Collective fluid flow system and its implications for gas hydrate accumulation in the north slope of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
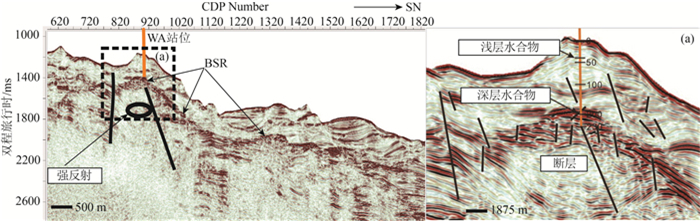
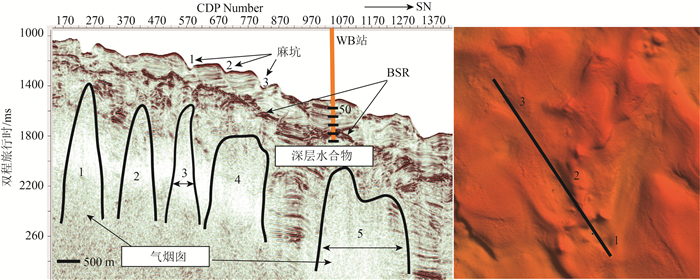
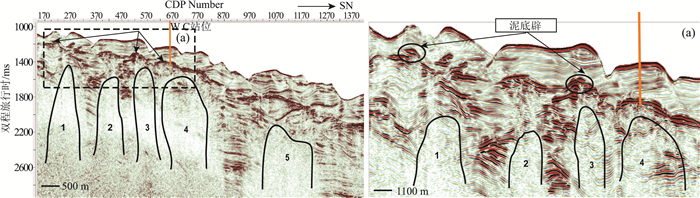
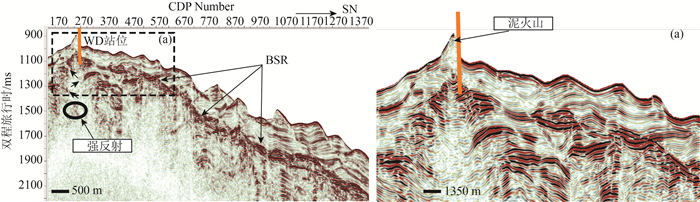
利用台西南盆地三维高精度地震资料,对南海北部陆坡聚集流体活动系统进行了分析和研究。在研究区识别出了断层、气烟囱、泥火山、泥底辟等聚集流体活动系统。研究区聚集流体活动系统主要特征包括:①断层与气烟囱相伴生;②气烟囱发育的区域与似海底反射(BSR)分布区域基本吻合,在气烟囱上方可以识别出一定长度的BSR;③泥底辟/泥火山导致周围和上覆地层形成了大量小尺度断层和微裂隙,中、深部流体可沿破裂带向上运移至天然气水合物稳定带内形成天然气水合物。因此,研究区聚集流体活动系统为天然气水合物发育成藏提供了流体来源,有利于天然气水合物的聚集,对于揭示天然气水合物的富集规律意义重大,能够为其他区域天然气水合物勘探提供借鉴。
Abstract:Based on 3D high-precision seismic data used to analyze the collective fluid flow systems in the Taixinan Basin, a collective fluid flow system including faults, gas chimneys, mud volcano, and mud diapir was identified in the study area.The main characteristics of the collective fluid flow system in the study are manifested as follows: a, association of faults with gas chimneys; b, consistence of the development area of gas chimneys with the distribution area of Bottom Simulating Reflection (BSR), and a certain length of BSR identified above the gas chimney; c, development of a large number of small scale faults and micro-fissures in the surrounding and overlying strata resulting from mud diapirs/mud volcanoes, and formation of gas hydrate caused by upward migration of the middle and deep fluids along the rupture zone to the stable zone.Therefore, the collective fluid flow system in the study area provides a source of fluid for the development of gas hydrate, which is conducive to the accumulation of gas hydrate.It is of great significance for revealing the enrichment rule of gas hydrate and can provide references for gas hydrate exploration in other regions.
-
Key words:
- TaiXinan Basin /
- focused fluid /
- flow systems /
- gas hydrate /
- north slope of the South China sea
-

-
[1] 孙启良, 吴时国, 陈端新, 等. 南海北部深水盆地流体活动系统及其成藏意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(12): 4052-4062. doi: 10.6038/cjg20141217
[2] 吴能友, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域天然气水合物成藏的流体运移体系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6): 1641-1650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.06.027
[3] 王秀娟, 吴时国, 王大伟, 等. 琼东南盆地多边形断层在流体运移和天然气水合物成藏中的作用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(1): 122-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201001021.htm
[4] 吴时国, 孙启良, 吴拓宇, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区多边形断层的发现及其油气意义[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(1): 22-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.01.004
[5] 杨涛涛, 吕福亮, 王彬, 等. 琼东南盆地南部深水区气烟囱地球物理特征及成因分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 5(2): 2634-2641. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201305045.htm
[6] 尹川, 张金淼, 骆宗强, 等. 气烟囱模式识别技术在油气运移通道检测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 3(1): 1343-1349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201403048.htm
[7] 梁劲, 王静丽, 杨承志, 等. 珠江口盆地东部海域含天然气水合物沉积层的地球物理特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(2): 126-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201702024.htm
[8] 徐华宁, 陆敬安, 梁金强. 珠江口盆地东部海域近海底天然气水合物地震识别及地质成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704010.htm
[9] 沙志彬, 许振强, 付少英, 等. 珠江口盆地东部海域天然气水合物成藏气源特征探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(4): 116-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201904012.htm
[10] 梁金强, 付少英, 陈芳, 等. 南海东北部陆坡海底甲烷渗漏及水合物成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(5): 761-770. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201705011.htm
[11] Sibson R H. Fluid flow accompanying faulting, field evidence and models[C]//Simpson D W, Richards P G. Earthquake prediction an international review. American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series, 1981, 4: 593-603.
[12] Downey M W. Evaluating seals for hydrocarbon accumulations[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1984, 68: 1752-1763.
[13] Cartwright J, Santamarina C. Seismic characteristics of fluid escape pipes in sedimentary basins: Implications for pipe genesis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65: 126-140. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.03.023
[14] O'Brien G W, Lisk M, Duddy I R, et al. Plateconvergence, foreland development and fault reactivation: Primary controls on brine migration, thermal histories and trap breach in the Timor Sea, Australia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1999, 16: 533-560. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(98)00070-1
[15] Finkbeiner T, Zoback M F, Stump B. Stress, porepressure, and dynamically constrained hydrocarbon columns in the South Eugene Island 330 field, northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85: 1007-1035.
[16] Heggland R. Detection of gas migration from a deep source by the use of exploration 3D seismic data[J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 137: 41-47. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(96)00077-1
[17] Ligtenberg J H. Detection of fluid migration pathways in seismic data: Implications for fault seal analysis[J]. Basin Research, 2005, 17: 141-154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2005.00258.x
[18] Riedel M, Collett T S, Kumar P, et al. Seismic imaging of a fractured gas hydrate system in the Krishna-Godavari Basin offshore India[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27: 1476-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.06.002
[19] Long D, Lammers S, Linke P, Gas hydrates relevance to world margin stability and climate change[J]. Geophysics Research, 2011, 2: 55-68. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA39443954
[20] 许翠霞, 边海光, 马朋善, 等. 气烟囱的地球物理响应特征及油气勘探[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(4): 1831-1836. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201404046.htm
[21] Yoo D G, Kang N K, Yi B Y, et al. Occurrence and seismic characteristics of gas hydrate in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 236-247. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.001
[22] Haacke R R, Hyndman R D, Park K P, et al. Migration and venting of deep gases into the ocean through hydrate choked chimneys offshore Korea[J]. Geology, 2009, 37: 531-534. doi: 10.1130/G25681A.1
[23] Chun J H, Ryu B J, Son B K, et al. Sediment mounds and other sedimentary features related to hydrate occurrences in a columnar seismic blanking zone of the Ulleung Basin, East Sea, Korea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28: 1787-1800. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.06.006
[24] Kim G Y, Yi B Y, Yoo D G, et al. Evidence of gas hydrate from downhole logging data in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28: 1979-1985. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.01.011
[25] Ryu B J, Collett T S, Riedel M, et al. Scientific results of the Second Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition in the Ulleung Basin (UBGH2)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 47: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.007
[26] 拜阳, 宋海斌, 关永贤, 等. 利用反射地震和多波束资料研究南海西北部麻坑的结构特征与成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 7(5): 2208-2222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201407016.htm
[27] 邸鹏飞, 黄华谷, 黄保家, 等. 莺歌海盆地海底麻坑的形成与泥底辟发育和流体活动的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 5(4): 26-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY201205006.htm
[28] 关永贤, 罗敏, 陈琳莹, 等. 南海西部海底巨型麻坑活动性示踪研究[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 6(2): 628-639. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201406007.htm
[29] 何家雄, 祝有海, 翁荣南, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地泥底辟及泥火山特征及其与油气运聚关系[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2010, 35(1): 75-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201001011.htm
[30] 陈江欣, 关永贤, 宋海斌, 等. 麻坑、泥火山在南海北部与西部陆缘的分布特征和地质意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(3): 919-938. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201503019.htm
[31] 解习农, 李思田, 胡祥云, 等. 莺歌海盆地泥-流体底辟树型输导系统及其成因机制[J]. 中国科学: D辑地球科学, 1999, 29(3): 247-256.
[32] 王家豪, 庞雄, 王存武, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷中央底辟带的发现与识别[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2006, 31(2): 209-2135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200602009.htm
[33] Ginsburg G D, Ivanov V L, Soloviev V A. Natural gas hydrates of the world's oceans[J]. Oil and Gas Content of the World's oceans. PGO Sevmorgeologia, 1984, 3: 141-158.
[34] Ginsburg G D. Gas hydrate accumulation at the Hakon Mosby mud volcano[J]. Geo-marine Letters, 1999, 19: 57-67. doi: 10.1007/s003670050093
[35] Milkov A V. Worldwide distribution of submarine mud valcanoes and associated gas hydrates[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 167: 29-42. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00022-0
[36] Bouriak S, Vanneste M, Saoutkine A. Inferred gas hydrates and clay diapirs near the Storegga Slide on the southern edge of the Voring Platean, offshore Norway[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 163: 125-148. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00115-2
[37] Egorov A V, Grane K, Vogt P R, et al. Gas hydrates that outcrop on the sea floor: Stability models[J]. Geo-marine Letters, 1999, 19: 68-75. doi: 10.1007/s003670050094
[38] 于兴河, 张志杰, 苏新, 等. 中国南海天然气水合物沉积成藏条件初探及其分布[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 311-315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.029
[39] 宋海斌, 郝天珧, 江为为, 等. 南海地球物理场特征与基底断裂体系研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(1): 24-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.01.003
[40] 陈多福, 苏正, 冯东, 等. 海底天然气渗漏系统水合物成藏过程及控制因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(3): 39-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY200503006.htm
[41] 苏丕波, 何家雄, 梁金强. 南海北部陆坡深水区天然气水合物成藏系统及其控制因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(7): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201707001.htm
[42] 郭依群, 杨胜雄, 梁金强. 南海北部神狐海域高饱和度天然气水合物分布特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 24-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704004.htm
[43] 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 陆敬安. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征及主控因素新认识[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704002.htm
[44] 张伟, 梁金强, 何家雄, 等. 南海北部神狐海域GMGS1和GMGS3钻探区天然气水合物运聚成藏的差异性[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(3): 138-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201803022.htm
-



 下载:
下载: