Analysis of geothermal temperature and genetic model in Zhaojue County of Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
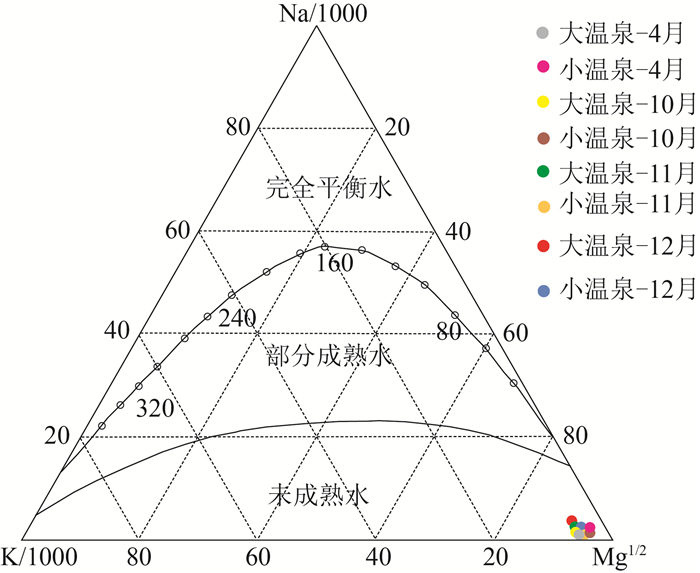
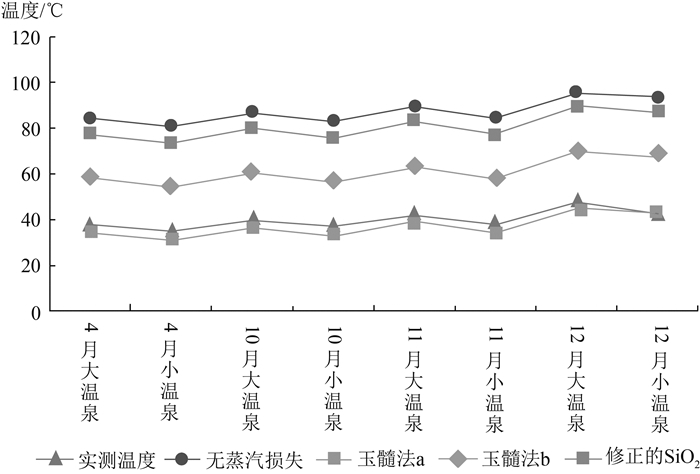
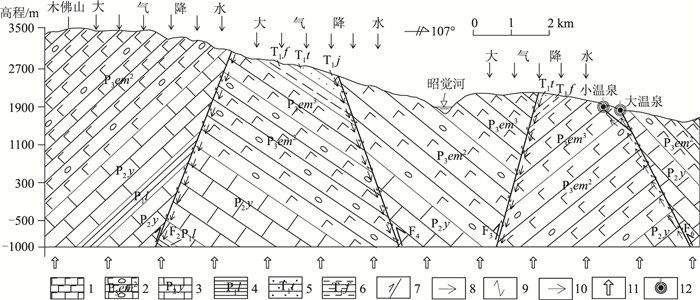
热储温度是划分地热系统成因类型和评价地热资源潜力的重要参数。为合理开发和利用四川昭觉县的地热资源,巩固脱贫攻坚成果,选择四川昭觉县竹核温泉为研究对象,利用无蒸汽损失石英和有蒸汽损失石英温标法、玉髓法a和玉髓法b,修正的SiO2温标法,K-Mg、Na-Li、Na-K、Na-K-Ca等阳离子温标法计算深部热储温度,并利用Na-K-Mg三角图解法和矿物饱和指数法检验所用方法的可靠性。结果表明,研究区利用SiO2(无蒸汽损失)温标法和修正后的SiO2温标法计算所得出的热储平均温度更适用,其中竹核温泉中大温泉的热储温度范围在81~93℃之间,平均热储温度86℃,小温泉的热储温度范围在77~90℃之间,平均热储温度82℃;竹核温泉来自深部的大地热流,受控于木佛山断层和竹核断层2条主控断裂。
Abstract:Geothermal temperature is an important parameter for classifying the genetic types of geothermal systems and evaluating the geothermal resource potential.In order to rationally develop and utilize the geothermal resources in Zhaojue County of Sichuan Province, and consolidate the achievements of poverty alleviation, the geothermal temperature of the Zhuhe hot springs in this area was studied.Various methods were used to calculate its deep thermal storage temperature, including steam-free loss quartz and steam loss quartz temperature scales, chalcedony a and b, modified SiO2 temperature scale, K-Mg, Na-Li, Na-K, Na-K-Ca and other cationic temperature scales.The reliability of the above methods is tested by Na-K-Mg triangulation method and mineral saturation index method.The results show that the average temperature calculated by SiO2 (without steam loss) temperature scale method and modified SiO2 temperature scale method are most suitable for this hot springs.The thermal temperature of its large hot springs ranges from 81℃ to 93℃, averaging 86℃, and that of small hot springs from 77℃ to 90℃, averaging 82℃.It reveals that the Zhuhe hot springs results from the deep terrestrial heat flow and is controlled by Mufoshan fault and Zhuhe fault.
-
Key words:
- hot springs /
- thermal storage /
- geothermal temperature scale /
- heat source mechanism /
- western Sichuan
-

-
表 1 四川昭觉县竹核温泉取样情况
Table 1. Sampling of the Zhuhe hot springs in Zhaojue County of Sichuan Province
采样点 2019年4月 2019年10月 2019年11月 2019年12月 大温泉 小温泉 大温泉 小温泉 大温泉 小温泉 大温泉 小温泉 取样时泉口温度/℃ 38.00 35.00 40.00 37.00 42.00 38.00 48.00 43.00 pH 7.96 7.83 8.20 7.93 8.06 7.95 8.09 7.91 TDS/(mg·L-1) 109.78 153.69 150.67 152.19 156.10 155.60 175.23 168.24 溶解氧/(mg·L-1) 4.14 2.46 4.27 2.48 4.05 2.54 4.16 2.51 HCO3-/(mg·L-1) 62.26 155.65 137.95 145.02 159.20 159.20 155.23 166.87 SO42-/(mg·L-1) 11.53 11.06 12.28 11.54 12.20 11.20 10.73 10.28 Cl-/(mg·L-1) 5.58 4.38 7.54 6.35 2.00 2.00 6.71 5.86 CO32-/(mg·L-1) 0.00 0.00 1.74 1.74 0.00 0.00 7.63 0.00 Ca2+/(mg·L-1) 15.31 21.65 15.97 23.87 16.30 23.80 15.67 21.70 Mg2+/(mg·L-1) 1.86 2.98 1.87 2.73 1.60 2.70 1.63 2.56 K+/(mg·L-1) 3.16 2.50 3.45 2.72 3.50 2.80 4.62 3.66 Na+/(mg·L-1) 41.22 33.29 38.85 30.72 40.90 33.50 50.62 40.74 F-/(mg·L-1) 1.80 1.46 1.63 1.40 1.80 1.40 1.59 1.20 SiO2/(mg·L-1) 33.68 31.10 35.68 32.66 38.15 33.59 43.94 41.42 Fe/(μg·L-1) 5.70 8.60 6.70 9.20 7.20 8.60 6.90 8.20 Ba/(μg·L-1) 68.74 46.45 45.00 40.50 67.60 46.40 79.50 50.20 Sr/(μg·L-1) 230.29 220.20 220.00 250.00 270.00 270.00 260.00 250.00 Mn/(μg·L-1) 0.66 0.08 0.53 0.17 0.91 0.22 0.96 0.13 Al/(μg·L-1) 3.02 2.24 5.78 2.96 9.81 3.23 12.80 3.48 Pb/(μg·L-1) < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 < 0.04 Li/(μg·L-1) 95.00 70.00 154.00 115.00 144.00 111.00 256.00 199.00 Cu/(μg·L-1) 0.61 0.64 0.58 0.75 0.41 0.45 0.57 0.20 Zn/(μg·L-1) < 0.09 1.24 < 0.09 < 0.09 < 0.09 < 0.09 < 0.09 < 0.09 表 2 竹核温泉地下热水热储温度
Table 2. Heat storage thermometer of geothermal water in zhuhe hot springs
℃ 采样时间 采样点 泉口温度 SiO2温标 阳离子温标 温度平均值 石英 玉髓 修正的SiO2法 K-Mg法 Na-Li法 Na-K法 Na-K-Ca法 无蒸汽损失 有蒸汽损失 玉髓法a 玉髓法b 2019年4月 大温泉 38 84.24 87.29 34.29 58.53 77.32 59.21 201.48 1916.80 -1.70 80.78 小温泉 35 80.90 84.36 31.06 55.14 73.74 49.30 253.10 1946.78 -8.19 77.32 2019年10月 大温泉 40 86.71 89.44 36.68 61.03 79.96 61.00 312.95 1718.47 0.83 83.33 小温泉 37 82.95 86.15 33.04 57.21 75.93 51.91 305.02 1719.32 -7.33 79.44 2019年11月 大温泉 42 89.60 91.97 39.50 63.97 83.07 63.08 301.42 1763.94 0.53 86.34 小温泉 38 84.13 87.19 34.18 58.42 77.20 52.62 296.39 1794.95 -7.32 80.67 2019年12月 大温泉 48 95.88 97.42 45.61 70.36 89.82 69.16 395.22 1683.71 5.21 92.85 小温泉 43 93.23 95.13 43.03 67.67 86.97 58.90 342.23 1702.80 -2.30 90.10 -
[1] 庞忠和, 罗霁, 程远志, 等. 中国深层地热能开采的地质条件评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(1): 134-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001018.htm
[2] 王贵玲, 刘彦广, 朱喜, 等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202001002.htm
[3] 屈泽伟, 张恒, 胡亚召, 等. 川西地区地热资源概况及开发区划探讨[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(5): 1233-1242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.05.032
[4] 张健, 李午阳, 唐显春, 等. 川西高温水热活动区的地热学分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(8): 899-915. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201708003.htm
[5] 罗敏, 任蕊, 袁伟, 等. 西川地热资源类型、分布及成因模式[J]. 四川地质学报, 2016, 36(1): 47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.01.010
[6] 孙东, 曹楠, 刘馨泽, 等. 川西甘孜州地热资源特征及开发利用前景[J]. 四川地质学报, 2019, 39(1): 133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2019.01.031
[7] 徐明, 朱传庆, 田云涛, 等. 四川盆地钻孔温度测量及现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(4): 1052-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.04.020
[8] 朱克亮, 赵斌. 四川安县罗浮山温泉热储层的初步研究[J]. 兴义民族师范学院学报, 2013, (3): 19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0673.2013.03.006
[9] 闫秋实, 高志友, 尹观. 四川宜宾金沙江河谷区地热资源成藏条件分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(4): 847-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201204023.htm
[10] 李晓, 舒勤峰. 四川屏山灯盏窝温泉地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2017, 28(4): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2017.04.014
[11] 周训, 曹琴, 尹菲, 等. 四川盆地东部高褶带三叠系地层卤水和温泉的地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(11): 1908-1920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201511003.htm
[12] 张林, 雷宛, 胡旭, 等. 高密度电法与音频大地电磁法在四川某地热勘探中的应用[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2018, (6): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2018.06.012
[13] 武斌, 曹俊兴, 邹俊, 等. 音频大地电磁测深法在川西地热勘查研究中的应用[J]. 工程勘察, 2011, (9): 91-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201109020.htm
[14] 赵佳怡, 张薇, 张汉雄, 等. 四川巴塘地热田水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(4): 81-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904012.htm
[15] 卞跃跃, 赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(4): 491-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201804012.htm
[16] 蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 等. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(1): 312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
[17] 刘峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 等. 江西宁都县北部大地热流特征及地热资源成因机制[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1883-1890. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20201202&flag=1
[18] 王贵玲, 蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 1923-1937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002
[19] 汪集暘, 熊亮萍, 庞忠和. 中低温对流型地热系统[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2000.
[20] 刘元晴, 周乐, 吕琳, 等. 山东鲁中山区地热地质特征及热水成因[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1908-1918. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20201205&flag=1
[21] Li J X, Sagoe G, Yang G, et al. The application of geochemistry to bicarbonate thermal springs with high reservoir temperature: A case study of the Batang geothermal field, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2019, 371: 20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2018.12.005
[22] Pérez-Zárate D, Santoyo E, Acevedo-Anicasio A, et al. Evaluation of artificial neural networks for the prediction of deep reservoir temperatures using the gas-phase composition of geothermal fluids[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2019, 129: 49-68. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300418302929
[23] Blasco M, Auqué L F, Gimeno M J, et al. Mineral equilibria and thermodynamic uncertainties in the geothermometrical characterisation of carbonate geothermal systems of low temperature. The case of the Alhama-Jaraba system (Spain)[J]. Geothermics, 2019, 78: 170-182. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.11.004
[24] 史猛, 张杰, 殷焘, 等. 胶东半岛中低温对流型地热资源水化学特征分析[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(S1): 138-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1018.htm
[25] 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 等. 应用地热温标估算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4): 605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003
[26] Cinti D, Procesi M, Tassi F, et al. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry in the western sector of the Sabatini Volcanic District and the Tolfa Mountains (Central Italy)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 284(1/2): 160-181. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254111000945
[27] 郑西来, 刘鸿俊. 地热温标中的水-岩平衡状态研究[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1996, 18(1): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX601.014.htm
[28] 甘浩男, 蔺文静, 闫晓雪, 等. 粤中隐伏岩体区地热赋存特征及热异常成因分析[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 2096-2106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.017
[29] 谭梦如, 周训, 张彧齐, 等. 云南勐海县勐阿街温泉水化学和同位素特征及成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(3): 70-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201903010.htm
[30] 许鹏, 谭红兵, 张燕飞, 等. 特提斯喜马拉雅带地热水化学特征与物源机制[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1142-1154 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201806006.htm
[31] 刘明亮, 何曈, 吴启帆, 等. 雄安新区地热水化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 2221-2231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006032.htm
[32] 余琴, 杨平恒, 王长江, 等. 重庆市统景温泉水化学特征及混合作用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(1): 59-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201701007.htm
[33] 程群, 杨华林, 曾敏. 重庆市主城区岩溶地热水资源的形成与保护[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(3): 217-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201503003.htm
[34] 柯柏林, 林天懿, 李文, 等. 北京西山谷积山背斜地热系统成因模式及远景区预测[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(8): 1378-1385. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190814&flag=1
[35] Fournier R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics, 1977, 5(1/4): 41-50. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375650577900074
[36] Arnorsson S. Chemical equilibria in Icelandic geothermal systems-implications for chemical geothermometry investigations[J]. Geothermics, 1983, 12(2/3): 119-128. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375650583900226
[37] Dulanya Z, Morales-Simfors N, Sivertun A. Comparative study of the silica and cation geothermometry of the Malawi hot springs: potential alternative energy source[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2010, 57(4): 321-327. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.11.001
[38] Giggenbach W F. Geothermal solute equilibria derivation of Na-K- Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(12): 2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
[39] Fouillac C, Michard G. Sodium/lithium ratio in water applied to geothermometry of geothermal reservoirs[J]. Geothermics, 1981, 10(1): 55-70. doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(81)90025-0
[40] Fournier R O, Truesdell A H. An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37(5): 1255-1275 doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4
[41] 王治祥, 蒋晶, 邹胜章. 渝东南深部地热温度解析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5): 663-669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201905003.htm
[42] Reed M H, Sptcher N. Calculation of pH and mineral equilibia in hydrothermal waters with application to geothermometry and studies of boiling and dilution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48: 1479-1492. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0016703784904046
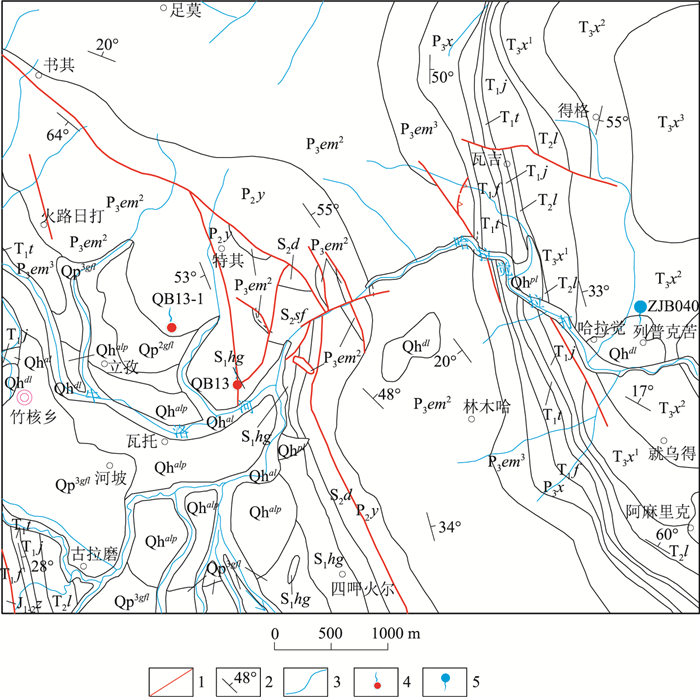
① 郑小敏, 曹俊, 沈洪江, 等. 昭觉县幅(H48E024004)1: 5万区域地质图说明书. 四川省地质矿产勘查开发局区域地质调查队, 2015.
-



 下载:
下载: