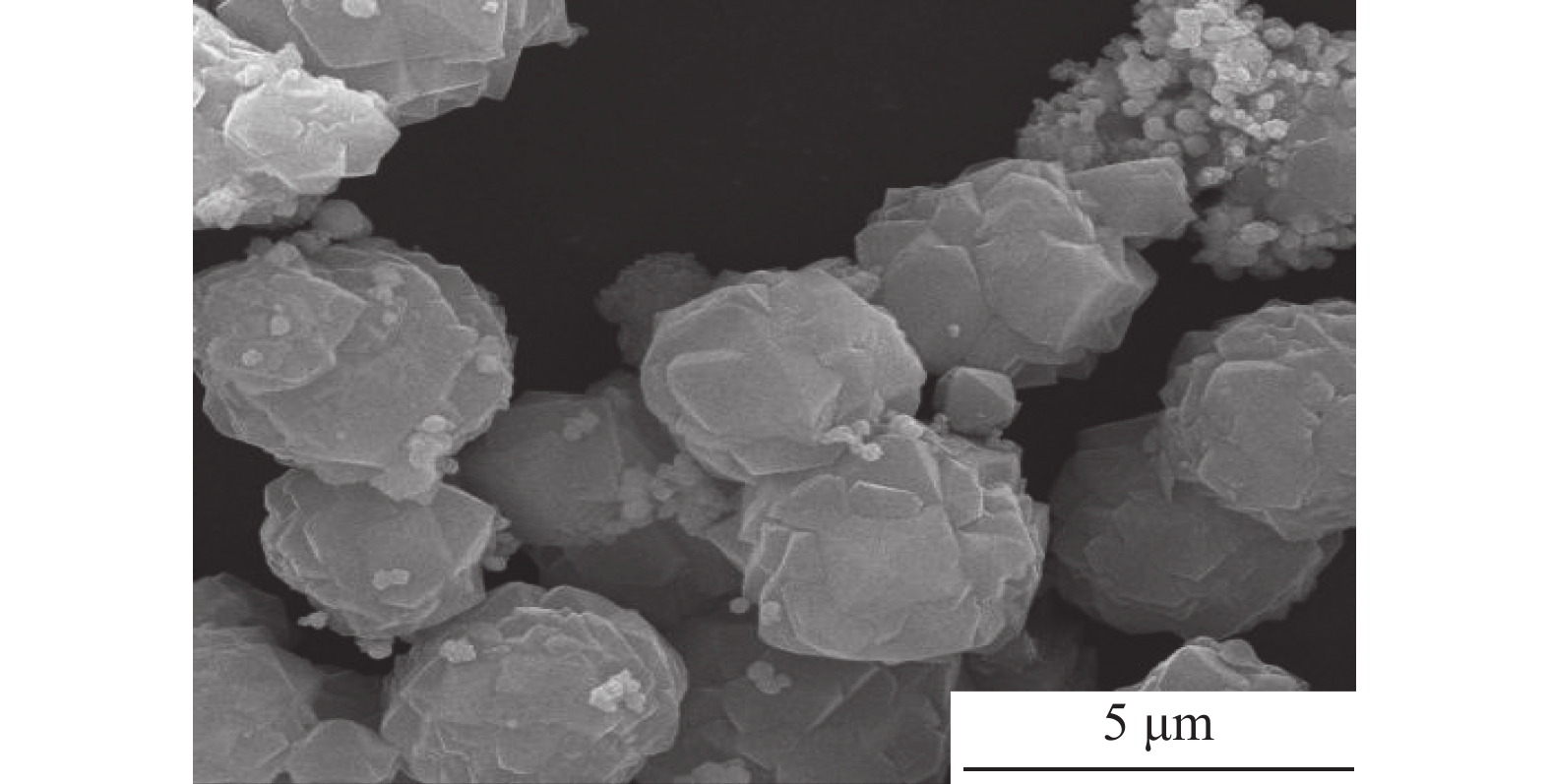
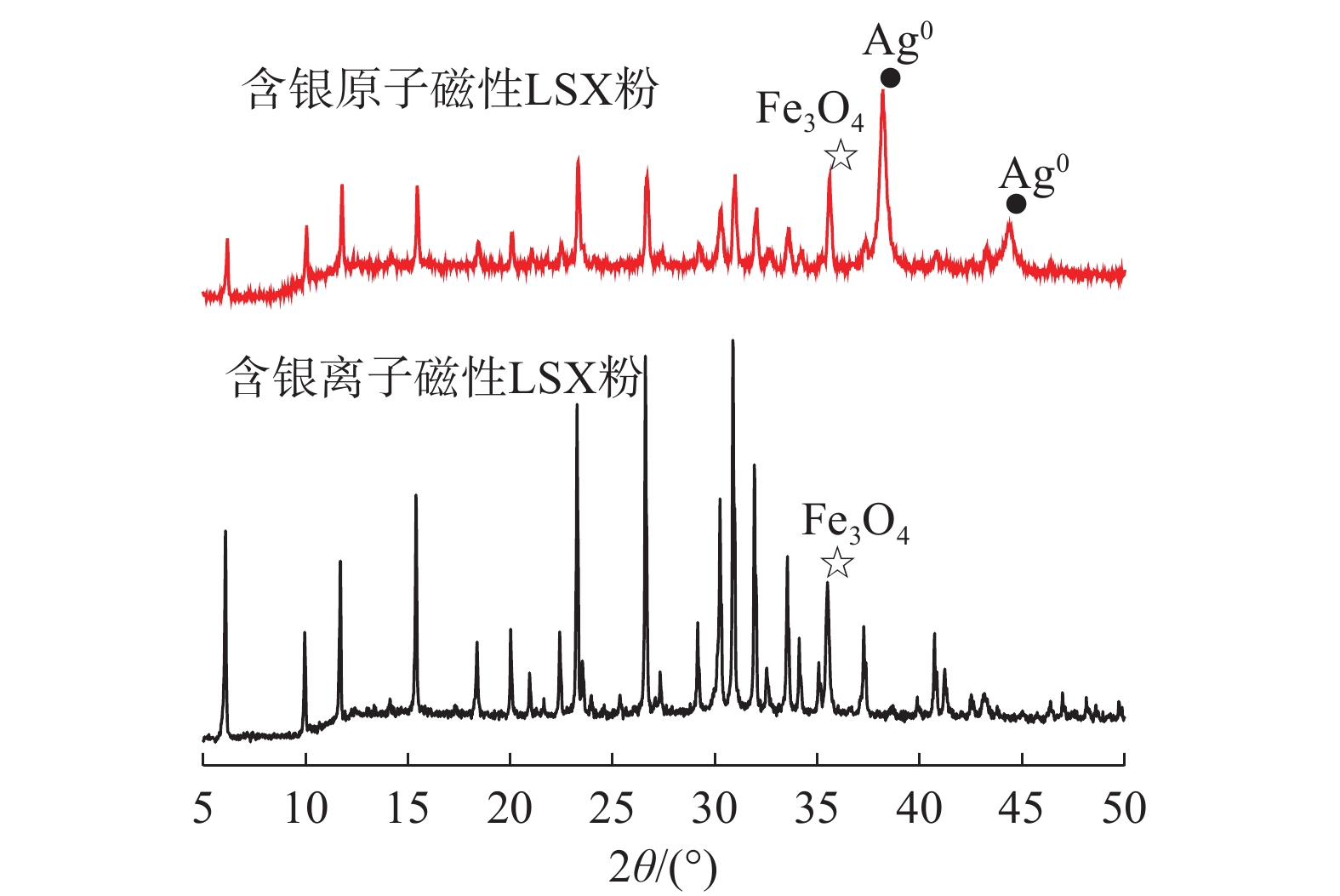
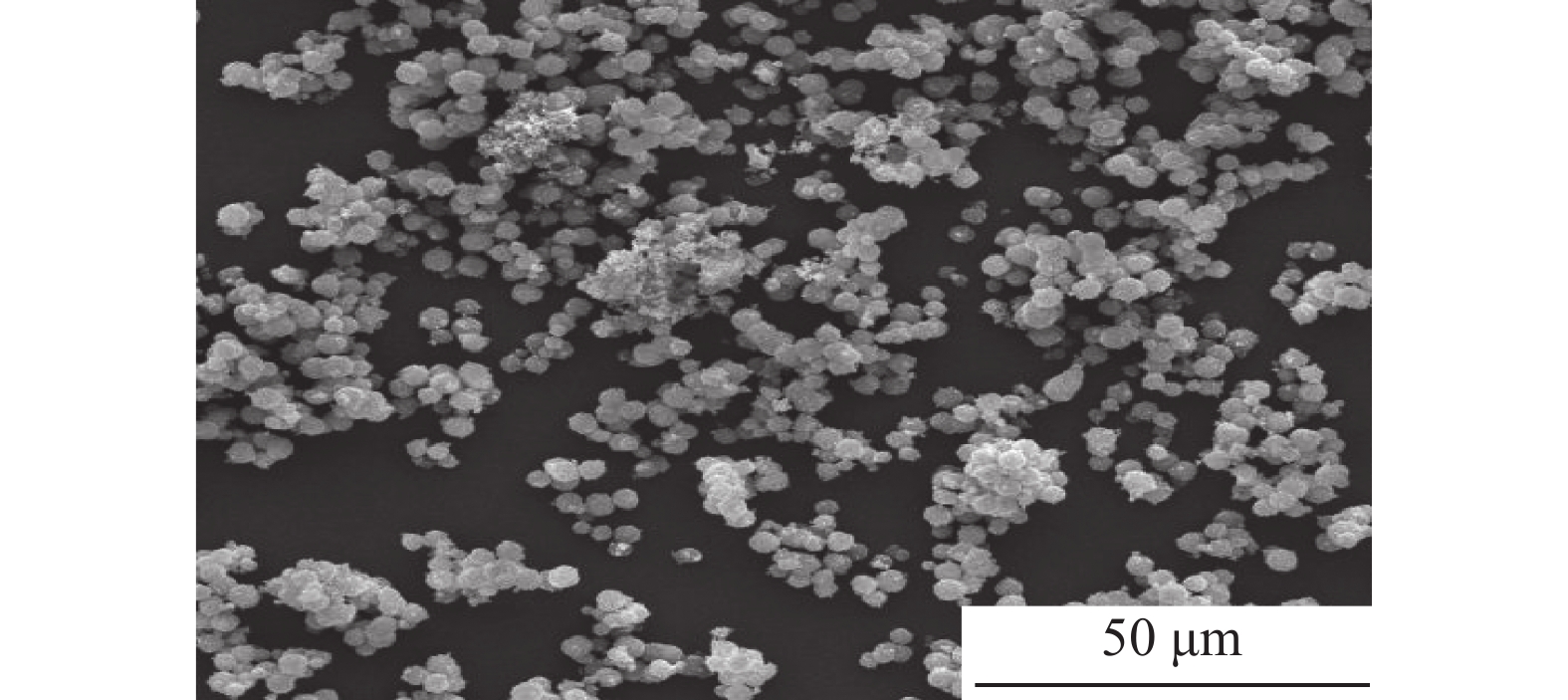
这是一篇材料学领域的论文。采用胶体导向剂与Fe3O4制备了磁性LSX分子筛原粉,经银离子交换与水合肼还原后生成了含银原子的磁性LSX分子筛,利用扫描电镜、振动样品磁强计、X衍射分析仪、光电子能谱仪、比表面吸附仪对样品的表面形貌、磁性、物相结构、元素组成与比表面积进行了分析表征,结果表明磁性LSX分子筛为LSX分子筛与Fe3O4的复合材料,微孔比表面积为679.38 m2/g,合成时胶体导向剂较佳加入量0.5%,磁性随Fe3O4加入量增加而增大,经银交换后与水合肼还原后的磁性LSX分子筛,比表面积减少。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of materials science. Magnetic LSX molecular sieves were prepared by colloidal directing agent and Fe3O4. After silver ion exchange and hydrazine hydrate reduction, magnetic LSX molecular sieves containing silver atoms were prepared, the surface morphology, magnetic properties, phase structure, elemental composition and specific surface area of the samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, X-ray diffraction analyzer, photoelectron spectroscopy and specific surface adsorption instrument. The results showed that magnetic LSX molecular sieve is the composite material of LSX molecular sieve and Fe3O4. The micropore specific surface area was 679.38 m2/g. The optimum dosage of colloidal guide agent was 0.5%. The magnetic properties increased with the increase of Fe3O4 content. The specific surface area of magnetic LSX molecular sieve reduced after silver exchange with hydrazine hydrate.
-
Key words:
- Directing agent /
- Magnetic /
- LSX molecular sieve /
- Silver ion /
- Silver atom
-

-
表 1 磁性LSX原粉静态水吸附量
Table 1. Static water adsorption capacity of magnetic LSX raw powders
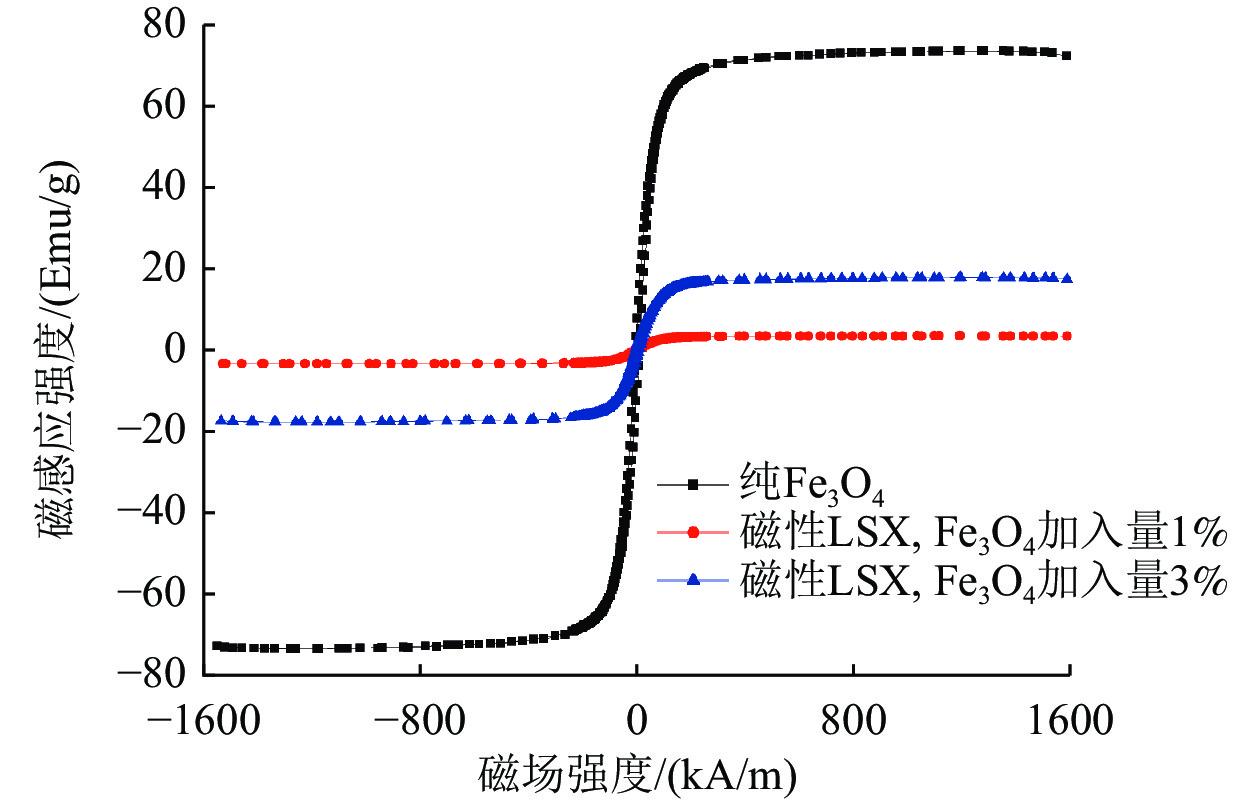
编号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 胶体导向剂加入量/% 0 0.5 1 1.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Fe3O4加入量/% 0 0 0 0 1 3 5 25 ℃/75%Rh吸水量/% 30 30.6 26.9 12.3 25.3 20.1 17.7 注:1号样品为商业化LSX粉体,无磁性,用于性能对照。 表 2 三种材料的饱和磁场强度与饱和磁感应强度
Table 2. Saturation magnetic field intensity and saturation magnetic induction intensity of three materials
名称 饱和磁场
强度/(kA/m)饱和磁感应
强度/(emu/g)纯Fe3O4 1 184.0 73.50 磁性LSX,Fe3O4加入量1% 1 189.6 3.41 磁性LSX,Fe3O4加入量3% 1 188.8 17.71 表 3 磁性LSX型分子筛的拟合参数与比表面积
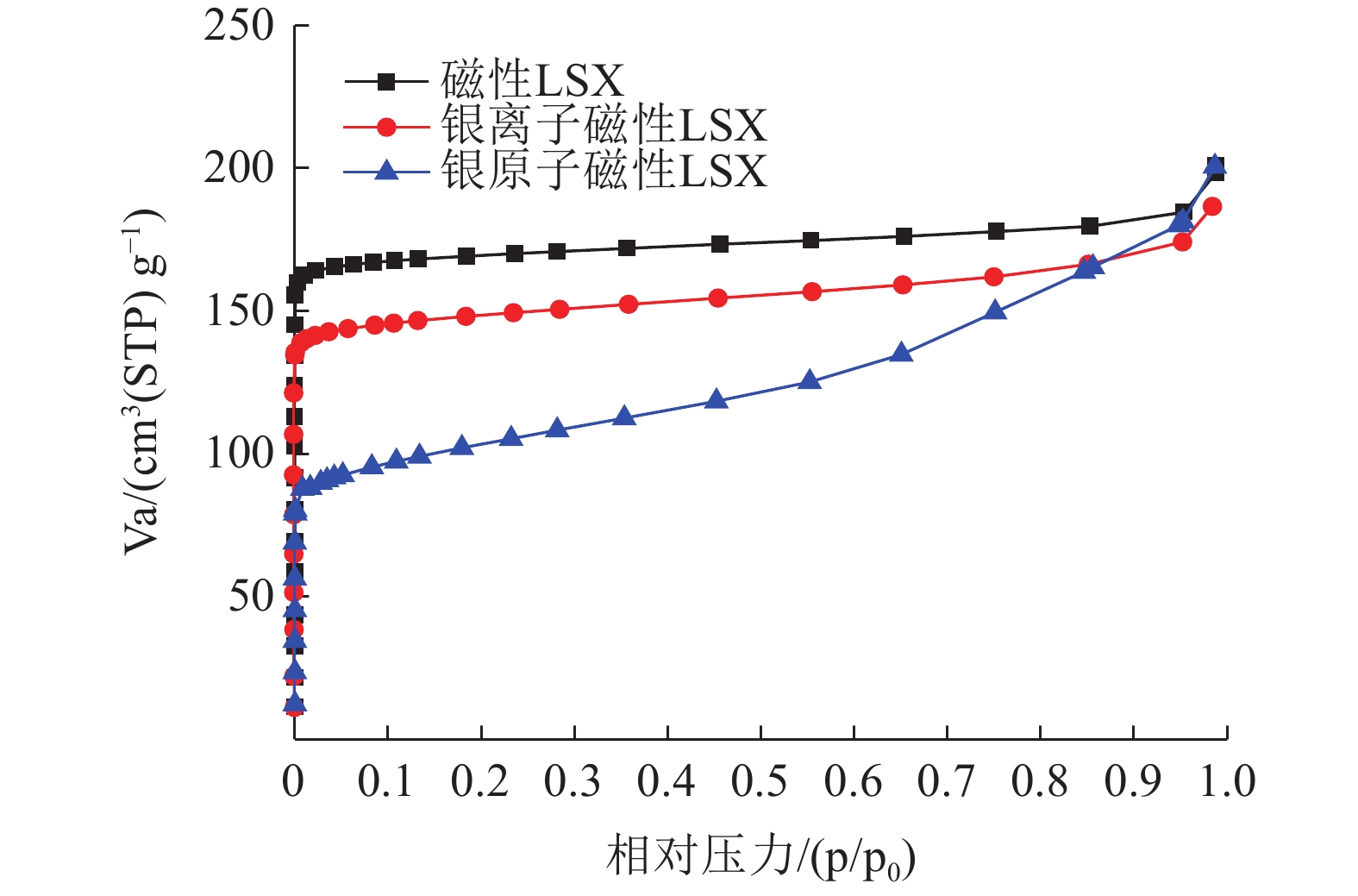
Table 3. Fitting parameters and specific surface area of magnetic LSX molecular sieve
名称 拟合
截距/
mL拟合
斜率/
mL拟合
系数微孔比
表面积
S/(m2/g)磁性LSX原粉 -2.35×10-6 0.006 42 0.999 77 679.38 含银离子的磁性LSX -2.41×10-6 0.007 39 0.999 83 590.18 含银原子的磁性LSX 2.06×10-6 0.011 35 0.999 97 384.07 -
[1] 曹吉林, 闫栋梁, 刘秀伍, 等. 磁性4A沸石制备及其对水中氯乙酸吸附[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2008, 24(5):400-407.CAO J L, YAN D L, LIU X W, et al. Preparation of magnetic 4A zeolite and its adsorption of chloroacetic acid in water[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2008, 24(5):400-407.
CAO J L, YAN D L, LIU X W, et al. Preparation of magnetic 4A zeolite and its adsorption of chloroacetic acid in water[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2008, 24(5):400-407.
[2] 曹研彦. 4A磁性分子筛的制备及吸附性能研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2016.CAO Y Y. Preparation and adsorption properties of 4A magnetic molecular sieves [D]. Taiyuan: North Central University, 2016.
CAO Y Y. Preparation and adsorption properties of 4A magnetic molecular sieves [D]. Taiyuan: North Central University, 2016.
[3] 王维清, 冯启明, 董发勤, 等. 磁性5A沸石的制备及其性能[J]. 功能材料, 2010, 41(1):26-28.WANG W Q, FENG Q M, DONG F Q, et al. Preparation of magnetic 5A zeolite and its properties[J]. Functional Materials, 2010, 41(1):26-28.
WANG W Q, FENG Q M, DONG F Q, et al. Preparation of magnetic 5A zeolite and its properties[J]. Functional Materials, 2010, 41(1):26-28.
[4] 杨建利, 杨小刚, 李刚, 等. 超声法制备磁性分子筛及其性能研究[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(5):1099-1102.YANG J L, YANG X G, LI G, et al. Preparation of magnetic molecular sieves by ultrasonic method and study of their properties[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2019, 48(5):1099-1102.
YANG J L, YANG X G, LI G, et al. Preparation of magnetic molecular sieves by ultrasonic method and study of their properties[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2019, 48(5):1099-1102.
[5] 彭巧玲, 成岳, 胡星. 磁性ZSM-5分子筛的合成及吸附性能研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2014, 50(11):25-28.PENG Q L, CHENG Y, HU X. Synthesis and adsorption properties of magnetic ZSM-5 molecular sieves[J]. Chinese Ceramics, 2014, 50(11):25-28.
PENG Q L, CHENG Y, HU X. Synthesis and adsorption properties of magnetic ZSM-5 molecular sieves[J]. Chinese Ceramics, 2014, 50(11):25-28.
[6] Nah I W, Hwang K Y, Shul Y G. A simple synt hesis of magnetically modified zeolite[J]. Powder Technology, 2007, 177(2):99-101. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2007.02.044
[7] Wu Y, Li C, Bai J, et al. T he fabrication of porous 4A-zeolite-supported Ag nanoparticles catalysts and its catalytic activity for styrene epoxidation[J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 1616-1622.
[8] Mu hammad J K, Suriya K Kamyar S, et al. Green synt hesis and characterization of pullulan mediated silver nanoparticles through ultraviolet irradiation [J]. Materials, 2019, 12(15): 2382-2393.
[9] Maolin Pang, Jiangyong Hu, Hua Chun Zeng. Synthesis, morphological control, and antibacterial properties of hollow/solid Ag2S/Ag heterodimers[J]. J Am C hem Soc, 2010, 132:10771-10785. doi: 10.1021/ja102105q
[10] J F Moulder, W F Stickle, P E Sobol, et al. Handbook of X ray p hotoelectron spectroscopy: a reference book of standard spectra for identification and interpretation of XPS data, physical electronics[J]. Inc. , Eden Prairie, Minnesota, 1995.
[11] Hernandez M A, Rojas F, Lara V h. Nitrogen-sorption characterization of the microporous structure of clinoptilolite-type zeolites[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2000, 7:443-454. doi: 10.1023/A:1009662408173
-



 下载:
下载: