Identification of the relics of paleo-seamount in orogens: A case study from the geological mapping in Qingshashan and Donggou areas within the Lajishan suture zone
-
摘要:
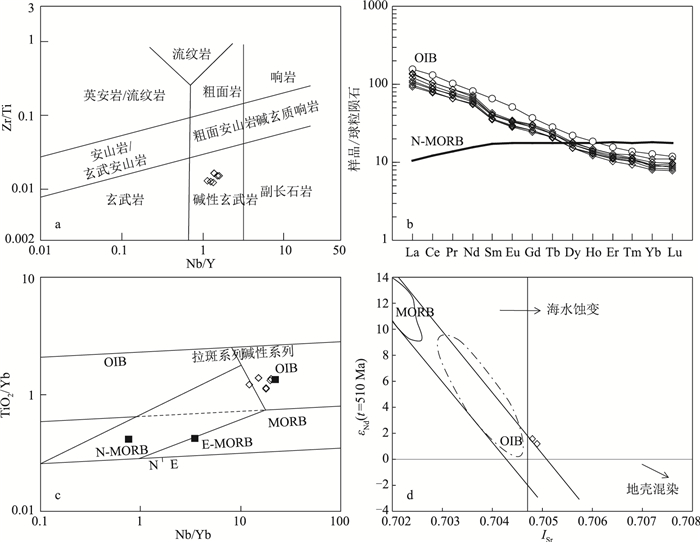
造山带内海山/洋岛残片的识别是确定古缝合带和古洋盆存在的直接地质证据。祁连造山带被普遍认为是原特提斯洋盆俯冲和闭合的产物,然而南祁连地区是否存在古洋盆长期存在争议。通过对拉脊山关键地段早古生代岩石开展大比例尺地质填图和室内综合研究,在青沙山和东沟地区识别出连续的由洋岛型枕状玄武岩、火山碎屑岩、泥岩、凝灰岩和灰岩组成的火山-沉积组合序列,它们分别呈构造窗和构造残片产出,是拉脊山增生杂岩的重要组成部分,代表中寒武世—早奥陶世原特提斯洋内海山残片。这些海山残片的识别不仅表明拉脊山地区存在早古生代洋盆和缝合带,同时为造山带古洋盆构造演化研究提供了新思路。
Abstract:Identification of the relics of seamount/oceanic island in orogens can provide critical geological evidence for the presence of the suture zone and paleo-ocean basin.The Qilian Orogen is widely considered as the product of subduction and closure of the Proto-Tethyan Ocean.However, whether there exists a paleo-ocean basin in the South Qilian is still hotly debated.Based on large-scale geological mapping and comprehensive study on the Early Paleozoic rocks in the key area of Lajishan, a successive volcanic-sedimentary sequence composed of OIB-type pillow basalt, pyroclastic rock, mudstone, tuff, and limestone was recognized in the Qingshashan and Donggou areas.The rocks are outcropped as the tectonic slice and tectonic window respectively.The volcanic-sedimentary sequence is the major components of the accretionary complex within Lajishan, and represents the relics of Middle Cambrian to Early Ordovician seamounts within the Proto-Tethyan Ocean.The identification of these relics of seamount not only indicates that there exist Early Paleozoic ocean basin and suture zone in the Lajishan area but also provides a new idea for the study of tectonic evolution of the paleo-ocean basin in orogens.
-
Key words:
- seamount /
- suture zone /
- paleo-ocean basin /
- large-scale geological mapping /
- Lajishan
-

-
表 1 青沙山枕状玄武岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of the pillow basalts in the Qingshashan area
样品号 12QSS1 12QSS2 12QSS3 12QSS4 12QSS5 12QSS6 12QSS7 SiO2 42.72 42.24 43.51 39.86 40.29 42.22 44.57 TiO2 2.17 2.01 2.04 1.82 1.80 1.89 2.24 Al2O3 14.34 14.27 13.34 12.26 11.74 12.96 14.67 Fe2O3 11.74 12.82 12.09 11.79 10.27 10.74 12.07 FeO 1.53 1.10 1.60 1.56 2.03 2.14 1.31 MnO 0.13 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.12 0.12 0.10 MgO 4.40 3.99 6.14 5.99 5.47 5.34 4.91 CaO 7.76 7.80 8.23 11.69 12.94 9.59 5.60 Na2O 4.78 4.98 4.45 3.14 3.77 3.75 4.42 K2O 1.45 1.14 0.90 1.48 0.91 1.62 2.58 P2O5 0.44 0.44 0.48 0.46 0.40 0.46 0.48 烧失量 7.68 8.27 6.12 8.90 9.51 8.18 6.52 总计 99.14 99.17 99.02 99.08 99.25 99.01 99.47 TFeO 12.09 12.64 12.48 12.17 11.27 11.80 12.17 Mg# 39 36 47 47 46 45 42 La 22.9 22.2 31.7 28.9 26.0 32.3 25.1 Ce 48.6 47.7 64.3 58.3 54.5 63.7 53.4 Pr 6.30 6.21 8.16 7.47 6.93 8.11 7.08 Nd 26.0 26.3 32.6 31.0 27.8 34.0 29.2 Sm 5.40 5.47 6.35 6.29 5.50 6.59 6.10 Eu 1.66 1.70 1.94 1.93 1.73 2.01 1.89 Gd 5.04 5.33 6.09 5.88 5.33 6.22 5.83 Tb 0.78 0.78 0.88 0.88 0.77 0.92 0.88 Dy 3.91 3.90 4.30 4.31 3.85 4.57 4.49 Ho 0.74 0.72 0.79 0.81 0.70 0.85 0.84 Er 1.86 1.81 1.92 2.00 1.69 2.12 2.14 Tm 0.27 0.26 0.28 0.28 0.24 0.29 0.32 Yb 1.57 1.45 1.51 1.60 1.36 1.69 1.86 Lu 0.22 0.21 0.23 0.24 0.20 0.25 0.28 δEu 0.97 0.96 0.95 0.97 0.98 0.96 0.97 REE 125.25 124.04 161.05 149.89 136.60 163.62 139.41 LREE/HREE 7.70 7.58 9.07 8.37 8.66 8.68 7.38 (La/Yb)N 10.46 10.98 15.06 12.96 13.71 13.71 9.68 Li 17.0 15.6 15.7 14.5 11.9 14.1 18.5 Sc 21.8 21.8 21.2 20.1 19.5 20.6 22.5 V 239 258 223 205 191 199 227 Cr 335 414 354 327 306 306 311 Ni 185 220 229 210 203 190 148 Co 47.4 47.8 52.7 50.8 46.6 51.7 42.9 Cu 81.3 50.0 83.1 103.0 69.9 101.0 100.0 Pb 3.17 4.12 3.42 3.93 4.10 4.76 2.41 Cs 4.67 7.41 3.24 2.48 3.57 3.45 3.36 Ga 18.6 18.2 19.2 20.0 16.6 19.1 17.6 Rb 21.0 19.8 15.6 31.0 14.9 29.1 34.4 Ba 327 253 289 419 237 520 435 Sr 475 446 504 442 511 448 393 Th 2.21 2.10 3.22 2.94 2.77 3.08 2.19 U 0.40 0.43 0.57 0.61 0.55 0.62 0.43 Nb 23.6 22.1 30.3 28.5 26.7 30.3 22.9 Ta 1.30 1.26 1.84 1.67 1.60 1.74 1.34 Zr 159 152 185 180 163 185 173 Hf 3.87 3.70 4.33 4.18 3.89 4.37 3.94 Y 17.7 17.8 20.0 20.9 17.0 22.2 20.2 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 青沙山枕状玄武岩全岩Rb-Sr和Sm-Nd同位素组成
Table 2. Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of the pillow basalts in the Qingshashan area
样品号 年龄/Ma 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)t 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ (143Nd/144Nd)t εNd(0) εNd(t) fSm/Nd 12QSS2 510 0.1285 0.705828 0.000015 0.70489 0.1257 0.512462 0.000011 0.512042 -3.4 1.2 -0.36 12QSS3 510 0.0896 0.705452 0.000011 0.70480 0.1178 0.512455 0.000012 0.512062 -3.6 1.6 -0.40 -
[1] Wilson J T. A Possible Origin of the Hawaiian Islands[J]. Candian Journal of Physics, 1963, 41: 863-870. doi: 10.1139/p63-094
[2] Menard H W. Marine Geology of the Pacific[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1964: 1-271.
[3] Isozaki Y, Maruyama S, Furuoka F. Accreted oceanic materials in Japan[J]. Tectonophysics, 1990, 181: 179-205. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90016-2
[4] Wakita K. OPS mélange: a new term for mélanges of convergent margins of the world[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(5/8): 529-539.
[5] 冯益民, 张越. 大洋板块地层(OPS)简介及评述[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(4): 523-531. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180401&flag=1
[6] 闫臻, 王宗起, 付长垒, 等. 混杂岩基本特征与专题地质填图[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 167-191. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020301&flag=1
[7] Condie K C. Plate Tectonics and Crustal Evolution[M]. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann, 1997: 1-282.
[8] Robertson A H F. Role of tectonic facies concept in orogenic analysis and its application to Tethys in the Eastern Mediterranean region[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37: 139-213. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90028-0
[9] 李继亮. 增生型造山带的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10): 947-951. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200409168&flag=1
[10] 肖文交, 李继亮, 宋东方, 等. 增生型造山带结构解析与时空制约[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(5): 1661-1687.
[11] White W M. Oceanic island basalts and mantle plumes: The geochemical perspective[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2010, 38: 133-160. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152450
[12] Sano H, Kanmera K. Paleogeographic reconstruction of accreted oceanic rocks, Akiyoshi, southwest Japan[J]. Geology, 1988, 16(7): 600. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0600:PROAOR>2.3.CO;2
[13] Safonova I Y, Santosh M. Accretionary complexes in the Asia-Pacific region: Tracing archives of ocean plate stratigraphy and tracking mantle plumes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25: 126-158. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.008
[14] Moore J C, Silver E A. Continental margin tectonics: submarine accretionary prisms[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1987, 25(6): 1305-1312. doi: 10.1029/RG025i006p01305
[15] Cloos M, Shreve R L. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, melange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins: 1. Background and description[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1988, 128(3): 455-500.
[16] 张继恩, 陈艺超, 肖文交, 等. 洋底凸起地质体及其对造山带中蛇绿岩组分的贡献[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(7): 1977-1990.
[17] Wakita K. Origin of chaotically mixed rock bodies in the Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceoussedimentary complex of the Mino terrane, central Japan[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Japan, 1988, 39: 675-757.
[18] Safonova I, Maruyama S, Kojima S, et al. Recognizing OIB and MORB in accretionary complexes: A new approach based on ocean plate stratigraphy, petrology and geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 33: 92-114. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.013
[19] 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 张建新, 等. 北祁连走廊南山加里东俯冲杂岩增生地体及其动力学[J]. 地质学报, 1994, 68(1): 1-15.
[20] 张雪亭, 杨生德. 青海省板块构造研究1/100万青海省大地构造说明书[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-221.
[21] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yong Y, et al. Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the Qilian Shan, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(3/4): 323-333.
[22] Yan Z, Aitchison J, Fu C L, et al. Hualong Complex, South Qilian terrane: U-Pb and Lu-Hf constraints on Neoproterozoic micro-continental fragments accreted to the northern Proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266: 65-85. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.05.001
[23] Xia L Q, Li X M, Yu J Y, et al. Mid-late Neoproterozoic to early paleozoic volcanism and tectonic evolution of the Qilianshan, NW China[J]. Geo. Res. J. , 2016, 9/12: 1-41.
[24] Fu C L, Yan Z, Wang Z Q, et al. Lajishankou Ophiolite Complex: Implications for Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Events in the South Qilian Belt[J]. Tectonics, 2018, 37(5): 1321-1346. doi: 10.1029/2017TC004740
[25] Li S Z, Zhao S J, Liu X, et al. Closure of the Proto-Tethys Ocean and Early Paleozoic amalgamation of microcontinental blocks in East Asia[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 37-75. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.011
[26] 付长垒, 闫臻, 王秉璋. 秦祁结合部清水-张家川基性岩形成时代和构造归属探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(10): 3141-3160. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.12
[27] 钱青, 张旗, 孙晓猛. 北祁连九个泉玄武岩的形成环境及地幔源区特征: 微量元素和Nd同位素地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(3): 385-394.
[28] 闫臻, 李继亮, 雍拥, 等. 北祁连石灰沟奥陶纪碳酸盐岩-硅质岩形成的构造环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(10): 2384-2394.
[29] Yan Z, Xiao W J, Windley B F, et al. Silurian clastic sediments in the North Qilian Shan, NW China: Chemical and isotopic constraints on their forearc provenance with implications for the Paleozoic evolution of the Xizang Plateau[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 231(3): 98-114.
[30] Song S G, Niu Y L, Su L, et al. Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004
[31] Zhang J X, Yu S Y, Mattinson C G. Early Paleozoic polyphase metamorphism in northern Xizang, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41: 267-289. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.11.009
[32] Fu C L, Yan Z, Aitchison J C, et al. Multiple subduction processes of the Proto-Tethyan Ocean: Implication from Cambrian intrusions along the North Qilian suture zone[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 87: 207-223. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.06.007
[33] 左国朝, 张淑玲, 程建生, 等. 祁连地区蛇绿岩带划分及其构造意义[C]//张旗等. 蛇绿岩与地球动力学研究. 蛇绿岩与地球动力学研讨会, 北京, 1996: 129-134.
[34] 曾广策, 邱家骧, 朱云海. 拉鸡山造山带的蛇绿岩套及古构造环境[J]. 青海地质, 1997, (1): 1-6.
[35] 邱家骧, 曾广策, 王思源, 等. 拉脊山早古生代海相火山岩与成矿[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997: 1-118.
[36] 侯青叶, 张宏飞, 张本仁, 等. 祁连造山带中部拉脊山古地幔特征及其归属: 来自基性火山岩的地球化学证据[J]. 中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(1): 61-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.01.008
[37] 李瑞保, 裴先治, 王兴, 等. 祁连造山带东段中寒武世深沟组中-基性火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(4): 589-603. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180407&flag=1
[38] 高延林. 青藏高原板块构造图及其编制方法[J]. 青海科技, 2000, 7(4): 14-18.
[39] 王二七, 张旗, Burchfiel C B. 青海拉鸡山: 一个多阶段抬升的构造窗[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(4): 493-500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.04.013
[40] Zhang Y Q, Song S G, Yang L M, et al. Basalts and picrites from a plume-type ophiolite in the South Qilian Accretionary Belt, Qilian Orogen: Accretion of a Cambrian Oceanic Plateau?[J]. Lithos, 2017, 278/281: 97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.027
[41] Gao Z, Zhang H F, Yang H, et al. Geochemistry of Early Paleozoic boninites from the Central Qilian block, Northwest China: Constraints on petrogenesis and back-arc basin development[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 158: 227-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.02.022
[42] Fu C L, Yan Z, Guo X Q, et al. Assembly and dispersal history of continental blocks within the Altun-Qilian-North Qaidam mountain belt, NW China[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(4): 424-447. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1428831
[43] Yan Z, Fu C L, Aitchison J C, et al. Retro-foreland Basin Development in Response to Proto-Tethyan Ocean Closure, NE Xizang Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 2019, 38(12): 4229-4248. doi: 10.1029/2019TC005560
[44] Fu C L, Yan Z, Aitchison J C, et al. Abyssal and Suprasubduction Peridotites in the Lajishan Ophiolite Belt: Implication for Initial Subduction of the Proto-Tethyan Ocean[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2019, 127(4): 393-410. doi: 10.1086/703488
[45] 付长垒, 闫臻, 王宗起, 等. 南祁连拉脊山口增生楔的结构与组成特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(7): 2049-2064.
[46] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[47] 林天瑞, 彭善池, 周志强. 青海化隆拉脊山寒武纪球接子类三叶虫[J]. 古生物学报, 2015, 54(2): 184-206.
[48] Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[49] Okamura Y. Large-Scale mélange formation due to seamount subduction: An example from the Mesozoic accretionary complex in central Japan[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1991, 99: 661-674. doi: 10.1086/629531
[50] Cloos M. Lithospheric buoyancy and collisional orogenesis: Subduction of oceanic plateaus, continental margins, island arcs, spreading ridges, and seamounts[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1993, 105(6): 715-737. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1993)105<0715:LBACOS>2.3.CO;2
[51] 周志强, 曹宣铎, 赵江天, 等. 祁连山东部早古生代地层和沉积-构造演化[J]. 西北地质科学, 1996, 17(1): 1-58.
[52] 林天瑞, 彭善池, 周志强, 等. 青海化隆拉脊山寒武纪多节类三叶虫[J]. 古生物学报, 2013, 52(4): 424-458.
-




 下载:
下载: