Preparation of Mn-Zn Spinel Ferrite by Solid-phase Sintering of Zinc-containing Electric Furnace Dust
-
摘要:
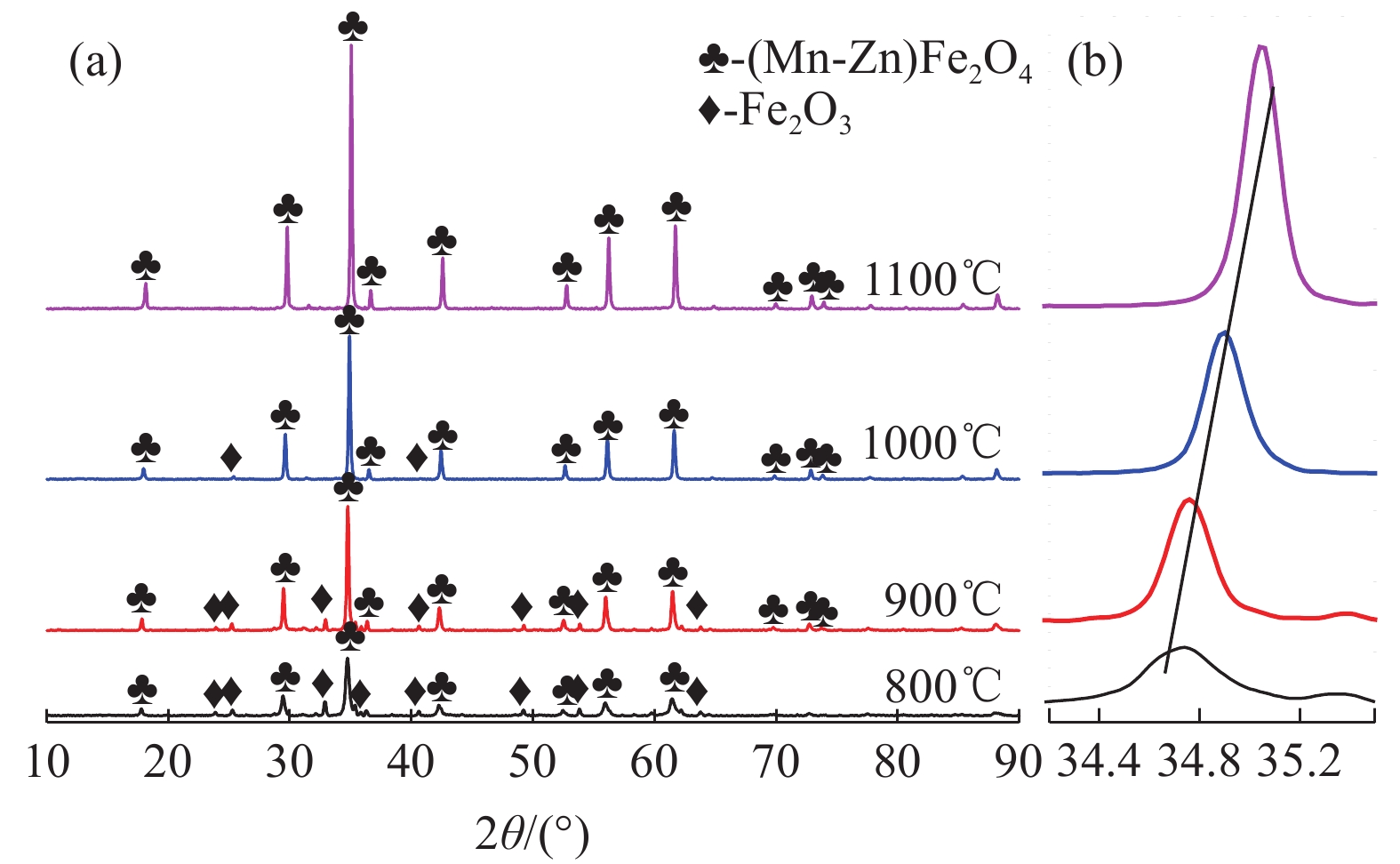
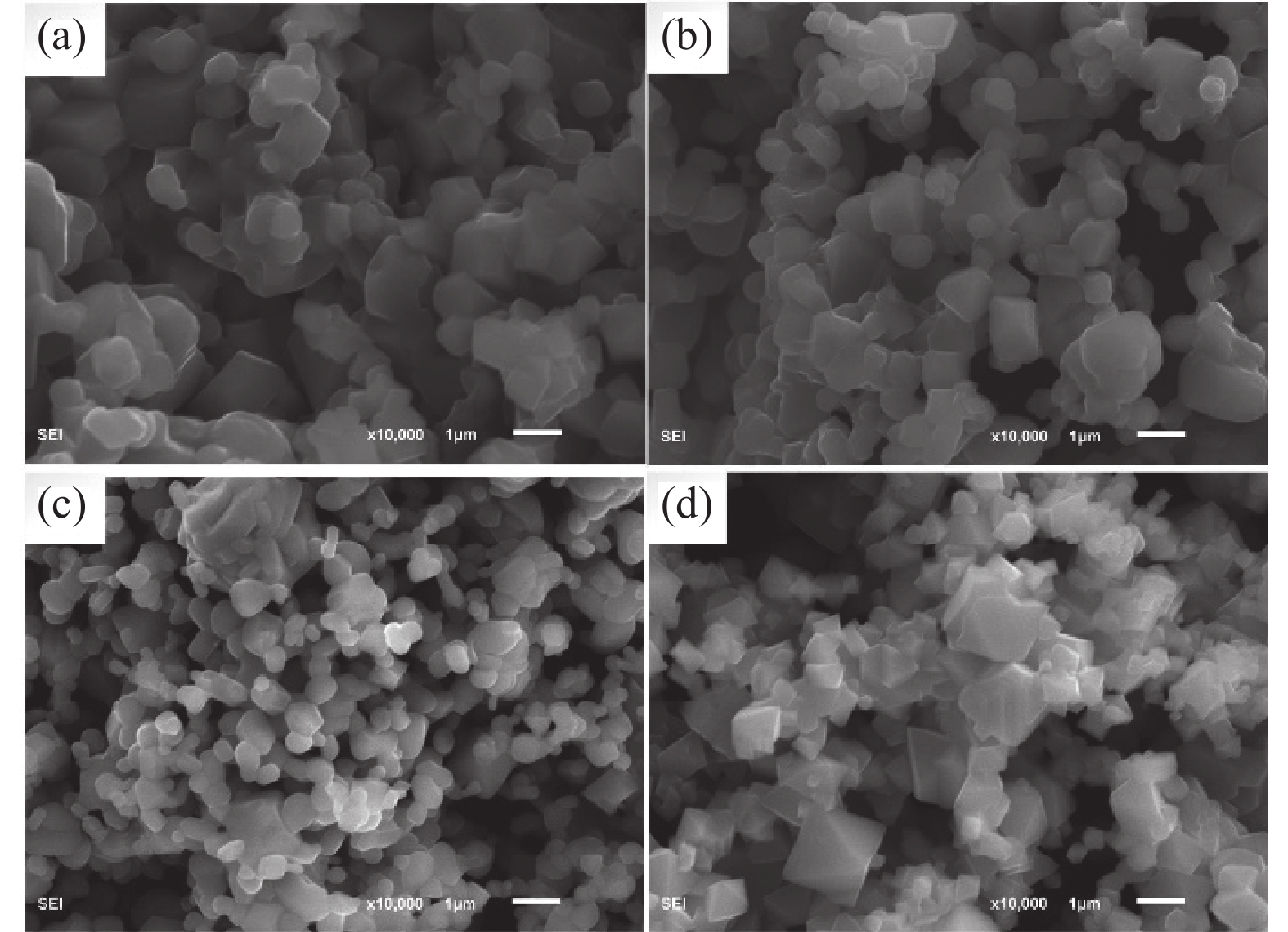
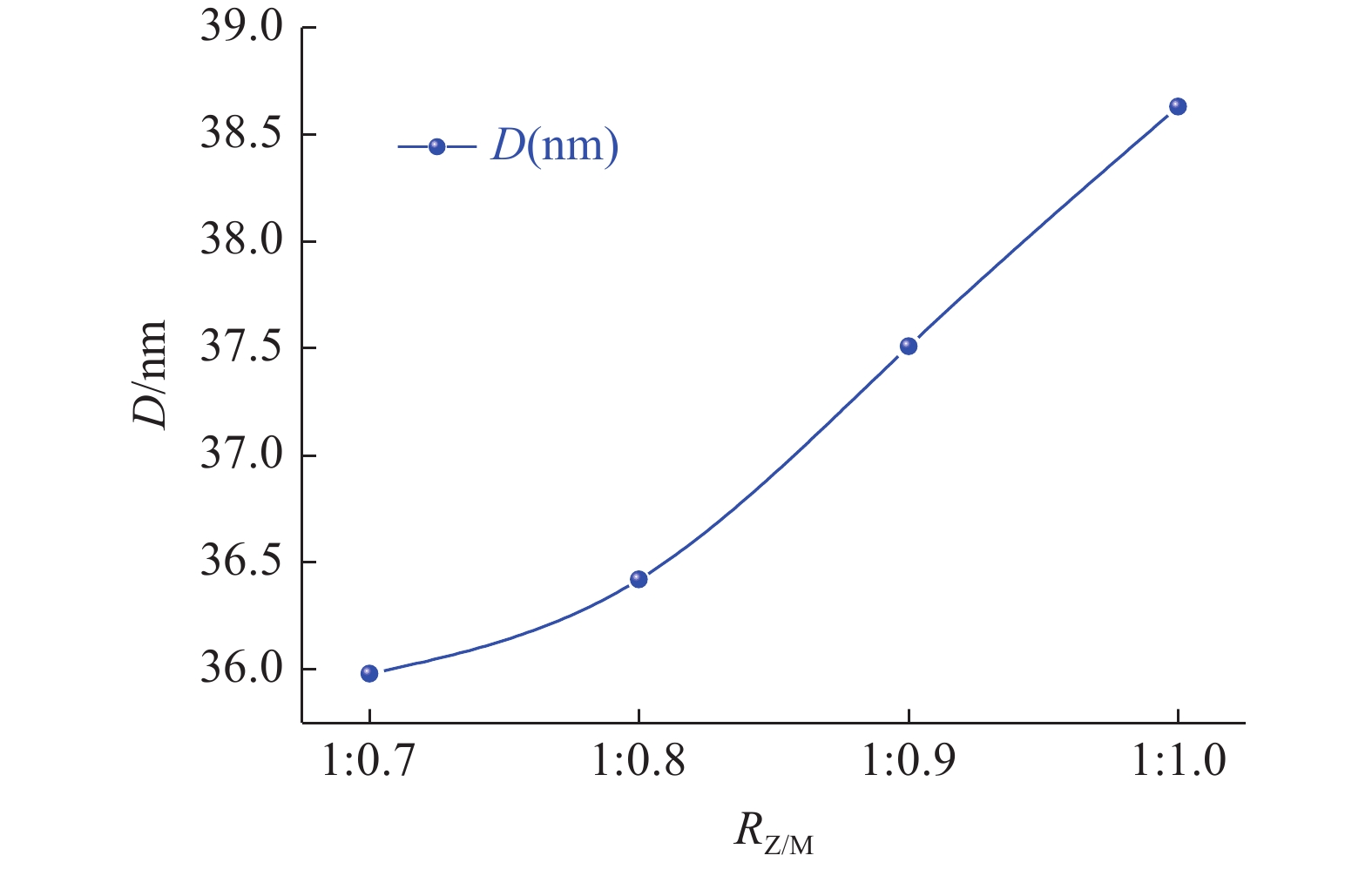
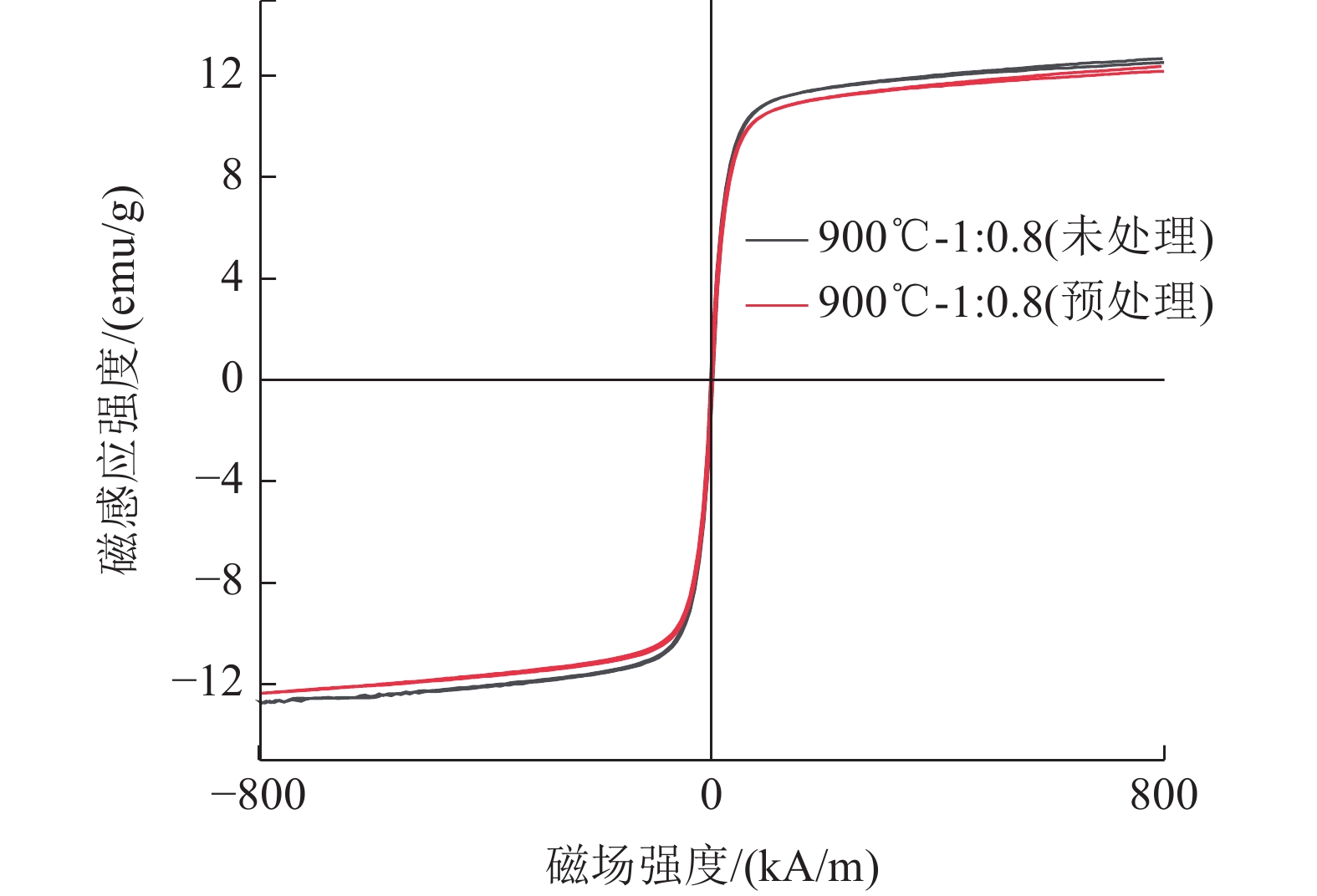
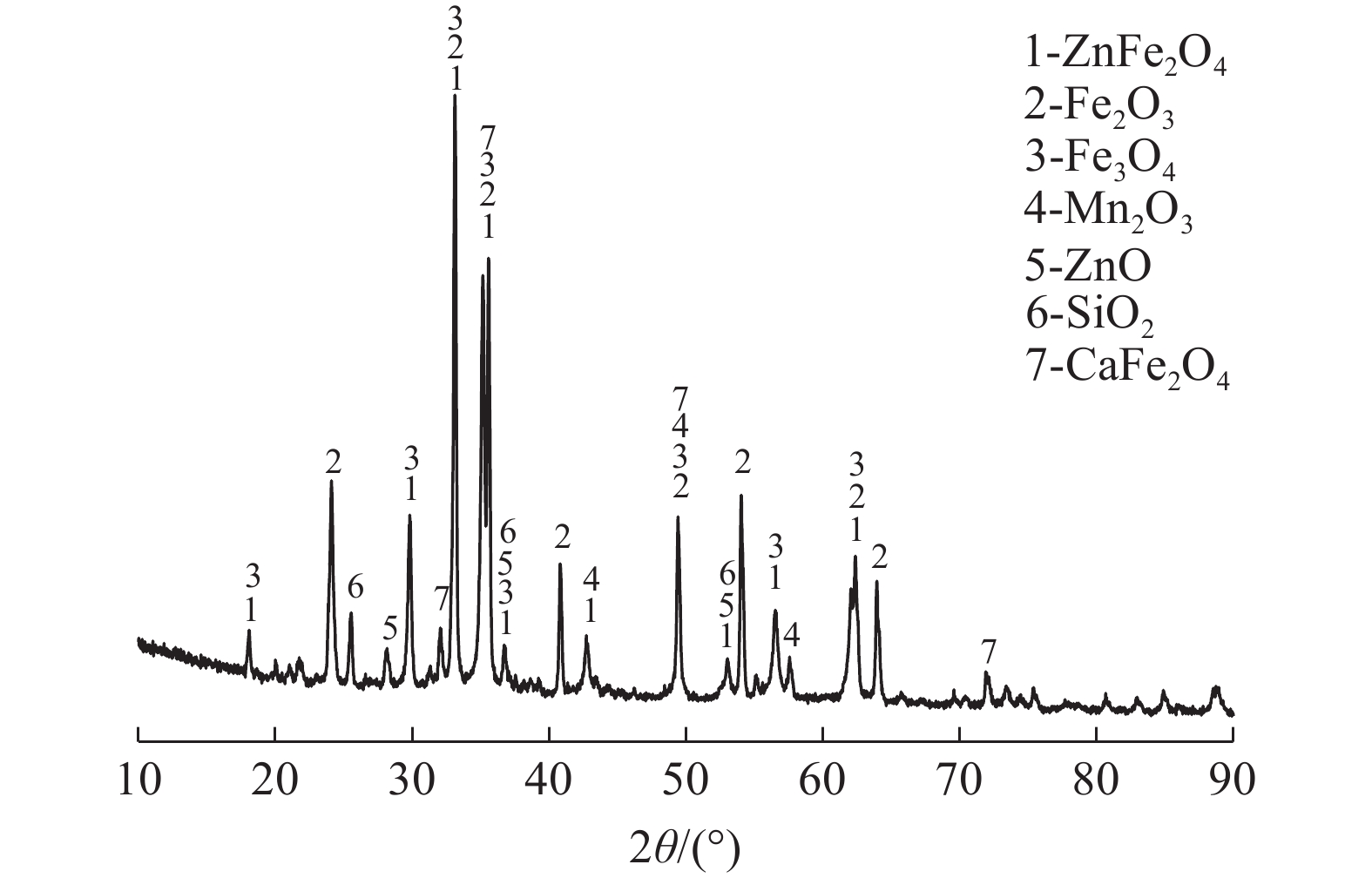
这是一篇冶金工程领域的论文。锰锌尖晶石铁氧体由于其具有高磁导率和高频低损耗等优点,被广泛应用于各领域。为充分利用电炉粉尘中的Fe、Zn、Mn等元素,以碱浸法处理过的含锌电炉粉尘为原料,加入MnSO4·H2O,采用固相烧结法制备Mn-Zn尖晶石铁氧体。通过XRD、SEM-EDS、VSM等,探讨温度、配比(RZ/M)、预处理对Mn-Zn铁氧体的合成及磁性能的影响。结果表明,当反应温度升高,锰锌铁氧体中的晶粒间吞并速度加剧,饱和磁感应强度和晶粒尺寸增加,而矫顽力减小。当RZ/M变化到1∶1.0,饱和磁感应强度、矫顽力和晶粒尺寸均增加。预处理后的电炉粉尘中的SiO2含量降低,合成的锰锌铁氧体的磁饱和强度增加。因此,经过浓度为2 mol/L的碱液预处理后,在质量比为1∶1.0、煅烧温度为1 100 ℃的固相反应条件下合成的锰锌尖晶石铁氧体性能较好,其饱和磁感应强度(Ms)为17.902 emu/g,矫顽力(Hc)为3.21 kA/m。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of metallurgical engineering. Mangane-zinc spinel ferrite has been widely used in various fields due to its advantages of high permeability, high frequency and low loss. In order to make full use of Fe, Zn, Mn and other elements in electric arc furnace dust (EAFD), Mn-Zn spinel ferrite was prepared by solid phase sintering method with alkali leaching zinc-containing EAFD as raw materials and MnSO4·H2O added. The effects of temperature, mass ratio (RZ/M) and pretreatment on the synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrite were investigated by XRD, SEM-EDS and VSM. The results show that with the increase of reaction temperature, the speed of inter-grain merging in the Mn-Zn ferrite increases, the magnetic saturation induction and crystal grain size increase, and the coercivity decreases. When RZ/M changes to 1∶1.0, the magnetic saturation induction, coercivity and grain size increase. After pretreatment, the content of SiO2 in the EAFD decreases, and the magnetic saturation strength of the synthesized manganese-zinc ferrite increases. Therefore, after pretreatment with 2 mol/L alkali solution, the performance of manganzn-spinel ferrite synthesized at the condition of mass ratio 1∶1.0 and calcination temperature 1 100 ℃ is the best. Its saturation magnetic induction intensity (Ms) is 17.902 emu/g, and coercivity (Hc) is 3.21 kA/m.
-

-
表 1 含锌电炉粉尘的化学成分/%
Table 1. Chemical composition of the zinc-containing electric furnace dust
Fe2O3 ZnO CaO C SiO2 MgO MnO K2O SO3 其他 73.32 14.21 2.98 2.83 2.04 1.09 1.38 0.73 0.66 0.76 表 2 含锌电炉粉尘的元素组成/%
Table 2. Elemental composition of zinc-containing electric furnace dust
样品 TFe Zn Ca Mn Si K Pb 其他 预处理前 78.113 13.062 3.892 1.446 1.151 0.657 0.085 1.594 预处理后 81.303 12.092 2.908 1.720 0.703 0.598 0.226 0.450 -
[1] 谭宇佳, 郭宇峰, 姜涛, 等. 含锌电炉粉尘处理工艺现状及发展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(3):44-50.TAN Y J, GUO Y F, JIANG T, et al. Current Status and Development of Zinc-containing Electric Furnace Dust Treatment Proces[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3):44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.03.007
TAN Y J, GUO Y F, JIANG T, et al. Current Status and Development of Zinc-containing Electric Furnace Dust Treatment Proces[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3):44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.03.007
[2] GAO J M, CHENG F. Effect of Metal Substitution on the Magnetic Properties of Spinel Ferrites Synthesized from Zinc-Bearing Dust[J]. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 2018(7):1965-1970.
[3] WANG HG, LIU W, JIA N, et al. Facile synthesis of metal-doped Ni-Zn ferrite from treated Zn-containing electricarc furnace dust[J]. Ceramics International, 2017(2):1980-1987.
[4] 朱军, 李维亮, 刘曼博, 等. 锌湿法冶炼渣的污染物分析及综合利用技术[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):59-65.ZHU J, LI WL, LIU M B, etal. Analysis of Contaminants and Comprehensive Utilization Technology of Zinc Hydrometallurgical Slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):59-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.009
ZHU J, LI WL, LIU M B, etal. Analysis of Contaminants and Comprehensive Utilization Technology of Zinc Hydrometallurgical Slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):59-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.009
[5] 朱应旭, 李兴彬, 邓志敢, 等. 含锌电炉烟尘氨浸预处理研究[J]. 有色金属工程, 2019(11):45-52.ZHU Y X, LI X B, DENG Z G, et al. Study on Ammonia Leaching Pretreatment of Zinc-containing Electric Are Furnace[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2019(11):45-52.
ZHU Y X, LI X B, DENG Z G, et al. Study on Ammonia Leaching Pretreatment of Zinc-containing Electric Are Furnace[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2019(11):45-52.
[6] 张晋霞, 冯洪均, 王龙, 等. 含锌冶金尘泥氨浸溶蚀实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):124-129.Zhang J X, Feng H J, Wang L, et al. Study on Treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia Leaching Process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
Zhang J X, Feng H J, Wang L, et al. Study on Treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia Leaching Process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
[7] 张家敏, 易建宏, 甘国友, 等. 微波烧结制备Mn-Zn铁氧体软磁材料[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2014(3):204-210.ZHANG J M, YI J H, GAN G Y, et al. Microwave sintering of Mn-Zn ferrite soft magnetic materials[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2014(3):204-210.
ZHANG J M, YI J H, GAN G Y, et al. Microwave sintering of Mn-Zn ferrite soft magnetic materials[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2014(3):204-210.
[8] 张家敏, 易建宏, 甘国友. 微波烧结Mn-Zn铁氧体的微观结构演变特征[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2014(2):17-23.ZHANG J M, YI J H, GAN G Y, et al. Microstructure characteristics of microwave sintered Mn-Zn ferrite soft magnetic materials[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014(2):17-23. doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20140204
ZHANG J M, YI J H, GAN G Y, et al. Microstructure characteristics of microwave sintered Mn-Zn ferrite soft magnetic materials[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014(2):17-23. doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20140204
[9] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 李松, 等. 含锌钢铁冶金渣尘处理技术现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):1-7.MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LIS, et al. Present Situation of Zinc Metallurgical Slags and Dusts Treatment Technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.001
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LIS, et al. Present Situation of Zinc Metallurgical Slags and Dusts Treatment Technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.001
[10] 刘敏, 陈奕初, 张珂, 等. 预压压强对镍锌铁氧体微观结构和磁性能的影响[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2021(3):68-71.LIU M, CHEN Y C, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of preloading pressure on the microstructure and magnetic properties of NiZn ferrite[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2021(3):68-71.
LIU M, CHEN Y C, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of preloading pressure on the microstructure and magnetic properties of NiZn ferrite[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2021(3):68-71.
[11] 王飞飞, 王琴琴, 张英才, 等. 锰锌铁氧体的制备及应用进展[J]. 铜仁学院学报, 2017(12):50-54.WANG F F, WANG Q Q, ZHANG Y C, et al. Research Development on the Fabrication and Application of Manganese Zinc Ferrite Materials[J]. Journal of Tongren University, 2017(12):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9639.2017.12.012
WANG F F, WANG Q Q, ZHANG Y C, et al. Research Development on the Fabrication and Application of Manganese Zinc Ferrite Materials[J]. Journal of Tongren University, 2017(12):50-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9639.2017.12.012
[12] KEBEDE K. KEFENI, TITUS A. M. MSAGATI, BHEKIE B. MAMBA. Ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterisation and applications in electronic device[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2017(1):37-55.
[13] 李佳伟, 李解, 林嘉威, 等. 白云鄂博超级铁精矿固相烧结制备M型锶铁氧体[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020(12):29-37.LI J W, LI J, LIN J W, et al. M-type Strontium Ferrite Prepared from Bayan Obo Super Iron Concentrate by Solid State Sintering[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020(12):29-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.12.005
LI J W, LI J, LIN J W, et al. M-type Strontium Ferrite Prepared from Bayan Obo Super Iron Concentrate by Solid State Sintering[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020(12):29-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.12.005
[14] GAO J M, YAN Z K, JING L, et al. Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Zn substituted Ni-Co-Mn-Mg ferrites[J]. Materials Letters, 2015(15):122-124.
[15] 丁文澜. 环境温度对永磁铁氧体球磨的影响[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2014(1):43-46.DING W L. Effect of Ambient Temperature on Permanent Ferrite Ball Milling[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2014(1):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5548.2014.01.010
DING W L. Effect of Ambient Temperature on Permanent Ferrite Ball Milling[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2014(1):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5548.2014.01.010
[16] 席国喜, 李伟伟, 路迈西. Mn-Zn铁氧体掺杂改性研究进展[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2007(2):19-22.XI G X, LI W W, LU M X, et al. Research Advance in Property Modification of Mn-Zn Ferrites by Doping and Substituing[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2007(2):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2007.02.004
XI G X, LI W W, LU M X, et al. Research Advance in Property Modification of Mn-Zn Ferrites by Doping and Substituing[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2007(2):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2007.02.004
[17] GHARAGOZLOU M. Synthesis, characterization and influence of calcination temperature on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline spinel Co-ferrite prepared by polymeric precursor method[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009(1):660-665.
[18] Birajdar A A, Shirsath S E, Kadam R H, et al. Role of Cr3+ ions on the microstructure development, and magnetic phase evolution of Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012(1):316-322.
[19] 陈昌, 李杨, 张岩昊, 等. 电炉粉尘预处理对其合成Ni-Zn铁氧体性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019(7):628-636.CHEN C, LI Y, ZHANG Y H, et al. Effect of pretreatment on magnetic property of synthesized Ni-Zn ferrite from electric arc furnace dust[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019(7):628-636.
CHEN C, LI Y, ZHANG Y H, et al. Effect of pretreatment on magnetic property of synthesized Ni-Zn ferrite from electric arc furnace dust[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019(7):628-636.
-



 下载:
下载: