Geochemical characteristics, isotopic ages and tectonic environment of Sangejing Formation in Beishan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
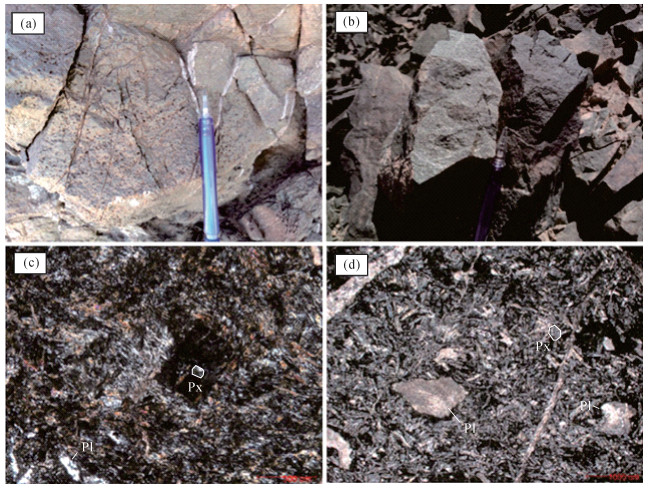
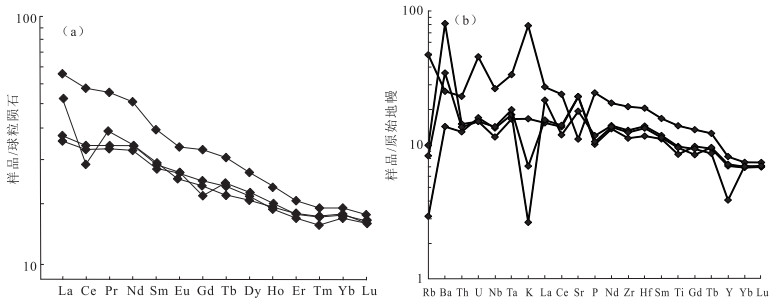
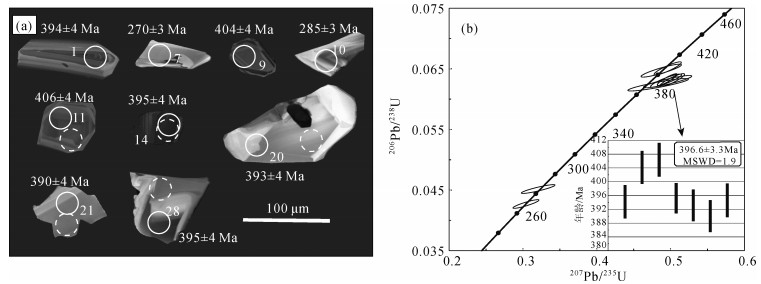
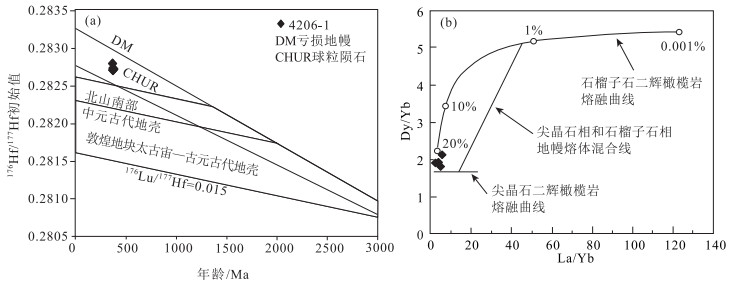
北山造山带中段白云山蛇绿岩带南部出露的三个井组火山-沉积地层,主要由枕状玄武岩与气孔杏仁状玄武岩组成,空间上与凝灰质碎屑岩、薄层粘土质硅质岩及厚层状碳酸盐岩整合接触。获得三个井组玄武岩年龄加权平均值为396.6±3.3 Ma,为早泥盆世。岩石地球化学研究表明,玄武岩主量元素特征显示其主体属于亚碱性系列拉斑玄武岩;稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线主体呈现轻稀土元素富集的右倾型,稀土元素总量为35.88×10-6~129.41×10-6,LREE/HREE值为1.62~3.84,(La/Yb)N值为1.02~3.42。结合区域上大面积发育的S型、A型花岗岩共同构成双峰式岩浆组合特征,推断三个井组处于造山后伸展的构造环境。结合前人资料及区域对比推断,北山地区北山洋闭合于早泥盆世之前。锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究表明,三个井组玄武岩εHf(t)为(+4.67~+8.02),tDM1=692~826 Ma,结合微量元素Dy/Yb值(1.77~2.13),推断三个井组玄武岩是新元古代地幔源区的亏损尖晶石相地幔橄榄岩向石榴子石相地幔橄榄岩过渡的较高程度部分熔融的产物。
Abstract:A set of island arc basalts is exposed in Sangejing Formation in the south of Baiyunshan ophiolite belt in the middle part of Beishan orogenic belt.It is mainly composed of pillow basalt and porous almond basalt, conformable contact with tuffaceous clastic rocks, thin-layered clayey siliceous rocks and thick-layered carbonate rocks.The weighted average age of basalts in Sangejing Formation is 396.6±3.3 Ma, suggesting Early Devonian.A study of the rock geochemistry shows that the major elements characteristics of the basalts of the Sangejing Formation indicate that the main body of the basalts belongs to the subalkaline tholeiite series.The main part of the normalized distribution curve of chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the basalts exhibit the right-oblique type of enrichment of LREE, with ∑REE being 35.88×10-6~129.41×10-6, LREE/HREE being 1.62~3.84, and (La/Yb)N being 1.02~3.42.The bimodal magmatic assemblage consists of Sangejing basalts, and S-type and A-type granites are developed extensively in this region.It is inferred that the Sangejing Formation occurred after an orogenic extensional tectonic environment.Based on previous data and regional comparison, it is inferred that the Beishan Ocean in Beishan area was closed before the Early Devonian.A study of Lu-Hf Isotope of zircon indicates that the Sangejing basalt has the data εHf(t)=(+4.67~+8.02), tDM1=692~826 Ma and Dy/Yb=1.77~2.13, and that the Sangejing basalts were formed by partial melting of the depleted spinel-facies mantle peridotite to garnet-facies mantle peridotite in the Neoproterozoic mantle source area.
-
Key words:
- Beishan orogenic belt /
- Sangejing Formation /
- bimodal magma /
- geochemistry /
- Lu-Hf isotope
-

-
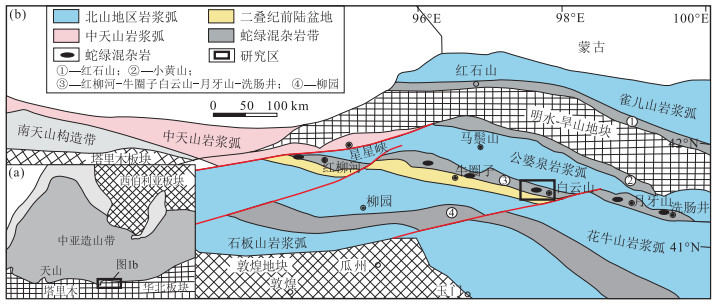
图 1 北山造山带蛇绿岩时空分布(a)和中亚造山带构造简图(b)(据参考文献[11]修改)
Figure 1.
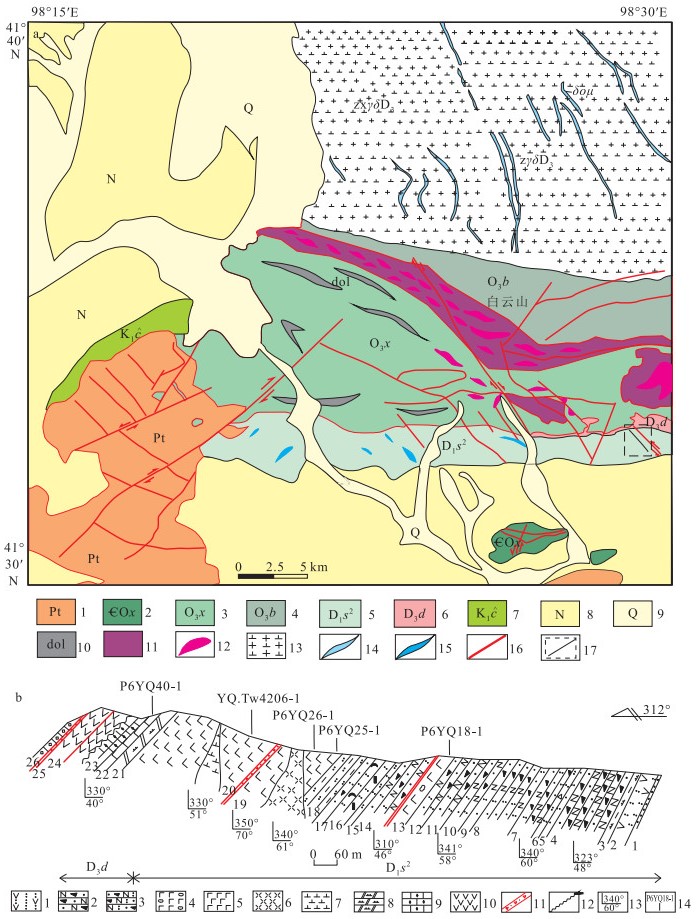
图 2 月牙山幅地质简图(a)和三个井组PM06实测剖面(b)①
Figure 2.
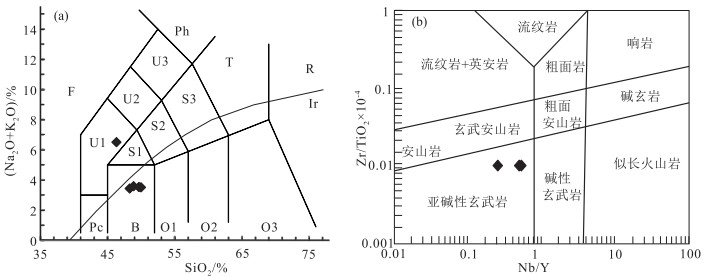
图 4 火山岩TAS图解(a)[43]和玄武岩Nb/Y-TiO2×10-4图解(b)
Figure 4.
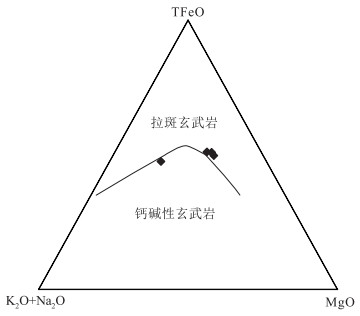
图 5 AFM图解[45]
Figure 5.
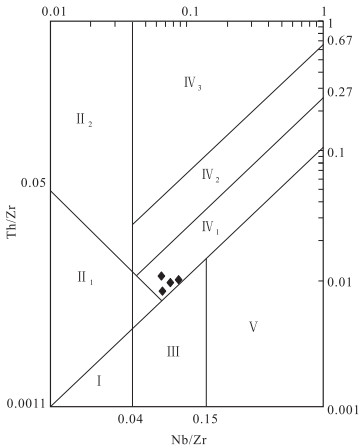
图 9 玄武岩大地构造环境Nb/Zr-Th/Zr双对数判别图[55]
Figure 9.
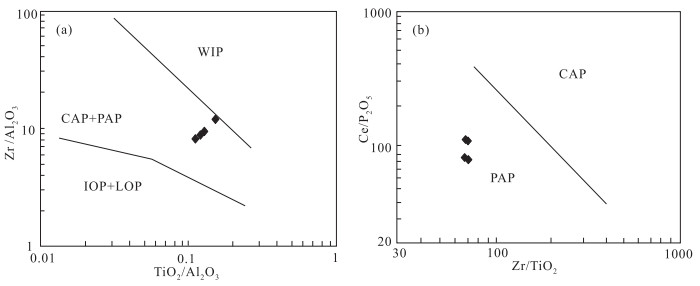
图 10 三个井组玄武岩TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3图解(a)和Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5图解(b)[56]
Figure 10.
表 1 三个井组玄武岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1. Geochemical data of major, trace elements and REE for Sangejing Formation basalt
样号 P6YQ18-1 P6YQ25-1 P6YQ25-2 YQ4206-1 SiO2 41.48 48.36 46.87 47.41 Al2O3 16.55 14.92 14.55 15.68 Fe2O3 2.74 4.24 7.06 4.37 FeO 5.34 5.82 3.58 6.13 CaO 11.50 11.82 11.89 9.28 MgO 2.83 6.08 6.37 6.84 K2O 2.06 0.45 0.20 0.08 Na2O 3.75 2.93 3.12 3.28 TiO2 2.66 1.76 1.98 1.99 P2O5 0.47 0.21 0.22 0.24 MnO 0.13 0.16 0.19 0.15 灼失量 9.91 2.61 2.99 3.87 总计 99.42 99.36 99.02 99.32 Mg# 43.19 56.96 58.77 67.93 Hf 5.73 3.55 4.06 4.21 Zr 213 124 137 142 Cr 154 211 239 236 Ni 57.00 73.60 93.70 73.80 Ga 22.50 19.20 20.40 19.10 Rb 29.40 6.22 5.20 1.84 Sr 230 476 478 371 Y 282 267 32.2 392 Nb 18.50 8.05 9.61 9.39 Cs 2.29 0.13 0.24 0.15 Ba 173 554 237 94.4 Ta 1.35 0.63 0.74 0.68 Pb 1.94 1.83 2.12 2.18 Th 1.93 1.20 1.14 1.05 U 0.94 0.31 0.31 0.33 La 18.30 9.90 10.40 14.60 Ce 41.80 23.90 24.50 20.80 Pr 6.07 3.63 3.70 4.25 Nd 27.40 17.60 18.20 18.60 Sm 6.90 4.85 4.97 5.15 Eu 2.22 1.75 1.74 1.65 Gd 7.63 5.73 4.97 5.49 Tb 1.30 1.00 1.02 0.92 Dy 7.70 6.22 6.37 5.99 Ho 1.50 1.23 1.28 1.26 Er 3.88 3.31 3.39 3.46 Tm 0.56 0.48 0.51 0.52 Yb 3.61 3.30 3.35 3.39 Lu 0.54 0.50 0.51 0.50 ∑LREE 102.69 61.63 63.51 65.05 ∑HREE 26.72 21.77 21.4 21.53 LREE/HREE 3.84 2.83 2.97 3.02 (La/Yb)N 3.42 2.02 2.09 2.9 δEu 0.94 1.02 1.07 0.95 Nb/Y 0.50 0.26 0.30 0.54 ΔNb 0.79 0.86 0.01 0.97 注:Mg#=100×Mg/(Mg+Fe),△Nb=1.74+lg(Nb/Y)-1.92×lg(Zr/Y);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 三个井组玄武岩样品(4206-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb数据
Table 2. LA-ICP-MS zircons U-Th-Pb data of Sangejing Formation basalt(4206-1)
测点号 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Pb/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 4206.1.01 86 105 7 0.82 0.057 0.002 0.494 0.014 0.057 0.002 484 58 408 11 394 4 4206.1.02 100 195 13 0.52 0.057 0.002 0.501 0.017 0.057 0.002 471 80 413 14 402 5 4206.1.03 105 998 34 0.11 0.053 0.001 0.266 0.006 0.053 0.001 329 30 240 5 231 4 4206.1.04 91 125 9 0.73 0.055 0.002 0.486 0.014 0.055 0.002 430 62 402 12 397 4 4206.1.05 19 62 4 0.31 0.053 0.003 0.469 0.026 0.053 0.003 326 120 390 21 401 5 4206.1.06 57 115 7 0.50 0.054 0.005 0.416 0.041 0.054 0.005 383 221 353 35 349 4 4206.1.07 147 116 6 1.26 0.052 0.002 0.304 0.012 0.052 0.002 270 86 270 10 270 3 4206.1.08 88 300 19 0.29 0.056 0.001 0.492 0.010 0.056 0.001 465 43 406 8 396 4 4206.1.09 140 182 13 0.77 0.055 0.002 0.487 0.018 0.055 0.002 397 84 403 15 404 4 4206.1.10 66 82 4 0.80 0.052 0.002 0.321 0.015 0.052 0.002 263 107 282 13 285 3 4206.1.11 90 172 12 0.52 0.055 0.001 0.496 0.012 0.055 0.001 424 51 409 10 406 4 4206.1.12 418 555 40 0.75 0.056 0.001 0.504 0.007 0.056 0.001 457 28 414 6 406 4 4206.1.13 51 246 115 0.21 0.163 0.002 0.109 0.156 0.163 0.002 2486 19 2445 38 2396 30 4206.1.14 383 294 23 1.30 0.057 0.001 0.495 0.009 0.057 0.001 485 37 409 7 395 4 4206.1.15 65 110 7 0.59 0.056 0.003 0.490 0.030 0.056 0.003 461 135 405 25 395 4 4206.1.16 133 162 10 0.82 0.054 0.001 0.398 0.010 0.054 0.001 387 52 340 8 333 4 4206.1.17 135 282 18 0.48 0.055 0.002 0.468 0.014 0.055 0.002 396 66 390 11 388 4 4206.1.18 538 332 206 1.62 0.166 0.002 0.910 0.144 0.166 0.002 2521 19 2515 33 2509 25 4206.1.19 223 587 38 0.38 0.056 0.001 0.493 0.009 0.056 0.001 449 39 407 8 399 4 4206.1.20 40 56 4 0.72 0.057 0.002 0.496 0.022 0.057 0.002 499 94 409 18 393 4 4206.1.21 44 58 4 0.76 0.056 0.003 0.483 0.027 0.056 0.003 460 119 400 22 390 4 4206.1.22 261 337 13 0.77 0.052 0.001 0.259 0.006 0.052 0.001 286 43 234 5 229 3 4206.1.23 122 226 75 0.54 0.110 0.001 4.704 0.062 0.110 0.001 1791 21 1768 23 1748 17 4206.1.24 257 710 46 0.36 0.056 0.001 0.486 0.008 0.056 0.001 431 34 402 7 397 4 4206.1.25 136 175 12 0.78 0.058 0.001 0.491 0.011 0.058 0.001 519 45 406 9 386 4 4206.1.26 176 623 38 0.28 0.056 0.001 0.488 0.007 0.056 0.001 464 27 403 6 393 4 4206.1.27 198 558 36 0.35 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.008 0.056 0.001 447 30 409 6 402 4 4206.1.28 87 215 14 0.41 0.058 0.001 0.502 0.011 0.058 0.001 518 41 413 9 395 4 4206.1.29 152 424 27 0.36 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.007 0.056 0.001 468 28 409 6 399 4 4206.1.30 249 399 31 0.62 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.012 0.056 0.001 448 44 409 9 402 4 4206.1.31 17 280 95 0.06 0.116 0.001 5.523 0.073 0.116 0.001 1900 21 1904 25 1908 19 4206.1.32 661 1208 137 0.55 0.068 0.001 1.029 0.016 0.068 0.001 882 24 718 11 667 8 表 3 三个井组玄武岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据
Table 3. Lu-Hf isotope data of Sangejing Formation basalt
测点号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 176Hf/177Hfi 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 4206.01.11 406 0.020250 0.000876 0.282678 0.282672 0.000029 -3.31 5.40 811 1052 -0.97363 4206.01.14 395 0.017497 0.000782 0.282692 0.282686 0.000029 -2.82 5.67 789 1026 -0.97646 4206.01.20 393 0.013875 0.000589 0.282664 0.282660 0.000027 -3.82 4.68 825 1087 -0.98225 4206.01.21 390 0.019975 0.000787 0.282762 0.282756 0.000069 -0.36 8.02 692 873 -0.97630 4206.01.28 395 0.012072 0.000507 0.282662 0.282658 0.000022 -3.90 4.67 826 1090 -0.98474 -
[1] Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S.Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J].Nature, 1993, 364:299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[2] Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B.Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J].Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Earth Sciences, 2000, 91:181-193. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300007367
[3] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Journal of the Geological Society, London, 2007, 164:31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
[4] Kovalenko V I, Yarmolyuk V V, Kovach V P, et al.Isotopic provinces, mechanism of generation and sources of the continental curst in the Central Asian mobile belt:geological and isotopic evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:605-627. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00130-5
[5] Xiao W J, Han C M, Yuan C, et al.Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of North Xinjiang, NW China:implications for the tectonic evolution of Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32:102-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.10.008
[6] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yuan C, et al.Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids[J].American Journal of Science, 2009, 309; 221-270. doi: 10.2475/03.2009.02
[7] Cawood P A, Kröner A, Collins W J, et al.Earth accretionary orogens through Earth history[C]//Cawood P A, Kröner A.Earth accretionary systems in space and time.Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 2009, 318: 1-36.
https://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035566457210_4abf.html [8] Jahn B M.The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and growth of the continental crust in the Phanerozoic[C]//Malpas J, Fletcher C J N, Ali J R, et al, Aspects of the tectonic evolution of China.Geological Society, London, 2004: 3-100.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249551250_The_Central_Asian_Orogenic_Belt_and_growth_of_the_continental_crust_in_the_Phanerozoic [9] Xiao W, Mao Q G, Windley B F, et al.Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J].American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:1553-1594. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.12
[10] Song D F, Xiao W J, Han C M, et al.Progressive accretionary tectonics of the Beishan orogenic collage, Southern Altaids:insights from zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic data of high-grade complexes[J].Precambrian Research, 2013, 227:368-388. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.06.011
[11] Wang S D, Zhang K X, Song B W, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Niujuanzi ophiolitic mélange, Gansu Province, NW China:implications for tectonic evolution of the Beishan Orogenic collage[J].Original Paper, 2017, 6:1-21.
[12] Ding J X, Han C M, Xiao W J, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes of the granitic rocks associated with tungsten deposits in Beishan district, NW China, Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Petrogenesis, metallogenic and tectonic implications[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 89:441-462. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.06.018
[13] 胡新茁, 赵国春, 胡新悦, 等.内蒙古北山地区月牙山蛇绿质构造混杂岩带地质特征、形成时代及大地构造意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(2/3):425-436. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2015020318&flag=1
[14] 左国朝, 何国琦.北山板块构造及成矿规律[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1990:1-226.
[15] 龚全胜, 刘明强, 梁明宏, 等.北山造山带大地构造相及构造演化[J].西北地质, 2003, 36(1):11-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200301002
[16] 龚全胜, 刘明强, 李海林, 等.甘肃北山造山带类型及基本特征[J].西北地质, 2002, 35(3):28-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200203004
[17] 于福元, 李金宝, 王涛.东天山红柳河地区蛇绿岩U-Pb同位素年龄[J].地球学报, 2006, 27(3):213-216. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb200603004
[18] 张元元, 郭召杰.甘新交界红柳河蛇绿岩形成和侵位年龄的准确限定及大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):804-809. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200804019
[19] Wu T R, Zheng R G, Zhang W, et al.Tectonic framework of Beishan MountainNorthern Alxa Area and the time constraints for the closing of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J].Proceedings of the Fifth Workshop on 1:5000000 International Geological Map of Asia, 2011:95-98.
[20] 侯青叶, 王忠, 刘经宝, 等.北山月牙山蛇绿岩地球化学特征及SHRIMP定年[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):1008-1018. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201205022
[21] 李向民, 余吉远, 王国强, 等.甘肃北山地区芨芨台子蛇绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(12):2025-2031. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201212011
[22] Tian Z H, Xiao W J, Windley B F, et al.Structure, age, and tectonic development of the Huoshishan-Niujuanzi ophiolitic mélange, Beishan, southernmost Altaids[J].Gondwana Research, 2014, 25:820-841. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.006
[23] 王国强, 李向民, 徐学义, 等.甘肃北山红石山蛇绿岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(6):1685-1694. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201406011
[24] 孙立新, 张家辉, 任邦方, 等.北山造山带白云山蛇绿混杂岩的地球化学特征、时代及地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(2):131-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201702001
[25] Ao S J, Xiao W J, Han C M, et al.Cambrian to early Silurian ophiolite and accretionary processes in the Beishan collage, NW China:implications for the architecture of the Southern Altaids[J].Geological Magazine, 2012, 149(4):606-625. doi: 10.1017/S0016756811000884
[26] Guo Q Q, Xiao W J, Hou Q L, et al.Construction of Late Devonian Dundunshan arc in the Beishan orogen and its implication for tectonics of southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Lithos, 2014, 184:361-378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=12623046eb693c8acdf0846752adffb9
[27] Guo Q Q, Chung S L, Xiao W J, et al.Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Devonian arc volcanic rocks in southern Beishan orogen, NW China:Geochemical and Nd-Sr-Hf isotopic constraints[J].Lithos, 2017, 84-96. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493717300324
[28] Zhu J, Lv X B, Peng S G.U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications of the early Devonian granitoids in the Liuyuan area, Beishan, NW China[J].Geosciences Journal, 2016, 20(5):609-625. doi: 10.1007/s12303-016-0004-2
[29] Wang X Y, Yuan C, Zhang Y Y, et al.S-type granite from the Gongpoquan arc in the Beishan Orogenic collage, southern Altaids:Implications for the tectonic transition[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 153:206-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.037
[30] 郑荣国, 吴泰然, 张文, 等.甘肃北山中带早泥盆世的构造-岩浆作用:来自公婆泉花岗岩体年代学和地球化学证据[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(4):603-616. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=42762532
[31] 李向民, 余吉远, 王国强, 等.甘肃北山红柳园地区泥盆系三个井组和墩墩山群LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其意义[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(10):1501-1507. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20111003&flag=1
[32] Chen F K, Hegner E, Todt W.Zircon ages, Nd isotopic and chemical compositions of orthogneisses from the Black Forest, Germany:Evidence for a Cambrian magmatic arc[J].Internatianal Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 88:791-802. doi: 10.1007/s005310050306
[33] Chen F K, Siebel W, Satir M, et al.Geochronology of the Karadere basement(NW Turkey)and implications for the geological evolution of the Istanbul zone[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 91:469-481. doi: 10.1007/s00531-001-0239-6
[34] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J].Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2):537-571. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/content/51/1-2/537
[35] Ludwig K R.Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J].Berkeley Geochronology Center, California, Berkeley, 2003, 1-39. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/306157481_Isoplot_v_30_a_geochronological_toolkit_for_Microsoft_Excel
[36] Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al.Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2006.234(1/2):105-126. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254106002452
[37] Sderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D, et al.The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004.219(3/4):311-324. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c0792ad455eb65fadd619aef64d4bef9
[38] Bouvier A, Vervoort J D, Patchett P J.The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR:Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1/2):48-57. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X08003828
[39] Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al.The Hf-isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1):133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
[40] Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al.Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J].Precambrian Research, 2004, 131(3/4):231-282. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926804000178
[41] Wilson M.Igneous Petrogenesis:A global tectonic approach[M].London:Chapman and Hall, 1989.
[42] Rapp R P.Heterogeneous source regions for Archean granitoids[C]//Wit M J, Ashwal L D.Green Stone Belts.Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997: 35-37.
[43] Eric A K.Middlemost.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth-Science Reviews 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
[44] Winchester J A, Floyd P A.Geochemical discrimination of different magmas series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 20:325-343.
[45] Irvine T N, Baragar W R A.A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J].Can.J.Earth Sci., 1971, 8:523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
[46] Boynton W V.Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P.Rare earth element geochemistry.Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308632289_Geochemistry_of_the_rare_earth_elements_Meteorite_studiesA [47] Sun S S, McDonough WF.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989:313-345. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=specpubgsl&resid=42/1/313
[48] 杨杰, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等.东昆仑南缘布青山地区哈尔郭勒玄武岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(2):335-349. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201402003
[49] Belousova E W, Griffinsuzanne Y, O'Reilly, et al.Igneous zircon:trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
[50] Hoskin P W O.Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18(4):423-439. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00266.x
[51] 王立武, 王颖, 杨静, 等.用碎屑锆石SHRIMP年代学方法恢复松辽盆地南部前中生代基底的源区特征[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(4):151-158. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200704016
[52] 李文国, 李庆富, 姜万德, 等.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996.
[53] 梁积伟, 陈玉良, 张文卿, 等.甘肃北山地区泥盆系三个井组碎屑锆石年龄及其地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201403001
[54] 王立武, 王颖, 杨静, 等.用碎屑锆石SHRIMP年代学方法恢复松辽盆地南部前中生代基底的源区特征[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(4):151-158. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200704016
[55] 孙书勤, 张成江, 赵松江.大陆板内构造环境的微量元素判别[J].大地构造与成矿, 2007, 2:104-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200701012
[56] Müller D, Rock N M S, Groves D I.Geochemical discrimination between shoshonotic and potassic volcanic rocks from different tectonic settings:A pilot study[J].Mineral Petrol., 1992, 46(2):359-289. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034348621910_45c6.html
[57] Harrison T M, Blichert-Toft J, Muller W, et al.Heterogeneous Hadean hafnium:Evidence of continental crust at 4.4 to 4.5Ga[J].Science, 2005, 310(5756):1947-1950. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=19320131&site=ehost-live
[58] Wendlandt R F, Altherr R, Neumann E R, et al.Petrology, geochemistry, isotopes[C]//Olsen K H.Continental rifts: Evolution, strcture, tectonics.Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1995: 47-60.
[59] Deniel C.Geochemical and isotopic(Sr-Nd-Pb)evidence for plume-lithosphere interactions in the genesis of Grande Comoremagamas(Indian Ocean)[J].Chem.Geol., 1998, 144:281-303. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00139-3
[60] Miller C, Schuster R, Klötzli U, et al.Post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic magmatism in SW Tibet:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic constraints for mantle source characteristics and petrogenesis[J].Journal of Petrology, 1990, 40:1399-1424. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/content/40/9/1399
[61] He Z Y, Zhang Z M, Zong K Q, et al.Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic studies of the Xingxingxia Complex from Eastern Tianshan(NW China):Significance to the reconstruction and tectonics of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Lithos, 2014, 190:485-499. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260006872_Zircon_U-Pb_and_Hf_isotopic_studies_of_the_Xingxingxia_Complex_from_Eastern_Tianshan_NW_China_Significance_to_the_reconstruction_and_tectonics_of_the_southern_Central_Asian_Orogenic_Belt
[62] Huang B T, He Z Y, Zhang Z M, et al.Early Neoproterozoic granitic gneisses in the Chinese Eastern Tianshan:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2014, 21(8):1-14. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912014003642
[63] 叶晓峰, 宗克清, 张泽明, 等.北山造山带南缘柳园地区新元古代花岗岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2013, 32:307-317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201302010
[64] 姜洪颖, 贺振宇, 宗克清, 等.北山造山带南缘北山杂岩的锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素研究[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29:3949-3967. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201311024
[65] He Z Y, Zhang Z M, Zong K Q, et al.Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution of the Tarim Craton:Constrained by zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopes of meta-igneous rocks from Korla and Dunhuang[J].J.Asian Earth Sci., 2013, 78:54-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.022
[66] Zong K, Liu Y, Zhang Z, et al.The generation and evolution of Archean continental crust in the Dunhuang block, northeastern Tarim craton, northwestern China[J].Precambrian Res., 2013, 235:251-263. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.07.002
[67] Huang B T, He Z Y, Zong K Q, et al.Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of Neoproterozoic granitic gneisses from the Alatage area:Constraints on the Precambrian crustal evolution in the Chinese Central Tianshan Block[J].Chin.Sci.Bull., 2014, 59:100-112. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-0010-y
[68] Zhang J X, Yu S Y, Gong J H, et al.The latest Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic evolution of the Dunhuang block, eastern Tarim Craton, northwestern China:Evidence from zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analyses[J].Precambrian Res., 2013, 226:21-42. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.11.014
[69] 王树庆, 胡晓佳, 赵华雷.内蒙古苏左旗洪格尔地区新发现晚石炭世碱性花岗岩[J].地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(2):81-85. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz201902001
[70] 王智, 王惠初, 施建荣.内蒙古集宁地区徐武家变质辉长岩的形成背景及其地质意义[J].地质调查与研究, 2020, 42(2):97-113. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz202002005
① 田健, 段霄龙.内蒙古1: 5万月牙山K47E015010、儿驼山K47E016010幅区域地质矿产调查报告.2018.
② 地质部甘肃省地质局第二区域地质测量队.石板井幅1: 20万区域矿产调查报告.1972.
-



 下载:
下载: