Spherical quartz sandstone of Mesoarchean Yuanjiang Group in central Yunnan and its petrogenesis
-
摘要:
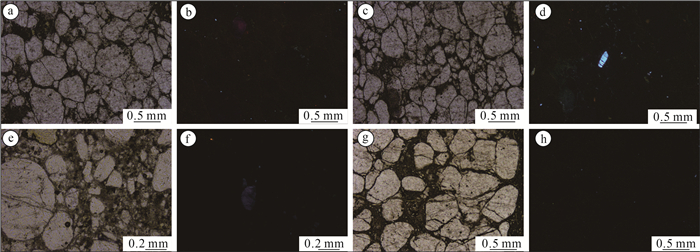
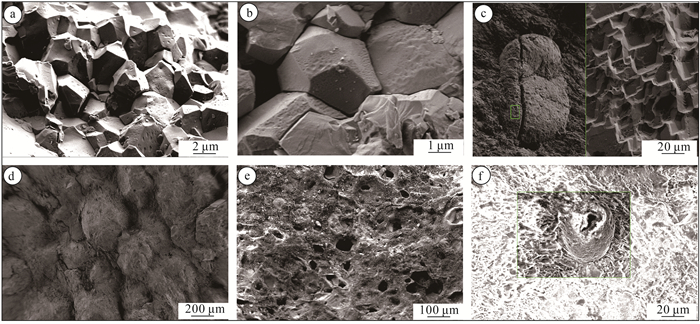
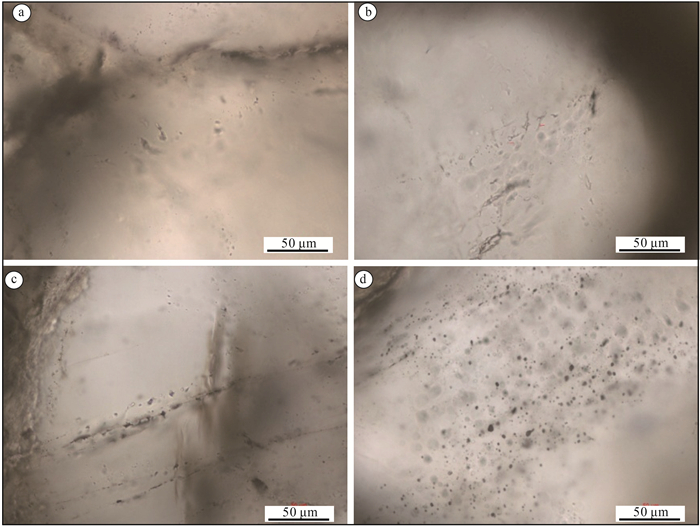
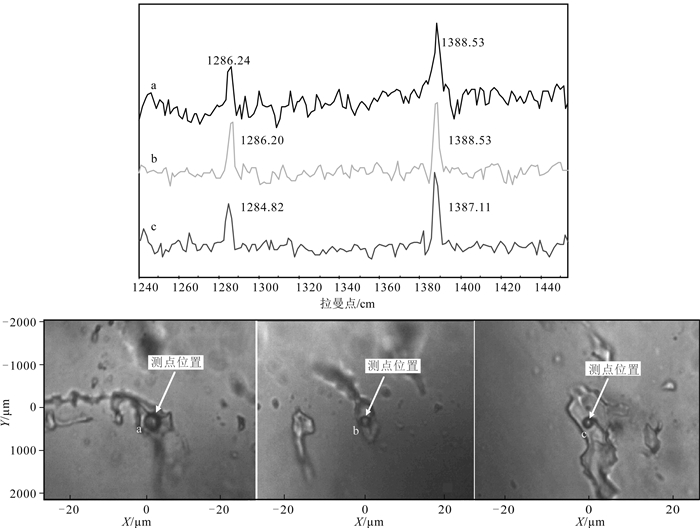
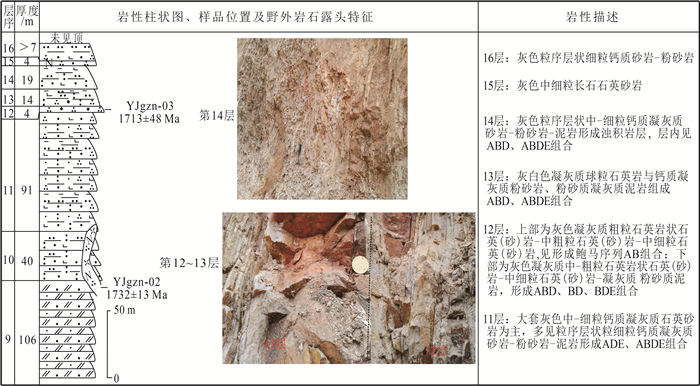
元江群是中国首次确定的中太古代浅变质地层,其记录了地球发展演化早期的一系列重大地质事件。在元江群下部的曼林组、岔河组中发育一类与火山岩、火山碎屑沉积岩、化学沉积的块状石英岩共生的特殊砂岩——球粒状石英砂岩。宏观上,球粒状石英砂岩既可与凝灰质泥质板岩、泥质板岩组成递变粒序层理,也可单独呈中-厚层状与凝灰岩、火山岩、石英岩相伴产出,表明这类球粒状石英砂岩形成于活动性较强的大地构造背景。多数石英颗粒在镜下呈近等轴的球状,部分颗粒在成岩过程中显示明显的塑性变形;球粒状石英颗粒在阴极发光照片中不发光或发微弱的蓝光。对其中的热液包裹体进行测试,结果表明,这些石英颗粒形成于温度为60~100℃的热水沉积环境,是在弱水动力条件下,SiO2含量过饱和的水体中沉淀形成的,属盆地内的自生矿物。对石英颗粒表面进行扫描,发现石英颗粒表面光滑,无擦痕,表明这些石英颗粒并未经历过长距离搬运,应属盆地内的原地-半原地沉积物。元江群下部曼林组中含有大量的凝灰质碎屑,与曼林组同期异相的迤纳厂组中普遍可见磁铁矿板岩、凝灰岩、块状含铜白云岩夹层等,指示了相似的沉积环境,表明当时火山活动较频繁,盆地水体温度总体较高,且变化较快。这类水体环境为最早的微生物提供了生存所需的能量,为中太古代末期蓝绿藻的大爆发奠定了基础。
Abstract:The Yuanjiang Group is a new lithostratigraphic unit in the central Yunnan region. It is the first time to identify the Mesoarchean shallow metamorphic strata in China, and it records a series of important geological events in the early stage of the earth's development and evolution. It was found that a typical quartz sandstone - spherical quartz sandstone was deposited in the Manlin Formation and Chahe Formation of the Lower Yuanjiang Group, associated with massive quartzite of volcanic, volcano-clastic and chemical sedimentary origin. On the macro level, the spherical quartz sandstone could be formed by graded bedding with tuff argillaceous slate and argillaceous slate, or it might be developed separately in medium-thick bedding with tuff, volcanic rock and quartzite, indicating that it was formed in an intensely active tectonic setting. The spherical quartz grains exhibit equal crystals, likely spherical crystal, showing no or slightly blue glass in the CL images, and could be formed by plastic growth. The results of hydrothermal inclusions test show that the quartz particles were formed from the SiO2-saturated water in the hydrothermal sedimentary environment of 60~100 ℃ under weak hydrodynamic conditions. They belong to authigenic minerals in the basin. Scanning the surface of quartz particles, it is found that the surface of quartz particles is smooth and has no scratches, indicating that these quartz particles were not transported over a long distance, and should belong to the autochthonous to semi-autochthonous sediments in the basin. The Manlin Formation in the Lower Yuanjiang Group contains a large number of tuffaceous detritus, and its contemporaneous different facies Yinachang Formation commonly contains magnetite slate, tuff, and massive copper-bearing dolomite intercalation, which indicates a similar sedimentary environment. It shows that the volcanic activity was more frequent, and the water temperature in the basin was generally higher and changed rapidly. Such a water environment provided the first microorganisms with the energy they needed to survive, seting the basis for a blue-green algae bloom at the end of the Middle Archean.
-

-
表 1 石英阴极发光特征分类[24]
Table 1. Classification of cathodeluminescence(CL)for quartz grains
发光颜色 温度条件 产状 以紫色为主,变化于蓝-紫、红-紫之间 >573℃,冷却快 火山岩 深成岩 接触变质岩 棕色 >373℃,冷却慢 深变质岩 变质的火成岩、变质的沉积岩 300~573℃ 浅变质岩 接触变质岩、区域变质岩、回火的沉积物 不发光 <300℃ 沉积物中的自生石英 表 2 曼林组球粒状石英砂岩中包裹体特征
Table 2. Data of temperature and salinity of spherical quartz grains from the Manlin Formation
序号 赋存矿物产状 包裹体分布形态 测温包裹体类型 包裹体形状 大小/μm 气液比/% 均一相态 T/℃ 盐度/NaCl % 1 石英颗粒微裂隙 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 15×9 10% 液相 146 23.18 2 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 20×6 10% 液相 144 23.18 3 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 5×5 10% 液相 138 23.18 4 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 11×7 5% 液相 125 23.18 5 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 5×3 5% 液相 120 23.18 6 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 5×2 10% 液相 134 23.18 7 石英颗粒微裂隙面 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 5×10 5% 液相 71 20.97 8 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 4×10 5% 液相 64 20.97 9 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 6×2 5% 液相 80 21.54 10 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 2×2 5% 液相 97 21.47 11 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 56×13 5% 液相 98 23.18 12 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 26×13 5% 液相 79 23.18 13 成带分布 富液体包裹体 规则 26×14 10% 液相 100 23.18 14 石英颗粒中 成群分布 富液体包裹体 规则 7×4 5% 液相 94 21.47 15 成群分布 富液体包裹体 规则 4×4 5% 液相 109 21.54 16 成群分布 富液体包裹体 规则 10×7 5% 液相 85 23.18 17 成群分布 富液体包裹体 规则 8×2 5% 液相 83 23.18 -
[1] 纪星星, 周诗, 陈棋, 等. 滇中地区昆阳群物源及构造环境[J]. 中国地质, 2016, (3): 857-878. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201603012.htm
[2] 尹福光, 孙志明, 白建科. 东川、滇中地区中元古代地层格架[J]. 地层学杂志, 2011, 35(1): 49-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201101009.htm
[3] 孙志明, 尹福光, 关俊雷, 等. 云南东川地区昆阳群黑山组凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(7): 896-900. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.07.009 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090709&flag=1
[4] 吕世琨, 戴恒贵. 康滇地区建立昆阳群(会理群)层序的回顾和重要赋矿层位的发现[J]. 云南地质, 2001, (1): 1-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2001.01.001
[5] 杜远生, 韩欣, 顾松竹, 等. 滇中中元古代昆阳群的地震事件沉积及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2001, 31(4): 283-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200104002.htm
[6] 牟传龙, 林仕良, 余谦. 四川会理-会东及邻区中元古界昆阳群沉积特征及演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2000, (1): 44-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2000.01.003
[7] 杜远生, 韩欣. 滇中中元古代昆阳群因民组碎屑风暴岩及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, (2): 259-262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.02.015
[8] 曹德斌. 滇中元江东昆阳群因民组-落雪组的厘定及其意义[J]. 云南地质, 1999, (2): 194-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199902009.htm
[9] 杜远生, 孙克祥, 李志伟. 云南元江地区中元古代昆阳群下亚群的沉积地质及控矿作用[J]. 地球科学, 1998, (1): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.1998.01.007
[10] 杜远生. 滇中地区中元古代昆阳群因民组中碎屑风暴岩的新发现[J]. 地球科学, 1998, (1): 33-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.1998.01.008
[11] 侯蜀光, 陆瑞芳, 薛顺荣, 等. 对滇中昆阳群因民组沉积相特征及其沉积类型的认识[J]. 云南地质, 1996(1): 31-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD601.002.htm
[12] 吴懋德, 段锦荪, 陈良忠. 云南昆阳群地质[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 1990: 1-224.
[13] 李静, 刘桂春, 刘军平, 等. 滇中地区早前寒武纪地质研究新进展[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(11): 1957-1969. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20181101&flag=1
[14] Folk R L. Petrology of sedimentary rocks[M]. Hemphill Publishing Company, Austin, 1980.
[15] Basu A, Young S, Suttner L, et al. Re-evaluation of the use of undulatory extinction and crystallinity in detrital quartz for provenance interpretation[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1975, 45(4): 873-882.
[16] Bernet M. Provenance Analysis by Single-Quartz-Grain SEM-CL/Optical Microscopy[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2005, 75(3): 492-500. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2005.038
[17] Boggs S, Kwon Y I, Goles G G, et al. Is Quartz Cathodoluminescence Color a Reliable Provenance Tool? A Quantitative Examination[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(3): 408-415. doi: 10.1306/102501720408
[18] Kwon Y I, Jr S B. Provenance interpretation of Tertiary sandstones from the Cheju Basin (NE East China Sea): a comparison of conventional petrographic and scanning cathodoluminescence techniques[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(1): 29-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073801002846
[19] Seyedolali A, Krinsley D H, Boggs S J, et al. Provenance interpretation of quartz by scanning electron microscope cathodoluminescence fabric analysis[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(9): 787-790. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0787:PIOQBS>2.3.CO;2
[20] Walker G, Burley S. Luminescence petrography and spectroscopic studies of diagenetic minerals[M]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1991: 83-96.
[21] 马收先, 孟庆任, 曲永强. 轻矿物物源分析研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2): 597-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201402021.htm
[22] Augustsson C, Bahlburg H. Cathodoluminescence spectra of detrital quartz as provenance indicators for Paleozoic metasediments in southern Andean Patagonia[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2004, 16(1): 15-26. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895981103000166
[23] Zinkernagel U. Cathodoluminescence of quartz and its application to sandstone petrology[J]. Contributions to Sedimentary Geology, 1978, 8: 1-69
[24] 史丹妮, 金巍. 砂岩中自生石英的来源、运移与沉淀机制[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 1999, 19(6): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXGD199906010.htm
[25] Tingate P R, Rezaee M R. Origin of quartz cement in Tirrawarra Sandstone, Southern Cooper Basin, South Australia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1997, 67(1): 168-177. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/50427580_Origin_of_quartz_cement_in_the_Tirrawarra_Sandstone_Southern_Cooper_Basin_South_Australia
[26] 于均民, 周晓峰, 刘立. 砂岩中石英胶结物的成因及其研究意义[J]. 世界地质, 2000, 19(1): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200001004.htm
[27] Worden R H, Barclay S A. Internally-sourced quartz cement due to externally-derived CO2 in sub-arkosic sandstones, North Sea[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2000, 69/70(0): 645-649. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0375674200001047
① 云南地质矿产勘查开发局. 1∶5万红光农场幅区地质图及说明书. 1994.
-



 下载:
下载: