High resolution flood records in the Yangtze subaqueous delta during the past century and control mechanism
-
摘要:
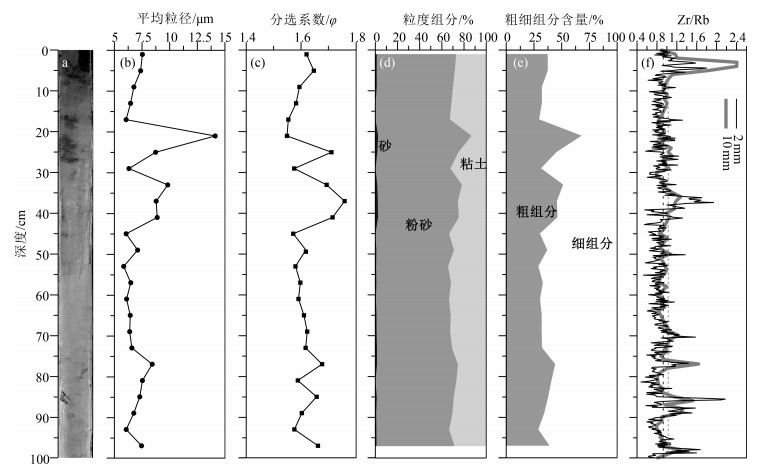
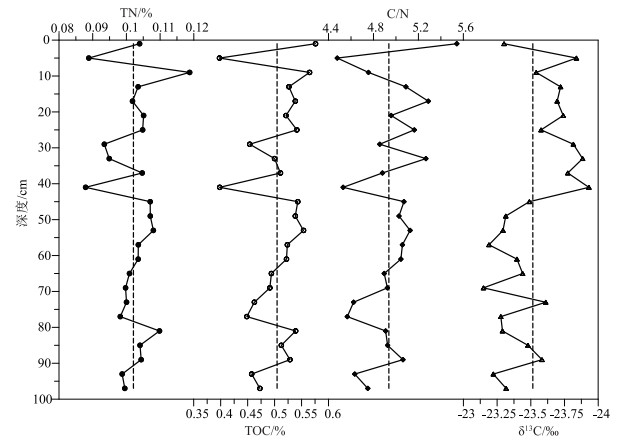
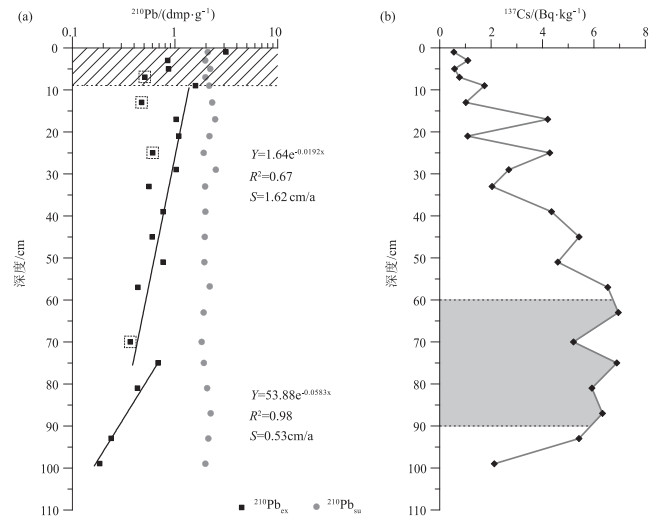
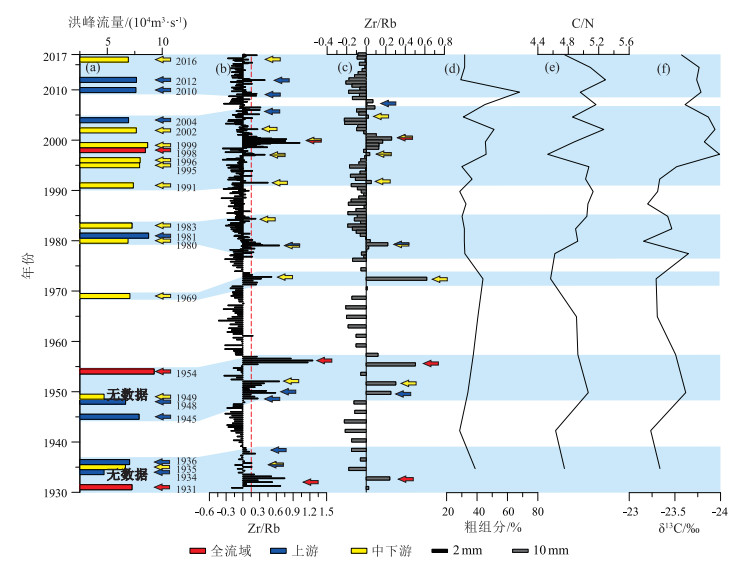
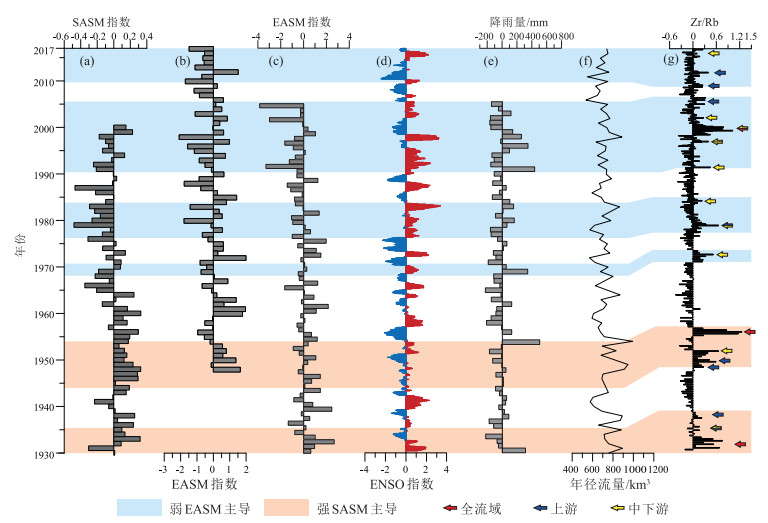
夏季洪涝灾害对长江流域社会经济造成了严重的影响,急需开展多时空尺度流域洪水发生规律和控制机理的研究,但因洪水器测数据年限短和缺少有效的古洪水沉积记录研究方法而难以实现。选取长江水下三角洲YEC1701柱状样顶部100 cm进行高分辨率XRF岩心连续扫描(XRFCS),粒度、有机碳、N元素、δ13C和210Pb定年分析,并与流域洪水器测或历史记录等进行对比研究,以期建立高效的古洪水沉积记录代用指标。结果表明,长江水下三角洲沉积物中Zr/Rb峰值通常对应粒度粗组分高值和较高的C/N值、偏负的δ13C值,所在层位的沉积年龄与流域洪水事件发生年份有很好的对应关系。由此判断,Zr/Rb值可作为判别长江古洪水沉积的重要代用指标。长江流域于1930—2017年间共发生22次洪水事件,利用XRFCS获得的10 mm和2 mm间隔Zr/Rb值可分别识别出其中的11次和18次,识别率为50%和80%。由此推荐XRFCS样品测试间隔要小于年沉积速率一半以内,以提高古洪水事件的识别率。多源洪水和降雨数据分析表明,长江洪水年际至千年尺度发生规律主要受厄尔尼诺-南方涛动和东亚夏季风、南亚夏季风活动的共同影响。但早期长江洪水资料分辨率较低,长江水下三角洲有较连续的洪水沉积记录,运用XRFCS毫米级分辨率的Zr/Rb值可重建全新世高分辨率的长江古洪水发生历史,更精细地分析气候变化对洪水发生规律的控制机理,为预测全球变化背景下长江洪水演变趋势提供依据。
Abstract:Summer flood hazards have a strong influence on the social economy of the Yangtze River Basin, so it is in dire need of investigating multiple spatiotemporal variations in floods and control mechanisms, but this is handled by short time extent of instrumental flood data and lack of effective research methods for palaeoflood deposition records.A sediment core (YEC1701)collected from the Yangtze subaqueous delta was studied in detail with its top 100 cm through using high-resolution XRF core scanner (XRFCS), and measurements of grain size, organic carbon and nitrogen, stable carbon isotope (δ13C), and210Pb compositions.The above study results were compared with the observing instruments or documental flood data to establish an effective proxy for paleo-flood depositions by comparison with instrumental or documental flood data.The results show that the peak value of Zr/Rb in the subaqueous delta sediments of the Yangtze River usually corresponds to the high value of coarse grain composition, the high value of C/N, and the negative value of δ13C.The sedimentary age of the strata in the delta corresponds well to the year of flood events in the basin.Therefore, the Zr/Rb ratio can be used as an important proxy index for the identification of palaeo-flood sediments in the Yangtze River.Totally, 22 flood events occurred in the period 1930-2017 in the Yangtze River basin, 11 and 18 of which were identified by the XRFCS Zr/Rb data in terms of 10 mm and 2 mm measurement intervals with effective recognition rates of 50% and 80% respectively.It is therefore recommended to perform XRFCS measurement with a smaller interval than half of sedimentation rates for better recognition rates of flood events.Multiple source data of river floods and precipitations were analyzed to show that river floods in Yangtze River basin are majorly influenced by ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation), EASM (East Asian summer monsoon) and SASM (South Asian summer monsoon) over different time scales from multiple years to millennium.However, the time resolution for earlier flood records is very low, and it can be greatly improved by employing XRFCS mm-scaled Zr/Rb ratio of continuous flood depositions in the Yangtze subaqueous delta.This will also improve our understanding of controlling mechanisms of flood events and then better prediction of flood variation in response to global climate change.
-
Key words:
- Yangtze /
- flood deposition /
- Zr/Rb ratio /
- ENSO /
- East Asian summer monsoon
-

-
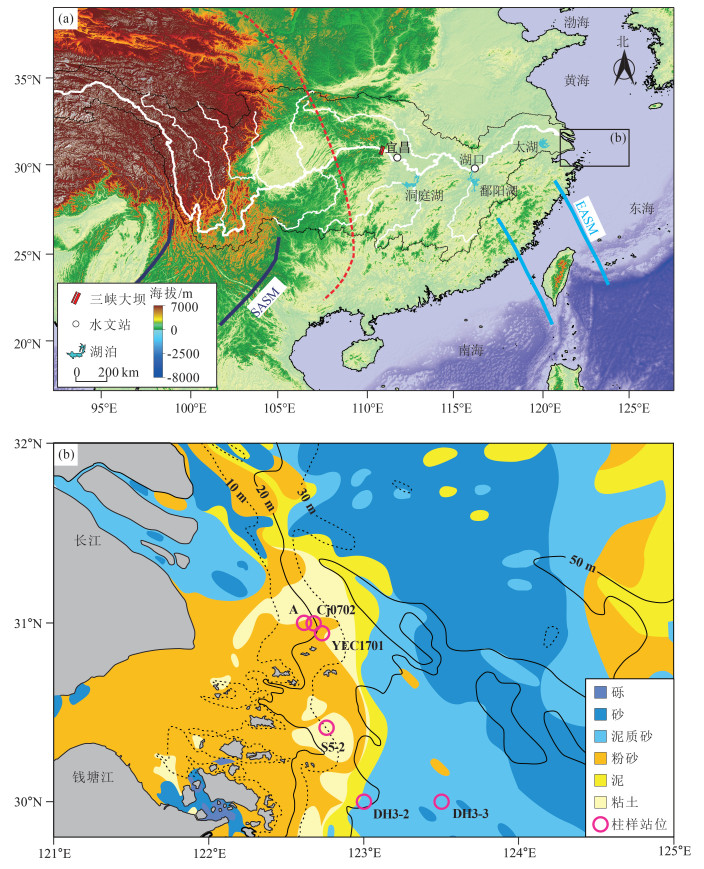
图 1 长江流域主要水系(a)和长江口及周边海域表层沉积物分布特征(b,据参考文献[28]修改)
Figure 1.
图 3 柱状样沉积物粒级-标准偏差曲线对比(其他柱样位置和数据来源详见图 1)
Figure 3.
表 1 长江流域历史洪水信息
Table 1. Historical floods of Yangtze River
年份 洪峰流量/(m3·s-1) 水文站 区域 参考文献 2016 61300 汉口 中下游 [40] 2012 71200 三峡入库 上游 [41] 2010 70000 宜昌 上中游 [42] 2004 61100 宜昌 上游 [43] 2002 70300 汉口 中下游 [44] 1999 84500 大通 中下游 [4] 1998 81700 大通 全流域 [4] 1996 75200 大通 中游 [4] 1995 74500 大通 中下游 [4] 1991 66700 汉口 下游 [4] 1983 65000 汉口 中游及汉江流域 [4] 1981 85700 寸滩 上游 [4] 1980 60100 汉江 中下游 [4] 1969 62400 汉口 中下游 [4] 1954 92600 大通 全流域 [4] 1949 - - 中下游 [4] 1948 57000 宜昌 上游 [45] 1945 73800 寸滩 上游 [4] 1936 62000 宜昌 上游 [45] 1935 56900 宜昌 中游 [46] 1934 - - 上游 [4] 1931 65000 宜昌 全流域 [45] -
[1] Schulte L, Schillereff D, Santisteban J I, et al. Pluridisciplinary analysis and multi-archive reconstruction of paleofloods[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019: 103220. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818119301493
[2] Schulte L, Schillereff D, Santisteban J I. Pluridisciplinary analysis and multi-archive reconstruction of paleofloods: Societal demand, challenges and progress[J]. Global Planet Change, 2019, 177: 225-238. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.03.019
[3] CRED(The Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters) and UNDRR(United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction). The human cost of disasters: an overview of the last 20 years(2000-2019)[EB/OL]. (2020). [2021-04-07]. UN Reports. https://www.undrr.org/publication/human-cost-disasters-2000-2019.
[4] 施雅风, 姜彤, 苏布达, 等. 1840年以来长江大洪水演变与气候变化关系初探[J]. 湖泊科学, 2004, (4): 289-297. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2004.04.001
[5] Jiang T, Zhang Q, Blender R, et al. Yangtze Delta floods and droughts of the last millennium: Abrupt changes and long term memory[J]. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 2005, 82(3/4): 131-141. doi: 10.1007/s00704-005-0125-4
[6] Wang M J, Zheng H B, Xie X, et al. A 600-year flood history in the Yangtze River drainage: Comparison between a subaqueous delta and historical records[J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2011, 56(2): 188-195. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ssam/10016538/2011/00000056/00000002/art00009
[7] Kochel R C, Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology[J]. Science, 1982, 215(4531): 353-361. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4531.353
[8] JonesA F, Macklin M G, Brewer P A. A geochemical record of flooding on the upper River Severn, UK, during the last 3750 years[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 179: 89-105. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.08.003
[9] Hu G, Li A, Liu J, et al. High resolution records of flood deposition in the mud area off the Changjiang River mouth during the past century[J]. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limn., 2014, 32(4): 909-920. doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3244-x
[10] Barbara L, Schmidt S, Urrutia-Fucugauchi J, et al. Fuerte River floods, an overlooked source of terrigenous sediment to the Gulf of California[J]. Cont. Shelf Res., 2016, 128: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.09.006
[11] Zhang K, Li A, Zhang J, et al. Recent sedimentary records in the East China Sea inner shelf and their response to environmental change and human activities[J]. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limn., 2018, 36(5): 81-99.
[12] Dypvik H, Harris N B. Geochemical facies analysis of fine-grained siliciclastics using Th/U, Zr/Rb and(Zr+Rb)/Sr ratios[J]. Chem. Geol., 2001, 181(1): 131-146. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254101002789
[13] Croudace I W, Rothwell R G. Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores[J]. Series: Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research, 2015, 17: 1-236. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-017-9849-5_1
[14] Liu L, Chen J, Ji J, et al. Variation of Zr/Rb ratios on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130000 years and its implications for winter monsoon[J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2002, 47(15): 1298-1302. doi: 10.1360/02tb9288
[15] 水利部长江水利委员会长江泥沙公报. [M]. 北京: 长江出版社, 2019.
[16] Kundzewicz Z W, Huang J, Pinskwar I, et al. Climate variability and floods in China-A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 211: 103434. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103434
[17] 王晨曦. 应急管理部: 今年洪涝灾害造成直接经济损失2143.1亿元[EB/OL]. (2020-09-03). [2021-04-07]. 中国网财经. http://finance.china.com.cn/news/20200903/5358440.shtml.
[18] Su J, Fan D. Internal Facies Architecture and Evolution History ofChangxing Mouth-Bar Complex in the Changjiang(Yangtze) Delta, China[J]. J. Ocean U. China, 2018, 6: 1281-1289. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=QDHB201806003
[19] Middelkoop H, Erkens G, Van der Perk M. The Rhine delta-a record of sediment trapping over time scales from millennia to decades[J]. J. Soils Sediments, 2010, 10: 628-639. doi: 10.1007/s11368-010-0237-z
[20] Zhao Y, Zou X, Gao J, et al. Recent sedimentary record of storms and floods within the estuarine-inner shelf region of the East China Sea[J]. The Holocene, 2016, 27(3): 439-449. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017Holoc..27..439Z
[21] Tian Y, Fan D, Zhang X, et al. Event deposits of intense typhoons in the muddy wedge of the East China Sea over the past 150 years[J]. Mar. Geol., 2019, 410: 109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.12.010
[22] 展望, 杨守业, 刘晓理, 等. 长江下游近代洪水事件重建的新证据[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(19): 1908-1913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201019010.htm
[23] Hedges J I, Keil R G, Benner R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean[J]. Org. Geochem., 1997, 27(5/6): 195-212. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304420304002130
[24] Meyers P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes[J]. Org. Geochem., 1997, 27(5/6): 213-250. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638097000491
[25] Lamb A L, Wilson G P, Leng M J. A review of coastal palaeoclimate and relative sea-level reconstructions using δ13C and C/N ratios in organic material[J]. Earth-Sci. Rev., 2006, 75: 29-57. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.10.003
[26] 陈吉余, 沈焕庭, 恽才兴. 长江河口动力过程和地貌演变[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1988.
[27] 火苗, 范代读, 陆琦, 等. 长江口南汇边滩冲淤变化规律与机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(5): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201005006.htm
[28] Fan D. Open-Coast Tidal Flats[M]//Principles of Tidal Sedimentology, 2012: 187-229.
[29] Fan D, Qi H, Sun X, et al. Annual lamination and its sedimentary implications in the Yangtze River delta inferred from High-resolution biogenic silica and sensitive grain-sizerecords[J]. Cont. Shelf Res., 2011, 31(2): 129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2010.12.001
[30] Rao Z, Li Y, Zhang J, et al. Investigating the long-termpalaeoclimatic controls on the δD and δ18O of precipitation during the Holocene in the Indian and East Asian monsoonal regions[J]. Earth-Sci. Rev., 2016, 159: 292-305. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.06.007
[31] Chen Z, Song B, Wang Z, et al. Late Quaternary evolution of the sub-aqueous Yangtze Delta, China: sedimentation, stratigraphy, palynology, and deformation[J]. Mar. Geol., 2000, 162(2): 423-441. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002532279900064X
[32] Liu J, Saito Y, Kong X, et al. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary, East China Sea, during the last 13000 years, with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years[J]. Quaternary Sci. Rev., 2010, 29(17): 2424-2438. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379110002106
[33] Shang S, Fan D, Ying P, et al. Late Quaternary environmental change in the central-western East China Sea[J]. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 2018, 492: 64-80. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.12.012
[34] Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment in the South China Sea(ODP Site 1144)[C]//Prell W L, Wong P, Blum P, et al. Proc ODP, Sci. Res., 2003, 184: 1-21.
[35] Sun Y, Gao S, Li J. Preliminary analysis of grain-size populations with environmentally sensitive terrigenous components in marginal seasetting[J]. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2003, 48(2): 184-187. doi: 10.1360/03tb9038
[36] 肖尚斌, 李安春. 东海内陆架泥区沉积物的环境敏感粒度组分[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, (1): 122-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.016
[37] 王晓慧, 吴伊婧, 范代读. 福建兴化湾外近海210Pb法沉积速率及校正方法[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(3): 527-536. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201903013.htm
[38] Xing L, Zhang H, Yuan Z, et al. Terrestrial and marine biomarker estimates of organic matter sources and distributions in surface sediments from the East China Seashelf[J]. Cont. Shelf Res., 2011, 31(10): 1106-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.04.003
[39] Luo X X, Yang S L, Zhang J. The impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the downstream distribution and texture of sediments along the middle and lower Yangtze River(Changjiang) and its estuary, and subsequent sediment dispersal in the East China Sea[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 179: 126-140. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.05.034
[40] 李妍清, 刘冬英, 熊莹. 2016年长江洪水遭遇分析[J]. 水资源研究, 2017(6): 568-576.
[41] 李文龙, 李鸿雁. 长江流域连续大洪水年机理分析及预报[J]. 水利水电技术, 2018, 49(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ201805001.htm
[42] 邹红梅, 陈新国. 2010年与1998年长江流域洪水对比分析[J]. 水利水电快报, 2011, (5): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0081.2011.05.004
[43] 李春香, 张辰亮, 虞海平, 等. 长江宜昌"2004·9"暴雨洪水分析[J]. 人民长江, 2008, 39(18): 9-10, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2008.18.004
[44] 黄为, 冯忠民. 长江2002年洪水与1996年洪水的对比分析[J]. 人民长江, 2003, 34(4): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.04.017
[45] 乔盛西, 陈正洪. 历史时期川江石刻洪水资料的分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 1999, 18(1): 4-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBQX199901001.htm
[46] Wang Z Y, Plate E J. Recent flood disasters inChina[J]. Water & Maritime Engineering, 2002, 154(3): 177-188. http://dx.doi.org/10.1680/maen.154.3.177.38719
[47] Li X, Bianchi T S, Allison M A, et al. Historical reconstruction of organic carbon decay and preservation in sediments on the East China Seashelf[J]. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo., 2013, 118(3): 1079-1093. doi: 10.1002/jgrg.20079
[48] 胡利民, 石学法, 王国庆, 等. 2011长江中下游旱涝急转前后河口表层沉积物地球化学特征研究[J]. 地球化学, 2014, (1): 39-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201401005.htm
[49] 高抒, 贾建军, 杨阳, 等. 陆架海岸台风沉积记录及信息提取[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(10): 141-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.10.010
[50] Xiao S, Li A, Liu J P, et al. Coherence between solar activity and the East Asian winter monsoon variability in the past 8000 years from Yangtze River-derived mud in the East China Sea[J]. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 2006, 237: 293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.12.003
[51] Moy C M, Seltzer G O, Rodbell D T, et al. Variability of El Niño/Southern Oscillation activity at millennial timescales during the Holocene epoch[J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6912): 159-162. doi: 10.1038/nature01163
[52] D'Arrigo R, Cook E R, Wilson R J, et al. On the variability of ENSO over the past six centuries[J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 2005, 32(3), L03711. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2004GL022055/full
[53] MacDonald G M, Case R A. Variations in the Pacific Decadal Oscillation over the pastmillennium[J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 2005, 32(8): L08703. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005GL022478
[54] 张瑞, 汪亚平, 潘少明. 近50年来长江入海径流量对太平洋年代际震荡变化的响应[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(5): 572-577. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.05.016
[55] Zhang Q, Xu C, Jiang T, et al. Possible influence of ENSO on annual maximum streamflow of the Yangtze River, China[J]. J. Hydrol., 2007, 333(2/4): 265-274. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002216940600429X
[56] Qian W, Lin X, Zhu Y, et al. Climatic regime shift and decadal anomalous events in China[J]. Climatic Change, 2007, 84(2): 167-189. doi: 10.1007/s10584-006-9234-z
[57] Jiang T, Zhang Q, Zhu D, et al. Yangtze floods and droughts(China) and teleconnections with ENSO activities(1470-2003)[J]. Quatern. Int., 2006, 144: 29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.05.010
[58] Chen J, Chen F, Feng S, et al. Hydroclimatic changes in China and surroundings during the Medieval Climate Anomaly and Little Ice Age: spatial patterns and possible mechanisms[J]. Quaternary Sci. Rev., 2015, 107: 98-111. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.10.012
[59] Kim H J, Hyeong K, Yoo C M, et al. Impact of strong El Niño events(1997/98 and 2009/10) on sinking particle fluxes in the 10°N thermocline ridge area of the northeastern equatorial Pacific[J]. Deep Sea Res., Part Ⅰ, 2012, 67(0): 111-120. http://www.dbpia.co.kr/Article/2757500
[60] Zhu Z, Feinberg J M, Xie S, et al. Holocene ENSO-related cyclic storms recorded by magnetic minerals in speleothems of central China[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad., USA, 2017, 114(5): 852-857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610930114
[61] Kundzewicz Z W, Szwed M, Pińskwar I. Climate Variability and Floods-A global Review[J]. Water, 2019, 11(7): 1399. doi: 10.3390/w11071399
[62] Guo Y, Huang C C, Zhou Y, et al. Extraordinary flood events and the response to monsoonal climatic change during the last 3000 years along the middle Yangtze River valley, China[J]. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl., 2016, 462: 70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.09.005
[63] Liu H, Gu Y, Huang X, et al. A 13000-year peatland palaeohydrological response to the ENSO-related Asian monsoon precipitation changes in the middle Yangtze Valley[J]. Quaternary Sci. Rev., 2019, 212: 80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.03.034
[64] Shen C, Wang W C, Gong W, et al. A Pacific Decadal Oscillation record since 1470 AD reconstructed from proxy data of summer rainfall over easternChina[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(3): L03702. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005GL024804/full
[65] Shi F, Li J, Wilson R J. A tree-ring reconstruction of the South Asian summer monsoon index over the pastmillennium[J]. Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 6739. http://www.nature.com/articles/srep06739
[66] Xu K, Li A, Liu J P, et al. Provenance, structure, and formation of the mud wedge along inner continental shelf of the East China Sea: A synthesis of the Yangtze dispersalsystem[J]. Mar. Geol., 2012, 291-294: 176-191. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.003
[67] Wang Z, Wei G, Chen J, et al. El Niño-Southern Oscillation variability recorded in estuarine sediments of theChangjiang River, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 441: 18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.07.009
[68] 李建平, 曾庆存. 一个新的季风指数及其年际变化和与雨量的关系[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2005, (3): 351-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200503008.htm
[69] IPCC. Climate change 2007: the physical science basis[C]//Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, et al. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge New York, 2007: 1-297.
[70] Ding Y, Wang Z, Sun Y. Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summermonsoon. Part Ⅰ: Observed evidences[J]. Int. J. Climatol., 2008, 28(9): 1139-1161. doi: 10.1002/joc.1615
[71] Wang H, Yang Z, Wang Y, et al. Reconstruction of sediment flux from theChangjiang(Yangtze River) to the sea since the 1860s[J]. J. Hydrol., 2008, 349(3/4): 318-332.
[72] 长江泥沙公报. 水利部长江水利委员会[M]. 北京: 长江出版社, 2006-2017.
[73] Liu J, Chen J, Zhang X, et al. Holocene East Asian summer monsoon records in northern China and their inconsistency with Chinese stalagmite δ18O records[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 148: 194-208. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.06.004
[74] 葛兆帅. 长江上游全新世特大洪水对西南季风变化的响应[J]. 地理研究, 2009, 28(3): 592-600. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2009.03.004
[75] Guo Y, Huang C C, Pang J, et al. Investigating extreme flood response to Holocene palaeoclimate in the Chinese monsoonal zone: A palaeoflood case study from the Hanjiang River[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 238: 187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.03.014
[76] 周秀骥, 赵平, 刘封, 等. 中世纪暖期、小冰期与现代东亚夏季风环流和降水年代-百年尺度变化特征分析[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(25): 2060-2067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201125005.htm
-



 下载:
下载: