Treatment of Arsenic Containing Waste Acid and Development of Arsenic Fixation Technology in Nonferrous Smelting
-
摘要: 有色冶炼的含砷污酸处置伴随着大量含砷危险废弃物的排放,给企业运行和外部环境造成了巨大压力。为避免环境污染和含砷危险废弃物二次处置,以"废渣减量化、无害化及资源化"为目的的污酸处置技术受到广泛的关注,对迁移性较强的含砷危废进行稳定化处置作为解决现有危废处置的中主要手段也是当前研究重点。本文综述了石灰铁盐法、硫化法、臭葱石沉淀法、浓缩法以及含砷污酸处置技术,结合污酸处置中产生的主要含砷固废特性,对污酸处置和固砷技术进行了详细的分析。根据当前污酸处置技术的工业应用和最新研究进展,对含砷污酸处置和固砷新技术进行了展望。Abstract: The disposal of arsenic-containing wastewater in nonferrous smelting is accompanied by the discharge of a large number of arsenic-containing hazardous wastes, which brings great pressure to the operation and external environment of enterprises. In order to avoid environmental pollution and the secondary disposal of arsenic-containing hazardous waste, the treatment technology of wastewater with the purpose of "waste residue reduction, harmless and recycling" has attracted wide attention. The stabilization treatment of arsenic-containing hazardous waste with strong migration is also the main means to solve the existing disposal of hazardous waste. In this paper, the lime iron salt method, sulfuration method, scorodite precipitation method, concentration method and arsenic-containing wastewater treatment technology are summarized. Combined with the main characteristics of solid waste containing arsenic in the wastewater treatment, the wastewater treatment and arsenic fixation technology are analyzed in detail. Based on the current industrial application and the latest research progress of wastewater treatment technology, the prospect of new technology of arsenic-containing wastewater treatment and arsenic fixation is prospected.
-
Key words:
- nonferrous smelting /
- arsenic /
- wastewater /
- arsenic fixation
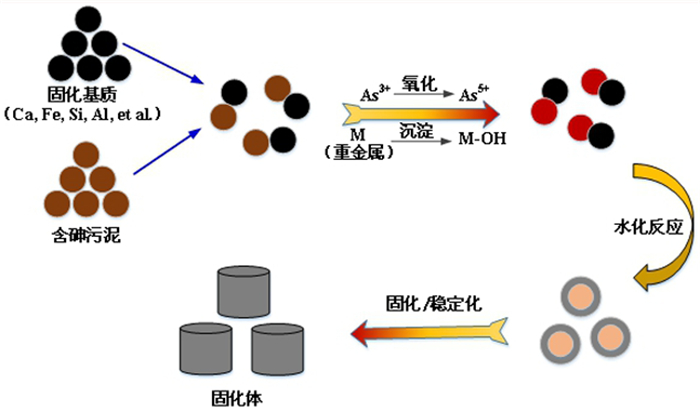
-

-
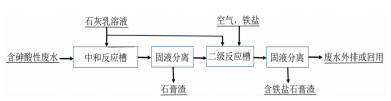
图 1 石灰-铁盐法除砷工艺流程[21]
Figure 1.
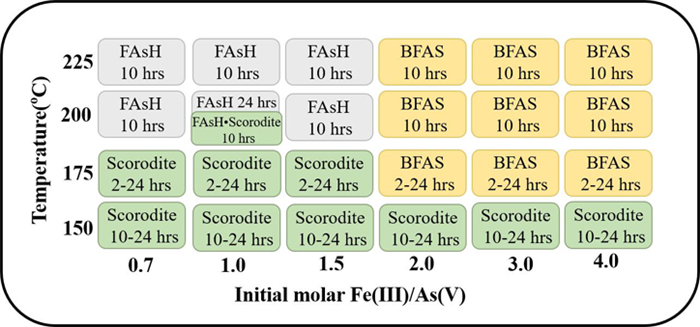
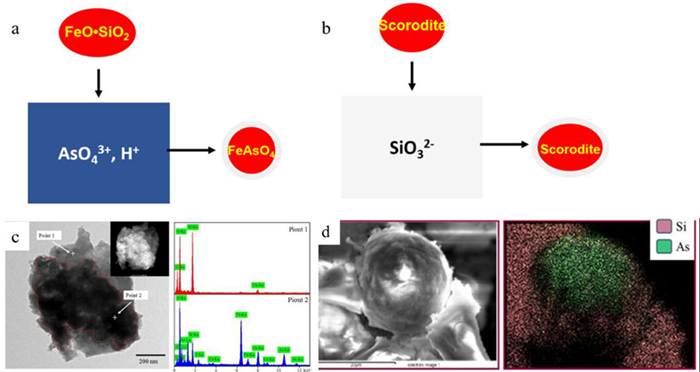
图 3 高压水热臭葱石合成路径或走向[33]
Figure 3.
表 1 含砷固废的特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of characteristics of solid waste containing arsenic
渣的种类 组成 毒性(As) 是否为危废 处置情况 石灰铁盐渣 石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)、砷酸钙(Ca3As2O8)、砷酸铁(FeAsO4) >5 mg/L 危险废弃物 第三方处理/渣库堆存 钙砷渣 砷酸钙(Ca3As2O8)或亚砷酸钙(Ca3(AsO3)2) >5 mg/L 危险废弃物 第三方处理/渣库堆存 硫化砷渣 硫化砷(As2S3) >5 mg/L 危险废弃物 第三方处理/渣库堆存 臭葱石 臭葱石(FeAsO4·2H2O)、砷酸铁(FeAsO4) < 5 mg/L 一般固体废弃物 第三方处理/渣库堆存 浓缩产物 三氧化二砷(As2O3) >5 mg/L 危险废弃物 第三方处理/渣库堆存 表 2 污酸处置工艺方法比较
Table 2. Comparison of treatment methods of wastewater
方法 工艺 特点 原料 运行条件 成本 废渣 技术成熟度 石灰铁盐法 石灰-聚合铁盐 工艺简单、处置成本低,无害化处置不彻底,二次危废渣量大 石灰、铁盐 对条件无特殊要求 低 大 成熟 硫化法 硫化钠+石灰铁盐法 硫化剂成本较高、硫化砷渣渣量大、二次石膏渣渣量大 硫化剂、石灰、铁盐 对条件无特殊要求 高 大 成熟 臭葱石沉淀法 中和-合成臭葱石-深度净化 无危废石膏渣产生,固砷矿物臭葱石毒性达标,废水可回用。反应条件敏感需一定外部热源 铁盐 一定外部热源 低 小 不成熟 浓缩法 浓缩-脱氟氯-重金属回收 可回收硫酸和重金属,能耗高、设备材质要求高 高温 常压蒸发 低 部分成熟 -
[1] LIU YIWEN, NGO HUUHAO, GUO WENSHAN, et al. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes:A review[J]. Environ Int, 2019, 123:10-19. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=af034777dc326147769b7194fd93498b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] MORALES-SIMFORS NURY, BUNDSCHUH JOCHEN, HERATH INDIKA, et al. Arsenic in Latin America:A critical overview on the geochemistry of arsenic originating from geothermal features and volcanic emissions for solving its environmental consequences[J]. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 716:135564. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b2d10099fee047e9c6a88eef714e0090&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 赵思佳.有色冶金工业含砷烟尘处理及利用研究进展[J].湖南有色金属, 2012, 28:20-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnysjs201203007
[4] WANG CHUNBO, LIU HUIMIN, ZHANG YUE, et al. Review of arsenic behavior during coal combustion:volatilization, transformation, emission and removal technologies[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2018, 68:1-28. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4473e64c31b6b534f81f2a1eafbfa059&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] MATSCHULLAT J. Arsenic in the geosphere-A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2000, 249:297-312. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=055eb9a7d5620bce34b5fe134d9a3636
[6] 刘树根, 田学达.含砷固体废物的处理现状与展望[J].湿法冶金, 2003, 12:11-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sfyj200504002
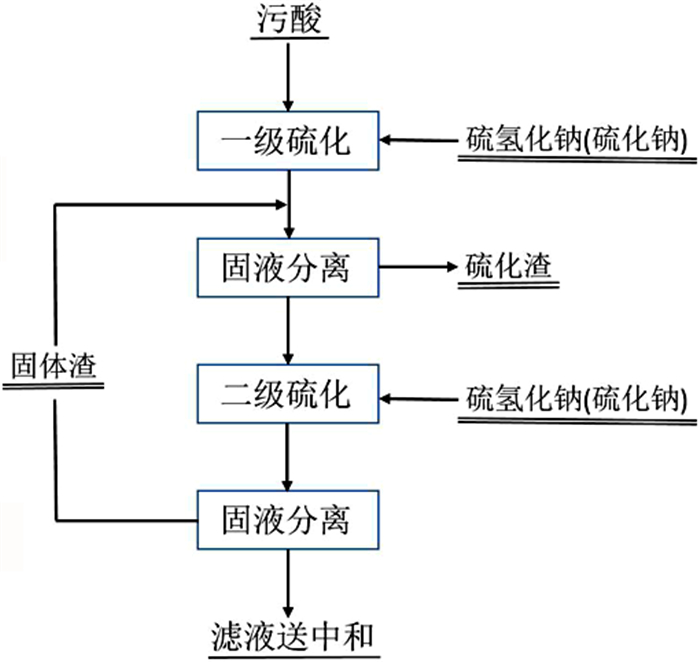
[7] 王培栋.硫化中和法除砷工艺探讨[J].新疆有色金属, 2012, 34:98-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tygc200902006
[8] BALLADARES EDUARDO, JEREZ O, PARADA F, et al. Neutralization and co-precipitation of heavy metals by lime addition to effluent from acid plant in a copper smelter[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 122:122-129. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0355015f1f725ed0517f4c30897b523c
[9] PAN ZHIHUA, ZHANG JUN, LIU WEIQING. Solidification/stabilization of zinc-lead tailings by alkali activated slag cement[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater Sci Ed, 2015, 30:105-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=whgydxxb-e201501021
[10] LIU DEGANG, MIN XIAOBO, KE YONG, et al. Co-treatment of flotation waste, neutralization sludge, and arsenic-containing gypsum sludge from copper smelting:solidification/stabilization of arsenic and heavy metals with minimal cement clinker[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2018, 25:7600-7607. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=321638be690ae90ad236e9475ae7ad4a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[11] RENEW JAY E, HUANG CHINGHUA, BURNS SUSAN E, et al. Immobilization of Heavy Metals by Solidification/Stabilization of Co-Disposed Flue Gas Desulfurization Brine and Coal Fly Ash[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30:5042-5051. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=814faedb7d31285a2580cc38567546ba&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] RATHORE VINEET KUMAR, MONDAL PRASENJIT. Stabilization of arsenic and fluoride bearing spent adsorbent in clay bricks:Preparation, characterization and leaching studies[J]. J Environ Manage, 2017, 200:160-169. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1f2c9502f1563038bc0929aa12e22cba&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] 廖天鹏, 祝星, 祁先进, 等.铜污泥中重金属形态分布及浸出毒性分析[J].化工进展2014, 33:21-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgjz201403051
[14] 三段逆流石灰法处理硫酸污水的试验[J].硫酸工业, 1974(3): 48-50.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LSGY197403010.htm [15] 刘祖鹏, 杜颖, 董冕, 等.污酸处理过程中基础问题分析[J].中国有色金属, 2018(S2):33-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSGY2018S2009.htm
[16] 易求实.三段石灰-铁盐法处理高砷污酸[J].硫酸工业, 2012(1):46-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lsgy201201015
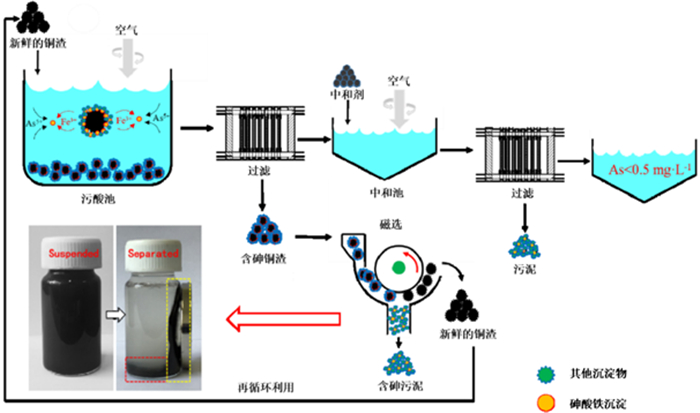
[17] QI XIANJIN, LI YONGKUI, WEI LONGHUA, et al. Disposal of high-arsenic waste acid by the stepwise formation of gypsum and scorodite[J]. Rsc Advances, 2020, 10:29-42. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=494cf0f81904e9eff0d05a974a4da538&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[18] 易求实.三段石灰-铁盐法处理高砷污酸[J].硫酸工业, 2012(1):46-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lsgy201201015
[19] 边德军, 任庆凯, 田曦, 等.有色金属冶炼含砷铁酸性废水处理工艺设计方案[J].环境科学与技术: 157-159.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FJKS201005038.htm [20] 贺瑞萍, 李从茂, 李昆洋, 等.铁盐法电絮凝联合除砷工艺的应用[J].硫酸工业: 19-22.
http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92246X/201406/663364333.html [21] 邢慧琳, 黄海辉.含砷酸性废水处理工艺现状与展望[J].中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(9):34-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgzyzhly201909011
[22] 郑雅杰, 彭映林, 李长虹.二段中和法处理酸性矿山废水[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(5):1215-1219. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zngydxxb201105007
[23] 姚瑛瑛, 杜颖, 郭莉, 等.双钙法"污酸"处理过程中特征污染物的迁移转化[C].中国环境科学学会, 2017: 735-743.
[24] ADELMAN J.G, ELOUATIKl S, DEMOPOULOS G.P. Investigation of sodium silicate-derived gels as encapsulants for hazardous materials-The case of scorodite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 292: 108-117.
[25] 黎铉海, 杜晓娟, 蒋书霞, 等.硫化氢法净化并循环使用含砷稀酸的试验研究[J].广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 39(5):1149-1153. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdxxb201405028
[26] 应国民.沉淀法脱除污酸中砷的研究[J].昆明理工大学, 2016, 32:12-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ky201702016
[27] 蔡晨龙, 杨应宝, 陈全坤, 等.污酸两段硫化除砷工艺[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2019, 12:34-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxysjs201904004
[28] 杨中超, 朱利军, 刘锐平, 等.强酸性高浓度含砷废水处理方法与经济性评价[J].环境工程学报, 2014, 8:2205-2210. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjwrzljsysb201406010
[29] 张文岐, 朱晓刚, 李晓恒, 等.铜冶炼废酸硫化法除砷工艺的改进实践[J].有色冶金节能, 2019, 35:14-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ycyjjn201903005
[30] NAZARI A.M, RADZINSKI R, GHAHREMAN A. Review of arsenic metallurgy: Treatment of arsenical minerals and the immobilization of arsenic[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 174: 258-281.
[31] DURTIZAC J.E., JAMBOR J.L. The synthesis of crystalline scorodite, FeAsO4·2H2O[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1988, 19: 377-384.
[32] GOMEZ M.A, BECZE L, CUTLER J.N, et al. Hydrothermal reaction chemistry and characterization of ferric arsenate phases precipitated from Fe2(SO4)3-As2O5-H2SO4 solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 107: 74-90.
[33] FUJITA T, TAGUCHI R, ABUMIYA M, et al. Novel atmospheric scorodite synthesis by oxidation of ferrous sulfate solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 90:92-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4d4f9abf276d6fef8cfec67a7484f6c5
[34] DEMOPOULOS G.P, DROPPERT D.J, WEERT G.V. Precipitation of crystalline scorodite (FeAsO4·2H2O) from chloride solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 38: 245-261.
[35] FUJITA T, FUJIEDA S, SHINODA K, et al. Environmental leaching characteristics of scorodite synthesized with Fe(Ⅱ) ions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 111-112:87-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d02a589ca14027c028a4cc9e79a42ebe
[36] CAI GUIYUAN, ZHU XIANG, LI KONGZHAI, et al. Self-enhanced and efficient removal of arsenic from waste acid using magnetite as an in situ iron donator[J]. Water Res, 2019, 157:269-280. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ddc8eca08a9c626ea339f73a63744d9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[37] LI YONGKUI, ZHU XING, QI XIANJIN, et al. Removal and immobilization of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater using copper slag by in situ encapsulation with silica gel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 394:124833. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=402a5db294eb4cb8d5e495d9dcf0f993&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[38] LI YONGKUI, ZHU XING, QI XIANJIN, et al. Efficient removal of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater in form of scorodite using copper slag[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020:122428. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652620324756
[39] 陈华盛, 夏光华, 刘晓来.冶炼污酸蒸发浓缩处理的试验研究[J].浙江化工, 2015:44-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZJHG201508014.htm
[40] 徐孝义, 张大超, 董冰岩, 等.高氟高氯酸性废水处理试验研究[J].江西理工大学学报, 2015, 36(3):13-18. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=6409477
[41] SAVAGE K.S, BIRD D.K, O'Day P.A. Arsenic speciation in synthetic jarosite[J]. Chem Geol, 2005, 215: 473-498.
[42] GOMEZGONZALEZ M.A, BOLEA E, O'Day P.A, et al. Combining single-particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and X-ray absorption spectroscopy to evaluate the release of colloidal arsenic from environmental samples[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 408: 1-11.
[43] LI XUN, ZHU XING, QI XIANJIN, et al. Pyrolysis of arsenic-bearing gypsum sludge being substituted for calcium flux in smelting process[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2018, 130:19-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e4ff90e04d4c88176a94fc55503d6c09
[44] DING JIAQI, WANG XIN, WANG LINLING, et al. A review of industrial arsenic-containing sludge:characteristics and treatment technologies[J]. Environment Engineering, 2019, 37:167-172.
[45] FAN CHENGCHENG, WANG BAOMIN, ZHANG TINGTING. Review on Cement Stabilization/Solidification of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2018:12-25. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ded8850dd595ab33d38b66ae7e556945&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[46] GONG YANYAN, ZHAO DONGYE, WANG QILIN. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids:Technical progress over the last decade[J]. Water Research, 2018, 147:440-460. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=41bf642e508095834ee55d65ad01b1ef&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[47] TONIOLO N, BOCCACCINI A.R. Fly ash-based geopolymers containing added silicate waste. A review[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43: 14545-14551.
[48] TRAN HUYEN, GOWRIPALAN N. Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Immobilisation using Geopolymerisation Techniques-A review[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2018, 16:124-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_3583064
[49] YOUSUF M, MOLLAH A, VEMPATI R.K, et al. The interfacial chemistry of solidification/stabilization of metals in cement and pozzolanic material systems[J]. Waste management, 1995, 15: 137-148.
[50] HUANG XIAO, ZHANG RANLIANG, MUHAMMAD FAHEEM, et al. Solidification/stabilization of chromite ore processing residue using alkali-activated composite cementitious materials[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 168:300-308. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=fbe7a99ccc0861d0591d3a03940ac884&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[51] LUNA GALIANO Y, FERNANDEZ PEREIRA C, VALE J. Stabilization/solidification of a municipal solid waste incineration residue using fly ash-based geopolymers[J]. 2011, 185: 373-381.
[52] DUTRE, VANDECASTEELE. Solidification/stabilization of arsenic-containing waste: Leach tests and behavior of arsenic in the leachate[J], 1995, 15: 55-62.
[53] CAMACHO LUCY MAR, MUNSON-MCGEE STUART H. Anomalous transient leaching behavior of metals solidified/stabilized by pozzolanic fly ash[J]., 2006, 137: 144-151.
[54] EL-ESWED BASSAM I, ALDAGAGl OMAR M, KHALILI FAWWAZ I. Efficiency and mechanism of stabilization/solidification of Pb(Ⅱ), Cd(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ), Th(IV) and U(VI) in metakaolin based geopolymers[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 140:148-156.
[55] KIM JUNG WOOK, JUNG MYUNG CHAE. Solidification of arsenic and heavy metal containing tailings using cement and blast furnace slag[J]. 2011, 33: 151-158.
[56] MING XIA, FAHEEM, MUHAMMAD, et al. Solidification/stabilization of lead-zinc smelting slag in composite based geopolymer[J], 2019, 17: 19-25.
[57] ORTABOY SINEM, LI JIAQI, GENG GUOQING, et al. Effects of CO2 and temperature on the structure and chemistry of C-(A-)S-H investigated by Raman spectroscopy[J]. RSC Adv, 2017, 7:48925-48933. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cb327ca781186ca881d2b4e5c7ed6b1b
[58] ZHAO ZONGWEN, CHAI LIYUAN, PENG BING, et al. Arsenic vitrification by copper slag based glass:Mechanism and stability studies[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2017, 466-467:21-28. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0691d549fbbca541f9df3e79ff62e531&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[59] 徐媛.含砷石膏渣水泥固化及强化机制研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2017, 31: 23-31.
[60] DUTRE V, VANDECASTEELE C. Solidification/stabilisation of hazardous arsenic containing waste from a copper refining process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1995, 40:55-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=11483706b40ca431e0e4f272002fc2e2
[61] YOON IN-HO, MOON DEOK HYUN, KIM KYOUNG-WOONG, et al. Mechanism for the stabilization/solidification of arsenic-contaminated soils with Portland cement and cement kiln dust[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91:2322-2328. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=04e6318f724a8cfc7bf74e2e394261c2
[62] MA XU, LI SHIFENG, YUAN ZIDAN, et al. Stabilization of Scorodite by Aluminum Silicate Microencapsulation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 145:04019010. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=150da576d28a93d9d34757f158198327
[63] KE PINGCHAO, LIU ZHIHONG. Synthesis, in-situ coating and characterization of scorodite with high leaching stability[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29:876-892. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgysjsxb-e201904022
[64] LEETMAA KARL, GUO FUQIANG, BECZE LEVENTE, et al. Stabilization of iron arsenate solids by encapsulation with aluminum hydroxyl gels[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2016, 91:123-134. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=309fa332a5a508c33bf6dc3b637d0f03&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[65] VIALS J, SUNYER A, MOLERA P, et al. Arsenic stabilization of calcium arsenate waste by hydrothermal precipitation of arsenical natroalunite[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104:247-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1fccae8b99bfe6f92cd92d490bd8e2ef
[66] QIU QILI, JIANG XUGUANG, LV GUOJUN, et al. Stabilization of Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash in Circulating Fluidized Bed by Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Treatment with Additives[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30:7588-7595. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9545612db3d376e66d5377537cf0dc35
[67] XU HUI, MIN XIAOBO, WANG YUNYAN, et al. Stabilization of arsenic sulfide sludge by hydrothermal treatment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 191:105229. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cf22bf83f2355dc533726e3165636d4f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[68] YAO LIWEI, MIN XIAOBO, XU HUI, et al. Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 2018, 15:1863-1873. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d55db01877c9805d548c34711d3bd80f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-



 下载:
下载: