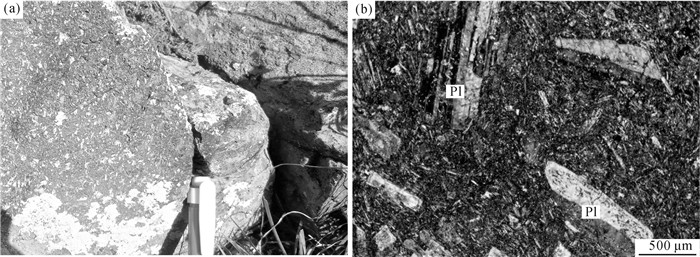
The Early Permian adakite in the Meilaotewula ophiolite of Inner Mongolia and intra-oceanic subduction in eastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean
-
摘要:
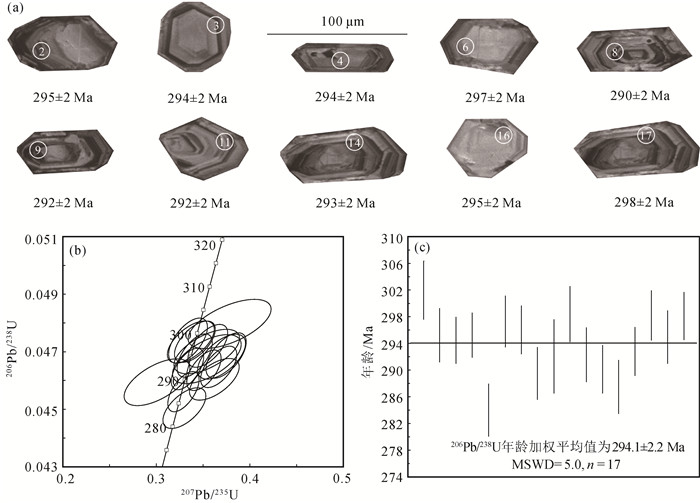
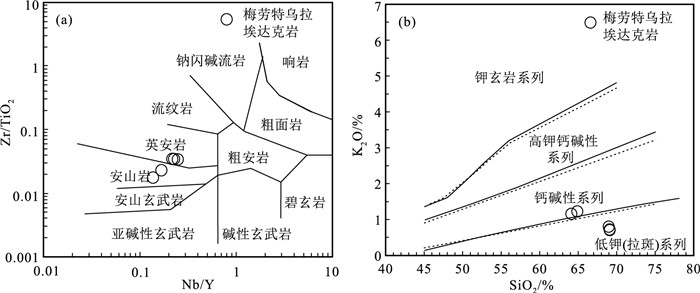
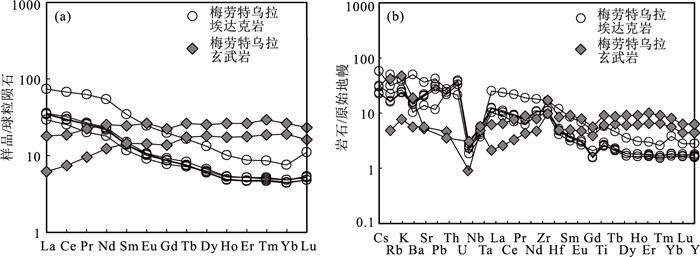
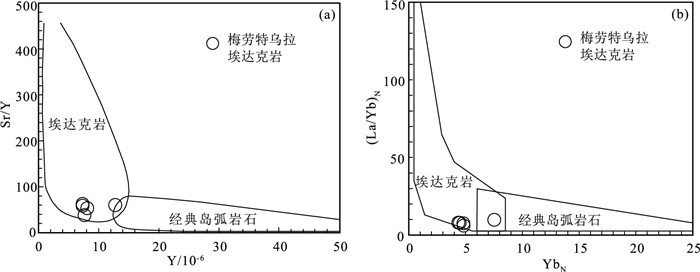
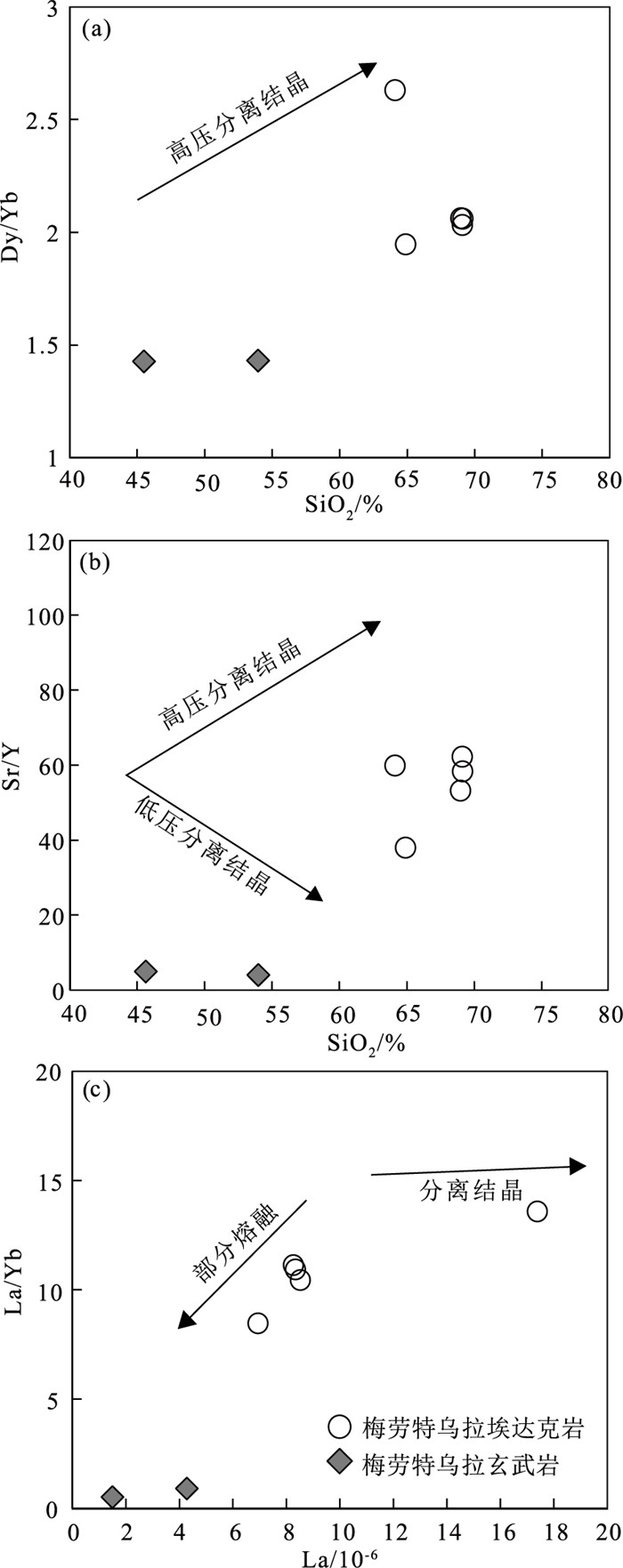
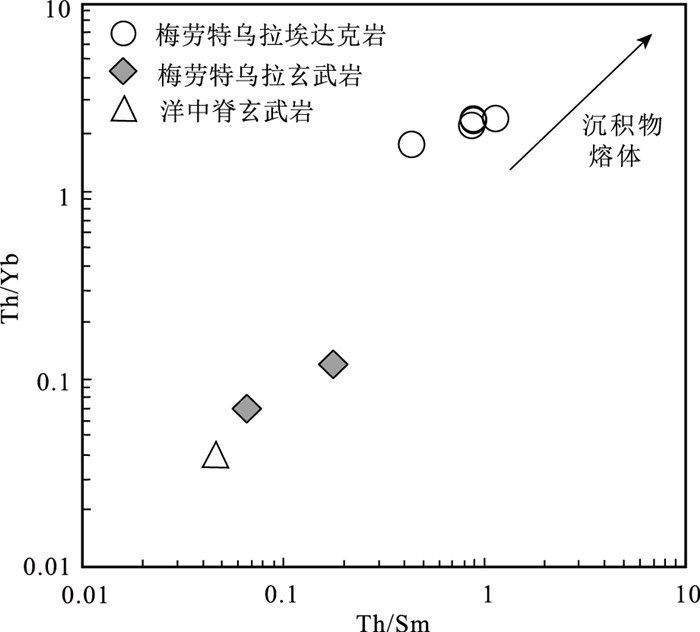
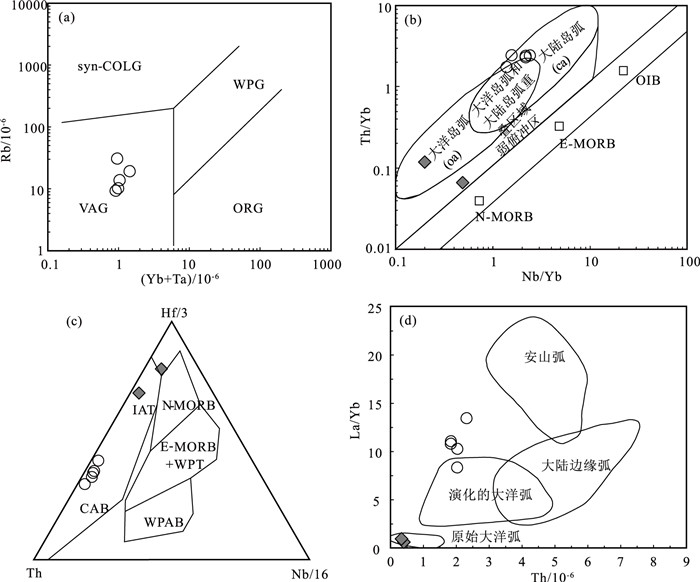
贺根山缝合带东部晚石炭世梅劳特乌拉SSZ型蛇绿岩中的埃达克岩,岩性为安山岩和英安岩。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,埃达克岩的形成时间为294.1±2.2 Ma,时代为早二叠世。地球化学特征显示,该埃达克岩属于低钾拉斑系列和中钾钙碱性岩石,具有高硅(SiO2=64.12%~69.12%)、高铝(Al2O3=16.05%~18.59%)、富钠贫钾(Na2O=5.08%~6.80%,K2O=0.70%~1.22%,Na2O/K2O=4.50~7.26)、高Sr(291.22×10-6~762.20×10-6),低Yb(0.74×10-6~1.28×10-6)、低Y(7.33×10-6~12.74×10-6)等特征。相对富集大离子亲石元素(如K、Rb和Sr),亏损高场强元素(如Nb、Ta、Zr、Ti和P),稀土元素总量较低(40.97×10-6~108.69×10-6),贫重稀土元素,无明显的负Eu异常,为典型的埃达克岩。梅劳特乌拉埃达克岩形成于俯冲带岛弧环境,可能为俯冲洋壳部分熔融而形成的埃达克质熔体,经俯冲带上升过程中与地幔楔橄榄岩发生相互作用而形成。埃达克岩和梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩(308 Ma)的蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩、层状-块状辉长岩、枕状拉斑玄武岩、玻安岩、富Nb玄武岩和高镁安山岩等构成洋内初始俯冲作用形成的较丰富且完整的岩石组合序列。研究结果表明,晚石炭世—早二叠世古亚洲洋东段开启了洋内初始俯冲作用。
Abstract:This paper reports the Early Permian adakite in the Meilaotewula SSZ-type ophiolite, Inner Mongolia.The Meilaotewula adakitic rocks are mainly composed of andesite and dacite, which were emplaced into the Late Carboniferous Meilaotewula suprasubduction zone(SSZ)ophiolite and were developed along the Hegenshan suture zone.The zircon U-Pb LA-ICP-MS dating result reveals that the Meilaotewula adakite is dated at 294.1±2.2 Ma, suggesting that it was formed during Early Permian.The adakite belongs to the low-K tholeiitic and medium-K calc-alkaline series.The rocks show such geochemical characteristics as high SiO2(64.12%~69.12%)and Al2O3(16.05%~18.59%)content with rich sodium and poor potassium(Na2O=5.08%~6.80%, K2O=0.70%~1.22%, Na2O/K2O=4.50~7.26).For trace elements, they show high content of Sr(291.22×10-6~762.20×10-6)and low content of Yb(0.74×10-6~1.28×10-6)and Y(7.33×10-6~12.74×10-6).In addition, they are relatively enriched in large-ion lithophile elements such as K, Rb, and Sr and depleted in high-field-strength elements such as Nb, Ta, Zr, Ti and P. Furthermore, they have low total rare-earth element(REE)content(40.97×10-6~108.69×10-6), with low heavy rare-earth elements(HREE)without obviously negative Eu anomaly.These geochemical characteristics indicate that the Meilaotewula andesite and dacite belong to adakite.The adakite was formed in the island arc environment of subduction zone, which might have originated from partial melting of subducted oceanic crust and then interacted with mantle wedge peridotite during the rise of subduction zone.The adakite and the Meilaotewula ophiolite(308 Ma)made up one abundant and complete rock assemblage, which was formed by the initial intraoceanic subduction.Therefore, Meilaotewula ophiolite consists of serpentined augite peridotite, beded-massive gabbro, pillow basalt, boninite, Nb-enriched basalt and high-Mg andesite.The results show that the initial intraoceanic subduction occurred in Late Carboniferous to Early Permian in southeastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean.
-
Key words:
- adakite /
- SSZ-type ophiolite /
- Early Permian /
- Palaeo-Asian Ocean /
- Inner Mongolia
-

-
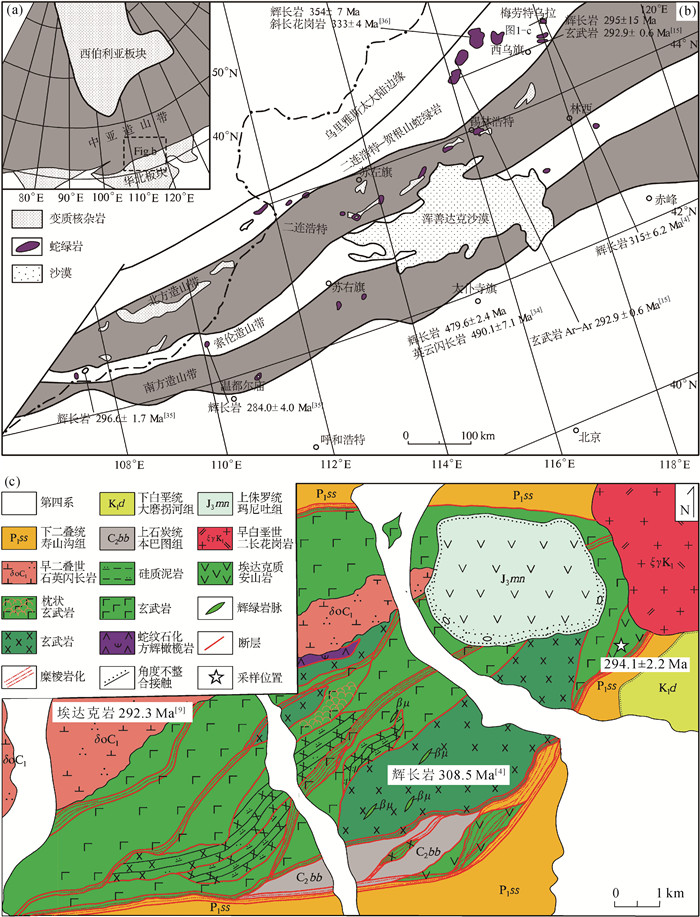
图 1 研究区大地构造位置示意图(a、b)和梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩地质简图(c, 据参考文献[9]修改)
Figure 1.
图 9 梅劳特乌拉埃达克岩Th/Sm-Th/Yb图解[81]
Figure 9.
表 1 梅劳特乌拉埃达克岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analyses of Meilaotewula adakite
点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 1 11 224 0.3842 0.0480 0.0003 0.3784 0.0181 0.0572 0.0027 0.0159 0.0005 302 2 326 16 2 16 332 0.3380 0.0469 0.0003 0.3747 0.0088 0.0580 0.0013 0.0147 0.0004 295 2 323 8 3 12 251 0.2677 0.0467 0.0003 0.3541 0.0150 0.0549 0.0023 0.0141 0.0005 294 2 308 13 4 19 398 0.3672 0.0469 0.0003 0.3411 0.0077 0.0528 0.0012 0.0127 0.0004 295 2 298 7 5 17 380 0.4201 0.0450 0.0003 0.3301 0.0094 0.0531 0.0015 0.0120 0.0004 284 2 290 8 6 18 381 0.3538 0.0472 0.0003 0.3551 0.0087 0.0546 0.0013 0.0117 0.0004 297 2 309 8 7 11 230 0.2803 0.0470 0.0003 0.3540 0.0143 0.0546 0.0022 0.0119 0.0005 296 2 308 12 8 11 244 0.2960 0.0459 0.0003 0.3008 0.0144 0.0475 0.0022 0.0122 0.0004 290 2 267 13 9 21 459 0.3726 0.0464 0.0003 0.3510 0.0075 0.0549 0.0011 0.0105 0.0002 292 2 305 7 10 17 361 0.4206 0.0474 0.0003 0.3340 0.0085 0.0511 0.0013 0.0105 0.0002 298 2 293 7 11 18 395 0.3231 0.0464 0.0003 0.3334 0.0071 0.0521 0.0011 0.0100 0.0003 292 2 292 6 12 17 369 0.3188 0.0460 0.0003 0.3621 0.0109 0.0570 0.0017 0.0107 0.0003 290 2 314 9 13 21 506 0.0628 0.0456 0.0003 0.3290 0.0068 0.0523 0.0011 0.0099 0.0002 288 2 289 6 14 20 455 0.2815 0.0465 0.0003 0.3667 0.0079 0.0572 0.0012 0.0097 0.0002 293 2 317 7 15 16 357 0.3805 0.0473 0.0003 0.3413 0.0089 0.0523 0.0013 0.0089 0.0002 298 2 298 8 16 15 319 0.3675 0.0468 0.0003 0.3698 0.0105 0.0573 0.0016 0.0106 0.0002 295 2 319 9 17 17 363 0.3823 0.0473 0.0003 0.3369 0.0102 0.0516 0.0015 0.0106 0.0003 298 2 295 9 表 2 梅劳特乌拉埃达克岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2. Major, trace elements and REE analytical results of Meilaotewula adakite
岩石名称 安山岩 安山岩 英安岩 英安岩 英安岩 样品号 XT3104 XT3106 XT3106-1 XT3107 XT3107-1 SiO2 64.12 64.90 68.99 69.09 69.12 TiO2 1.08 0.45 0.34 0.34 0.34 Al2O2 18.59 17.24 16.05 16.10 16.06 Fe2O2 2.81 0.84 1.40 1.48 1.41 FeO 1.22 2.17 0.97 0.90 0.97 MnO 0.046 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 MgO 0.54 2.40 1.30 1.28 1.30 CaO 1.65 2.66 3.49 3.39 3.40 Na2O 6.80 5.49 5.10 5.14 5.08 K2O 1.15 1.22 0.80 0.72 0.70 P2O2 0.235 0.10 0.12 0.12 0.12 烧失量 1.61 2.12 1.18 1.19 1.24 总计 99.86 99.90 99.89 99.88 99.88 Na2O/K2O 5.91 4.50 6.41 7.17 7.24 Mg# 21.16 60.16 52.10 51.64 51.94 La 17.39 6.95 8.53 8.35 8.27 Ce 41.53 15.7 19.6 18.4 18.0 Pr 5.93 1.93 2.57 2.48 2.42 Nd 25.27 8.36 10.8 10.4 10.2 Sm 5.30 1.80 2.30 2.15 2.10 Eu 1.43 0.53 0.62 0.61 0.59 Gd 4.04 1.59 1.92 1.80 1.76 Tb 0.62 0.27 0.31 0.28 0.28 Dy 3.37 1.60 1.69 1.55 1.53 Ho 0.58 0.30 0.30 0.28 0.28 Er 1.45 0.86 0.86 0.79 0.77 Tm 0.22 0.13 0.13 0.12 0.12 Yb 1.28 0.82 0.82 0.76 0.74 Lu 0.28 0.14 0.13 0.12 0.12 Y 12.74 7.66 8.11 7.34 7.33 Sc 8.64 8.02 5.17 4.61 4.81 Ni 6.0 19.0 9.74 8.68 8.72 Rb 19.8 31.5 14.0 10.5 10.0 Cr 5.0 16.6 13.4 11.9 12.7 Co 13.0 10.2 5.86 5.84 5.77 V 67.1 47.4 32.6 31.9 32.9 Zr 199.20 101.71 117.94 120.60 118.63 Hf 5.17 2.93 3.45 3.44 3.33 Ta 0.18 0.15 0.23 0.21 0.17 Sr 762.20 291.22 431.33 456.47 427.22 Ba 344.7 71.2 107 110 101 Nb 1.77 1.30 1.98 1.66 1.61 Cs 1.84 0.96 0.99 0.72 0.75 Ga 17.39 14.4 16.2 16.4 16.1 Pb 7.7 2.15 5.86 5.52 5.04 Th 2.32 2.02 2.04 1.84 1.84 U 0.82 0.44 0.77 0.69 0.68 ∑REE 108.69 40.97 50.60 48.07 47.16 LREE/HREE 8.18 6.19 7.23 7.43 7.41 (La/Yb)N 9.73 6.07 7.48 7.84 7.98 δEu 0.91 0.93 0.88 0.92 0.91 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
[1] Ruzhentsev S V, Mossakovskiy A A.Geodynamics and tectonic evolution of the central Asian paleozoic structures as the result of the interaction between the pacific and Indo-Atlantic segments of the Earth[J].Geotectonics, 1996, 29(4):294-311 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285858329_Geodynamics_and_tectonic_evolution_of_the_Central_Asian_Paleozoic_structures_as_the_result_of_the_interaction_between_the_Pacific_and_Indo-Atlantic_segments_of_the_Earth
[2] 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩的识别[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(4):1282-1290. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201204024
[3] 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙西乌旗白音布拉格蛇绿岩地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2719-2730. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201308009
[4] 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古西乌旗梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩的识别[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(5):1461-1470. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201505020
[5] 李英杰, 王金芳, 王根厚, 等.内蒙古迪彦庙蛇绿岩带达哈特前弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2018, 24(2):2719-2730. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201802019
[6] Kovalenko V I, Yarmolyuk V V, Kovach V P, et al.Isotope provinces, mechanisms of generation and sources of the continental crust in the Central Asian mobile belt:Geological and isotopic evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5):605-627. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00130-5
[7] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Huang B C, et al.End-Permian to mid-Triassic ermination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids:Implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J].Int.J.Earth Sci.Geol.Rundsch, 2009, 98:1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0407-z
[8] Li Y J, Wang G H, Santosh M, et al.Subduction initiation of the SE Paleo-Asian Ocean:Evidence from a well preserved intra-oceanic forearc ophiolite fragment in central Inner Mongolia[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020.535:116087. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116087
[9] Li Y J, Wang J F, Xin H T, et al.Subduction initiation in the southeastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean:Constraints from early Permian adakites in suprasubduction zone ophiolites, central Inner Mongolia, North China[J].Geological Journal, 2020, 55:2044-2061. doi: 10.1002/gj.3696
[10] 王荃, 刘雪亚, 李锦轶.中国华夏与安加拉古陆间的板块构造[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1991:151.
[11] 唐克东.中朝板块北侧褶皱带构造演化及成矿规律[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1992:305.
[12] Li J Y.Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions:Closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-Pacific plate[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3/4):207-224. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912005001598
[13] 张晋瑞, 魏春景, 初航.兴蒙造山带构造演化的新模式:来自内蒙古中部四期不同类型变质作用的证据[J].岩石学报, 2018, 34(10):2857-2872. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201810004.htm
[14] Chen B, Jahn B M, Wilde S A, et al.Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia, China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1/2):157-182. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001827
[15] Miao L C, Fan W M, Liu D Y, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex:Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2008, 32(5/6):348-370. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912007002222
[16] 邵济安.中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1991:1-135.
[17] 邵济安, 唐克东, 何国琦.内蒙古早二叠世构造古地理的再造[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(7):1858-1866. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201407002
[18] Tang K D.Tectonic development of Paleozoic foldbelts at the north margin of the Sino-Korean craton[J].Tectonics, 1990, 9(2):249-260. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/TC009i002p00249/full
[19] Tong Y, Jahn B M, Wang T, et al.Permian alkaline granites in the Erenhot-Hegenshan belt, northern Inner Mongolia, China:Model of generation, time of emplacement and regional tectonic significance[J].Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2015, 97:320-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.011
[20] 包志伟, 陈森煌, 张桢堂.内蒙古贺根山地区蛇绿岩稀土元素和Sr-Nd同位素研究[J].地球化学, 1994, 23(4):339-349. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1308893
[21] Liu J F, Li J Y, Chi X G, et al.A late Carboniferous to early early Permian subduction-accretion complex in Daqing pasture, southeastern Inner Mongolia:Evidence of northward subduction beneath the Siberian paleoplate southern margin[J].Lithos, 2013, 177:285-296. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.07.008
[22] Nozaka T, Liu Y.Petrology of the Hegenshan ophiolite and its implications for the tectonic evolution of northern China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202:89-104. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00774-4
[23] Robinson P T, 白文吉, 杨经绥, 等.内蒙古贺根山蛇绿岩岩石成因及地壳增生的地球化学制约[J].岩石学报, (增刊), 1995:112-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB5S1.008.htm
[24] Zhou M F, Zhang H F, Robinson P T, et al.Comments on Petrology of the Hegenshan ophiolite and its implication for the tectonic evolution of northern China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 217(1/2):207-210. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=911f4703edf4cb83d62b8c8f4e40e142
[25] 王树庆, 许继峰, 刘希军, 等.内蒙古朝克山蛇绿岩地球化学:洋内弧后盆地的产物?[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(12):2869-2879. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200812021
[26] 王成, 任利民, 张晓军, 等.内蒙古崇根山蛇绿岩前弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 3:1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201903001
[27] Shervais J W.Birth, death and resurrection:the life cycle of sprasubduction zone ophiolites[J].Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2001, 2(1):148-159. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2001GGG.....2.1010S
[28] Reagan M K, Ishizuka O, Stern R J, et al.Fore-arc basalts and subduction initiation in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana system[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11:Q03X12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2009gc002871
[29] Reagan M K, Pearce J A, Petronotis K, et al.Subduction initiation and ophioite crust:New insights from IODP drilling[J].International Geology Review, 2017, 59:1439-1450. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1276482
[30] Whattam S A, Stern R J.The 'subduction initiation rule':A key for linking ophiolites, intra oceanic forearcs, and subduction initiation[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 162:1031-1045. doi: 10.1007/s00410-011-0638-z
[31] Li H Y, Taylor R N, Prytulak J, et al.Radiogenic isotopes document the start of subduction in the Western Pacific[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 518:197-210. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2019.04.041
[32] Jahn B M, Windley B, Natal'in B, et al.Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5):599-603. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00124-X
[33] Badarch G, Cunningham W D, Windley B F.A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87-110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2
[34] Jian P, Liu D Y, Kröner A, et al.Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China:implications for continental growth[J].Lithos, 2008, 101(3/4):233-259. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493707001508
[35] Jian P, Liu D Y, Kröner A, et al.Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc-trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia[J].Lithos, 2010, 118(1/2):169-190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=40ff8aa320c272880289a116d19525f3
[36] Jian P, Kröner A, Windley B F, et al.Carboniferous and Cretaceous mafic-ultramafic massifs in Inner Mongolia(China):A SHRIMP zircon and geochemical study of the previously presumed integral "Hegenshan ophiolite"[J].Lithos, 2012, 142-143:48-66. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.007
[37] 邵济安, 张丽莉, 周新华, 等.对内蒙古贺根山蛇绿岩的新认识[J].岩石学报, 2020, 35(09):2864-2872. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201909016
[38] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[39] Anderson T.Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
[40] Ludwig K R.Isotope:A plotting and regression program for radiogenic-isotope data[J].US Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1991, 39:91-445. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10008802019
[41] Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronological Center, Special Publication, 2003, 4:1-71. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/306157481_Isoplot_v_30_a_geochronological_toolkit_for_Microsoft_Excel
[42] Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al.Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
[43] 刘建辉, 刘敦一, 张玉海, 等.使用SHRIMP测定锆石铀-铅年龄的选点技巧[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(3):265-268. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykcs201103004
[44] 李长民.锆石成因矿物学与锆石微区定年综述[J].地质调查与研究, 2009, 32(3):161-174. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhwjyjjz200903001
[45] Su W B, Zhang S H, Warren D, et al.SHRIMP U-Pb ages of K-bentonite beds in the Xiamaling Formation:Implications for revised subdivision of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic history of the North China Craton[J].Gondwana Research, 2008, 14(3):543-553. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.04.007
[46] Belousova E, Griffin W, O'reilly S Y, et al.Igneous zircon:trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
[47] Claesson S, Vetrin V, Bayanova T, et al.U-Pb zircon ages from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola peninsula, Russia:a record of geological evolution from the Archaean to the Palaeozoic[J].Lithos, 2000, 51(1/2):95-108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&md5=6cdb70f9b4446472f6199bd71ad85567&_udi=B6V6J-3YSY1JK-6&_user=6894003&_coverDate=03%2F01%2F2000&_rdoc=6&_fmt=high&_orig=browse&_origin=browse&_zone=rslt_list_item&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%235816%232000%23
[48] Winchester J A, Floyd P A.Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chemical Geology, 1977, 20:325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[49] Middlemost E A K.Magmas and Magmatic Rocks[M].London:Longman, 1985:1-266.
[50] Martin H.The mechanisms of petrogenesis of the Archaean conti nental crust-comparison with modem processes[J].Lithos, 1993, 30:373-388. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(93)90046-F
[51] Martin H.Adakitic magmas:Modern analogues of Archaean gran-itoids[J].Lithos, 1999, 46:411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
[52] Boynton W V.Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P E.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry.Developments in Geochemistry.Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1984: 63-114.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444421487500083 [53] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basins.Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[54] 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙.埃达克岩与构造环境[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(2):706-713. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200302001
[55] 张旗, 许继峰, 王焰, 等.埃达克岩的多样性[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10):959-965. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200409170&flag=1
[56] Defant M J, Drummond M S.Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J].Nature, 1990, 347:662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[57] Kelemen P B, Hangh K, Ureenem A R.One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[C]//Rudnick R L.Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3: 593-659.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080959757003235 [58] 熊小林, 蔡志勇, 牛贺才, 等.东天山晚古生代埃达克岩成因及铜金成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):967-976. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200503034
[59] 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等.中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17:236-244. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200102008
[60] 张旗, 秦克章, 王元龙, 等.加强埃达克岩研究, 开创中国Cu、Au等找矿工作的新局面[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(2):195-204. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200402002
[61] Wang Q, Zhao Z H, Xu J F, et al.Petrologenesis and metallogeneais of the Y anshanian adakite-like rock in the Eastem Yangtze Block[J].Science in China, Series D, 2003, 46(Supp):164-176. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG2003S2013.htm
[62] Wang Q, McDermott F, Xu J F, et al.Cenozoic K-rich adakitic volcanic rocks in the Hohxil area, northem Tibet:Lower-crustal melting in an intracontinental setting[J].Geology, 2005, 33:465-468. doi: 10.1130/G21522.1
[63] 刘红涛, 张旗, 刘建明, 等.埃达克岩与斑岩铜矿-浅成热液金矿:有待深人研究的岩浆成矿关系[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20:205-218.
[64] Xu J F, Shinjio R, Defant M J, et al.Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China:Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J]Geology, 2002, 12:1111-1114. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2002Geo....30.1111X
[65] 许继峰, 王强.Adakitic火成岩对大陆地壳增厚过程的指示:以青藏北部火山岩为例[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10:401-406. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200304008
[66] Castillo P R.Adakite petrogenesis[J].Lithos, 2012, 134:304-316. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449371100274X
[67] Castillo P R.Janney P E, Solidum R U.Petrology and geochemistry ofCamiguin Island, southern Philippines:Insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1999, 134:33-51. doi: 10.1007/s004100050467
[68] Macpherson C G, Dreher S T, Thirlwall M F.Adakites without slab melting:High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 243:581-593. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.12.034
[69] Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D, et al.Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge:Experimental constraints at 3.8GPa[J].Chemical Geology, 1999, 160.335-356. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00106-0
[70] Defant M J, Kepezhinskas P.Evidence suggests slab melting in arc magmas[J].EOS, 2001, 82:62-69. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/01EO00038/pdf
[71] Rapp R P.Partial melting of metabasalts at 2-7GPa:Experimental results and implications for lower crustal and subduction zone processes[J].Minera logical Magazine, 1994, 58A:760. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1994.58A.2.132
[72] Green T H.Experimental sudies of trace-element partitioning applicable to igneous petrogenesis-Sedona, 16years later[J].Chemical Geology, 1994, 117:1-36. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90119-8
[73] Davidson J, MacPherson C, Turner S.Amphibole control in the differentiation of arc magmas[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71:A204-A204. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=de3f3a88540ad7964f9ccc920ec40613
[74] Chung S L, Chu M F, Ji J Q, et al.The nature and timing of crustal thickening in southern Tibet:Geochemical and zircon Hf isotopic constrains from postcollisional adakitics[J].Tectonophysics, 2009, 177:18-36. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195109004259
[75] 刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 等.内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年:早古生代洋壳消减的证据[J].地质学报, 2003, 77(3):317-330. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200303004
[76] 王璐, 赵庆英, 李鹏川, 等.内蒙古巴林右旗东梁岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地球化学特征[J].世界地质, 2016, 35(2):370-386. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz201602008
[77] 王焰, 张旗, 钱青.埃达克(adakite)的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].地质科学, 2000, 35(2):251-256. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200002016
[78] 许立权, 邓晋福, 陈志勇.内蒙古达茂旗北部奥陶纪埃达克岩类的识别及其意义[J].现代地质, 2003, 17(4):428-434. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200304011
[79] Rapp R P, Watson E B.De hydration melting of meta basalt at 8~32kbar:Implications for continental growth and crustmantle recycling[J].Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[80] Atherton M P, Petford N.Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J].Nature, 1993, 362(6416):144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
[81] Zheng Y Ch, Hou Z Q, Gong Y L, et al.Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakite-like intrusions of the Gangdese Plutonic Belt, southern Tibet:Implications for mid-ocean ridge subduction and crustal growth[J].Lithos, 2014, 190/191(3):240-263. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493713004155
[82] Ishizuka O, Tani K, Reagan M.KIzu-Bonin-Mariana forearc Crust as a modern ophiolite Analogue[J].Elements, 2014, 10:115-120. doi: 10.2113/gselements.10.2.115
[83] Stern R J M, Reagan Q, Ishizuka Y O, et al.To under stand subduction initiation, study forearc crust:To understand forearc crust, study ophiolites[J].Lithosphere, 2012, 4:469-483. doi: 10.1130/L183.1
[84] Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S.Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[C]//Kokelaar B P, Howells M F.Marginal Basin Geology.Geological Society of London, Special Publication, 1984, 16: 77-94.
Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites [85] Pearce J A.Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oce-anic crust[J].Lithos, 2008, 100:14-48. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.016
[86] Wood D A.The application of Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary volcanic province[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50:11-30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
[87] Condie K C.Geochemistry and tectonic setting of early Protero zoic supracrustal rocks in theSouthwest United States[J].Journal of Geology, 1986, 94:845-861. doi: 10.1086/629091
[88] 李奋其, 李益多, 张士贞.西藏朗县地区增生楔杂岩带90Ma岛弧型深成岩浆活动和意义[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(1):142-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201601011
[89] 郝百武.内蒙古那仁乌拉埃达克质花岗岩的发现、成因、锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].矿物岩石, 2012, 32(1):28-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201201005
[90] 曾俊杰, 郑有业, 齐建宏, 等.内蒙古固阳地区埃达克质花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地球科学, 2008, 33(6):755-762. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200806003
[91] 李承东, 张福勤, 苗来成, 等.吉林色洛河晚二叠世高镁安山岩SHRIMP锆石年代学及其地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(4):767-776. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200704008
[92] Sengör, A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S.Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth inEurasia[J].Nature, 1993, 364:299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[93] Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A.Paleotectonics ofAsia: fragments of a synthesis[C]//Yin A, Harrison M.The tectonic evolution of Asia.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996: 486-641.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284695939_Paleotectonics_of_Asia_Fragments_of_a_syn_thesis [94] Dilek Y, Furnes H.Structure and geochemistry of Tethyan ophiolites and their petrogenesis in subduction rollback systems[J].Lithos, 2009, 113:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.022
[95] Dilek Y, Furnes H.Ophiolite genesis and global tectonics:Geochemical and tectonic fingerprinting of ancient oceanic lithosphere[J].GSA Bulletin, 2011, 123:387-411. doi: 10.1130/B30446.1
[96] Dilek Y, Furnes H.Ophiolites and their origins[J].Elements, 2014, 10:93-100. doi: 10.2113/gselements.10.2.93
[97] Ishizuka O, Kimura J I, Li Y B, et al.Early stages in the evolution of Izu-Bonin arc volcanism:New age, chemical, & isotopic constraints[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 250:385-401. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.08.007
[98] Shang Q H.The discovery and significance of Permian radiolarians Northern Orogenic Belt in the northern and middle Inner Mongolia[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49:2574-2579. doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-24-2574
-



 下载:
下载: