A geophysical technology for thematic geological mapping: Short period dense array
-
摘要:
以问题和需求为驱动的专题地质填图强调,针对某个主要地质体、沉积盆地、重要成矿带、地震带断裂系统等,采用现代化的技术手段开展针对性的专题调查和填图,以解决目标地质体结构、沉积盆地基底起伏、成矿地质体规模、断裂系统分布等重大问题。地球物理是专题填图不可缺少的手段之一,近10年发展起来的短周期密集台阵技术,因其布设灵活、应用广泛、精度高、成本低等特点备受关注。通过介绍短周期密集台阵发展现状,以及在城市、矿山、地震灾害区、沉积盆地等不同地质地貌条件下,利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景和技术方案建议,力图通过短周期密集台阵的调查构建结构成像方法,丰富和完善专题填图的技术方法体系。
Abstract:Thematic geological mapping driven by the demands and problems emphasizes that for different geological environments such as a major geological body, sedimentary basin, important metallogenic belt and fault system, modern technical means can be adopted to carry out thematic geological investigation and mapping, so as to solve some major problems of above-mentioned geological environments.Geophysics, as one indispensable means in thematic mapping, its short-period dense array technology developed in recent 10 years has attracted much attention due to flexible layout, wide application, high precision and low cost.This paper mainly introduces the current situation of short period dense array, and its application to near surface structure investigation under different geological and geomorphic conditions such as cities, mines, earthquake and sedimentary basins, etc.The application prospect and technical scheme suggestions of its technology in thematic geological mapping is put forward to improve and perfect the method system of thematic geological mapping technology by means of constructing structure imaging method through the investigation of short period dense array.
-
Key words:
- regional geology /
- thematic geological mapping /
- dense seismic array /
- shallow structure
-

-
图 1 唐山断裂及邻区短周期密集台阵部署位置图[8]
Figure 1.
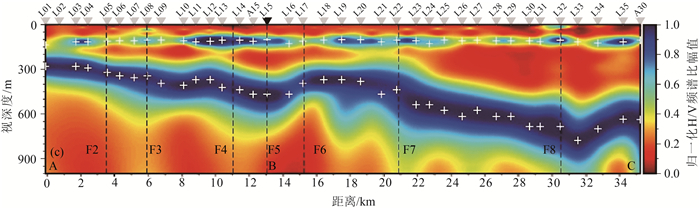
图 2 唐山断裂及邻区短周期密集台阵观测的浅层结构[19]
Figure 2.
图 3 唐山震区第四纪沉积厚度和基底埋深图[8]
Figure 3.
图 4 程海断裂短周期密集台阵位置及S波速度模型[22]
Figure 4.
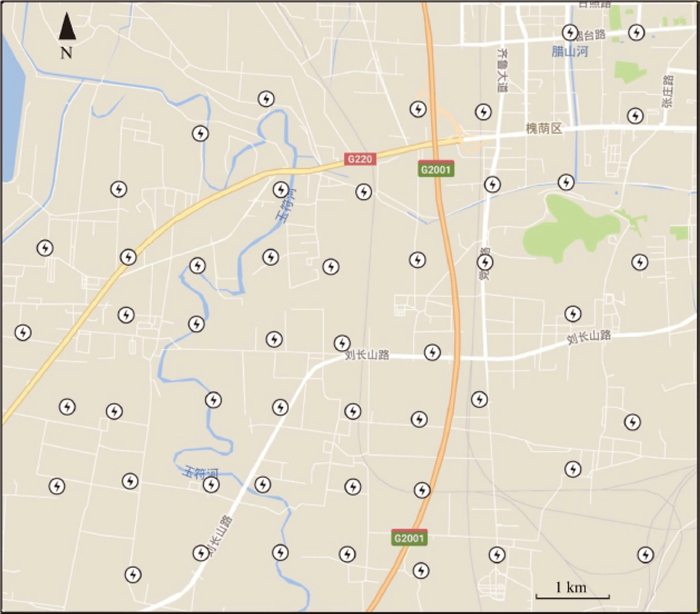
图 5 济南城区短周期密集台阵部署位置[9]
Figure 5.
图 6 济南城区不同深度(100 m、300 m、600 m、1000 m)横波速度切片图[9]
Figure 6.
图 7 合肥市地震台阵部署图和浅层速度剖面[24]
Figure 7.
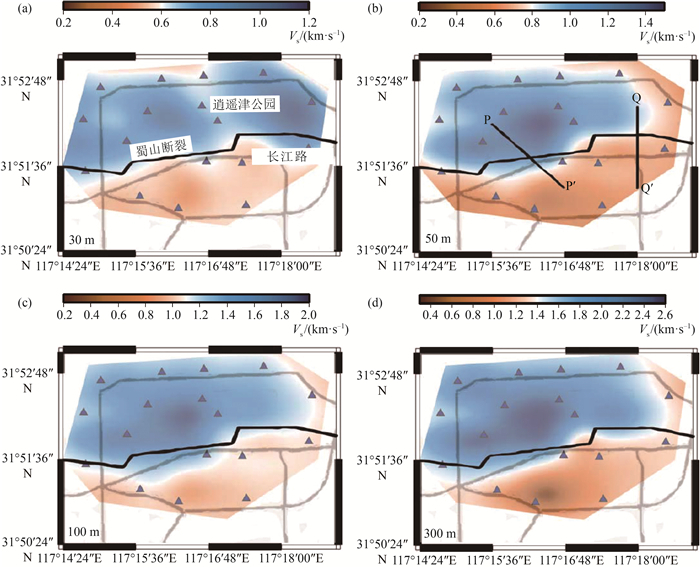
图 8 合肥市不同深度S波速度结构[24](a~d分别为30 m、50 m、100 m、300 m深度的结构)
Figure 8.
图 9 新丰江水库库区地震台阵位置及浅层速度结构[25]
Figure 9.
图 10 喀拉通克矿集区地震台阵部署位置及剪切波速度结构[26]
Figure 10.
图 11 美国西海岸San Jacinto断层的浅层速度结构与地形数据、断裂信息融合实例[36]
Figure 11.
-
[1] 王涛, 计文化, 胡建民, 等. 专题地质填图及有关问题讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(5): 633-641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.001
[2] 孟贵祥, 吕庆田, 严加永, 等. "穿透性"探测技术在覆盖区地质矿产调查中的应用研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(5): 637-650. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201905001.htm
[3] Lin F C, Li D Z, Clayton R W, et al. High-resolution 3D shallow crustal structure in Long Beach, California: Application of ambient noise tomography on a dense seismic array[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(4): 45-56. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/274518231_High-resolution_3D_shallow_crustal_structure_in_Long_Beach_California_Application_of_ambient_noise_tomography_on_a_dense_seismic_array?ev=auth_pub
[4] Yao H J, Wang B S, Tian X B, et al. Preface to the special issue of dense array seismology[J]. Earthquake Science, 2018, 31: 225-226. doi: 10.29382/eqs-2018-0225-1
[5] Inbal A, Clayton R W, Ampuero J P. Imaging widespread seismicity at midlower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(15): 6314-6323. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064942
[6] Inbal A, Ampuero J P, Clayton R W. Localized seismic deformation in the upper mantle revealed by dense seismic arrays[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6308): 88-92. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1370
[7] Liu Z, Tian X B, Gao R, et al. New images of the crustal structure beneath eastern Xizang from a high-density seismic array[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, (480): 33-41. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X17305587
[8] Bao F, Li Z W, Tian B F, et al. Sediment thickness variations of the Tangshan fault zone in North China from a dense seismic array and microtremor survey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, (185): 104045. https: //doi. org/10.1016/j. jseaes. 2019.104045 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912019303979
[9] 梁锋, 高磊, 王志辉, 等. 利用背景噪声层析成像研究济南浅层横波速度结构[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(3): 129-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201903020.htm
[10] Li Z W, Ni S D, Zhang B L, et al. Shallow magma chamber under the Wudalianchi Volcanic Field unveiled by seismic imaging with dense array[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 4951-496. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016gl068895
[11] 张明辉, 武振波, 马立雪, 等. 短周期密集台阵被动源地震探测技术研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(2): 495-511. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202002014.htm
[12] Liu Z, Tian X B, Gao R, et al. New images of the crustal structure beneath eastern Xizang from a high-density seismic array[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 480: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.09.048
[13] 张路, 白志明, 徐涛, 等. 哀牢山地区新生代岩浆活动与掀斜式抬升: 来自短周期密集台阵观测的证据[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50(8): 1069-1082. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202008003.htm
[14] Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. , 1957, 35: 415-456. http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=90217
[15] Nakamura Y. A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface[J]. Quarterly Reports, Railway Technical Research Institute, 1989, 30(1): 25-33. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10007555176
[16] Brenguier F, Duputel Z, Shapiro N M. Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(2): 126-130. doi: 10.1038/ngeo104
[17] Xu Z J, Song X D. Temporal changes of surface wave velocity associated with major Sumatra earthquakes from ambient noise correlation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(34): 14207-14212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901164106
[18] Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M, Barmin M, et al. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007, 169: 1239-1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
[19] Bao F, Li Z W, Yuen D, et al. Shallow structure of the Tangshan fault zone unveiled by dense seismic array and horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio method[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2018, 281: 46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2018.05.004
[20] 刘保金, 曲国胜, 孙铭心, 等. 唐山地震区地壳结构和构造: 深地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(4): 901-912. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.04.014
[21] 郭慧, 江娃利, 谢新生. 对1976年河北唐山MS7.8地震地表破裂带展布及位移特征的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(3): 506-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.03.002
[22] Yang H F, Duan Y H, Song J H, et al. Fine structure of the Chenghai fault zone, Yunnan, China, constrained from teleseismic travel time and ambient noise tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2020, 125: 1-14. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2020JB019565
[23] 林良俊, 李亚民, 葛伟亚, 等. 中国城市地质调查总体构想与关键理论技术[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1086-1101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706006.htm
[24] Li C, Yao H J, Fang H J, et al. 3D Near-surface shear-wave velocity structure from ambient-noise tomography and borehole data in the Hefei urban area, China[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 2016, 87(4): 882-892. doi: 10.1785/0220150257
[25] 王爽, 孙新蕾, 秦加岭, 等. 利用密集地震台网高频环境噪声研究广东新丰江库区浅层地下结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(2): 593-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201802018.htm
[26] Du P X, Wu J, Wang J, et al. Imaging Karatungk Cu-Ni mine in Xinjiang, western China with a passive seismic array[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(7): 601. doi: 10.3390/min10070601
[27] 田忠华, 刘福来, 许王, 等. 构造变形在变质岩专题填图中的作用及其意义——以辽南辽河群试点填图区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1942-1952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.005
[28] 童英, 郭磊, 王涛, 等. 同源花岗岩谱系填图——内蒙古二连宝德尔石林花岗岩填图试点[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1963-1970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.007
[29] 薛怀民, 曹光跃, 刘哲. 陆相火山岩区岩性组合-岩相填图试验——以内蒙古西太仆寺破火山为例[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 2030-2035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.012
[30] 许欢, 柳永清, 旷红伟, 等. 燕山西部尚义盆地沉积岩区专题地质填图方法与成果[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1893-1918. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.002
[31] 闫臻, 王宗起, 付长垒, 等. 混杂岩基本特征与专题地质填图[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 167-191. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020301&flag=1
[32] 张进, 曲军峰, 张庆龙, 等. 基岩区构造地质填图方法思考、实践、探索[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 192-221. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020302&flag=1
[33] Yao H J, Hilst R D V D, Hoop M V D. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Xizang from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis-I. Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2006, 166(2): 732-744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03028.x
[34] Yao H J, Pierre G, Collins J A, et al. Structure of young East Pacific Rise lithosphere from ambient noise correlation analysis of fundamental- and higher-mode Scholte-Rayleigh waves[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoence, 2011, 343(8): 571-583. http://www.em-consulte.com/en/article/664890
[35] Bowden D C, Tsai V C, Lin F C. Site amplification, attenuation, and scattering from noise correlation amplitudes across a dense array in Long Beach, CA[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(5): 1360-1367. doi: 10.1002/2014GL062662
[36] Mordret A, Roux P, Boué P, et al. Shallow three-dimensional structure of the San Jacinto fault zone revealed from ambient noise imaging with a dense seismic array[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2019, 216: 896-905. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggy464
-




 下载:
下载: