Application of hyperspectral remote sensing technology to regional geological survey and mapping in bedrock area
-
摘要:
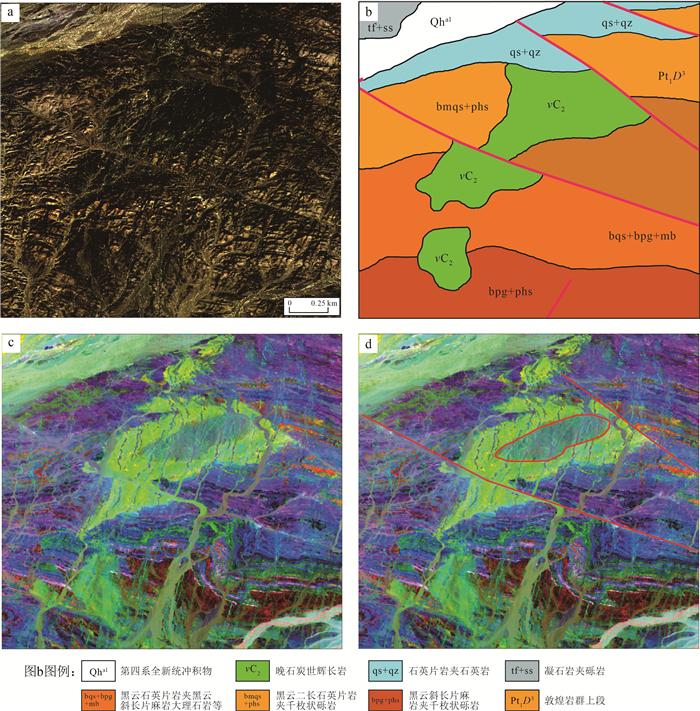
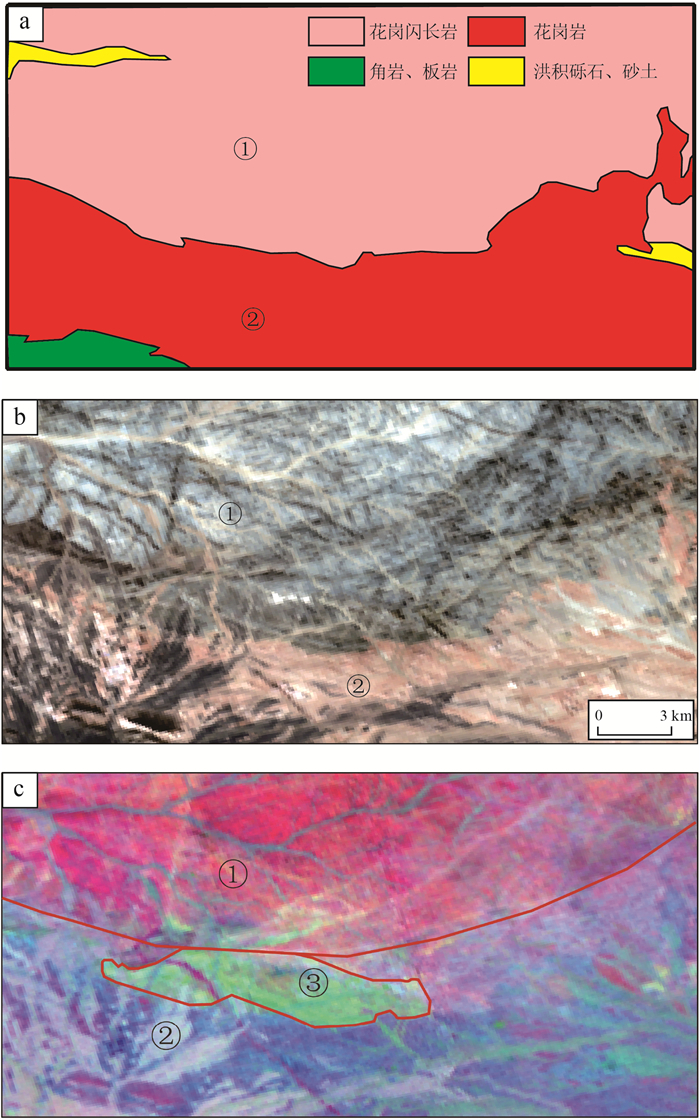
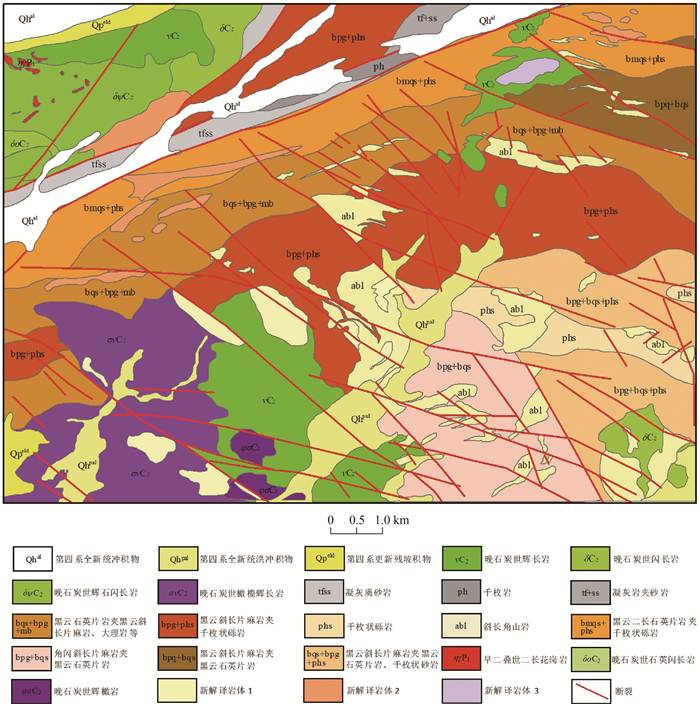
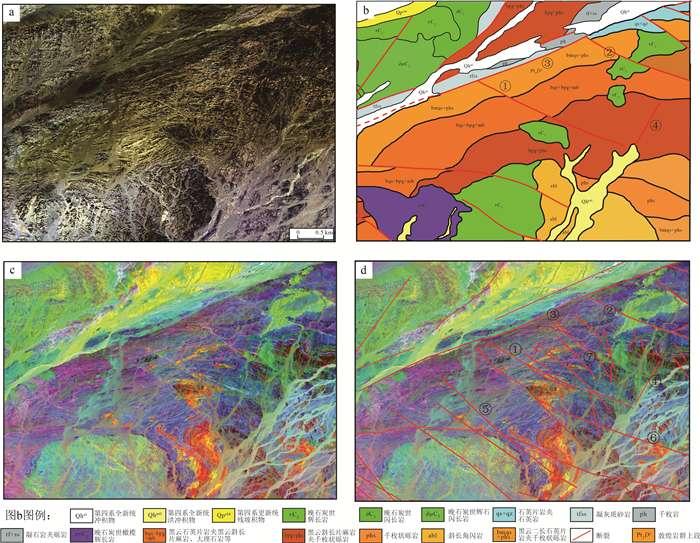
高光谱遥感以其超高的光谱维数据优势,使对地物的精细识别和区分能力较传统多光谱遥感数据有质的提升。以HyMap高光谱数据和高分五号高光谱数据为数据源,选择中国西部基岩区区域开展了高光谱遥感岩性-构造解译工作。通过图像增强处理后,对研究区地层单元、岩体/脉、构造等进行了遥感地质解译。对比已有的地质调查结果,发现高光谱遥感数据相较多光谱/高分数据对岩性-构造信息的展布情况显示得更加清晰和直观,同时其对不同岩性段、不同岩相带,以及细小构造等区分能力突出,表现出明显的技术优势。研究认为,高光谱遥感可为基岩区区域地质填图提供更加客观、真实的地质体、构造展布情况,能提高地质调查填图的效率和质量。
Abstract:Compared with the traditional multi-spectral remote sensing data, hyperspectral remote sensing has the advantage of ultra-high spectral dimension data, which makes its ability of fine recognition and discrimination of ground objects improved qualitatively.Using HyMap hyperspectral data and GF-5 hyperspectral data as data sources, the litho-structural interpretation was carried out in the bedrock area of western China.Through image enhancement processing, remote sensing geological interpretation of stratigraphic units, intrusives/veins and structures in the study area was carried out.Compared with the existing geological survey results, it is found that the hyperspectral remote sensing data is more clear and intuitive than the multispectral and high resolution data in the distribution of litho-structural information.Meanwhile, the hyperspectral remote sensing data have prominent ability to distinguish different lithology, different lithofacies and small structures, showing obvious technical advantages.The results show that hyperspectral remote sensing can provide more objective and real geological body and structure distribution for regional geological mapping in the bedrock area, and improve the efficiency and quality of geological mapping.
-
Key words:
- hyperspectral remote sensing /
- geological mapping /
- HyMap /
- GF-5 /
- remote sensing geology
-

-
表 1 HyMap主要技术指标
Table 1. Main technical indicators of HyMap
内容 主要指标 波长范围/nm 波段带宽/nm 光谱采样间隔/nm 波段数 VIS: 400~905 < 15 < 15 36 NIR: 880~1410 < 18 < 18 36 SWIR1:1400~1960 < 18 < 18 36 SWIR2:1950~2500 < 18 < 18 36 总波段数 144 视场角(FOV) 60° 表 2 高分五号主要技术指标
Table 2. Main technical indicators of GF-5
内容 主要指标 波长范围/nm 波段带宽/nm 光谱采样间隔/nm 波段数 VNIR: 390~1029 3.67~4.8 3.67~4.8 180 SWIR: 1005~2513 7.6~8.89 7.6~8.89 150 总波段数 330 空间分辨率/m 30 表 3 WorldView-2数据主要技术指标
Table 3. Main technical indicators of WorldView-2
内容 主要指标 传感器 全色波段 多光谱 空间分辨率/m 0.5 1.8 波长/nm 450~1040 蓝:450~510
绿:510~580
红:630~690
近红:770~895
黄:585~625 -
[1] 张志军, 刘世华, 孔迪, 等. 北巴颜喀拉山1: 5万区域地质调查中的遥感解译应用[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 30(5): 1141-1149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201605019.htm
[2] 侯德华, 张国立, 王硕, 等. 基于GF-2影像西藏桑耶地区岩性-构造遥感解译[J]. 中国地质调查, 2018, 5(5): 66-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201805009.htm
[3] 于洪苹, 滕正双. 基于多源遥感影像的吉林敦化塔东铁矿断裂构造解译[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(2): 223-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK202002013.htm
[4] 王阳明, 张景发, 刘智荣, 等. 基于多源遥感数据西藏山南地区活动断层解译[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2018, 30(3): 230-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201803031.htm
[5] 张瑞丝, 曹汇, 曾敏, 等. 基于ASTER光谱特征的科技廊带岩性填图: 以新疆塔什库尔干地区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(12): 3835-3846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201612018.htm
[6] Rowan L C, Mars J C, Simpson C J. Lithologic mapping of the Mordor, NT, Australia ultramafic complex by using the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer(ASTER)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 99(1/2): 105-126. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0034425705001690
[7] 李晓民, 李冬玲, 武平生, 等. 西昆仑甜水海西典型地区环境地质遥感调查进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(3): 57-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201703009.htm
[8] 燕云鹏, 刘刚, 李瑜, 等. 西北边境地区冰冻圈遥感调查与监测(2013-2015年)主要进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(3): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201703008.htm
[9] 陈玲, 梁树能, 周艳, 等. 国产高分卫星数据在高海拔地区地质调查中的应用潜力分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2015, 27(1): 140-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201501023.htm
[10] 鲁恒新, 徐岳仁, 陈立泽, 等. 国产GF-2和ZY-3卫星数据在活动断裂定量研究中的应用——以哈思山南麓断裂带为例[J]. 地震, 2017, 37(1): 121-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2017.01.013
[11] 王晓鹏, 杨志强, 康高峰, 等. WorldView-2高分辨率卫星数据在西昆仑塔什库尔干地区遥感地质调查中的应用[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2014, 29(3): 428-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201403019.htm
[12] 焦润成, 秦彦平, 张淑云, 等. WorldView-2数据在沉积岩地区的遥感岩性增强方法初探——以新疆喀什阿尔塔什地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(4): 277-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.04.030
[13] 李娜, 甘甫平, 董新丰, 等. 高分五号卫星高光谱数据岩性-构造解译初步应用评价[J]. 上海航天, 2019, 36(S2): 187-191, 198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHT2019S2028.htm
[14] 孙允珠, 蒋光伟, 李云端, 等. "高分五号"卫星概况及应用前景展望[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2018, 39(3): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2018.03.001
[15] 田野, 赵春晖, 季亚新. 主成分分析在高光谱遥感图像降维中的应用[J]. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2007, 23(5): 58-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBY200705018.htm
[16] Chen C M. Comparison of Principal Components Analysis and Minimum Noise Fraction Transformation for Reducing the Dimensionality of Hyperspectral Imagery[J]. Geographical Research, 2000, 33(1): 163-178. http://ir.lib.ntnu.edu.tw/handle/309250000Q/101139
[17] 周家晶. WorldView-2数据在遥感岩性解译中的应用方法研究——以西昆仑克孜勒地区为例[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2012.
-



 下载:
下载: