Regional geological and mineral resources characteristics of Iceland
-
摘要:
冰岛是欧洲的第二大岛屿,在成因类型上,是由于地幔柱上涌而形成的碱性玄武岩区,属于周期性的海底岩浆活动和海底火山喷发而形成的火山岛。全岛主要由玄武岩组成,并可分为4个主要地层单元,分别为中新世-早上新世岩层、晚上新世-早更新世岩层、晚更新世岩层及冰后期岩层。构造方面,冰岛火山断裂系统发育,可分为3个火山侧翼带和4个火山裂谷带。冰岛地热资源极丰富,其具有分布广、类型多、温度高、地热流体多为淡水等特征。近年来,冰岛发现了一系列金矿(化)点,主要分布在冰岛沿海地区,可分为3个成矿带,与地热系统具有密切的时空分布关系,成因类型多为浅成低温热液型金矿床,与中国新疆西天山地区阿希金矿床具有相似的成矿环境和地质特征。在系统收集前人资料的基础上,简要介绍了冰岛地质特征及演化历史,阐述了冰岛地热、金矿资源分布规律,旨在为中国地质科技人员了解冰岛的地质和矿产资源特征提供参考依据。
-
关键词:
- 冰岛 /
- 区域地质 /
- 地热资源 /
- 浅成低温热液型金矿床
Abstract:Located in central North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland is an island lying between the North Atlantic and Greenland Sea.It is the second largest island in Europe.It is an alkaline basalt area, which belongs to the periodic submarine magmatism and submarine volcano eruption resulting from mantle plume upwelling.The island is mainly composed of basalt, and can be divided into four major stratigraphic units, i.e., the Tertiary unit, the Plio-Pleistocene unit, the Upper Pleistocene unit and the Postglacial unit.The Icelandic volcano fracture system can betectonically divided into three flank zones and four volcanic rift zones.The geothermal resources in Iceland have such features as wide distribution, various types, high temperature, and freshwater nature of the geothermal fluid.In recent years, geological departments have found a series of gold deposits(mineralization spots)in Iceland.Mainly distributed in the coastal areas of Iceland, they can be divided into three metallogenic belts.Being epithermal deposits, the gold deposits have a close relationship with the geothermal system.It should be mentioned that they are very similar to the Axi gold deposit in northern Xinjiang.Based on previous data, this paper introduces the geological features and evolution history of Iceland briefly, and elaborates the distribution of geothermal and gold resources so as to provide a reference for Chinese scientists and technicians.
-
Key words:
- Iceland /
- geological features /
- geothermal resources /
- epithermal type gold deposit
-

-
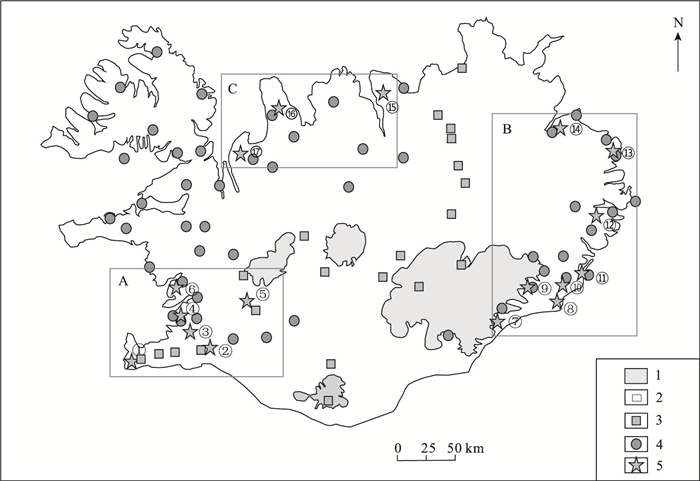
图 3 冰岛矿产资源分布图(据参考文献[4]修改)
Figure 3.
图 4 冰岛地热系统形成模式简图(据参考文献[7]修改)
Figure 4.
表 1 冰岛区域地层
Table 1. Regional stratigraphic table of Iceland
地质时代 地质时代 地质时代 同位素测年 地层组成 第四纪 全新世 0.0117 Ma 冰后期玄武质熔岩、火山碎屑岩及冲(洪)积物等(小于0.01 Ma) 更新世 晚更新世
早更新世0.126 Ma
2.588 Ma晚更新世玄武质熔岩(0.01~0.8 Ma) 新近纪 上新世 晚上新世
早上新世3.600 Ma
5.333 Ma晚上新世—早更新世冰河沉积物、冰碛沉积物及玻质玄武岩(0.8~3.3 Ma) 中新世 晚中新世
中中新世
早中新世7.246 Ma
11.62 Ma
~15 Ma中新世—早上新世玄武质熔岩夹陆相沉积物(3.3~15 Ma) 表 2 冰岛苏尔姆德斯达鲁尔金矿床与新疆阿希金矿矿床地质特征对比
Table 2. Contrast of geological features between the Thormodsdalur and Axi gold deposits
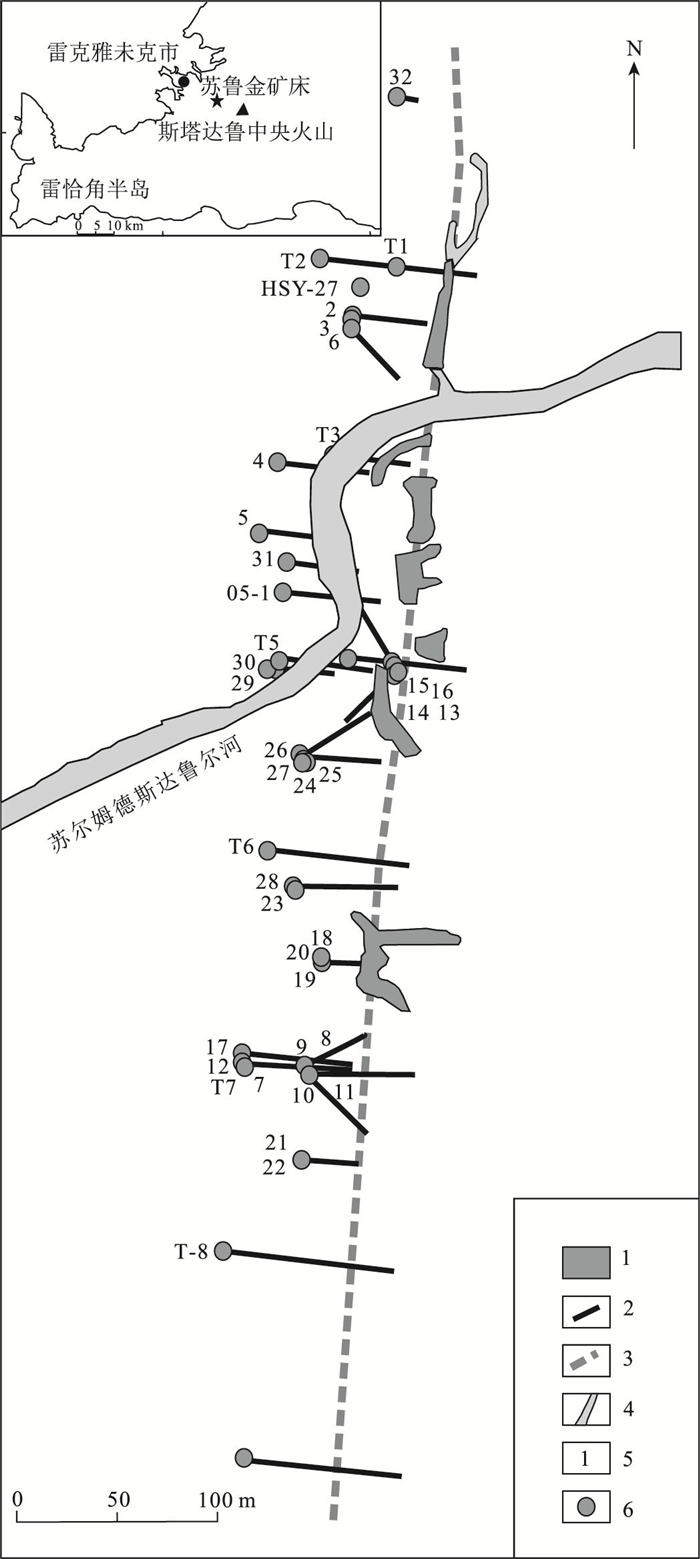
矿床 苏尔姆德斯达鲁尔金矿床 阿希金矿床 地质背景 构造环境 大西洋中脊扩张带雷克恰火山断裂带 伊犁-中天山板块北部吐拉苏火山岩断陷盆地 容矿围岩 更新世碱性玻质玄武岩及熔岩 下石炭统大哈拉军山组安山质火山角砾岩、英安岩、安山质岩 矿床特征 矿体形态 脉状,细脉状 脉状、细脉状 矿石类型 含金网状石英脉、浸染状矿石 多金属硫化物石英脉型、白铁矿碳酸盐石英脉型、黄铁绢英岩型、黄铁矿蚀变型 矿石构造 细脉状、网脉状或浸染状 星散浸染状、稀疏浸染状、细脉浸染状构造 金属矿物 磁黄铁矿、黄铁矿、银金矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、自然金 自然金、银金矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、毒砂、赤铁矿、褐铁矿、含银矿物 非金属矿物 石英、绢云母、冰长石、方解石等 石英、玉髓、绢云母、方解石、菱铁矿、白云石、冰长石、高岭石、浊沸石等 金矿物 自然金、银金矿 自然金、银金矿 蚀变类型 硅化、绢英岩化、青磐岩化、冰长石化、浊沸石化 硅化、绢英岩化、碳酸盐化、青磐岩化、浊沸石化、冰长石化 元素组合 Au-Ag-Bi-Se-Te Au-Ag-As-Sb-Bi-Hg-Se-Te 盐度/% 低 0.7~3.1 成矿温度/℃ 180~200 120~180 成矿深度/km 0.3~0.5 <0.7 成矿时代/Ma 1.5~2.0 306~308(U-Pb) 物质来源 火山岩浆 火山岩浆 热液来源 大气水为主 岩浆大气混合水 参考文献 [4, 6-7] [12-19] -
[1] Tórarinsson S, Einarsson T.Geology of Iceland[M].33 IGC 2008 Excursion, 2008, 5: 1-15.
[2] 武选民, 柏琴, 苑惠明, 等.冰岛地热资源开发利用现状[J].水文地质工程地质, 2007, 2007(5):1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.05.002
[3] Sigmundsson F.Iceland Geodynamics: Crustal Deformation and Divergent Plate Tectonics[M].Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co.K, 2010: 1-66.
[4] Franzson H, Friðleifsson G Ó, Jónasson H.Gold exploration in Iceland[C]//12th SGA Biennial Meeting, 2013, Proceedings Volume 4: 1862-1865.
[5] Trønnes R G.Geology and geodynamics of Iceland[C]//Planke S.Iceland, 2002: 23-43.
http://www.researchgate.net/publication/237641738_Geology_and_geodynamics_of_Iceland [6] Franzson H, Guðlaugsson S Б, Friðleifsson G Ó.Petrophysical Properties of Icelandic Rocks[C]//Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Symposium on Petrophysics, 2010: 15-16.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306160485_Petrophysical_properties_of_Icelandic_rocks [7] Wilfred A E, Friðleifsson G Ó.The Science Program of the Iceland Deep Drilling Project(IDDP): a Study of Supercritical Geothermal Resources[C]//Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2010 Bali, Indonesia, 2010: 25-29.
http://www.researchgate.net/publication/228556206_The_Science_Program_of_the_Iceland_Deep_Drilling_Project_IDDP_a_study_of_supercritical_geothermal_resources [8] 汤松然.冰岛高温地热钻井与完井[J].国外地质勘探技术, 1982, (5):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GWDK198205001.htm
[9] Harðardóttir V, Hannington M, Hedenquist J.Metal concentrations and metal deposition in deep geothermal wells at the Reykjanes high-temperature area, Iceland[J].Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2013, 7:338-341. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.159
[10] Harðardóttir V.Metal-rich scales in the Reykjanes Geothermal System, SW-Iceland: Sulfide minerals in a seawater-dominated hydrothermal environment[M].Earth Sciences University of Ottawa, 2011: 280-288.
[11] James V G, Simon A K.Evolution of vertical faults at an extensional plate boundary, southwest Iceland[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2004, 26:537-557. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2003.07.003
[12] 韦成友, 薛春纪, 姬金生, 等.东天山西滩浅成低温热液金矿床地球化学[J].矿床地质, 2000, 19(4):322-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2000.04.005
[13] 廖启林, 戴塔根, 邓吉牛, 等.新疆北部主要金矿床的成矿地球化学特征[J].矿床地质, 2000, 19(4):298-305. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200004002
[14] Zheng J H, Shen P, Li C H.Ore genesis of Axi post-collisional epithermal gold deposit, western Tianshan, NW China:Constraints from U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes, and pyrite in situ sulfur isotopes[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117(1):103290. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e45e478bc0c65e4a543cc6e6aa34e0e7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] 毋瑞身, 刘海山, 田昌烈, 等.新疆阿希地区金矿概论[J].贵金属地质, 1996, 5(1):5-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1097-MPG.0b013e31819ca18e/
[16] 范新丽, 黄薇, 袁尔乾.西天山阿希地区金矿的金元素富集过程探讨[J].新疆地质, 2002, 20(3):224-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.03.010
[17] 关瑞林.阿希金矿控矿构造、矿体特征及成因探讨[J].新疆有色金属, 2008, 1:3-5. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjysjs200801002
[18] Liu Z, Mao X, Ackerman L, et al.Two-stage gold mineralization of the Axi epithermal Au deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China:Evidence from Re-Os dating, S isotope, and trace elements of pyrite[J].Miner Deposita, 2019.DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00903-6.
[19] Liu Z K, Mao X C, Deng H, et al.Hydrothermal processes at the Axi epithermal Au deposit, western Tianshan:Insights from geochemical effects of alteration, mineralization and trace elements in pyrite[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 102:368-385. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.09.009
[20] 郭玉乾, 方维萱, 刘家军.浅成低温热液金银多金属矿床矿化分带及找矿标志[J].矿产与地质, 2009, 23(1):7-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2009.01.002
[21] 陈根文, 夏斌, 肖振宇, 等.浅成低温热液矿床特征及在我国的找矿方向[J].地质与资源, 2001, 10(3):165-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2001.03.007
[22] 江思宏, 聂凤军, 张义, 等.浅成低温热液型金矿床研究最新进展[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(2):401-408. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.02.010
[23] Corbett G.Epithermal gold for explorationists[C]//Applied Geoscientific Practice and Research in Australia.AIG Journal, 2002: 1-26.
[24] 翟伟.酸性硫酸盐型和冰长石绢云母型金矿床地质特征对比[J].新疆地质, 1996, 17(2):152-156. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XJDI902.007.htm
① 商务部国际贸易经济研究院等.对外投资合作国别指南——冰岛.2013.
-




 下载:
下载: